Fig. 1
From: Exploring patterns enriched in a dataset with contrastive principal component analysis
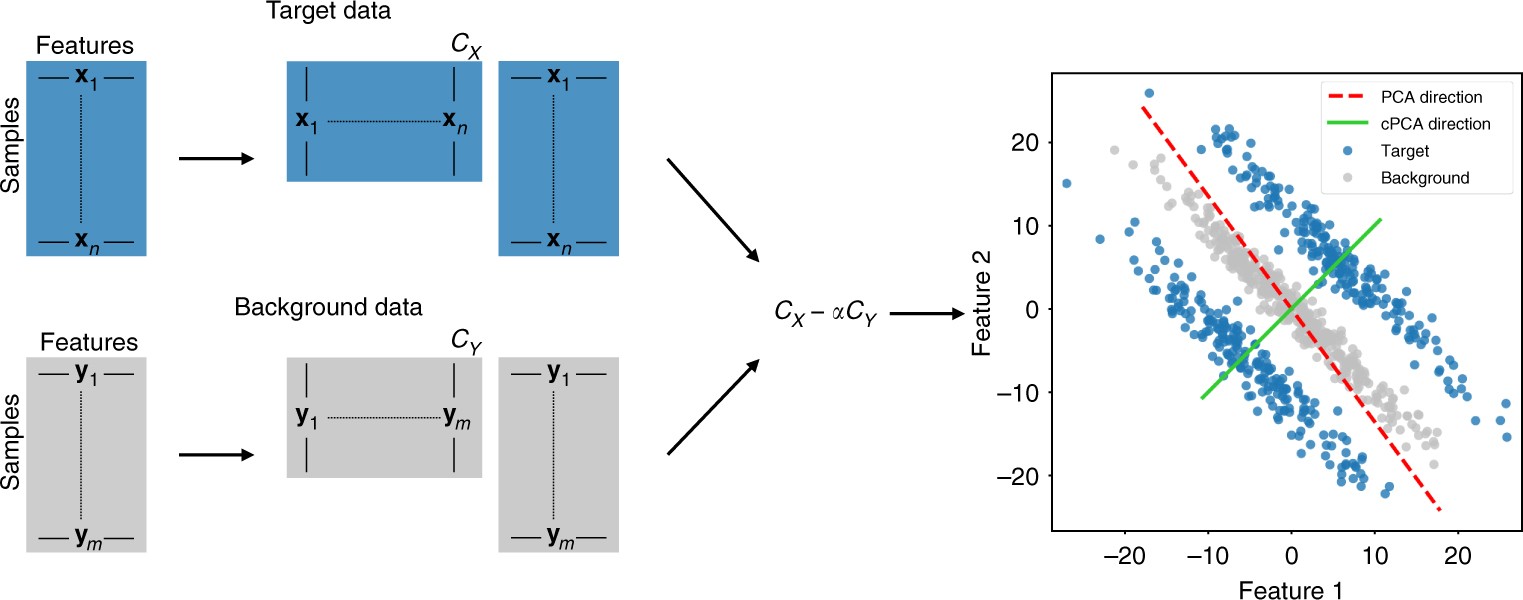
Schematic Overview of cPCA. To perform cPCA, compute the covariance matrices C X , C Y of the target and background datasets. The singular vectors of the weighted difference of the covariance matrices, C X − α · C Y , are the directions returned by cPCA. As shown in the scatter plot on the right, PCA (on the target data) identifies the direction that has the highest variance in the target data, while cPCA identifies the direction that has a higher variance in the target data as compared to the background data. Projecting the target data onto the latter direction gives patterns unique to the target data and often reveals structure that is missed by PCA. Specifically, in this example, reducing the dimensionality of the target data by cPCA would reveal two distinct clusters
