Abstract
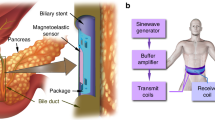
Airway stents play a vital role in managing central airway obstruction (CAO) caused by lung cancer and other pulmonary diseases by providing structural support to collapsed airways and restoring airflow. However, complications such as stent migration often require urgent medical intervention while early monitoring is essential to reduce the risk. Regular monitoring through bronchoscopy requires anesthesia in the hospital, which causes pain and an economic burden on patients. Computed tomography involves risky radiation and lacks the ability to provide continuous, real-time feedback outside of hospital settings. Here we report a fundamental mechanism of wireless tracking based on magnetic field in a wirelessly powered sensory ring integrated on an airway stent. The sensory ring is designed for continuous, real-time monitoring of stent position and orientation. This sensory ring, integrating an on-board magnetic sensor, and a wearable magnetic field generation system, enable accurate localization by detecting the magnetic field generated externally. The sensory ring is powered wirelessly via a charging coil, ensuring long-term operation. Our system achieves tracking accuracy of 0.5 mm and 2.2 degrees, with a temporal resolution of 0.2 Hz. Beyond migration monitoring, the sensor also detects airway deformation, offering the potential to sense pathological changes associated with lung cancer and other pulmonary conditions. By eliminating the need for radiation-based imaging or bronchoscopy, this approach enables safe, long-term surveillance of stent patency and surrounding tissue conditions. The proposed sensing mechanism and platform are also adaptable in other organs, such as the esophagus, for monitoring stent migration and deformation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data is contained within the manuscript and supplementary files.
Code availability
The C++ and MATLAB codes for tracking can be accessed via the link: https://github.com/dong-mrlab/stent_migration.
References
Mudambi, L., Miller, R. & Eapen, G. A. Malignant central airway obstruction. J. Thorac. Dis. 9, S1087–S1110 (2017).
Keshishyan, S. et al. Infections causing central airway obstruction: role of bronchoscopy in diagnosis and management. J. Thorac. Dis. 9, 1707–1724 (2017).
Ernst, A., Feller-Kopman, D., Becker, H. D. & Mehta, A. C. Central airway obstruction. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 169, 1278–1297 (2004).
Folch, E. & Keyes, C. Airway stents. Ann. Cardiothorac. Surg. 7, 273–283 (2018).
Bashour, S. I. & Lazarus, D. R. Airway stents in interventional pulmonology. J. Respir. 4, 62–78 (2024).
Sabath, B. F. & Casal, R. F. Airway stenting for central airway obstruction: a review. Mediastinum 7, 18 (2023).
Wang, Z. et al. Utility and safety of airway stenting in airway stenosis after lung transplant: a systematic review. Front. Med. 10, 1061447 (2023).
Mencattelli, M. et al. In vivo molding of airway stents. Adv. Funct. Mater. 31, 2010525 (2021).
Lee, H. J. et al. Airway stent complications: the role of follow-up bronchoscopy as a surveillance method. J. Thorac. Dis. 9, 4651–4659 (2017).
Murgu, S. D. & Colt, H. G. Complications of silicone stent insertion in patients with expiratory central airway collapse. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 84, 1870–1877 (2007).
Zakaluzny, S. A., Lane, J. D. & Mair, E. A. Complications of tracheobronchial airway stents. Otolaryngol.–Head. Neck Surg. 128, 478–488 (2003).
Guibert, N., Saka, H. & Dutau, H. Airway stenting: technological advancements and its role in interventional pulmonology. Respirology 25, 953–962 (2020).
Lin, S.-M. et al. Metallic stent and flexible bronchoscopy without fluoroscopy for acute respiratory failure. Eur. Respir. J. 31, 1019–1023 (2008).
Shang, J. et al. A flexible catheter-based sensor array for upper airway soft tissues pressure monitoring. Nat. Commun. 16, 287 (2025).
Godoy, M. C. B. et al. Multidetector CT evaluation of airway stents: what the radiologist should know. Radiographics 34, 1793–1806 (2014).
Okajima, Y. et al. Luminal plugging on chest CT scan. Chest 158, 121–130 (2020).
Dialani, V. et al. MDCT detection of airway stent complications: comparison with bronchoscopy. Am. J. Roentgenol. 191, 1576–1580 (2008).
Wang, Y., Ge, R. & Dong, | Xiaoguang. Toward wireless implantable robotic systems driven by magnetic field for personalized therapy. Adv. Robot. Res. 202500077 https://doi.org/10.1002/ADRR.202500077 (2025).
Herbert, R., Lim, H.-R., Rigo, B. & Yeo, W.-H. Fully implantable wireless batteryless vascular electronics with printed soft sensors for multiplex sensing of hemodynamics. Sci. Adv. 8, 1175 (2022).
Kwon, K. et al. A battery-less wireless implant for the continuous monitoring of vascular pressure, flow rate and temperature. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 7, 1215–1228 (2023).
Bateman, A. et al. Implantable membrane sensors and long-range wireless electronics for continuous monitoring of stent edge restenosis. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 17, 42781–42790 (2025).
Chen, X., Assadsangabi, B., Hsiang, Y. & Takahata, K. Enabling angioplasty-ready “Smart” stents to detect in-stent restenosis and occlusion. Adv. Sci. 5, 1700560 (2018).
Vishnu, J. & Manivasagam, G. Perspectives on smart stents with sensors: from conventional permanent to novel bioabsorbable smart stent technologies. Med. Devices Sens. 3, e10116 (2020).
Wang, Y. et al. Sensory artificial cilia for in situ monitoring of airway physiological properties. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 121, e2412086121 (2024).
Rigo, B. et al. Soft implantable printed bioelectronic system for wireless continuous monitoring of restenosis. Biosens. Bioelectron. 241, 115650 (2023).
Oyunbaatar, N.-E. et al. Implantable self-reporting stents for detecting in-stent restenosis and cardiac functional dynamics. ACS Sens. 8, 4542–4553 (2023).
Yi, Y., Wang, B. & Li, C. Sensors-based monitoring and treatment approaches for in-stent restenosis. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 111, 490–498 (2023).
Su, S. et al. A wearable, reconfigurable, and modular magnetic tracking system for wireless capsule robots. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inf. 20, 13600–13611 (2024).
Fu, Y. & Guo, Y.-X. Wearable permanent magnet tracking system for wireless capsule endoscope. IEEE Sens. J. 22, 8113–8122 (2022).
Song, S. et al. Magnetic tracking of wireless capsule endoscope in mobile setup based on differential signals. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 70, 1–1 (2021).
Son, D., Dong, X. & Sitti, M. A simultaneous calibration method for magnetic robot localization and actuation systems. IEEE Trans. Robot. 35, 343–352 (2019).
Taylor, C. R. et al. Magnetomicrometry. Sci Robot 6, eabg0656 (2021).
Huang, Z. et al. Three-dimensional integrated stretchable electronics. Nat. Electron. 1, 473–480 (2018).
Zhao, Q. et al. Highly stretchable and customizable microneedle electrode arrays for intramuscular electromyography. Sci. Adv. 10, 7202 (2024).
Yin, J., Wang, S., Tat, T. & Chen, J. Motion artefact management for soft bioelectronics. Nat. Rev. Bioeng. 2, 541–558 (2024).
Jin, R. & Jung, B. Magnetic tracking system for heart surgery. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 16, 275–286 (2022).
Kim, K. et al. Mucosa-interfacing capsule for in situ sensing the elasticity of biological tissues. Adv. Mater. Technol. 10, 2401487 (2025).
Gleich, B., Schmale, I., Nielsen, T. & Rahmer, J. Miniature magneto-mechanical resonators for wireless tracking and sensing. Science 380, 966–971 (2023).
Taylor, C. R., Abramson, H. G. & Herr, H. M. Low-latency tracking of multiple permanent magnets. IEEE Sens J. 19, 11458–11468 (2019).
Sherman, J. T., Lubkert, J. K., Popovic, R. S. & DiSilvestro, M. R. Characterization of a novel magnetic tracking system. IEEE Trans. Magn. 43, 2725–2727 (2007).
Dai, H., Yang, W., Xia, X., Su, S. & Ma, K. A three-axis magnetic sensor array system for permanent magnet tracking. in Proc. 2016 IEEE International Conference on Multisensor Fusion and Integration for Intelligent Systems (MFI) vol. 0 476–480 (IEEE, 2016).
Franz, A. M. et al. Electromagnetic tracking in medicine—a review of technology, validation, and applications. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 33, 1702–1725 (2014).
Fan, X., Dong, X., Karacakol, A. C., Xie, H. & Sitti, M. Reconfigurable multifunctional ferrofluid droplet robots. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 117, 27916–27926 (2020).
Wang, Y., Sharma, S., Maldonado, F. & Dong, X. Wirelessly actuated ciliary airway stent for excessive mucus transportation. Adv. Mater. Technol. 8, 2301003 (2023).
Sharma, S. et al. Wireless peristaltic pump for transporting viscous fluids and solid cargos in confined spaces. Adv. Funct. Mater. 34, 2405865 (2024).
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge funding support from National Institutes of Health under R21EB035200 and from Vanderbilt University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: X.D. Methodology: X.D., R.G., and Y.W. Investigation: R.G., Y.W., C.N., and H.F. Visualization: R.G., Y.W., and X.D. Supervision: X.D. Writing—original draft: X.D., R.G. Writing—review and editing: X.D., R.G., Y.W., C.D., F.M., V.S., and Y.Z. All authors have read and approved the manuscript. R.G. and Y.W. are equally contributed co-first authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
Vanderbilt University has filed a provisional patent application related to this work. The authors declare that they have no other competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Ge, R., Wang, Y., Negron, C. et al. A wireless implantable sensory ring for continuous airway stent migration tracking. npj Flex Electron (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41528-025-00526-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41528-025-00526-0