Abstract
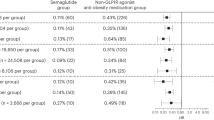
Semaglutide was approved in June 2021 for weight loss in non-diabetic, obese patients. While package inserts include sexual dysfunction as a side effect, no study has assessed the degree of this risk. The objective of our study is to assess the risk of developing erectile dysfunction after semaglutide is prescribed for weight loss in obese, non-diabetic men. The TriNetX Research database was used to identify men without a diagnosis of diabetes ages 18 to 50 with BMI > 30 who were prescribed semaglutide after June 1st, 2021. Men were excluded if they had a prior erectile dysfunction diagnosis, any phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors prescription, intracavernosal injections, penile prosthesis placement, history of testosterone deficiency, testosterone prescription, pelvic radiation, radical prostatectomy, pulmonary hypertension, or were deceased. We further restricted our cohort to non-diabetic, obese men by excluding men with a prior diabetes mellitus diagnosis, a hemoglobin A1c > 6.5%, or having ever received insulin or metformin. Men were then stratified into cohorts of those that did and did not receive a semaglutide prescription. The primary outcome was the risk of new ED diagnosis and/or new prescription of phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors at least one month after prescription of semaglutide. The secondary outcome was risk of testosterone deficiency diagnosis. Risk was reported using risk ratios with 95% confidence intervals (95% CI). 3,094 non-diabetic, obese men ages 18–50 who received a prescription of semaglutide were identified and subsequently matched to an equal number cohort of non-diabetic, obese men who never received a prescription of semaglutide. After matching, average age at index prescription for non-diabetic, obese men was 37.8 ± 7.8 and average BMI at index prescription was 38.6 ± 5.6. Non-diabetic men prescribed semaglutide were significantly more likely to develop erectile dysfunction and/or were prescribed phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors (1.47% vs 0.32%; RR: 4.5; 95% CI [2.3, 9.0]) and testosterone deficiency (1.53% vs 0.80%; RR: 1.9; 95% CI [1.2, 3.1]) when compared to the control cohort of non-diabetic men who never received a semaglutide prescription.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Commissioner O of the. FDA. FDA; 2021. [cited 2024 Feb 4]. FDA Approves New Drug Treatment for Chronic Weight Management, First Since 2014. Available from: https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-approves-new-drug-treatment-chronic-weight-management-first-2014
Rubino D, Abrahamsson N, Davies M, Hesse D, Greenway FL, Jensen C, et al. Effect of continued weekly subcutaneous semaglutide vs placebo on weight loss maintenance in adults with overweight or obesity: the STEP 4 randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2021;325:1414.
Lincoff AM, Brown-Frandsen K, Colhoun HM, Deanfield J, Emerson SS, Esbjerg S, et al. Semaglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in obesity without diabetes. New Engl J Med. 2023;0:null.
Smits MM, Van Raalte DH. Safety of semaglutide. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021;12:645563.
Elterman DS, Bhattacharyya SK, Mafilios M, Woodward E, Nitschelm K, Burnett AL. The quality of life and economic burden of erectile dysfunction. Res Rep Urol. 2021;13:79–86.
Hadi YB, Lakhani DA, Naqvi SF, Fatima NU, Sarwari AR. Outcomes of SARS-CoV-2 infection in patients with cystic fibrosis: a multicenter retrospective research network study. Respir Med. 2021;188:106606.
Agrawal P, Singh SM, Able C, Kohn TP, Herati AS. Sleep disorders are associated with testosterone deficiency and erectile dysfunction—a U.S. claims database analysis. Int J Impot Res. 2024;36:78–82.
Nackeeran S, Havanur A, Ory J, Althof S, Ramasamy R. Erectile dysfunction is a modifiable risk factor for major depressive disorder: analysis of a federated research network. J Sexual Med. 2021;18:2005–11.
Zarotsky V, Huang MY, Carman W, Morgentaler A, Singhal PK, Coffin D, et al. Systematic literature review of the risk factors, comorbidities, and consequences of hypogonadism in men. Andrology. 2014;2:819–34.
Laumann EO, Paik A, Rosen RC. Sexual dysfunction in the United States: prevalence and predictors. JAMA. 1999;281:537–44.
Genchi VA, Rossi E, Lauriola C, D’Oria R, Palma G, Borrelli A, et al. Adipose tissue dysfunction and obesity-related male hypogonadism. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23:8194.
Sairam K, Kulinskaya E, Boustead GB, Hanbury DC, Mcnicholas TA. Prevalence of undiagnosed diabetes mellitus in male erectile dysfunction. BJU Int. 2001;88:68–71.
Flegal KM, Carroll MD, Kit BK, Ogden CL. Prevalence of obesity and trends in the distribution of body mass index among US adults, 1999–2010. JAMA. 2012;307:491–7.
Molina-Vega M, Asenjo-Plaza M, Banderas-Donaire MJ, Hernández-Ollero MD, Rodríguez-Moreno S, Álvarez-Millán JJ, et al. Prevalence of and risk factors for erectile dysfunction in young nondiabetic obese men: results from a regional study. Asian J Androl. 2020;22:372–8.
Andersen I, Heitmann BL, Wagner G. Obesity and sexual dysfunction in younger Danish men. J Sex Med. 2008;5:2053–60.
Han TS, Tajar A, O’Neill TW, Jiang M, Bartfai G, Boonen S, et al. Impaired quality of life and sexual function in overweight and obese men: the European Male Ageing Study. Eur J Endocrinol. 2011;164:1003–11.
Janiszewski PM, Janssen I, Ross R. Abdominal obesity and physical inactivity are associated with erectile dysfunction independent of body mass index. J Sex Med. 2009;6:1990–8.
Di Vincenzo A, Busetto L, Vettor R, Rossato M. Obesity, male reproductive function and bariatric surgery. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2018;9:769.
Sarwer DB, Spitzer JC, Wadden TA, Rosen RC, Mitchell JE, Lancaster K, et al. Sexual functioning and sex hormones in persons with extreme obesity and seeking surgical and nonsurgical weight loss. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2013;9:997–1007.
Wake DJ, Strand M, Rask E, Westerbacka J, Livingstone DEW, Soderberg S, et al. Intra-adipose sex steroid metabolism and body fat distribution in idiopathic human obesity. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2007;66:440–6.
Jeibmann A, Zahedi S, Simoni M, Nieschlag E, Byrne MM. Glucagon-like peptide-1 reduces the pulsatile component of testosterone secretion in healthy males. Eur J Clin Invest. 2005;35:565–72.
Caltabiano R, Condorelli D, Panza S, Boitani C, Musso N, Ježek D, et al. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor is expressed in human and rodent testis. Andrology. 2020;8:1935–45.
Li S, Lu MM, Zhou D, Hammes SR, Morrisey EE. GLP-1: a novel zinc finger protein required in somatic cells of the gonad for germ cell development. Dev Biol. 2007;301:106–16.
Grau-Bové C, González-Quilen C, Cantini G, Nardini P, Espina B, Bani D, et al. GLP1 exerts paracrine activity in the intestinal lumen of human colon. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23:3523.
Ferreira JP, Böhm M, Rossignol P, Zannad F. Impact of anti-hypertensive therapy in the sexual health of men and women: an analysis from the SPRINT trial. Am J Hypertens. 2021;34:760–72.
Henderson T, Shepheard J, Sundararajan V. Quality of diagnosis and procedure coding in ICD-10 administrative data. Med Care. 2006;44:1011–9.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Corey Able: Idea generation, data collection, data analysis, manuscript writing, manuscript editing. Brian Liao: Data collection, data analysis, manuscript writing. Gal Saffati: Manuscript writing, manuscript editing. Ankith Maramanda: Manuscript writing, manuscript editing. James Applewhite: Manuscript writing, manuscript editing. Ali A. Nasrallah: Idea generation, manuscript writing, manuscript editing. Joseph Sonstein: Idea refinement, manuscript editing. Laith Alzweri: Idea refinement, manuscript editing. Taylor Kohn: Idea refinement, data analysis, manuscript editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Attestation Statement
Data regarding any of the subjects in the study has not been previously published. Available data will be made available to the editors of the journal for review or query upon request.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Able, C., Liao, B., Saffati, G. et al. Prescribing semaglutide for weight loss in non-diabetic, obese patients is associated with an increased risk of erectile dysfunction: a TriNetX database study. Int J Impot Res 37, 315–319 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41443-024-00895-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41443-024-00895-6
This article is cited by
-
Comment on: Male sexual dysfunction associated with GLP-1 receptor agonists: a cross-sectional analysis of FAERS data
International Journal of Impotence Research (2025)
-
Comment on: Male sexual dysfunction associated with GLP-1 receptor agonists: a cross-sectional analysis of FAERS data
International Journal of Impotence Research (2025)
-
Male sexual dysfunction associated with GLP-1 receptor agonists: a cross-sectional analysis of FAERS data
International Journal of Impotence Research (2025)
-
Comment on: Prescribing semaglutide for weight loss in non-diabetic, obese patients is associated with an increased risk of erectile dysfunction: a TriNetX database study
International Journal of Impotence Research (2025)
-
Response to Comment on: Male sexual dysfunction associated with GLP-1 receptor agonists: a cross-sectional analysis of FAERS data
International Journal of Impotence Research (2025)