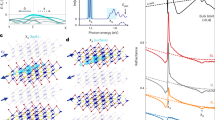
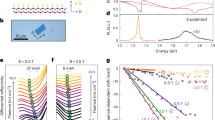
Abstract
Excitons in recently discovered two-dimensional magnetic semiconductors have emerged as a promising vehicle for optoelectronic and spin-photonic applications. To exploit novel possibilities magnetic degrees of freedom offer, insight into the interplay of magnetism, lattice and optical excitations becomes essential. We consider Chromium Sulphur Bromide, which has two kinds of excitons, XB at 1.8 eV and XA at 1.38 eV. Here we show, through a combination of many body perturbation theory and experiment, that XB is an order of magnitude more sensitive to magnetic and lattice perturbations than XA. We trace the difference to the latter being localised (Frenkel-like), while the former is delocalised (Wannier-Mott-like) – a coexistence rarely seen in two-dimensional materials. This finding is supported by the strong temperature and magnetic field (up to 85 Tesla) dependent shifts in optical response for XB (much smaller for XA), and we show it is related to XB’s tendency for delocalisation (in-plane and out-of-plane) and enhanced coupling with Ag phonon modes.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The magneto—optical data generated and/or analysed during the study are available without restrictions in the Zenodo database under the following online repository accesion code: https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.17941646.
References
Wang, G. et al. Colloquium: Excitons in atomically thin transition metal dichalcogenides. Rev. Mod. Phys. 90, 021001 (2018).
Raja, A. et al. Dielectric disorder in two-dimensional materials. Nat. Nanotechnol. 14, 832 (2019).
Raja, A. et al. Coulomb engineering of the bandgap and excitons in two-dimensional materials. Nat. Commun. 8, 15251 (2017).
Dyksik, M. et al. Brightening of dark excitons in 2d perovskites. Sci. Adv. 7, eabk0904 (2021).
Zhang, X.-X. et al. Magnetic brightening and control of dark excitons in monolayer wse2. Nat. Nanotechnol. 12, 883 (2017).
Rosati, R. et al. Dark exciton anti-funneling in atomically thin semiconductors. Nat. Commun. 12, 7221 (2021).
Tran, K. et al. Evidence for moiré excitons in van der waals heterostructures. Nature 567, 71 (2019).
Malic, E., Perea-Causin, R., Rosati, R., Erkensten, D. & Brem, S. Exciton transport in atomically thin semiconductors. Nat. Commun. 14, 3430 (2023).
Zhao, S. et al. Excitons in mesoscopically reconstructed moiré heterostructures. Nat. Nanotechnol. 18, 572 (2023).
Gong, C. et al. Discovery of intrinsic ferromagnetism in two-dimensional van der waals crystals. Nature 546, 265 (2017).
Lee, J.-U. et al. Ising-type magnetic ordering in atomically thin feps3. Nano Lett. 16, 7433 (2016).
Huang, B. et al. Layer-dependent ferromagnetism in a van der waals crystal down to the monolayer limit. Nature 546, 270 (2017).
Gibertini, M., Koperski, M., Morpurgo, A. F. & Novoselov, K. S. Magnetic 2d materials and heterostructures. Nat. Nanotechnol. 14, 408 (2019).
Wang, Q. H. et al. The magnetic genome of two-dimensional van der waals materials. ACS Nano 16, 6960 (2022).
Jiang, S., Li, L., Wang, Z., Mak, K. F. & Shan, J. Controlling magnetism in 2d cri3 by electrostatic doping. Nat. Nanotechnol. 13, 549 (2018).
Huang, B. et al. Electrical control of 2d magnetism in bilayer cri 3. Nat. Nanotechnol. 13, 544 (2018).
Wu, M., Li, Z., Cao, T. & Louie, S. G. Physical origin of giant excitonic and magneto-optical responses in two-dimensional ferromagnetic insulators. Nat. Commun. 10, 2371 (2019a).
Seyler, K. L. et al. Ligand-field helical luminescence in a 2d ferromagnetic insulator. Nat. Phys. 14, 277 (2018).
Wilson, N. P. et al. Interlayer electronic coupling on demand in a 2d magnetic semiconductor. Nat. Mater. 20, 1657 (2021).
Dirnberger, F. et al. Magneto-optics in a van der waals magnet tuned by self-hybridized polaritons. Nature 620, 533 (2023).
Zhang, P. et al. All-optical switching of magnetization in atomically thin cri3. Nat. Mater. 21, 1373 (2022).
Mak, K. F., Shan, J. & Ralph, D. C. Probing and controlling magnetic states in 2d layered magnetic materials. Nat. Rev. Phys. 1, 646 (2019).
Grzeszczyk, M. et al. Strongly Correlated Exciton-Magnetization System for Optical Spin Pumping in CrBr3 and CrI3. Adv. Mater. 35, 2209513 (2023).
Göser, O., Paul, W. & Kahle, H. Magnetic properties of crsbr. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 92, 129 (1990).
Ziebel, M. E. et al. Crsbr: An air-stable, two-dimensional magnetic semiconductor. Nano Lett. 24, 4319 (2024).
Shao, Y. et al. Magnetically confined surface and bulk excitons in a layered antiferromagnet. Nat. Mater. 24, 391–398 (2025).
Marques-Moros, F., Boix-Constant, C., Mañas-Valero, S., Canet-Ferrer, J. & Coronado, E. Interplay between optical emission and magnetism in the van der waals magnetic semiconductor crsbr in the two-dimensional limit. ACS Nano 17, 13224 (2023).
Bae, Y. J. et al. Exciton-coupled coherent magnons in a 2d semiconductor. Nature 609, 282 (2022).
Ruta, F. L. et al. Hyperbolic exciton polaritons in a van der waals magnet. Nat. Commun. 14, 8261 (2023).
Wannier, G. H. The structure of electronic excitation levels in insulating crystals. Phys. Rev. 52, 191 (1937).
Kang, S. et al. Coherent many-body exciton in van der waals antiferromagnet nips3. Nature 583, 785 (2020).
Dirnberger, F. et al. Spin-correlated exciton–polaritons in a van der waals magnet. Nat. Nanotechnol. 17, 1060 (2022).
Frenkel, J. On the transformation of light into heat in solids. i. Phys. Rev. 37, 17 (1931a).
Frenkel, J. On the transformation of light into heat in solids. ii. Phys. Rev. 37, 1276 (1931b).
Jelley, E. E. Spectral absorption and fluorescence of dyes in the molecular state. Nature 138, 1009 (1936).
West, B. A., Womick, J. M., McNeil, L., Tan, K. J. & Moran, A. M. Ultrafast dynamics of frenkel excitons in tetracene and rubrene single crystals. J. Phys. Chem. C. 114, 10580 (2010).
Cunningham, B., Grüning, M., Pashov, D. & van Schilfgaarde, M. QS\(G\widehat{W}\): Quasiparticle Self Consistent GW with Ladder Diagrams in W. Phys. Rev. B 108, 165104 (2023).
Tanabe, Y. & Sugano, S. On the absorption spectra of complex ions ii. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 9, 766 (1954).
Sugano, S. Multiplets of transition-metal ions in crystals (Elsevier, 2012).
Rydberg, J. R. Xxxiv. on the structure of the line-spectra of the chemical elements. Lond., Edinb., Dublin Philos. Mag. J. Sci. 29, 331 (1890).
Ritz, W. On a new law of series spectra. Astrophys. J. 28, 237 (1908).
Lin, K. et al. Strong exciton-phonon coupling as a fingerprint of magnetic ordering in van der Waals layered CrSBr. ACS Nano 18, 2898 (2024).
Wang, T. et al. Magnetically-dressed crsbr exciton-polaritons in ultrastrong coupling regime. Nat. Commun. 14, 5966 (2023).
van Schilfgaarde, M., Kotani, T. & Faleev, S. Quasiparticle self-consistent g w theory. Phys. Rev. Lett. 96, 226402 (2006).
Pashov, D. et al. Questaal: a package of electronic structure methods based on the linear muffin-tin orbital technique. Comp. Phys. Comm. 249, 107065 (2020).
Klein, J. et al. The Bulk van der Waals layered magnet CrSBr is a quasi-1D material. ACS Nano 17, 5316 (2023).
Qian, T.-X., Zhou, J., Cai, T.-Y. & Ju, S. Anisotropic electron-hole excitation and large linear dichroism in the two-dimensional ferromagnet crsbr with in-plane magnetization. Phys. Rev. Res. 5, 033143 (2023).
Watson, M. D. et al. Giant exchange splitting in the electronic structure of a-type 2d antiferromagnet crsbr. npj 2D Mater. Appl. 8, 54 (2024).
Smolenski, S. et al. Large exciton binding energy in a bulk van der waals magnet from quasi-1d electronic localization. Nat. Commun. 16, 1134 (2025).
Bianchi, M. et al. Paramagnetic electronic structure of crsbr: Comparison between ab initio gw theory and angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy. Phys. Rev. B 107, 235107 (2023).
Acharya, S. et al. A theory for colors of strongly correlated electronic systems. Nat. Commun. 14, 5565 (2023).
Acharya, S. et al. Real-and momentum-space description of the excitons in bulk and monolayer chromium tri-halides. npj 2D Mater. Appl. 6, 1 (2022).
Acharya, S. et al. Electronic structure of chromium trihalides beyond density functional theory. Phys. Rev. B 104, 155109 (2021a).
Qiu, D. Y., Da Jornada, F. H. & Louie, S. G. Optical spectrum of mos 2: many-body effects and diversity of exciton states. Phys. Rev. Lett. 111, 216805 (2013).
Shi, J. et al. Giant magneto-exciton coupling in 2D van der Waals CrSBr. ACS nano 19, 29977–29987 (2025).
Komar, R. et al. Colossal magneto-excitonic effects in 2d van der waals magnetic semiconductor crsbr. arXiv preprint arXiv:2409.00187 (2024).
Nash, K. J., Skolnick, M. S., Claxton, P. A. & Roberts, J. S. Diamagnetism as a probe of exciton localization in quantum wells. Phys. Rev. B 39, 10943 (1989).
Telford, E. J. et al. Coupling between magnetic order and charge transport in a two-dimensional magnetic semiconductor. Nat. Mater. 21, 754 (2022).
Telford, E. J. et al. Layered antiferromagnetism induces large negative magnetoresistance in the van der waals semiconductor crsbr. Adv. Mater. 32, 2003240 (2020).
Datta, B. et al. Magnon-mediated exciton–exciton interaction in a van der Waals antiferromagnet. Nat. Mater. 24, 1027–1033 (2025).
Togo, A., Chaput, L., Tadano, T. & Tanaka, I. Implementation strategies in phonopy and phono3py. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 35, 353001 (2023).
Togo, A. First-principles phonon calculations with phonopy and phono3py. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 92, 012001 (2023).
Baldini, E. et al. Electron–phonon-driven three-dimensional metallicity in an insulating cuprate. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 117, 6409 (2020).
Weber, C. et al. Role of the lattice in the light-induced insulator-to-metal transition in vanadium dioxide. Phys. Rev. Res. 2, 023076 (2020).
Acharya, S. et al. Metal-insulator transition in copper oxides induced by apex displacements. Phys. Rev. X 8, 021038 (2018).
Linhart, W. et al. Optical markers of magnetic phase transition in crsbr. J. Mater. Chem. C. 11, 8423 (2023).
Pawbake, A. et al. Raman scattering signatures of strong spin-phonon coupling in the bulk magnetic van der waals material crsbr. Phys. Rev. B 107, 075421 (2023).
Aryasetiawan, F. & Gunnarsson, O. Electronic structure of NiO in the GW approximation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 74, 3221 (1995).
Wu, M., Li, Z., Cao, T. & Louie, S. G. Physical origin of giant excitonic and magneto-optical responses in two-dimensional ferromagnetic insulators. Nat. Commun. 10, 2371 (2019b).
Acharya, S. et al. Importance of charge self-consistency in first-principles description of strongly correlated systems. npj Comput. Mater. 7, 1 (2021b).
Friedrich, C., Müller, M. C. & Blügel, S. Band convergence and linearization error correction of all-electron GW calculations: The extreme case of zinc oxide. Phys. Rev. B 83, 081101 (2011).
Acknowledgements
This work was authored in part by the National Renewable Energy Laboratory for the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) under Contract No. DE-AC36-08GO28308. For S.A., D.P., and MvS, funding was provided by the Computational Chemical Sciences programme within the Office of Basic Energy Sciences, U.S. Department of Energy. S.A., D.P., and M.v.S. acknowledge the use of the National Energy Research Scientific Computing Centre, under Contract No. DE-AC02-05CH11231 using NERSC award BES-ERCAP0021783 and we also acknowledge that a portion of the research was performed using computational resources sponsored by the Department of Energy’s Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy and located at the National Renewable Energy Laboratory and computational resources provided by the Oakridge leadership Computing Facility. The views expressed in the article do not necessarily represent the views of the DOE or the U.S. Government. The U.S. Government retains and the publisher, by accepting the article for publication, acknowledges that the U.S. Government retains a nonexclusive, paid-up, irrevocable, worldwide license to publish or reproduce the published form of this work, or allow others to do so, for U.S. Government purposes. Z.S and K.M. were supported by project LUAUS25268 from Ministry of Education Youth and Sports (MEYS) and by the project Advanced Functional Nanorobots (reg. No. CZ.02.1.01/0.0/0.0/15_003/0000444 financed by the EFRR). The publication was created as part of a project co-financed by the Polish Ministry of Science and Higher Education under contract no. 2025/WK/01.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
M.Ś. carried out all optical experiments, drafted the text and figures representing experimental results of the main manuscript and the supplementary information. M.R. participated in low magnetic field measurements and data processing, K.P. and P.Pe supported high magnetic field measurements. M.D. participated in data analysis and interpretation. D.P. contributed to the theoretical calculations. K.M. synthesised the CrSBr crystal with the support and supervision of Z.S. M.v.S. contributed to the theoretical calculation and manuscript writing. F.D. was involved in data interpretation and manuscript writing. M.B., together with P.P. supervised magnetic field measurements, participated in data analysis interpretation, and manuscript writing. S.A. performed theoretical calculations, helped in interpreting the observations, conceived the main theme of the work and contributed to manuscript writing.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
: Nature Communications thanks Yu Ye and the other anonymous reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work. A peer review file is available.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Śmiertka, M., Rygała, M., Posmyk, K. et al. Distinct magneto-optical response of Frenkel and Wannier excitons in CrSBr. Nat Commun (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-026-68482-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-026-68482-5