Abstract
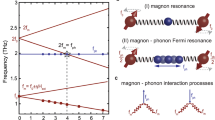
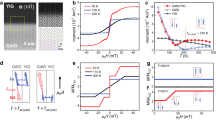
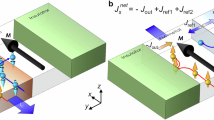
Antiferromagnetically coupled ferrimagnets exhibit both ferromagnetic resonance and exchange resonance modes. The antiferromagnetic exchange resonance mode, characterized by a higher magnon frequency than the ferromagnetic resonance mode, holds promise for fast spintronic applications. However, as higher magnon frequencies are typically associated with shorter magnon lifetimes, the exchange resonance mode is expected to decay more rapidly than the ferromagnetic resonance mode, leading to challenges for long-lived information transfer and coherent dynamics. Here we demonstrate that this inverse relationship between frequency and lifetime can be broken in ferrimagnets with two inequivalent magnetic sublattices. Using time-resolved magneto-optical Kerr effect spectroscopy on CoGd, we observe that the exchange resonance mode exhibits a longer magnon lifetime than the ferromagnetic resonance mode near the angular momentum compensation point. Our theoretical and simulation models reveal that this inversion of magnon lifetime arises from the inequivalence in magnetic damping of the two sublattices. The unique combination of higher frequency and longer lifetime in the exchange resonance mode of ferrimagnets highlights its potential for high-speed and energy-efficient spintronic devices.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available within the article and the Supplementary Information.
References
Tveten, E. G., Qaiumzadeh, A., Tretiakov, O. A. & Brataas, A. Staggered dynamics in antiferromagnets by collective coordinates. Phys. Rev. Lett. 110, 127208 (2013).
Kim, K. J. et al. Fast domain wall motion in the vicinity of the angular momentum compensation temperature of ferrimagnets. Nat. Mater. 16, 1187–1192 (2017).
Okuno, T. et al. Spin-transfer torques for domain wall motion in antiferromagnetically coupled ferrimagnets. Nat. Electron. 2, 389–393 (2019).
Divinskiy, B., Chen, G., Urazhdin, S., Demokritov, S. O. & Demidov, V. E. Effects of spin-orbit torque on the ferromagnetic and exchange spin-wave modes in ferrimagnetic Co-Gd alloy. Phys. Rev. Appl. 14, 044016 (2020).
Mishra, R. et al. Anomalous current-induced spin torques in ferrimagnets near compensation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 118, 167201 (2017).
Cai, K. et al. Ultrafast and energy-efficient spin–orbit torque switching in compensated ferrimagnets. Nat. Electron. 3, 37–42 (2020).
Quessab, Y., Xu, J. W., Morshed, M. G., Ghosh, A. W. & Kent, A. D. Interplay between spin-orbit torques and Dzyaloshinskii-Moriya interactions in ferrimagnetic amorphous alloys. Adv. Sci. 8, e2100481 (2021).
Mekonnen, A. et al. Femtosecond laser excitation of spin resonances in amorphous ferrimagnetic Gd1-xCox alloys. Phys. Rev. Lett. 107, 117202 (2011).
Schlickeiser, F. et al. Temperature dependence of the frequencies and effective damping parameters of ferrimagnetic resonance. Phys. Rev. B 86, 214416 (2012).
Deb, M., Molho, P. & Barbara, B. Magnetic damping of ferromagnetic and exchange resonance modes in a ferrimagnetic insulator. Phys. Rev. B 105, 014432 (2022).
Kim, S. K. et al. Ferrimagnetic spintronics. Nat. Mater. 21, 24–34 (2022).
Davydova, M. D., Zvezdin, K. A., Becker, J., Kimel, A. V. & Zvezdin, A. K. H−T phase diagram of rare-earth–transition-metal alloys in the vicinity of the compensation point. Phys. Rev. B 100, 064409 (2019).
Kim, C. et al. Distinct handedness of spin wave across the compensation temperatures of ferrimagnets. Nat. Mater. 19, 980–985 (2020).
Krichevsky, D. M. et al. Unconventional spin dynamics in the noncollinear phase of a ferrimagnet. Phys. Rev. B 108, 174442 (2023).
Ignatyeva, D. O., Gusev, N. A., Zvezdin, A. K. & Belotelov, V. I. Spin-reorientation and phase diagram for a ferrimagnet with compensation point in inclined magnetic field. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 623, 172968 (2025).
Ignatyeva, D. O. et al. High-amplitude ferromagnetic soft mode at the spin-reorientation transition in an iron garnet film excited by ultrashort laser pulses. Phys. Rev. B 111, 224424 (2025).
Stanciu, C. D. et al. Ultrafast spin dynamics across compensation points in ferrimagnetic GdFeCo: The role of angular momentum compensation. Phys. Rev. B 73, 220402 (2006).
Binder, M. et al. Magnetization dynamics of the ferrimagnet CoGd near the compensation of magnetization and angular momentum. Phys. Rev. B 74, 134404 (2006).
Mikeska, H. J. & Steiner, M. Solitary excitations in one-dimensional magnets. Adv. Phys. 40, 191–356 (1991).
Gomonaĭ, E. V. & Loktev, V. M. Distinctive effects of a spin-polarized current on the static and dynamic properties of an antiferromagnetic conductor. Low Temp. Phys. 34, 198–206 (2008).
Hals, K. M., Tserkovnyak, Y. & Brataas, A. Phenomenology of current-induced dynamics in antiferromagnets. Phys. Rev. Lett. 106, 107206 (2011).
Swaving, A. C. & Duine, R. A. Current-induced torques in continuous antiferromagnetic textures. Phys. Rev. B 83, 054428 (2011).
Kim, S. K., Tserkovnyak, Y. & Tchernyshyov, O. Propulsion of a domain wall in an antiferromagnet by magnons. Phys. Rev. B 90, 104406 (2014).
Tveten, E. G., Müller, T., Linder, J. & Brataas, A. Intrinsic magnetization of antiferromagnetic textures. Phys. Rev. B 93, 104408 (2016).
Kim, S. K., Lee, K.-J. & Tserkovnyak, Y. Self-focusing skyrmion racetracks in ferrimagnets. Phys. Rev. B 95, 140404 (2017).
Dzyaloshinsky, I. A thermodynamic theory of “weak” ferromagnetism of antiferromagnetics. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 4, 241–255 (1958).
Moriya, T. Anisotropic superexchange interaction and weak ferromagnetism. Phys. Rev. 120, 91–98 (1960).
Kim, D. H. et al. Bulk Dzyaloshinskii-Moriya interaction in amorphous ferrimagnetic alloys. Nat. Mater. 18, 685–690 (2019).
Boventer, I. et al. Room-temperature antiferromagnetic resonance and inverse spin-Hall voltage in canted antiferromagnets. Phys. Rev. Lett. 126, 187201 (2021).
Wang, H. et al. Spin pumping of an easy-plane antiferromagnet enhanced by Dzyaloshinskii-Moriya interaction. Phys. Rev. Lett. 127, 117202 (2021).
Ellis, M. O. A., Ostler, T. A. & Chantrell, R. W. Classical spin model of the relaxation dynamics of rare-earth doped permalloy. Phys. Rev. B 86, 174418 (2012).
Kamra, A. & Belzig, W. Spin pumping and shot noise in ferrimagnets: Bridging ferro- and antiferromagnets. Phys. Rev. Lett. 119, 197201 (2017).
Liu, Q., Yuan, H. Y., Xia, K. & Yuan, Z. Mode-dependent damping in metallic antiferromagnets due to intersublattice spin pumping. Phys. Rev. Mater. 1, 061401 (2017).
Kamra, A., Troncoso, R. E., Belzig, W. & Brataas, A. Gilbert damping phenomenology for two-sublattice magnets. Phys. Rev. B 98, 184402 (2018).
Troncoso, R. E., Lund, M. A., Brataas, A. & Kamra, A. Cross-sublattice spin pumping and magnon level attraction in van der Waals antiferromagnets. Phys. Rev. B 103, 144422 (2021).
Tang, J. & Cheng, R. Absence of cross-sublattice spin pumping and spin-transfer torques in collinear antiferromagnets. APL Mater. 11, 111117 (2023).
Ostler, T. A. et al. Ultrafast heating as a sufficient stimulus for magnetization reversal in a ferrimagnet. Nat. Commun. 3, 666 (2012).
Mentink, J. H. et al. Ultrafast spin dynamics in multisublattice magnets. Phys. Rev. Lett. 108, 057202 (2012).
Baral, A. & Schneider, H. C. Magnetic switching dynamics due to ultrafast exchange scattering: A model study. Phys. Rev. B 91, 100402 (2015).
Yang, D. et al. Spin-orbit torque manipulation of sub-terahertz magnons in antiferromagnetic α-Fe2O3. Nat. Commun. 15, 4046 (2024).
Lei, J. et al. Observation of quantized spin wave modes in nano-constriction spin Hall nano-oscillators. Appl. Phys. Lett. 126, 222406 (2025).
Karahan, E. A. et al. Deep-learning enabled generalized inverse design of multi-port radio-frequency and sub-terahertz passives and integrated circuits. Nat. Commun. 15, 10734 (2024).
Jensen, J. & Mackintosh, A. R. Rare earth magnetism: structures and excitations. (Oxford University Press, 1991).
Acknowledgements
The work was partially supported by the National Research Foundation (NRF) Singapore Investigatorship (NRFI06-2020-0015) (H.Y.), Ministry of Education-Singapore Tier 2 (T2EP50124-0017) (H.Y.), the National Foundation of Korea (RS-2022-NR068225, RS-2024-00436660, RS-2025-00516229) (K.-J.L.), and Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd (IO221024-03172-01, IO241218−11518-01) (K.-J.L. and H.Y.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
C.X., D.Y., and H.P. constructed the TR-MOKE setup. C.X. carried out the TR-MOKE experiments. S.Z., C.Z., and J.L. fabricated and characterized samples. S.-J.K. and K.-J.L. developed the theory and conducted the simulations. C.X., S.-J.K., K.-J.L., and H.Y. wrote the paper with the help of all authors. H.Y. and K.-J.L. supervised the study.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Communications thanks Denis Krichevsky and the other anonymous reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work. A peer review file is available.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, C., Kim, SJ., Zhao, S. et al. Inversion of magnon lifetime of ferromagnetic and exchange resonance modes in ferrimagnets. Nat Commun (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-026-69453-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-026-69453-6