Abstract
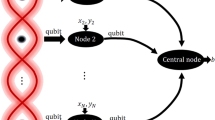
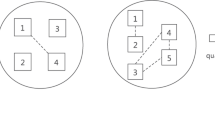
Entanglement is fundamental to quantum physics and information processing. In this work, we introduce the Few-Shot Randomized Measurement (FSRM) method, developing an unbiased estimator for mixed-state entanglement from just three experimental shot outcomes. By incorporating the Bell measurement (BM), we supplement the traditional computational-basis measurement to enhance the randomized measurement scheme, which is scalable to n-qubit systems via BMs on qubit pairs. Our approach enables direct estimation of entanglement through random unitary evolution in a photonic system. Compared to the classical shadow method, BM-enhanced FSRM requires no prior knowledge of the local unitaries, offering greater robustness against unitary imperfections. Additionally, we find that utilizing more versatile measurement settings with fewer repeats per setting is more efficient under fixed measurement resources. Our protocol and experimental demonstration represent a significant advancement in the efficient and practical characterization of quantum states.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data needed to evaluate the conclusions in the paper are present in the paper and/or the Supplementary Materials.Code for the S5 in the Supplementary Note 3 can be find in https://www.scidb.cn/en/detail?dataSetId=b645025cb89f40af9fedbe68925a200c, https://doi.org/10.57760/sciencedb.nbsdc.0021.
Code availability
Code for the S5 in the Supplementary Note 3 can be find in https://www.scidb.cn/en/detail?dataSetId=b645025cb89f40af9fedbe68925a200c.
References
Horodecki, R., Horodecki, P., Horodecki, M. & Horodecki, K. Quantum entanglement. Rev. Mod. Phys. 81, 865–942 (2009).
Amico, L., Fazio, R., Osterloh, A. & Vedral, V. Entanglement in many-body systems. Rev. Mod. Phys. 80, 517–576 (2008).
Nielsen, M. A. & Chuang, I. L. Quantum Computation and Quantum Information, 10th ed. (Cambridge University Press, 2011).
Guhne, O. & Toth, G. Entanglement detection. Phys. Rep. 474, 1 – 75 (2009).
Friis, N., Vitagliano, G., Malik, M. & Huber, M. Entanglement certification from theory to experiment. Nat. Rev. Phys. 1, 72–87 (2019).
Chruściński, D. & Sarbicki, G. Entanglement witnesses: construction, analysis and classification. J. Phys. A Math. Theor. 47, 483001 (2014).
Silva, G., Glancy, S. & Vasconcelos, H. M. Investigating bias in maximum-likelihood quantum-state tomography. Phys. Rev. A 95, 022107 (2017).
Bengtsson, I. & Życzkowski, K. Geometry of Quantum States: An Introduction to Quantum Entanglement (Cambridge University Press, 2017).
Weilenmann, M., Dive, B., Trillo, D., Aguilar, E. A. & Navascués, M. Entanglement detection beyond measuring fidelities. Phys. Rev. Lett. 124, 200502 (2020).
Gühne, O., Mao, Y. & Yu, X.-D. Geometry of faithful entanglement. Phys. Rev. Lett. 126, 140503 (2021).
Hu, X.-M. et al. Optimized detection of high-dimensional entanglement. Phys. Rev. Lett. 127, 220501 (2021).
Liu, P., Liu, Z., Chen, S. & Ma, X. Fundamental limitation on the detectability of entanglement. Phys. Rev. Lett. 129, 230503 (2022).
Vidal, G. & Werner, R. F. Computable measure of entanglement. Phys. Rev. A 65, 032314 (2002).
Plenio, M. B. Logarithmic negativity: A full entanglement monotone that is not convex. Phys. Rev. Lett. 95, 090503 (2005).
Neven, A. et al. Symmetry-resolved entanglement detection using partial transpose moments. npj Quantum Inf. 7, 1–12 (2021).
Yu, X.-D., Imai, S. & Gühne, O. Optimal entanglement certification from moments of the partial transpose. Phys. Rev. Lett. 127, 060504 (2021).
Gray, J., Banchi, L., Bayat, A. & Bose, S. Machine-learning-assisted many-body entanglement measurement. Phys. Rev. Lett. 121, 150503 (2018).
Zhou, Y., Zeng, P. & Liu, Z. Single-copies estimation of entanglement negativity. Phys. Rev. Lett. 125, 200502 (2020).
Elben, A. et al. Mixed-state entanglement from local randomized measurements. Phys. Rev. Lett. 125, 200501 (2020).
Elben, A. et al. The randomized measurement toolbox. Nat. Rev. Phys. 5, 9–24 (2023).
Cieśliński, P. et al. Analysing quantum systems with randomised measurements. Phys. Rep. 1095, 1–48 (2024).
Vermersch, B., Elben, A., Sieberer, L. M., Yao, N. Y. & Zoller, P. Probing scrambling using statistical correlations between randomized measurements. Phys. Rev. X 9, 021061 (2019).
van Enk, S. J. & Beenakker, C. W. J. Measuring \({\rm{Tr}}{\rho }^{n}\) on single copies of ρ using random measurements. Phys. Rev. Lett. 108, 110503 (2012).
Elben, A., Vermersch, B., Dalmonte, M., Cirac, J. I. & Zoller, P. Rényi entropies from random quenches in atomic hubbard and spin models. Phys. Rev. Lett. 120, 050406 (2018).
Brydges, T. et al. Probing rényi entanglement entropy via randomized measurements. Science 364, 260–263 (2019).
Garcia, R. J., Zhou, Y. & Jaffe, A. Quantum scrambling with classical shadows. Phys. Rev. Res. 3, 033155 (2021).
Elben, A. et al. Many-body topological invariants from randomized measurements in synthetic quantum matter. Sci. Adv. 6, eaaz3666 (2020).
Rath, A., Branciard, C., Minguzzi, A. & Vermersch, B. Quantum fisher information from randomized measurements. Phys. Rev. Lett. 127, 260501 (2021).
Elben, A., Vermersch, B., Roos, C. F. & Zoller, P. Statistical correlations between locally randomized measurements: a toolbox for probing entanglement in many-body quantum states. Phys. Rev. A 99, 052323 (2019).
Huang, H.-Y., Kueng, R. & Preskill, J. Predicting many properties of a quantum system from very few measurements. Nat. Phys. 16, 1050–1057 (2020).
Zhou, Y. & Liu, Q. Performance analysis of multi-shot shadow estimation. Quantum 7, 1044 (2023).
Helsen, J. & Walter, M. Thrifty shadow estimation: reusing quantum circuits and bounding tails. Phys. Rev. Lett. 131, 240602 (2023).
Liu, Z., Zeng, P., Zhou, Y. & Gu, M. Characterizing correlation within multipartite quantum systems via local randomized measurements. Phys. Rev. A 105, 022407 (2022).
Elben, A. et al. Cross-platform verification of intermediate scale quantum devices. Phys. Rev. Lett. 124, 010504 (2020).
Kim, T., Fiorentino, M. & Wong, F. N. Phase-stable source of polarization-entangled photons using a polarization sagnac interferometer. Phys. Rev. A 73, 012316 (2006).
Englert, B.-G., Kurtsiefer, C. & Weinfurter, H. Universal unitary gate for single-photon two-qubit states. Phys. Rev. A 63, 032303 (2001).
O’Brien, J. L., Pryde, G. J., White, A. G., Ralph, T. C. & Branning, D. Demonstration of an all-optical quantum controlled-not gate. Nature 426, 264–267 (2003).
Kiesel, N., Schmid, C., Weber, U., Ursin, R. & Weinfurter, H. Linear optics controlled-phase gate made simple. Phys. Rev. Lett. 95, 210505 (2005).
Okamoto, R., Hofmann, H. F., Takeuchi, S. & Sasaki, K. Demonstration of an optical quantum controlled-not gate without path interference. Phys. Rev. Lett. 95, 210506 (2005).
Luis, A. & Sánchez-Soto, L. L. Complete characterization of arbitrary quantum measurement processes. Phys. Rev. Lett. 83, 3573 (1999).
Ketterer, A., Wyderka, N. & Gühne, O. Characterizing multipartite entanglement with moments of random correlations. Phys. Rev. Lett. 122, 120505 (2019).
Liu, S., He, Q., Huber, M., Gühne, O. & Vitagliano, G. Characterizing entanglement dimensionality from randomized measurements. PRX Quantum 4, 020324 (2023).
Wyderka, N. et al. Complete characterization of quantum correlations by randomized measurements. Phys. Rev. Lett. 131, 090201 (2023).
Seif, A., Cian, Z.-P., Zhou, S., Chen, S. & Jiang, L. Shadow distillation: quantum error mitigation with classical shadows for near-term quantum processors. PRX Quantum 4, 010303 (2023).
Zhou, Y. & Liu, Z. A hybrid framework for estimating nonlinear functions of quantum states. npj Quantum Inf. 10, 62 (2024).
Hu, H.-Y., LaRose, R., You, Y.-Z., Rieffel, E. & Wang, Z. Logical shadow tomography: Efficient estimation of error-mitigated observables. Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/2203.07263 (2022).
Peng, X.-J. et al. Experimental hybrid shadow tomography and distillation. Preprint at https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevApplied.23.014075 (2024).
Lubasch, M., Joo, J., Moinier, P., Kiffner, M. & Jaksch, D. Variational quantum algorithms for nonlinear problems. Phys. Rev. A 101, 010301 (2020).
Yamamoto, K., Endo, S., Hakoshima, H., Matsuzaki, Y. & Tokunaga, Y. Error-mitigated quantum metrology via virtual purification. Phys. Rev. Lett. 129, 250503 (2022).
Liu, Q., Li, Z., Yuan, X., Zhu, H. & Zhou, Y. Auxiliary-free replica shadow estimation. Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/2407.20865 (2024).
Koh, D. E. & Grewal, S. Classical shadows with noise. Quantum 6, 776 (2022).
Chen, S., Yu, W., Zeng, P. & Flammia, S. T. Robust shadow estimation. PRX Quantum 2, 030348 (2021).
Langford, N. K. et al. Demonstration of a simple entangling optical gate and its use in bell-state analysis. Phys. Rev. Lett. 95, 210504 (2005).
Acknowledgements
G.C., C.F.L. et.al. other authors claim support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos.~12350006, 92576202), Quantum Science and Technology-National Science and Technology Major Project (Nos. 2021ZD0301200), and USTC Research Funds of the Double First-Class Initiative (Grant No.~YD2030002026). Y.Z. acknowledges the support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) Grant No.~12205048 and 12575012, the Quantum Science and Technology-National Science and Technology Major Project Grant Nos.~2024ZD0301900 and 2021ZD0302000, the Shanghai QiYuan Innovation Foundation, the Shanghai Municipal Commission of Science and Technology with Grant No.~25511103200, the Shanghai Science and Technology Innovation Action Plan Grant No.~24LZ1400200, the Shanghai Pilot Program for Basic Research - Fudan University 21TQ1400100 (25TQ003), and the CCF-Quantum CTek Superconducting Quantum Computing CCF-QC2025006.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Theory Development: G.C.L. and Y.Z.. Experiment: G.C.L. Writing: G.C.L., Z.Y., G.C., L.C., X.S.H., S.Q.Z., H.X., and Y.L. Supervision: Y.Z., G.C., C.F.L., and G.C.G.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, GC., Chen, L., Hong, XS. et al. Few-shot estimation of entanglement with Bell measurement assistance. npj Quantum Inf (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41534-025-01172-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41534-025-01172-0