Abstract
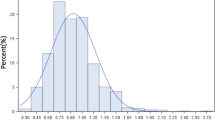
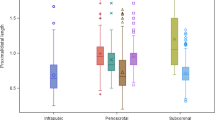
Despite the widespread use of narrow diameter inflatable penile prosthesis (IPP) cylinders in patients with corporal fibrosis, outcomes data is sparse. We evaluated patients who underwent IPP placement with AMS™ 700 Controlled Expansion Restricted (CXR) cylinders from 2007–2021. Patient characteristics, device details, and surgical outcomes were assessed. A non-validated questionnaire was also distributed to patients to assess satisfaction. Among 982 IPPs placed over the study period at our institution, 49 (5.0%) used CXR cylinders. Indications for narrow cylinders: prior explant for infection (67.3%), ischemic priapism (16.3%), and idiopathic fibrosis (16.3%). Median corporal length was 19 cm (IQR 17–21 cm). Discordant intraoperative corporal measurements (24.5%) and RTE lengths (26.5%) were common. Post-operative complications occurred in 8 patients (16.3%) and included 3 infections (6.1%), 2 cylinder herniations (4.1%), 2 mechanical failures (4.1%), and one case of glans necrosis (2.0%). Five of these (10.2%) required explantation, while 4 (8.2%) were managed with revision. Over the follow-up period, 73.5% of patients reported satisfaction with rigidity. Primary drivers of dissatisfaction were perceived loss of penile length and girth. The AMS™ 700 CXR is a useful tool for challenging corporal fibrosis cases and shows acceptable surgical outcomes with moderate patient acceptability.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Trost LW, Baum N, Hellstrom WJ. Managing the difficult penile prosthesis patient. J Sex Med. 2013;10:893–907.
Wilson SK, Simhan J, Gross MS. Cylinder insertion into scarred corporal bodies: prosthetic urology’s most difficult challenge: some suggestions for making the surgery easier. Int J Impot Res. 2020;32:483–94.
Gonzalez‐Cadavid NF. Mechanisms of penile fibrosis. J Sex Med. 2009;6:353–62.
Martínez‐Salamanca JI, Mueller A, Moncada I, Carballido J, Mulhall JP. Penile prosthesis surgery in patients with corporal fibrosis: a state-of-the-art review. J Sex Med. 2011;8:1880–9.
Henry GD, Karpman E, Brant W, Christine B, Kansas BT, Khera M, et al. The who, how and what of real-world penile implantation in 2015: the PROPPER registry baseline data. The Journal of urology. 2016;195:427–33.
Habous M, Giona S, Tealab A, Sherif H, Abdelwahab O, Binsaleh S, et al. Penile length is preserved after implant surgery. BJU Int. 2019;123:885–90.
Lin H, Wang G, Wang R. Vacuum erectile device for penile rehabilitation. J Integr Nephrol Androl. 2014;1:4–10.
Mehr J, Santarelli S, Green TP, Beetz J, Panuganti S, Wang R. Emerging roles of penile traction therapy and vacuum erectile devices. Sex Med Rev. 2022;10:421–33.
Sellers T, Dineen M, Salem EA, Wilson SK. Vacuum preparation, optimization of cylinder length and postoperative daily inflation reduces complaints of shortened penile length following implantation of inflatable penile prosthesis. Adv Sex Med. 2013;3:14–18.
Tsambarlis PN, Chaus F, Levine LA. Successful placement of penile prostheses in men with severe corporal fibrosis following vacuum therapy protocol. J Sex Med. 2017;14:44–46.
Krughoff K, Bearelly P, Apoj M, Munarriz N, Thirumavalavan N, Pan S, et al. Multicenter surgical outcomes of penile prosthesis placement in patients with corporal fibrosis and review of the literature. Int J Impot Res. 2022;34:86–92.
Yafi FA, Sangkum P, McCaslin IR, Hellstrom WJ. Strategies for penile prosthesis placement in Peyronie’s disease and corporal fibrosis. Curr Urol Rep. 2015;16:21.
Garber BB, Lim C. Inflatable penile prosthesis insertion in men with severe intracorporal fibrosis. Curr Urol. 2016;10:92–96.
Mooreville M, Adrian S, Delk JR, Wilson SK. Implantation of inflatable penile prosthesis in patients with severe corporeal fibrosis: introduction of a new penile cavernotome. J Urol. 1999;162:2054–7.
Karpman E, Griggs R, Twomey C, Henry GD. Dipping Titan implants in Irrisept solution (0.05% chlorhexidine gluconate) and exposure to various aerobic, anaerobic, and fungal species. J Sex Med. 2023;20:1025–31.
Akakpo W, Pineda MA, Burnett AL. Critical analysis of satisfaction assessment after penile prosthesis surgery. Sex Med Rev. 2017;5:244–51.
Rosen RC, Cappelleri J, Smith M, Lipsky J, Pena B. Development and evaluation of an abridged, 5-item version of the International Index of Erectile Function (IIEF-5) as a diagnostic tool for erectile dysfunction. Int J Impot Res. 1999;11:319–26.
Althof SE, Corty EW, Levine SB, Levine F, Burnett AL, McVary K, et al. EDITS: development of questionnaires for evaluating satisfaction with treatments for erectile dysfunction. Urology. 1999;53:793–9.
Campbell S, Kim C, Allkanjari A, Nose B, Selph J, Lentz A. Small diameter penile implants: a survey on current utilization and review of literature. J Sex Med. 2022;19:S70–S71.
Chung PH, Siegel JA, Tausch TJ, Klein AK, Scott JM, Morey AF. Inflatable penile prosthesis as tissue expander: what is the evidence? Int Braz J Urol. 2017;43:911–6.
Wilson SK, Delk JR, Mulcahy JJ, Cleves M, Salem EA. SURGERY: upsizing of inflatable penile implant cylinders in patients with corporal fibrosis. J Sex Med. 2006;3:736–42.
Salter CA, Bach PV, Jenkins L, Bennett N, Yafi FA, Khatib FE, et al. Development and validation of the satisfaction survey for inflatable penile implant (SSIPI). J Sex Med. 2021;18:1641–51.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
BEJ: Survey design, survey implementation, data review, statistical analysis, manuscript preparation, manuscript review. BTL: Survey design, survey implementation, data review. MEV: Survey design, survey implementation, data review, statistical analysis, manuscript preparation, manuscript review. GSC: Survey design, survey implementation, data review. BPF: Data review, statistical analysis, manuscript preparation, manuscript review. AFM: survey design, survey implementation, manuscript review.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
AFM: Boston Scientific (consultant, speaker), Coloplast Corporation (consultant, speaker). MEV: Boston Scientific (consultant). All other authors have no disclosures.
Ethics approval
This study was approved by the University of Texas Southwestern IRB (STU318 2020-1187). Given its retrospective nature, informed consent was waived after IRB review.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Johnson, B.E., Langford, B.T., VanDyke, M.E. et al. Long-term experience with AMS-700 CXR inflatable penile prosthesis in high-risk patients with corporal fibrosis. Int J Impot Res 37, 66–71 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41443-024-00962-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41443-024-00962-y
This article is cited by
-
Commentary on: Long-term experience with AMS-700 CXR inflatable penile prosthesis in high-risk patients with corporal fibrosis
International Journal of Impotence Research (2025)
-
Advances in penile prosthetics: current trends and future directions in erectile dysfunction treatment
International Journal of Impotence Research (2025)
-
Glans necrosis following penile procedures: a systematic review of etiology, frequency, and management
International Journal of Impotence Research (2025)
-
Penile prosthesis implantation: a systematic review of intraoperative and postoperative complications
International Journal of Impotence Research (2025)