Abstract
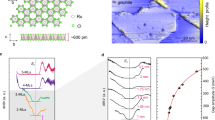
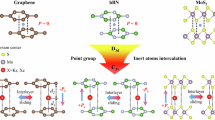
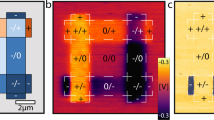
We demonstrate electrically switchable, non-volatile dipoles in graphene/thin hBN/α-RuCl3alpha-RuCl3 heterostructures, stabilized purely by interfacial charge transfer across an atomically thin dielectric barrier. This mechanism requires no sliding or twisting to explicitly break inversion symmetry and produces robust ferroelectric-like hysteresis loops that emerge prominently near 30 K. Systematic measurements under strong in-plane and out-of-plane magnetic fields reveal negligible effects on the hysteresis characteristics, confirming that the primary mechanism driving the dipole switching is electrostatic. Our findings establish a distinct and robust route to electrically tunable ferroelectric phenomena in van der Waals heterostructures, opening opportunities to explore the interplay between interfacial charge transfer and temperature-tuned barrier crossing of dipole states at the atomic scale.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Source data for all main and supplementary text figures are provided with this paper and are also available via the Figshare repository at https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.30747287
References
Dawber, M., Rabe, K. M. & Scott, J. F. Physics of thin-film ferroelectric oxides. Rev. Mod. Phys. 77, 1083 (2005).
Bune, A. V. et al. Two-dimensional ferroelectric films. Nature 391, 874 (1998).
Fong, D. D. et al. Ferroelectricity in ultrathin perovskite films. Science 304, 1650 (2004).
Wang, C., You, L., Cobden, D. & Wang, J. Towards two-dimensional van der waals ferroelectrics. Nat. Mater. 22, 542 (2023).
Zhou, Y., Dong, S., Shan, C., Ji, K. & Zhang, J. Two-dimensional ferroelectricity induced by octahedral rotation distortion in perovskite oxides. Phys. Rev. B 105, 075408 (2022).
Wu, M. Two-dimensional van der waals ferroelectrics: scientific and technological opportunities. ACS Nano 15, 9229 (2021).
Wu, M. & Jena, P. The rise of two-dimensional van der waals ferroelectrics. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Comput. Mol. Sci. 8, e1365 (2018).
Xiao, J. et al. Intrinsic two-dimensional ferroelectricity with dipole locking. Phys. Rev. Lett. 120, 227601 (2018).
Ding, W. et al. Prediction of intrinsic two-dimensional ferroelectrics in In2Se3 and other III2-VI3 van der waals materials. Nat. Commun. 8, 14956 (2017).
Yuan, S. et al. Room-temperature ferroelectricity in MoTe2 down to the atomic monolayer limit. Nat. Commun. 10, 1775 (2019).
Higashitarumizu, N. et al. Purely in-plane ferroelectricity in monolayer SnS at room temperature. Nat. Commun. 11, 2428 (2020).
Chang, K. et al. Discovery of robust in-plane ferroelectricity in atomic-thick SnTe. Science 353, 274 (2016).
Gou, J. et al. Two-dimensional ferroelectricity in a single-element bismuth monolayer. Nature 617, 67 (2023).
Chang, K. et al. Microscopic manipulation of ferroelectric domains in SnSe monolayers at room temperature. Nano Lett. 20, 6590 (2020).
Liu, F. et al. Room-temperature ferroelectricity in CuInP2S6 ultrathin flakes. Nat. Commun. 7, 12357 (2016).
Ghosh, T. et al. Ultrathin free-standing nanosheets of Bi2O2Se: Room temperature ferroelectricity in self-assembled charged layered heterostructure. Nano Lett. 19, 5703 (2019).
Fei, Z. et al. Ferroelectric switching of a two-dimensional metal. Nature 560, 336 (2018).
Vizner Stern, M. et al. Interfacial ferroelectricity by van der waals sliding. Science 372, 1462 (2021).
Meng, P. et al. Sliding induced multiple polarization states in two-dimensional ferroelectrics. Nat. Commun. 13, 7696 (2022).
Wang, Z., Gui, Z. & Huang, L. Sliding ferroelectricity in bilayer honeycomb structures: a first-principles study. Phys. Rev. B 107, 035426 (2023).
Niu, R. et al. Giant ferroelectric polarization in a bilayer graphene heterostructure. Nat. Commun. 13, 6241 (2022).
Ji, J., Yu, G., Xu, C. & Xiang, H. General theory for bilayer stacking ferroelectricity. Phys. Rev. Lett. 130, 146801 (2023).
Yang, L., Ding, S., Gao, J. & Wu, M. Atypical sliding and moiré ferroelectricity in pure multilayer graphene. Phys. Rev. Lett. 131, 096801 (2023).
Zhang, S. et al. Visualizing moiré ferroelectricity via plasmons and nano-photocurrent in graphene/twisted-WSe2 structures. Nat. Commun. 14, 6200 (2023).
Yasuda, K., Wang, X., Watanabe, K., Taniguchi, T. & Jarillo-Herrero, P. Stacking-engineered ferroelectricity in bilayer boron nitride. Science 372, 1458 (2021).
Woods, C. et al. Charge-polarized interfacial superlattices in marginally twisted hexagonal boron nitride. Nat. Commun. 12, 347 (2021).
Li, L. & Wu, M. Binary compound bilayer and multilayer with vertical polarizations: two-dimensional ferroelectrics, multiferroics, and nanogenerators. ACS Nano 11, 6382 (2017).
Chen, X., Xuan, X., Guo, W. & Zhang, Z. Ferroelectricity in van der waals multilayers via interfacial polarization engineering. npj 2D Mater. Appl. 9, 10 (2025).
Zheng, Z. et al. Unconventional ferroelectricity in moiré heterostructures. Nature 588, 71 (2020).
Rogée, L. et al. Ferroelectricity in untwisted heterobilayers of transition metal dichalcogenides. Science 376, 973 (2022).
Rossi, A. et al. Direct visualization of the charge transfer in a graphene/α-RuCl3 heterostructure via angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy. Nano Lett. 23, 8000 (2023).
Rizzo, D. et al. Charge-transfer plasmon polaritons at graphene/α-RuCl3 interfaces. Nano Lett. 20, 8438 (2020).
Rizzo, D. et al. Polaritonic probe of an emergent 2D dipole interface. Nano Lett. 23, 8426 (2023).
Plumb, K. et al. α-RuCl3: a spin-orbit assisted Mott insulator on a honeycomb lattice. Phys. Rev. B 90, 041112 (2014).
Banerjee, A. et al. Proximate Kitaev quantum spin liquid behaviour in a honeycomb magnet. Nat. Mater. 15, 733 (2016).
Banerjee, A. Neutron scattering in the proximate quantum spin liquid α-RuCl3. Science 356, 1055 (2017).
Yokoi, T. et al. Half-integer quantized anomalous thermal Hall effect in the Kitaev material candidate α-RuCl3. Science 373, 568 (2021).
Sears, J. et al. Magnetic order in α-RuCl3: a honeycomb-lattice quantum magnet with strong spin-orbit coupling. Phys. Rev. B 91, 144420 (2015).
Mashhadi, S. et al. Spin-split band hybridization in graphene proximitized with α-RuCl3 nanosheets. Nano Lett. 19, 4659 (2019).
Zhou, B. et al. Evidence for charge transfer and proximate magnetism in graphene-α-RuCl3 heterostructures. Phys. Rev. B 100, 165426 (2019).
Balgley, J. et al. Ultrasharp lateral p-n junctions in modulation-doped graphene. Nano. Lett. 22, 4124 (2022).
Rizzo, D. J. et al. Nanometer-scale lateral p-n junctions in graphene/α-RuCl3 heterostructures. Nano. Lett. 22, 1946 (2022).
Kim, S. et al. Spin and valley-polarized multiple fermi surfaces of α-RuCl3/bilayer graphene heterostructure. Appl. Phys. Lett. 123, 173101 (2023).
Wang, Y. et al. Modulation doping via a two-dimensional atomic crystalline acceptor. Nano Lett. 20, 8446 (2020).
Wang, X. et al. Interfacial ferroelectricity in rhombohedral-stacked bilayer transition metal dichalcogenides. Nat. Nanotechnol. 17, 367 (2022).
Weston, A. et al. Interfacial ferroelectricity in marginally twisted 2D semiconductors. Nat. Nanotechnol. 17, 390 (2022).
Yang, Q., Wu, M. & Li, J. Origin of two-dimensional vertical ferroelectricity in WTe2 bilayer and multilayer. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 9, 7160 (2018).
Zheng, Y. et al. Graphene field-effect transistors with ferroelectric gating. Phys. Rev. Lett. 105, 166602 (2010).
Lee, T. Y. et al. Ferroelectric polarization-switching dynamics and wake-up effect in Si-doped HfO2. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 11, 3142 (2019).
Illarionov, Y. Y. et al. The role of charge trapping in MoS2/SiO2 and MoS2/hBN field-effect transistors. 2D Mater. 3, 035004 (2016).
Macucci, M. et al. On current transients in MoS2 field effect transistors. Sci. Rep. 7, 11575 (2017).
Ziatdinov, M. et al. Atomic-scale observation of structural and electronic orders in the layered compound α-RuCl3. Nat. Commun. 7, 13774 (2016).
Zheng, X. et al. Incommensurate charge super-modulation and hidden dipole order in layered Kitaev material α-RuCl3. Nat. Commun. 15, 7658 (2024).
Liu, Z. et al. Dynamic interfacial quantum dipoles in charge transfer heterostructures https://arxiv.org/abs/2508.01027 (2025).
Kim, D. et al. Full-dry flipping transfer method for van der waals heterostructure. Curr. Appl. Phys. 59, 165 (2024).
Kim, Y. et al. Even denominator fractional quantum hall states in higher landau levels of graphene. Nat. Phys. 15, 154 (2019).
Kim, D. et al. Robust interlayer-coherent quantum Hall states in twisted bilayer graphene. Nano Lett. 23, 163 (2023).
Kim, S. et al. Orbitally controlled quantum Hall states in decoupled two-bilayer graphene sheets. Adv. Sci. 10, 2300574 (2023).
Kresse, G. & Furthmüller, J. Efficient iterative schemes for ab initio total-energy calculations using a plane-wave basis set. Phys. Rev. B 54, 11169 (1996).
Perdew, J., Burke, K. & Ernzerhof, M. Generalized gradient approximation made simple. Phys. Rev. Lett. 77, 3865 (1996).
Dudarev, S., Botton, G., Savrasov, S., Humphreys, C. & Sutton, A. Electron-energy-loss spectra and the structural stability of nickel oxide: an LSDA+U study. Phys. Rev. B 57, 1505 (1998).
Bučko, T., Lebègue, S., Hafner, J. & Ángyán, J. Improved density dependent correction for the description of london dispersion forces. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 9, 4293 (2013).
Acknowledgements
We thank Erik Henriksen for helpful discussions.The work from DGIST was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) (Grant No. RS-2025-00557717, RS-2023-00274875, RS-2023-00269616) and the Nano and Material Technology Development Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by Ministry of Science and ICT (No. RS-2024-00444725). We also acknowledge the partner group program of the Max Planck Society. Part of this work was supported by Global Partnership Program of Leading Universities in Quantum Science and Technology (RS-2025-02317602). G.Y.C. is financially supported by Samsung Science and Technology Foundation under Project Number SSTF-BA2401-03, the NRF of Korea (Grants No. RS-2023-00208291, RS-2024-00410027, 2023M3K5A1094810, RS-2023-NR119931, RS-2024-00444725, RS-2023-00256050, IRS-2025-25453111, RS-2025-08542968) funded by the Korean Government (MSIT), the Air Force Office of Scientific Research under Award No. FA23862514026, and Institute of Basic Science under project code IBS-R014-D1. This work was performed in part at Aspen Center for Physics, which is supported by National Science Foundation grant PHY-2210452. K.-H.J. was supported by Global-Learning and Academic research institution for Master’s PhD students, and Postdocs (LAMP) Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Ministry of Education (No. RS-2024-00443714). The works at POSTECH were supported by National Research Foundation of Korea (No. RS-2024-00410027 and No. 2022M3H4A1A04074153). K.W. and T.T. acknowledge support from the JSPS KAKENHI (Grant Numbers 21H05233 and 23H02052), the CREST (JPMJCR24A5), JST and World Premier International Research Center Initiative (WPI), MEXT, Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
S.K., Y.K., and G.Y.C. conceived the project. S.K., J.C., and D.K. carried out the device fabrication and performed the low-temperature measurement with Y.K. and J.F. The theory was performed by K.-H.J. and G.Y.C., J.H.Y., and J.S.K. conducted Raman Spectroscopy. T.T. and K.W. synthesized the h-BN crystals. All authors contributed to the manuscript writing.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interest
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Communications thanks the anonymous reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work. A peer review file is available.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, S., Yun, J.H., Choe, J. et al. Ferroelectric switching of interfacial dipoles in α-RuCl3/graphene heterostructure. Nat Commun (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-025-68072-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-025-68072-x