Abstract
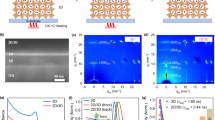
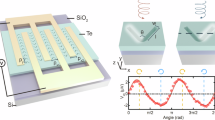
On-chip integrable circularly polarized light (CPL) detectors hold significant potential for applications in optical communications, bioimaging, quantum information, and intelligent sensing, enabling chip-scale chiral light detection and information processing. However, current developments in materials and structural designs struggle to achieve wide-spectral detection capability while maintaining high circular polarization discrimination. This limitation significantly constrains the practical applicability of such detectors in complex environments and object detection scenarios. Herein, we propose a CPL detector based on a twist-stacked black phosphorus (b-p) system. By utilizing twisted b-p as an artificially constructed unit with chiral response and designing a symmetry-stacked sandwich structure in space, we achieve bipolar circular polarization detection and imaging across a wide wavelength range (from visible light to mid-infrared), with peak responsivity reaching 0.1 A/W. This design demonstrates both theoretically and experimentally the feasibility of utilizing a twist-stacked b-p system for wide-spectral CPL detection. This advancement offers valuable insights for addressing the bottlenecks in chip-integrated CPL detection technology.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All the technical details for producing the figures are provided in the supplementary information. The data are available from the corresponding authors X. C. (chenxl@sustech.edu.cn); X. L. Y. (yuxlong6@mail.sysu.edu.cn); C. W. Q. (chengwei.qiu@nus.edu.sg) and W. B. G. (wbgao@ntu.edu.sg) upon request.
Code availability
All the technical details for implementing the simulation are provided in the Supplementary Information. Codes are available from the corresponding authors upon request.
References
Crassous, J. et al. Materials for chiral light control. Nat. Rev. Mater. 8, 365–371 (2023).
Hefern, M. C., Matosziuk, L. M. & Meade, T. J. Lanthanide probes for bioresponsive imaging. Chem. Rev. 114, 4496–4539 (2014).
Ishii, A. & Miyasaka, T. Direct detection of circular polarized light in helical 1D perovskite-based photodiode. Sci. Adv. 6, eabd3274 (2020).
Chen, C. et al. Circularly polarized light detection using chiral hybrid perovskite. Nat. Commun. 10, 1927 (2019).
Yang, Y., Da Costa, R. C., Fuchter, M. J. & Campbell, A. J. Circularly polarized light detection by a chiral organic semiconductor transistor. Nat. Photon. 7, 634–638 (2013).
Wan, L. et al. Sensitive near-infrared circularly polarized light detection via non-fullerene acceptor blends. Nat. Photon. 17, 649–655 (2023).
Schulz, M. et al. Chiral excitonic organic photodiodes for direct detection of circular polarized light. Adv. Funct. Mater. 29, 1900684 (2019).
Shi, W. et al. Fullerene desymmetrization as a means to achieve single-enantiomer electron acceptors with maximized chiroptical responsiveness. Adv. Mater. 33, 2004115 (2021).
Ward, M. D. et al. Highly selective high-speed circularly polarized photodiodes based on π-conjugated polymers. Adv. Opt. Mater. 10, 2101044 (2021).
Kim, N. Y. et al. Chiroptical-conjugated polymer/chiral small molecule hybrid thin films for circularly polarized light-detecting heterojunction devices. Adv. Funct. Mater. 29, 1808668 (2019).
Li, D. et al. Chiral lead-free hybrid perovskites for self-powered circularly polarized light detection. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 60, 8415–8418 (2021).
Wang, L. et al. A chiral reduced-dimension perovskite for an efficient flexible circularly polarized light photodetector. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 59, 6442–6450 (2020).
Li, W. et al. Circularly polarized light detection with hot electrons in chiral plasmonic metamaterials. Nat. Commun. 6, 8379 (2015).
Li, L. et al. Monolithic full-Stokes near-infrared polarimetry with chiral plasmonic metasurface integrated graphene-silicon photodetector. ACS Nano 14, 16634–16642 (2020).
Jiang, H. et al. Metasurface-enabled broadband multidimensional photodetectors. Nat. Commun. 15, 8347 (2024).
Jiang, H. et al. Chiral light detection with centrosymmetric-metamaterial-assisted valleytronics. Nat. Mater. 24, 861–867 (2025).
Zhang, G. et al. High discrimination ratio, broadband circularly polarized light photodetector using dielectric achiral nanostructures. Light.: Sci. Appl. 13, 275 (2024).
Dai, M. et al. On-chip mid-infrared photothermoelectric detectors for full-Stokes detection. Nat. Commun. 13, 4560 (2022).
Eswaraiah, V., Zeng, Q., Long, Y. & Liu, Z. Black phosphorus nanosheets: synthesis, characterization and applications. Small 12, 3480–3502 (2016).
Zhu, X. et al. 2D black phosphorus infrared photodetectors. Laser Photonics Rev. 19, 2400703 (2025).
Wang, F. et al. Multidimensional detection enabled by twisted black arsenic–phosphorus homojunctions. Nat. Nanotech. 19, 455–462 (2024).
Chen, X. et al. Widely tunable black phosphorus mid-infrared photodetector. Nat. Commun. 8, 1672 (2017).
Bullock, J. et al. Polarization-resolved black phosphorus/molybdenum disulfide mid-wave infrared photodiodes with high detectivity at room temperature. Nat. Photonics 12, 601–607 (2018).
Tian, R. et al. Chip-integrated van der Waals PN heterojunction photodetector with low dark current and high responsivity. Light.: Sci. Appl. 11, 101 (2022).
Wu, S. et al. Ultra-sensitive polarization-resolved black phosphorus homojunction photodetector defined by ferroelectric domains. Nat. Commun. 13, 3198 (2022).
Jiao, H. et al. HgCdTe/black phosphorus van der Waals heterojunction for high-performance polarization-sensitive midwave infrared photodetector. Sci. Adv. 8, eabn1811 (2022).
Xiong, Y. et al. Twisted black phosphorus–based van der Waals stacks for fiber-integrated polarimeters. Sci. Adv. 8, eabo0375 (2022).
Han, Z., Wang, F., Sun, J., Wang, X. & Tang, Z. Recent advances in ultrathin chiral metasurfaces by twisted stacking. Adv. Mater. 35, 2206141 (2023).
Zhao, Y. et al. Chirality detection of enantiomers using twisted optical metamaterials. Nat. Commun. 8, 14180 (2017).
Hu, H. et al. Tunable circular polarization responses of twisted black phosphorus metamaterials. Opt. Express 30, 47690–47700 (2022).
Wang, S.-Y. et al. Tunable optical rotation in twisted black phosphorus. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 12, 4755–4761 (2021).
Wu, B.-Y., Shi, Z.-X., Wu, F., Wang, M.-J. & Wu, X.-H. Strong chirality in twisted bilayer α-MoO3. Chin. Phys. B 31, 044101 (2022).
Wan, L., Liu, Y., Fuchter, M. J. & Yan, B. Anomalous circularly polarized light emission in organic light-emitting diodes caused by orbital–momentum locking. Nat. Photon. 17, 193–199 (2023).
Yuan, H. et al. Polarization-sensitive broadband photodetector using a black phosphorus vertical p–n junction. Nat. Nanotechnol. 10, 707–713 (2015).
Kim, D.-K. et al. P–N junction diode using plasma boron-doped black phosphorus for high-performance photovoltaic devices. ACS nano 13, 1683–1693 (2019).
Cai, Y., Zhang, G. & Zhang, Y.-W. Layer-dependent band alignment and work function of few-layer phosphorene. Sci. Rep. 4, 6677 (2014).
Lee, S. Y., Yun, W. S. & Lee, J. D. New method to determine the schottky barrier in few-layer black phosphorus metal contacts. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 9, 7873–7877 (2017).
Liu, S. et al. Thickness-dependent Raman spectra, transport properties and infrared photoresponse of few-layer black phosphorus. J. Mater. Chem. C. 3, 10974–10980 (2015).
Kresse, G. & Furthmüller, J. Efficient iterative schemes for ab initio total-energy calculations using a plane-wave basis set. Phys. Rev. B 54, 11169 (1996).
Kresse, G. & Furthmüller, J. Efficiency of ab-initio total energy calculations for metals and semiconductors using a plane-wave basis set. Comput. Mater. Sci. 6, 15–50 (1996).
Kresse, G. & Hafner, J. Ab initio molecular dynamics for liquid metals. Phys. Rev. B 47, 558 (1993).
Perdew, J. P., Burke, K. & Ernzerhof, M. Generalized gradient approximation made simple. Phys. Rev. Lett. 77, 3865 (1996).
Wang, Y. et al. Fast uncooled mid-wavelength infrared photodetectors with heterostructures of van der Waals on epitaxial HgCdTe. Adv. Mater. 34, e2107772 (2022).
Peng, M. et al. Blackbody-sensitive room-temperature infrared photodetectors based on low-dimensional tellurium grown by chemical vapor deposition. Sci. Adv. 7, eabf7358 (2021).
Jiang, H. et al. Synergistic-potential engineering enables high-efficiency graphene photodetectors for near- to mid-infrared light. Nat. Commun. 15, 1225 (2024).
Edgar, M. P., Gibson, G. M. & Padgett, M. J. Principles and prospects for single-pixel imaging. Nat. Photonics 13, 13–20 (2019).
Cheng, Z., Zhao, T. & Zeng, H. 2D material-based photodetectors for infrared imaging. Small Sci. 2, 2100051 (2022).
Youngblood, N., Chen, C., Koester, S. J. & Li, M. Waveguide-integrated black phosphorus photodetector with high responsivity and low dark current. Nat. Photonics 9, 247–252 (2015).
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by ASTAR (M21K2c0116, M24M8b0004), NTU Tamesek Lab (TLSP24-04), Singapore National Research Foundation (NRF-CRP30-2023-0003, NRF-CRP31-0001, NRF2023-ITC004-001 and NRF-MSG-2023-0002) and Singapore Ministry of Education Tier 2 Grant (MOE-T2EP50221-0005, MOE-T2EP50222-0018). X.-L.Y. is supported by the Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation (Grant No. 2023A1515011852). X. C. is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (62275117) and Shenzhen Excellent Youth Program (RCYX20221008092900001). X. W. is supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2024YFE0211900). X.-L.Y. is supported by the Shenzhen Natural Science Foundation (Grant No. JCYJ20250604174400001) and the Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation (Grant No. 2023A1515011852).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
H.J., W-b.G. and C.-W.Q. conceived the project. H.J., L.A., Y.Z., Y.Y., X.D., and J.F. performed the measurements. H.J. and L.A. fabricated the devices. H.J. analyzed the data. H.J., X.C., and X.Y. performed the theoretical analysis. H.J., X.Y., C.-W.Q. and W.-b.G. wrote the manuscript. C.-W.Q. and W-b.G. supervised the project. All the authors, including R.H., G.X., L.A., X.W., and X.C. contributed to the discussion of the results.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Communications thanks Yufeng Hao, Xiaomu Wang, and the other anonymous reviewer for their contribution to the peer review of this work. A peer review file is available.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, H., An, L., Chen, X. et al. Twist-stacked black phosphorus for wide-spectral chiral photodetection. Nat Commun (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-026-68531-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-026-68531-z