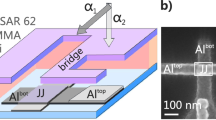
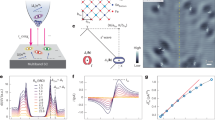
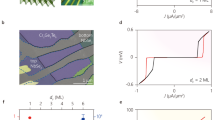
Abstract
Suppressing critical current density (Jc) fluctuations in Josephson junctions is essential for improving the reproducibility and scalability of superconducting quantum processors. Despite many elucidations of microscopic mechanisms, the physical modulation of Jc by atomic-scale disorder at the metal-insulator interface remains elusive. Here, we reveal that interfacial bonding topology distortions are the dominant source that regulates Jc uniformity. We identify a new disorder metric, Interface Bonding Topology Factor (IBTF), that captures bond-angle fluctuations and oxygen-coordination heterogeneity within Jc variations. Through multivariate analysis, Jc is exponentially correlated with interface disorder and barrier thickness (d) by Jc ∝ e−IBTF⋅d, explaining 91.88% of the observed Jc inhomogeneity. We establish IBTF as a tunable physical degree of freedom whose suppression efficacy enhances significantly with increasing d, and demonstrate its active modulation by twin boundary engineering in electrodes. This work provides a device-oriented strategy and a tunable physical metric beyond single-feature control for scalable high-performance quantum processors.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available within the paper and its Supplementary Information.
Code availability
Codes are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Paik, H. et al. Observation of high coherence in Josephson junction qubits measured in a three-dimensional circuit QED architecture. Phys. Rev. Lett. 107, 240501 (2011).
Kreikebaum, J. M., Morvan, A. & Siddiqi, I. Improving wafer-scale Josephson junction resistance variation in superconducting quantum coherent circuits. Supercond. Sci. Tech. 33, 06LT02 (2020).
Kjaergaard, M. et al. Superconducting qubits: Current state of play. Annu. Rev. Condens. Matter Phys. 11, 369–395 (2020).
Siddiqi, I. Engineering high-coherence superconducting qubits. Nat. Rev. Mater. 6, 875–891 (2021).
Somoroff, A. et al. Millisecond coherence in a superconducting qubit. Phys. Rev. Lett. 130, 267001 (2023).
de Leon, N. P. et al. Materials challenges and opportunities for quantum computing hardware. Science 372, eabb2823 (2021).
Kim, H. et al. Josephson junctions in the age of quantum discovery. Preprint at arXiv:2505.12724 (2025).
Morvan, A., Chen, L., Larson, J. M., Santiago, D. I. & Siddiqi, I. Optimizing frequency allocation for fixed-frequency superconducting quantum processors. Phys. Rev. Res. 4, 023079 (2022).
Anferov, A., Lee, K.-H., Zhao, F., Simon, J. & Schuster, D. I. Improved coherence in optically defined niobium trilayer-junction qubits. Phys. Rev. Appl. 21, 024047 (2024).
Nguyen, L. B. et al. Blueprint for a high-performance fluxonium quantum processor. PRX Quantum 3, 037001 (2022).
Zhang, E. J. et al. High-performance superconducting quantum processors via laser annealing of transmon qubits. Sci. Adv. 8, eabi6690 (2022).
Kim, H. et al. Effects of laser-annealing on fixed-frequency superconducting qubits. Appl. Phys. Lett. 121, 142601 (2022).
Pappas, D. P. et al. Alternating-bias assisted annealing of amorphous oxide tunnel junctions. Commun. Mater. 5, 1–7 (2024).
Odeh, M. et al. Non-Markovian dynamics of a superconducting qubit in a phononic bandgap. Nat. Phys. 21, 406–411 (2025).
Bilmes, A., Händel, A. K., Volosheniuk, S., Ustinov, A. V. & Lisenfeld, J. In-situ bandaged Josephson junctions for superconducting quantum processors. Supercond. Sci. Tech. 34, 125011 (2021).
Tolpygo, S. K., Bolkhovsky, V., Weir, T. J., Oliver, W. D. & Gouker, M. A. Fabrication process and properties of fully-planarized deep-submicron Nb/Al-AlOx/Nb Josephson junctions for VLSI circuits. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 25, 1 (2014).
Fritz, S. et al. Structural and nanochemical properties of AlOx layers in Al/AlOx/Al-layer systems for Josephson junctions. Phys. Rev. Mater. 3, 114805 (2019).
Stehli, A. et al. Coherent superconducting qubits from a subtractive junction fabrication process. Appl. Phys. Lett. 117, 124005 (2020).
Verjauw, J. et al. Path toward manufacturable superconducting qubits with relaxation times exceeding 0.1 ms. npj Quantum Inf. 8, 93 (2022).
Chen, J. et al. Optimization of Nb/Al-AlOx/Nb Josephson junctions through wafer-scale anodic oxidation: A systematic characterization and performance analysis. Supercond. Sci. Tech. 36, 105003 (2023).
Ke, C.-T. et al. Scaffold-assisted window junctions for superconducting qubit fabrication. Preprint at arXiv:2503.11010 (2025).
Bland, M. P. et al. Millisecond lifetimes and coherence times in 2D transmon qubits. Nature 647, 343–348 (2025).
Aref, T. et al. Characterization of aluminum oxide tunnel barriers by combining transport measurements and transmission electron microscopy imaging. J. Appl. Phys. 116, 1421 (2014).
Greibe et al. Direct observation of the thickness distribution of ultra thin AlOx barriers in Al/AlOx/Al Josephson junctions. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 48, 395308 (2015).
Zeng, L., Tran, D. T., Tai, C. W., Svensson, G. & Olsson, E. Atomic structure and oxygen deficiency of the ultrathin aluminium oxide barrier in Al/AlOx/Al Josephson junctions. Sci. Rep. 6, 29679 (2018).
Fritz, S., Radtke, L., Schneider, R., Weides, M. & Gerthsen, D. Optimization of Al/AlOx/Al-layer systems for Josephson junctions from a microstructure point of view. J. Appl. Phys. 125, 165301 (2019).
Lacquaniti, V. et al. Universality of transport properties of ultra-thin oxide films. New J. Phys. 14, 023025 (2012).
Kim, C. E., Ray, K. G. & Lordi, V. A density-functional theory study of the Al/AlOx/Al tunnel junction. J. Appl. Phys. 128, 155102 (2020).
Qiu, J. et al. Blurred interface induced control of electrical transport properties in Josephson junctions. Sci. Rep. 14, 17292 (2024).
Greibe, T. et al. Are pinholes the cause of excess current in superconducting tunnel junctions? A study of Andreev current in highly resistive junctions. Phys. Rev. Lett. 106, 097001 (2011).
Sulangi, M. A. et al. Disorder and critical current variability in Josephson junctions. J. Appl. Phys. 127, 033901 (2020).
Bayros, K., Cyster, M. J., Smith, J. S. & Cole, J. H. Influence of pinholes and weak-points in aluminum-oxide Josephson junctions. Phys. Rev. Mater. 8, 046202 (2024).
Martinis, J. M. et al. Decoherence in Josephson qubits from dielectric loss. Phys. Rev. Lett. 95, 210503 (2005).
Schlör, S., Lisenfeld, J., Müller, C., Bilmes, A. & Weides, M. Correlating decoherence in transmon qubits: Low frequency noise by single fluctuators. Phys. Rev. Lett. 123, 190502 (2019).
Müller, C., Cole, J. H. & Lisenfeld, J. Towards understanding two-level-systems in amorphous solids – Insights from quantum circuits. Rep. Prog. Phys. 82, 124501 (2019).
Mohseni, M. et al. How to build a quantum supercomputer: Scaling from hundreds to millions of qubits. Preprint at arXiv:2411.10406 (2024).
Cyster, M. J. et al. Simulating the fabrication of aluminium oxide tunnel junctions. npj Quantum Inf. 7, 12 (2021).
Roddatis, V. V. et al. The morphology of Al-based submicron Josephson junction. J. Appl. Phys. 110, 2079 (2011).
Liu, X., Pan, K., Zhang, Z. & Feng, Z. Unveiling atomic structure and chemical composition of the Al/AlOx/Al Josephson junctions in qubits. Appl. Surf. Sci. 640, 158337 (2023).
DuBois, T. C., Per, M. C., Russo, S. P. & Cole, J. H. Delocalized oxygen as the origin of two-level defects in Josephson junctions. Phys. Rev. Lett. 110, 077002 (2013).
DuBois, T. C., Russo, S. P. & Cole, J. H. Atomic delocalisation as a microscopic origin of two-level defects in Josephson junctions. New J. Phys. 17, 023017 (2014).
Lapham, P. & Georgiev, V. P. Computational study of oxide stoichiometry and variability in the Al/AlOx/Al tunnel junction. Nanotechnology 33, 265201 (2022).
Oh, J.-S. et al. Correlating aluminum layer deposition rates, Josephson junction microstructure, and superconducting qubits’ performance. Acta Mater. 284, 120631 (2025).
Zhu, Q. et al. Defect-driven selective metal oxidation at atomic scale. Nat. Commun. 12, 558 (2021).
Graser, S. et al. How grain boundaries limit supercurrents in high-temperature superconductors. Nat. Phys. 6, 609–614 (2010).
Wolf, F., Graser, S., Loder, F. & Kopp, T. Supercurrent through grain boundaries of cuprate superconductors in the presence of strong correlations. Phys. Rev. Lett. 108, 117002 (2012).
Smirnov, N. et al. Subangstrom ion beam engineering of buried ultrathin oxides for scalable quantum computing. Sci. Adv. 11, eads9744 (2025).
Newnham, R. E. & de Haan, Y. M. Refinement of the α Al2O3, Ti2O3, V2O3 and Cr2O3 structures. Zeitschrift für Kristallographie 117, 235–237 (1962).
Shan, Z. et al. O-terminated interface for thickness-insensitive transport properties of aluminum oxide Josephson junctions. Sci. Rep. 12, 1–10 (2022).
Shan, Z. et al. Effect of the Al/AlOx interfacial stacking sequence on the transport properties of alumina tunnel junctions. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 25, 8871–8881 (2023).
Qiu, J. et al. Impact of interfacial atomic ratios on stabilized transport properties in defective Josephson junctions. IEEE Trans. Electron Dev. 72, 488–493 (2025).
Taylor, J., Guo, H. & Wang, J. Ab initio modeling of quantum transport properties of molecular electronic devices. Phys. Rev. B 63, 245407 (2001).
Ambegaokar, V. & Baratoff, A. Tunneling between superconductors. Phys. Rev. Lett. 10, 486–489 (1963).
Stukowski, A. Visualization and analysis of atomistic simulation data with OVITO–the open visualization tool. Modell. Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng. 18, 015012 (2010).
Pearson, K. & Galton, F. Vii. Note on regression and inheritance in the case of two parents. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. 58, 240–242 (1895).
De Breuck, P. P., Hautier, G. & Rignanese, G. M. Materials property prediction for limited datasets enabled by feature selection and joint learning with MODNet. npj Comput. Mater. 7, 83 (2021).
Pedregosa, F. et al. Scikit-learn: Machine learning in Python. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 12, 2825–2830 (2011).
Ouyang, R., Curtarolo, S., Ahmetcik, E., Scheffler, M. & Ghiringhelli, L. M. SISSO: A compressed-sensing method for identifying the best low-dimensional descriptor in an immensity of offered candidates. Phys. Rev. Mater. 2, 083802 (2018).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Major Science and Technology Project of Henan Province (221100210400), and the Natural Science Foundation of Henan Province (222300420546). Computational resources were provided by the National Supercomputing Center in Zhengzhou. We thank Jianshe Liu, Wenlong Yu, Zhao Wang, and Dong Lan for their valuable insights and comments. We thank the School of Physics at Nanjing University for the nanofabrication. We thank the software services from Hzwtech.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
C.Han, H.S., and Z.S. conceived the study and planned the computational work. C.Han and J.Q. performed the first principles calculations, feature extraction, experimental characterization analysis, and machine-learning calculations with assistance from H.S., Y.S., and Z.S. H.S. and Y.S. characterized the sample. P.X., X.Y., W.W., S.W., Q.M., B.Y., L.W., and C.Hou advised on the machine learning method and interpretation of results. F.L., B.Z., and Z.S. supervised the study. All authors analyzed the data and contributed to reviewing and editing the manuscript and the Supplementary Information.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Han, C., Sun, H., Shen, Y. et al. Revealing the role of interface disorder in modulating critical current density of Josephson junctions. npj Comput Mater (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41524-025-01941-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41524-025-01941-7