Abstract
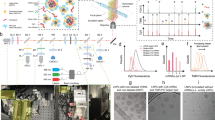
Lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) are currently the most advanced non-viral clinically approved messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) delivery systems. The ability of a mRNA vaccine to have a therapeutic effect is related to the capacity of LNPs to deliver the nucleic acid intact into cells. The role of LNPs is to protect mRNA, especially from degradation by ribonucleases (RNases) and to allow it to access the cytoplasm of cells where it can be translated into the protein of interest. LNPs enter cells by endocytosis and their size is a critical parameter impacting their cellular internalization. In this work, we studied different formulation process parameters impacting LNPs size. Taylor dispersion analysis (TDA) was used to determine the LNPs size and size distribution and the results were compared with those obtained by Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS). TDA was also used to study both the degradation of mRNA in the presence of RNases and the percentage of mRNA encapsulation within LNPs.

This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 6 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $43.17 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Additional data are available in the Supplementary Information file.
References
Rappuoli R, Pizza M, Del Giudice G, De Gregorio E. Vaccines, new opportunities for a new society. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2014;111:12288–93.
Pollard AJ, Bijker EM. A guide to vaccinology: from basic principles to new developments. Nat Rev Immunol. 2021;21:83–100.
Morens DM, Fauci AS. Emerging pandemic diseases: how we got to COVID-19. Cell. 2020;182:1077–92.
Hajj KA, Whitehead KA. Tools for translation: non-viral materials for therapeutic mRNA delivery. Nat Rev Mater. 2017;2:17056.
Nanomedicine and the COVID-19 vaccines. Nat Nanotechnol. 2020;15, 963–963.
Gebre MS, Brito LA, Tostanoski LH, Edwards DK, Carfi A, Barouch DH. Novel approaches for vaccine development. Cell. 2021;184:1589–603.
Wolff JA, Malone RW, Williams P, Chong W, Acsadi G, Jani A, et al. Direct gene transfer into mouse muscle in vivo. Science. 1990;247:1465–8.
Pardi N, Hogan MJ, Porter FW, Weissman D. mRNA vaccines—a new era in vaccinology. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2018;17:261–79.
Guan S, Rosenecker J. Nanotechnologies in delivery of mRNA therapeutics using nonviral vector-based delivery systems. Gene Ther. 2017;24:133–43.
Zhang X, Goel V, Robbie GJ. Pharmacokinetics of patisiran, the first approved RNA interference therapy in patients with hereditary transthyretin-mediated amyloidosis. J Clin Pharmacol. 2020;60:573–85.
Urits I, Swanson D, Swett MC, Patel A, Berardino K, Amgalan A, et al. A review of patisiran (ONPATTRO®) for the treatment of polyneuropathy in people with hereditary transthyretin amyloidosis. Neurol Ther. 2020;9:301–15.
Akinc A, Maier MA, Manoharan M, Fitzgerald K, Jayaraman M, Barros S, et al. The Onpattro story and the clinical translation of nanomedicines containing nucleic acid-based drugs. Nat Nanotechnol. 2019;14:1084–7.
Kim YC, Dema B, Reyes-Sandoval A. COVID-19 vaccines: breaking record times to first-in-human trials. Npj Vaccines. 2020;5:34.
Friedrichs S, Bowman DM. COVID-19 may become nanomedicine’s finest hour yet. Nat Nanotechnol. 2021;16:362–4.
Schoenmaker L, Witzigmann D, Kulkarni JA, Verbeke R, Kersten G, Jiskoot W, et al. mRNA-lipid nanoparticle COVID-19 vaccines: Structure and stability. Int J Pharm. 2021;601:120586.
Crommelin DJA, Anchordoquy TJ, Volkin DB, Jiskoot W, Mastrobattista E. Addressing the cold reality of mRNA vaccine stability. J Pharm Sci. 2021;110:997–1001.
Gilleron J, Querbes W, Zeigerer A, Borodovsky A, Marsico G, Schubert U, et al. Image-based analysis of lipid nanoparticle–mediated siRNA delivery, intracellular trafficking and endosomal escape. Nat Biotechnol. 2013;31:638–46.
Sabnis S, Kumarasinghe ES, Salerno T, Mihai C, Ketova T, Senn JJ, et al. A novel amino lipid series for mRNA delivery: improved endosomal escape and sustained pharmacology and safety in non-human primates. Mol Ther. 2018;26:1509–19.
Chapin-Bardales J, Gee J, Myers T. Reactogenicity following receipt of mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccines. JAMA. 2021;325:2201–2.
Cheng Q, Wei T, Farbiak L, Johnson LT, Dilliard SA, Siegwart DJ. Selective organ targeting (SORT) nanoparticles for tissue-specific mRNA delivery and CRISPR–Cas gene editing. Nat Nanotechnol. 2020;15:313–20.
Dammes N, Goldsmith M, Ramishetti S, Dearling JLJ, Veiga N, Packard AB, et al. Conformation-sensitive targeting of lipid nanoparticles for RNA therapeutics. Nat Nanotechnol. 2021;16:1030–8.
Wilhelm S, Tavares A, Dai Q, Ohta S, Audet J, Dvorak HF, et al. Analysis of nanoparticle delivery to tumours. Nat Rev Mater. 2016;1:16014.
Jiang W, Kim BYS, Rutka JT, Chan WCW. Nanoparticle-mediated cellular response is size-dependent. Nat Nanotechnol. 2008;3:145–50.
Conner SD, Schmid SL. Regulated portals of entry into the cell. Nature. 2003;422:37–44.
Rejman J, Oberle V, Zuhorn IS, Hoekstra D. Size-dependent internalization of particles via the pathways of clathrin- and caveolae-mediated endocytosis. Biochem J. 2004;377:159–69.
Petros RA, DeSimone JM. Strategies in the design of nanoparticles for therapeutic applications. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2010;9:615–27.
Andar AU, Hood RR, Vreeland WN, DeVoe DL, Swaan PW. Microfluidic preparation of liposomes to determine particle size influence on cellular uptake mechanisms. Pharm Res. 2014;31:401–13.
Evers MJW, Kulkarni JA, Van der Meel R, Cullis PR, Vader P, Schiffelers RM. State-of-the-art design and rapid-mixing production techniques of lipid nanoparticles for nucleic acid delivery. Small Methods. 2018;2:1700375.
Hoshyar N, Gray S, Han H, Bao G. The effect of nanoparticle size on in vivo pharmacokinetics and cellular interaction. Nanomed. 2016;11:673–92.
Chauhan VP, Jain RK. Strategies for advancing cancer nanomedicine. Nat Mater. 2013;12:958–62.
Le-Vinh B, Steinbring C, Wibel R, Friedl JD, Bernkop-Schnürch A. Size shifting of solid lipid nanoparticle system triggered by alkaline phosphatase for site specific mucosal drug delivery. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2021;163:109–19.
Trevaskis NL, Kaminskas LM, Porter CJH. From sewer to saviour—targeting the lymphatic system to promote drug exposure and activity. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2015;14:781–803.
Mitchell MJ, Billingsley MM, Haley RM, Wechsler ME, Peppas NA, Langer R. Engineering precision nanoparticles for drug delivery. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2021;20:101–24.
Blanco E, Shen H, Ferrari M. Principles of nanoparticle design for overcoming biological barriers to drug delivery. Nat Biotechnol. 2015;33:941–51.
Demelenne A, Servais AC, Crommen J, Fillet M. Analytical techniques currently used in the pharmaceutical industry for the quality control of RNA-based therapeutics and ongoing developments. J Chromatogr. A. 2021;1651:462283.
Fan Y, Marioli M, Zhang K. Analytical characterization of liposomes and other lipid nanoparticles for drug delivery. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2021;192:113642.
Malburet C, Leclercq L, Cotte JF, Thiebaud J, Bazin E, Garinot M, et al. Size and charge characterization of lipid nanoparticles for mRNA vaccines. Anal Chem. 2022;94:4677–85.
Chamieh J, Leclercq L, Martin M, Slaoui S, Jensen H, Østergaard J, et al. Limits in size of taylor dispersion analysis: representation of the different hydrodynamic regimes and application to the size-characterization of cubosomes. Anal Chem. 2017;89:13487–93.
Cipelletti L, Biron JP, Martin M, Cottet H. Measuring arbitrary diffusion coefficient distributions of nano-objects by Taylor Dispersion Analysis. Anal Chem. 2015;87:8489–96.
Zhang S, Li J, Lykotrafitis G, Bao G, Suresh S. Size-dependent endocytosis of nanoparticles. Adv Mater. 2009;21:419–24.
Belliveau NM, Huft J, Lin PJ, Chen S, Leung AK, Leaver TJ, et al. Microfluidic synthesis of highly potent limit-size lipid nanoparticles for in vivo delivery of siRNA. Mol Ther—Nucleic Acids. 2012;1:e37.
Yanez Arteta M, Kjellman T, Bartesaghi S, Wallin S, Wu X, Kvist AJ, et al. Successful reprogramming of cellular protein production through mRNA delivered by functionalized lipid nanoparticles. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2018;115:E3351.
Bao Y, Jin Y, Chivukula P, Zhang J, Liu Y, Liu J, et al. Effect of PEGylation on biodistribution and gene silencing of siRNA/lipid nanoparticle complexes. Pharm Res. 2013;30:342–51.
Kozma GT, Shimizu T, Ishida T, Szebeni J. Anti-PEG antibodies: properties, formation, testing and role in adverse immune reactions to PEGylated nano-biopharmaceuticals. Adv Liposome Res. 2020;154–155:163–75.
Hoang Thi TT, Pilkington EH, Nguyen DH, Lee JS, Park KD, Truong NP. The importance of poly(ethylene glycol) alternatives for overcoming PEG immunogenicity in drug delivery and bioconjugation. Polymers. 2020;12:298.
Nogueira SS, Schlegel A, Maxeiner K, Weber B, Barz M, Schroer MA, et al. Polysarcosine-functionalized lipid nanoparticles for therapeutic mRNA delivery. ACS Appl Nano Mater. 2020;3:10634–45.
Joh DY, Zimmers Z, Avlani M, Heggestad JT, Aydin HB, Ganson N, et al. Architectural modification of conformal PEG-bottlebrush coatings minimizes Anti-PEG antigenicity while preserving stealth properties. Adv Healthc Mater. 2019;8:1801177.
Ou H, Cheng T, Zhang Y, Liu J, Ding Y, Zhen J, et al. Surface-adaptive zwitterionic nanoparticles for prolonged blood circulation time and enhanced cellular uptake in tumor cells. Acta Biomater. 2018;65:339–48.
Pitek AS, Jameson SA, Veliz FA, Shukla S, Steinmetz NF. Serum albumin ‘camouflage’ of plant virus based nanoparticles prevents their antibody recognition and enhances pharmacokinetics. Biomaterials. 2016;89:89–97.
Gulati NM, Stewart PL, Steinmetz NF. Bioinspired shielding strategies for nanoparticle drug delivery applications. Mol Pharm. 2018;15:2900–9.
Roces CB, Lou G, Jain N, Abraham S, Thomas A, Halbert GW et al. Manufacturing considerations for the development of lipid nanoparticles using microfluidics. Pharmaceutics. 2020;12:1095.
Zhigaltsev IV, Belliveau N, Hafez I, Leung AK, Huft J, Hansen C, et al. Bottom-up design and synthesis of limit size lipid nanoparticle systems with aqueous and triglyceride cores using millisecond microfluidic mixing. Langmuir. 2012;28:3633–40.
Chiesa E, Greco A, Riva F, Tosca EM, Dorati R, Pisani S, et al. Staggered herringbone microfluid device for the manufacturing of chitosan/TPP nanoparticles: systematic optimization and preliminary biological evaluation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019;20:6212.
Cottet H, Biron JP, Martin M. Taylor dispersion analysis of mixtures. Anal. Chem. 2007;79:9066–73.
U.S. FDA. Drug products, including biological products, that contain nanomaterials—guidance for Industry. 2017.
Let’s talk about lipid nanoparticles. Nat Rev Mater. 2021;6, 99–99.
Reichmuth AM, Oberli MA, Jaklenec A, Langer R, Blankschtein D. mRNA vaccine delivery using lipid nanoparticles. Ther Deliv. 2016;7:319–34.
Funding
This work was partly funded by Sanofi Pasteur under a Cooperative Research and Development Agreement with the University of Montpellier and the CNRS.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CM, LL, J-FC, JT, and HC designed this study. CM and EB formulated the LNPs. CM performed the TDA and DLS experiments. LL, J-FC, JT, EB, MG, and HC reviewed the data. CM wrote the manuscript. LL, J-FC, JT, EB, MG, and HC reviewed and edited the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
Camille Malburet, Jean-François Cotte, Jérôme Thiebaud, Emilie Bazin and Marie Garinot are Sanofi employees and may hold shares or stocks in the company.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Malburet, C., Leclercq, L., Cotte, JF. et al. Taylor Dispersion Analysis to support lipid-nanoparticle formulations for mRNA vaccines. Gene Ther 30, 421–428 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41434-022-00370-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41434-022-00370-1