Fig. 1: Overview of FOREST.
From: RNA structure-wide discovery of functional interactions with multiplexed RNA motif library
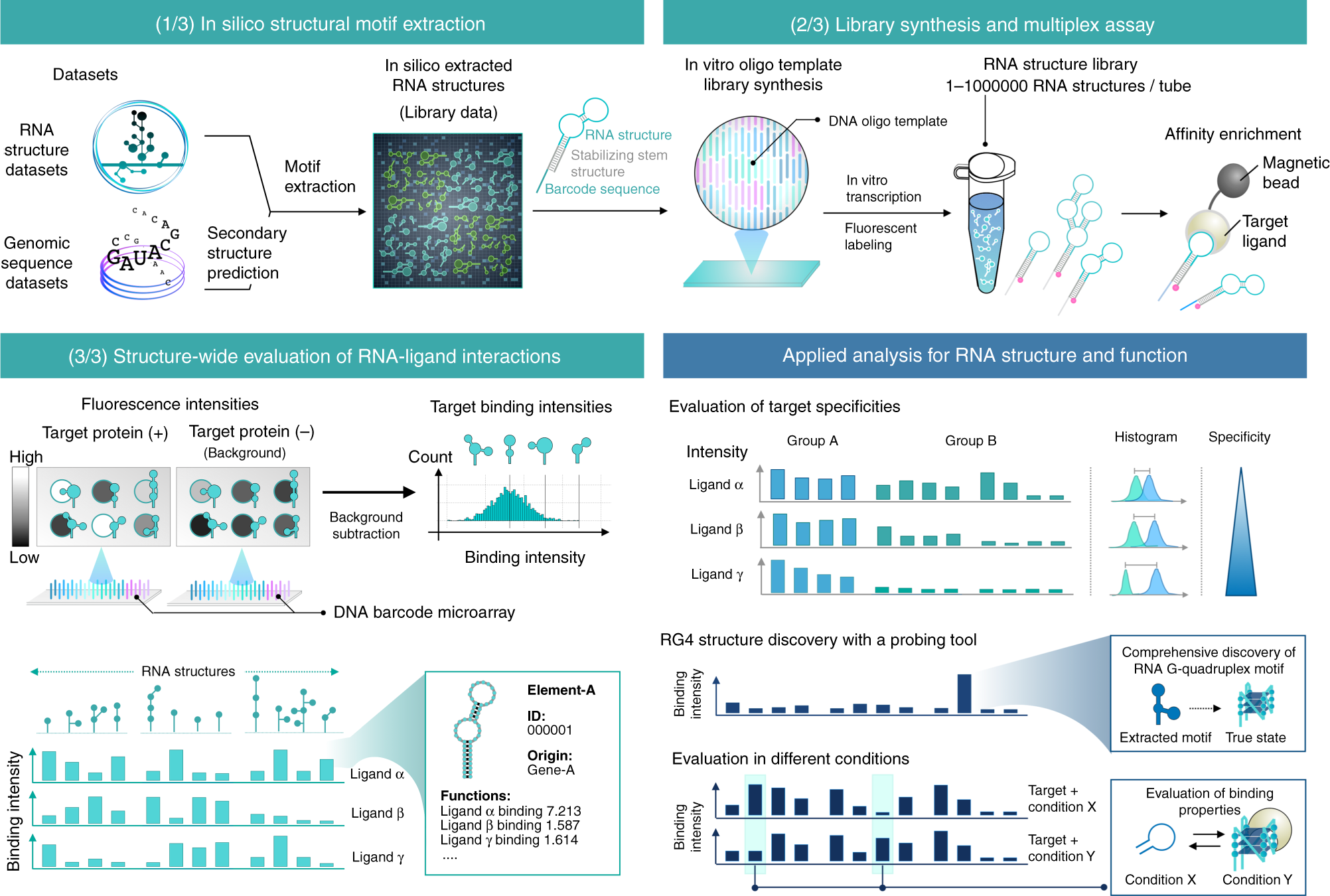
FOREST identifies functional and structured RNA motifs on a large scale. It consists of three procedures. (1) In silico RNA motif extraction. Target RNA motifs are systematically extracted from the structural RNA datasets. The definition of the target motif is flexibly determined. See also Fig. 2, Supplementary Figs. 1–4, and Methods. Extracted RNAs are conjugated to the stabilizing stem structure and RNA barcodes for massively parallel quantification of each RNA in the library. (2) After adding the T7 promoter sequence, reverse complementary DNA sequences are synthesized as an oligo pool. FOREST can quantify the function of all RNA structures in the library in combination with a biochemical assay (e.g., profiling of RNP interactions by RNA-affinity enrichment assay). (3) Analysis for structure-wide discovery of a functional RNA element. To quantify the abundance of the RNA probes, we use a DNA barcode microarray that captures complementary RNA barcodes via specific RNA–DNA hybridization. The output of massive quantification provides the functional score of each RNA, enabling the comprehensive identification of functional RNA-ligand interactions. The results of FOREST can be applied to further analyses, including the evaluation of binding properties at different conditions and the identification of structured RNAs (e.g., RNA G-quadruplexes) (right bottom).
