Fig. 1: Cellular synthetic gRNA CRISPR-Cas9 cleavage outcome screen.
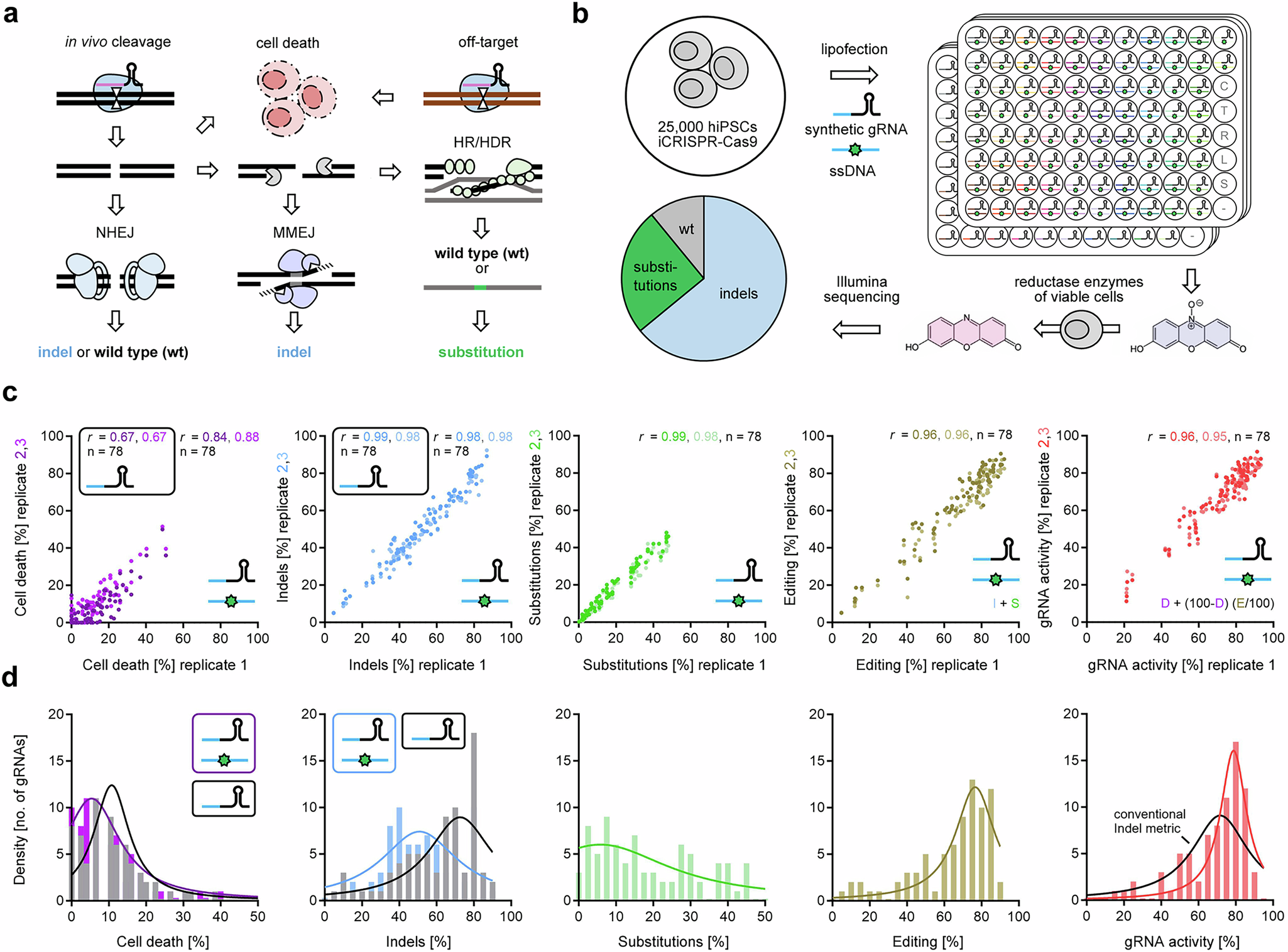
a Schematic of potential cellular cleavage outcomes after a CRISPR induced DSB. Cells can die as a consequence of the DSB or repair it by competing pathways (NHEJ, MMEJ, HR/HDR), which can result in perfect repair to the wild type sequence, insertions or deletions (indels), or targeted substitutions when a DNA donor is provided. b Chemically synthesized (synthetic) gRNA screen design. 409B2 hiPSCs expressing Cas9 were lipofected with synthetic oligonucleotides in one 96 well per target (n = 78 targets). Cell survival was measured by a resazurin fluorescence assay, followed by subsequent DNA isolation and Illumina sequencing of target PCR amplicons. c Scatter plots of replicates for percentage of cell death in purple, indels in blue, substitutions in green, editing (sum of indels and substitutions) in gold, and in vivo gRNA activity (quantification of cell death and editing) in red, when editing with gRNA and DNA donor. Darker and brighter dots indicate the correlation of replicate one with respect to replicate two and three, respectively. Pearson’s r for correlation (two-tailed) of independent biological replicates (n = 3) are stated (black frame for editing without DNA donor). All p values are <0.0001. d Histograms showing the density of the distribution of gRNAs that result in different mean (n = 3) percentages of cell death, indels, substitutions, editing, and gRNA activity, when editing with gRNA and DNA donor. For cell death and indels, gray bars represent the distribution for editing without DNA donor. Lines show the respective Lorentzian distributions (black for editing without DNA donor, colored for editing with DNA donor). Source data are provided as a Source Data file.
