Abstract
Quantum computers may outperform classical computers on machine learning tasks. Yet, quantum learning systems may suffer from catastrophic forgetting, which is widely believed to be an obstacle to achieving continual learning. Here, we report an experimental demonstration of quantum continual learning on a superconducting processor. In particular, we sequentially train a quantum classifier with three tasks, two about identifying real-life images and one on classifying quantum states, and demonstrate its catastrophic forgetting. To overcome this dilemma, we exploit the elastic weight consolidation strategy and show that the quantum classifier can incrementally retain knowledge across three tasks with an average accuracy exceeding 92.3%. Additionally, for sequential tasks involving quantum-engineered data, we demonstrate that the quantum classifier outperforms a classical classifier with a comparable number of parameters. Our results establish a viable strategy for empowering quantum learning systems with adaptability to sequential tasks.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Continual learning, also known as incremental learning or lifelong learning, aims to empower artificial intelligence with strong adaptability to the non-stationary real world1,2,3. It is a fundamental feature of natural intelligence, yet poses a notorious challenge for artificial intelligence based on deep neural networks. A major obstacle that hinders continual learning is catastrophic forgetting, where adaptation to a new task generally leads to a largely reduced performance on old tasks4,5. This dilemma reflects a delicate trade-off between learning plasticity and memory stability: different sequential tasks correspond to different distributions, and maintaining plasticity would compromise stability in general1. In recent years, numerous efforts have been devoted to tackling this problem and the field of continual learning has been expanding rapidly6,7,8,9,10, with potential applications including medical diagnosis11, autonomous driving12, and financial markets13.
In parallel, the field of quantum computing has also made striking progress recently, with the experimental demonstration of quantum supremacy14,15,16 and error correction codes17,18,19,20 marked as the latest breakthroughs. The interplay between quantum computing and machine learning gives rise to a new research frontier of quantum machine learning21,22,23,24. Different quantum learning algorithms25,26,27,28,29,30 have been proposed and some of them have been demonstrated in proof-of-principle experiments with current noisy intermediate-scale quantum (NISQ) devices31,32. However, to date most quantum learning models have been designed for a specific predefined task with a static data distribution and no experiment on quantum learning of multiple tasks sequentially has been reported. For quantum artificial intelligence systems to accommodate dynamic streams of data in the real world, the capability of continual learning is indispensable and crucial. To this end, a recent theoretical work has extended continual learning to the quantum domain33. It is found that similar to classical learning models based on neural networks, quantum learning systems based on variational quantum circuits would suffer from catastrophic forgetting as well. In addition, a uniform strategy, namely the elastic weight consolidation (EWC) method34, has also been proposed to overcome this problem and achieve quantum continual learning. Despite this stimulating theoretical progress, experimental demonstration of quantum continual learning with NISQ devices is challenging and remains uncharted hitherto. To accomplish this, one faces at least two apparent difficulties: (i) constructing an experimentally feasible quantum classifier with sufficient expressivity to accommodate multiple tasks with diverse non-stationary data distributions and (ii) obtaining Fisher information required for implementing the EWC method in the presence of inevitable experimental noise.
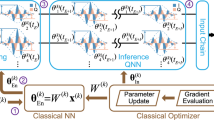
In this paper, we overcome these difficulties and report the first experimental demonstration of quantum continual learning with a fully programmable superconducting quantum processor (Fig. 1a). We construct a quantum classifier with more than two hundred variational parameters, by using an array of 18 transmon qubits featuring average simultaneous single- and two-qubit gate fidelities greater than 99.96% and 99.68% respectively. We demonstrate that, without EWC regulation, such a quantum classifier exhibits catastrophic forgetting when incrementally learning three tasks, including classifying real-life images and recognizing quantum phases (Fig. 1b). However, by employing the EWC method, we can achieve a proper balance between memory stability for previous tasks and learning plasticity for new tasks, thus attaining quantum continual learning (Fig. 1c,d). In addition, we compare the continual learning performance of quantum classifiers with that of classical classifiers in sequentially handling an engineered quantum task and a classical task. We demonstrate that the quantum classifier can incrementally learn the two tasks with an overall accuracy up to 95.8%, exceeding the best overall accuracy of 81.3% achieved by the classical classifier with a comparable number of parameters. This manifests quantum enhancement in continual learning scenarios.
a Exhibition of a 18-qubit quantum classifier running on a superconducting processor. The used transmon qubits are marked in orange. b Training data for three consecutive learning tasks. \({{\mathcal{T}}}_{1}\) concerns the classification of images depicting “T-shirt” and “ankle-boot” sampled from the Fashion-MNIST dataset35. \({{\mathcal{T}}}_{2}\) involves identifying images labeled as “Hand” and “Breast” from the magnetic resonance imaging dataset36. \({{\mathcal{T}}}_{3}\) is about recognizing quantum states in a symmetry-protected topological (SPT) phase and an antiferromagnetic (ATF) phase. c Illustration of elastic weight consolidation (EWC). EWC aims to balance memory stability for the previous task with learning plasticity for the new task. The memory stability is preserved by penalizing the deviation of the parameter θ from its optimal value θ⋆ for the previous task based on the importance of each parameter, which is measured by the Fisher information. d Conceptual diagram of catastrophic forgetting and continual learning. In a continual learning scenario, catastrophic forgetting refers to the dramatic performance drop on previous tasks after learning a new one. Continual learning is achieved when the learning system is able to maintain good performance on previous tasks while learning a new one.
Results
Framework and experimental setup
We first introduce the general framework for quantum continual learning33. We consider a continual learning scenario involving three sequential tasks, denoted as \({{\mathcal{T}}}_{k}\) (k = 1, 2, 3). As shown in Fig. 1b, \({{\mathcal{T}}}_{1}\) concerns classifying clothing images labeled as “T-shirts” and “ankle boot” from the Fashion-MNIST dataset35, \({{\mathcal{T}}}_{2}\) concerns classifying medical magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans labeled as “Hand” and “Breast”36, and \({{\mathcal{T}}}_{3}\) involves classifying quantum states in antiferromagnetic and symmetry-protected topological phases. The learning process consists of three stages for sequentially learning these tasks. For the k-th task, we define the following cross-entropy loss function
where Nk is the number of training samples, xk,i denotes the i-th training sample, \({{\bf{a}}}_{k,i}=({{\bf{a}}}_{k,i}^{0},{{\bf{a}}}_{k,i}^{1})\) denotes the ground true label of xk,i in the form of one-hot encoding, \(h\left({{\boldsymbol{x}}}_{k,i};{\boldsymbol{\theta }}\right)\) denotes the hypothesis function for the quantum classifier parameterized by θ, and \({{\bf{g}}}_{k,i}=({{\bf{g}}}_{k,i}^{0},{{\bf{g}}}_{k,i}^{1})\) denotes the probability of being assigned as label 0 and label 1 by the quantum classifier. The performance of the quantum classifier is evaluated on the test dataset for \({{\mathcal{T}}}_{k}\). In our experiment, we first train the quantum classifier with the above loss function for each task sequentially. After each learning stage, the quantum classifier has a good performance on the current task but experiences a dramatic performance drop on the previous ones, which demonstrates the phenomenon of catastrophic forgetting in quantum learning.
A salient strategy that can overcome catastrophic forgetting in quantum learning systems is the EWC method33,34, which preserves memories for previous tasks by penalizing parameter changes according to the importance of each parameter. To demonstrate its effectiveness, in the k-th stage some regularization terms are added to the cross-entropy loss for \({{\mathcal{T}}}_{k}\), yielding a modified loss function
where λk,t controls the regularization strength for \({{\mathcal{T}}}_{t}\) in the k-th stage; \({{\boldsymbol{\theta }}}_{t}^{\star }\) is the parameter obtained after the t-th stage; Ft,j denotes the Fisher information measuring the importance of the j-th parameter, which indicates how small changes to this parameter would affect the performance on \({{\mathcal{T}}}_{t}\). A schematic illustration of the main idea for quantum continual learning is shown in Fig. 1c, d.
Our experiments are conducted on a flip-chip superconducting quantum processor (Fig. 1a), which possesses 121 transmon qubits arranged in a two-dimensional array with tunable nearest-neighbor couplings. We choose 18 qubits (marked in orange in Fig. 1a) to implement a variational quantum classifier with a circuit depth of 20 and 216 trainable variational parameters (Fig. 2). To achieve a better learning performance, we push the average simultaneous two-qubit gate fidelities greater than 99.68% through optimizing the device fabrication and control processes. We mention that the gradients and Fisher information desired in updating the quantum classifier are obtained by measuring observables directly in the experiment based on the “parameter shift rule”37. Supplementary Section IIA provides more details about the characterization of the device.
The circuit consists of four blocks of operations with a total of 216 variational parameters. Each block performs three consecutive single-qubit rotation gates on all qubits, followed by two layers of CNOT gates applied to adjacent qubits. The quantum classifier adapts the interleaved block encoding strategy to encode classical data and naturally handles the quantum data (in the form of quantum states) as input. For each input data, the classifier determines the prediction label based on the local observable \(\langle {\widehat{\sigma }}_{9}^{z}\rangle\): label 0 and label 1 for \(\langle {\widehat{\sigma }}_{9}^{z}\rangle \ge 0\) and \(\langle {\widehat{\sigma }}_{9}^{z}\rangle < 0\), respectively.
Demonstration of catastrophic forgetting
To demonstrate catastrophic forgetting in quantum learning, we train sequentially the quantum classifier with the loss function defined in Equation (1) for the three tasks. Our experimental results are displayed in Fig. 3a. The learning process comprises three stages. In the first stage, the quantum classifier is trained to learn \({{\mathcal{T}}}_{1}\). After 20 epochs of parameter updating, the prediction accuracy for classifying clothing images reaches 99%.
a, b The prediction accuracy for three sequential tasks at each epoch during the continual learning process of the quantum classifier. Tasks \({{\mathcal{T}}}_{1}\), \({{\mathcal{T}}}_{2}\), and \({{\mathcal{T}}}_{3}\) are marked in green, blue, and orange, respectively. The right (left) figure shows the case where EWC (no EWC) is employed. c Distribution of the experimentally measured expected values \(\langle {\widehat{\sigma }}_{9}^{z}\rangle\), which determine the prediction label of input data, for all test samples after training. For each task, the solid line and dotted line correspond to two classes of data samples, respectively. A greater separation between the two distributions means better classification performance. d Distribution of Fisher information (FI) for all parameters after learning each task. e Average parameter change compared to the obtained parameters for previous tasks during the learning stage for the new task. The top (bottom) figure corresponds to the learning for \({{\mathcal{T}}}_{2}\) (\({{\mathcal{T}}}_{3}\)).
In the second stage, the quantum classifier is retrained on the training data for \({{\mathcal{T}}}_{2}\). After 28 epochs, it attains a classification accuracy of 99% on \({{\mathcal{T}}}_{2}\). However, after this training stage, the performance on \({{\mathcal{T}}}_{1}\) drops dramatically to 54%. In the third stage, the quantum classifier is further trained to recognize quantum phases. After 18 epochs, the quantum classifier achieves an accuracy of 100%. However, the accuracy for \({{\mathcal{T}}}_{2}\) and \({{\mathcal{T}}}_{1}\) dramatically falls to 64% and 55%. These experimental results clearly showcase the phenomenon of catastrophic forgetting in quantum learning.
Continual learning with EWC
In this section, we show that the above demonstrated catastrophic forgetting can be effectively overcome with the EWC method. To this end, we train sequentially the quantum classifier with the modified loss function that includes the EWC regularization as defined in Equation (2). Our experimental results are shown in Fig. 3b. We observe that after the second learning stage, the prediction accuracy for \({{\mathcal{T}}}_{2}\) reaches 95% while the accuracy for \({{\mathcal{T}}}_{1}\) still maintains 97%. After the third learning stage, the prediction accuracy for \({{\mathcal{T}}}_{3}\) reaches 96%, while it remains 88% and 93% for \({{\mathcal{T}}}_{2}\) and \({{\mathcal{T}}}_{1}\), respectively. This is in sharp contrast to the case without the EWC strategy, where it drops to 64% and 55%, respectively. After training, we plot the distribution of the experimentally measured \(\langle {\widehat{\sigma }}_{9}^{z}\rangle\), whose sign determines the assigned labels, for all test data samples, as shown in Fig. 3c. It is clear that when applying EWC, data samples from \({{\mathcal{T}}}_{1}\) and \({{\mathcal{T}}}_{2}\) with different labels are far more distinguishable than the case without EWC, which confirms that the learned knowledge for \({{\mathcal{T}}}_{1}\) and \({{\mathcal{T}}}_{2}\) is effectively preserved with EWC.
To further understand how EWC balances the stability-plasticity trade-off for quantum classifiers, we analyze the average parameter changes in cases with EWC. According to Equation (2), for parameters with larger Fisher information, their deviations from the optimal values for previous tasks will cause a relatively more significant increase in the loss function. Therefore, the parameters with large Fisher information tend to undergo only small adjustments when learning the new task, so as to minimize the increase in the loss function. To verify this understanding experimentally, we measure F1,i for each parameter after the first learning stage. As shown in Fig. 3d, we find that only 11 parameters have F1,i values larger than 0.01, while the other 205 parameters have F1,i values less than 0.01. Based on this, we divide all parameters into two groups and plot the average parameter change for each group during the second learning stage for \({{\mathcal{T}}}_{2}\). The results are shown in Fig. 3e. From this figure, it is clear that in the case with EWC, the parameters with large Fisher information (>0.01) experience smaller changes on average than the parameters with small Fisher information (<0.01). This is consistent with the goal of EWC, which is to ensure that more important parameters experience smaller changes, therefore better maintaining the performance on \({{\mathcal{T}}}_{1}\). The average parameter change in the third stage for learning \({{\mathcal{T}}}_{3}\) is also plotted in Fig. 3e, which shows a similar observation. Compared to the case without EWC, parameters with both large and small Fisher information exhibit smaller changes. This is consistent with the fact that the added regularization terms will in general constrain the change of parameters. These experimental results unambiguously demonstrate the effectiveness of EWC in mitigating catastrophic forgetting in quantum continual learning scenarios.
We remark that, after learning each task, only a small portion of all parameters have relatively large Fisher information. This reflects that memories for the task can be preserved by selectively stabilizing these parameters. The majority of parameters, with relatively small Fisher information, retain a relatively large space to learn new tasks in subsequent stages. This selective stabilization mechanism in EWC mirrors biological learning processes, where old memories are preserved by strengthening previously learned synaptic changes6. We also mention that, although various continual learning strategies other than the EWC method exist1, overcoming the catastrophic forgetting problem has been proved to be NP-hard in general38. As a result, we do not expect the EWC method for quantum continual learning demonstrated above to be universally applicable to arbitrary sequential tasks or to have the optimal performance on given tasks.
Quantum enhancement
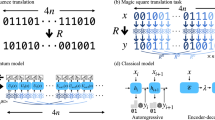
We consider two classification tasks with distinct data distributions: an engineered quantum task denoted as \({{\mathcal{T}}}_{1}^{{\prime} }\) and a classical task denoted as \({{\mathcal{T}}}_{2}^{{\prime} }\). As shown in Fig. 4a, \({{\mathcal{T}}}_{1}^{{\prime} }\) involves classifying engineered training data samples with target functions generated by a quantum model39,40,41, whereas \({{\mathcal{T}}}_{2}^{{\prime} }\) involves identifying medical images. To construct the dataset for \({{\mathcal{T}}}_{1}^{{\prime} }\), we choose clothing images of “T-shirt” and “ankle boot” as the source data and use principal component analysis (PCA) to compress the dimension of each image to ten. We generate the ground-truth label of each input data using a quantum model. To realize this, the ten-dimensional vector of each data is first encoded as a ten-qubit quantum state. The ground truth label is then taken as a local observable \(\langle {\widehat{\sigma }}_{1}^{z}\rangle\) evolved under a given quantum circuit with randomly chosen variational parameters (Materials and Methods). For \({{\mathcal{T}}}_{2}^{{\prime} }\), we use medical images as the source data. We similarly use PCA to compress each image to a ten-dimensional vector. The ground truth label of each data sample is its original label “hand” or “breast”.
a Training data for two sequential tasks \({{\mathcal{T}}}_{1}^{{\prime} }\) and \({{\mathcal{T}}}_{2}^{{\prime} }\). For \({{\mathcal{T}}}_{1}^{{\prime} }\), we choose clothing images as the source data and use principal component analysis (PCA) to reduce the dimension of each image to obtain a ten-dimensional vector. The ground truth label of each input sample is determined by a local observable \(\langle {\widehat{\sigma }}_{1}^{z}\rangle\) evolved under a quantum circuit with randomly chosen gate parameters. For \({{\mathcal{T}}}_{2}^{{\prime} }\), we choose medical images as the source data. We use PCA to compress each image to a ten-dimensional vector as the input data. The label of the input vector is determined by the category of its original images. b Schematic illustration of a quantum classifier and a classical classifier based on the feedforward neural network (FFNN). c Prediction accuracy for two sequential tasks as functions of training epochs during the continual learning process. For both quantum and classical classifiers, EWC is employed with the regularization strength set as 40. d Continual learning performance of the classical classifier as a function of regularization strength. For the classical classifier based on FFNN, we employ EWC with different regularization strengths. For each regularization strength, we train the classical classifier 50 times and plot the mean prediction accuracy for \({{\mathcal{T}}}_{1}^{{\prime} }\) and \({{\mathcal{T}}}_{2}^{{\prime} }\), and their averages. The optimal achievable overall performance, evaluated as the average of the accuracy on \({{\mathcal{T}}}_{1}^{{\prime} }\) and \({{\mathcal{T}}}_{2}^{{\prime} }\), is 81.3% for the classical classifier and 95.8% for the quantum classifier.
In a continual learning scenario involving these two tasks in sequence, we compare the performance of quantum and classical models. For quantum learning, we experimentally implement a ten-qubit quantum circuit classifier with a total of 90 variational parameters (Fig. 4b, left). The learning process consists of two stages. In each stage, the ten-dimensional vector of each input data is embedded as a ten-qubit quantum state, followed by the ten-qubit variational quantum classifier (Materials and Methods). In Fig. 4c, we present the experimental results. In the first stage, the quantum classifier is trained on \({{\mathcal{T}}}_{1}^{{\prime} }\), achieving 99.1% prediction accuracy after 20 epochs of parameter updating. In the second stage of learning \({{\mathcal{T}}}_{2}^{{\prime} }\), the EWC method is employed with a regularization strength of λq = 40. After 16 training epochs, the accuracy on \({{\mathcal{T}}}_{2}^{{\prime} }\) reaches 98%, while the accuracy on \({{\mathcal{T}}}_{1}^{{\prime} }\) slightly drops to 93.7%. The overall performance, typically evaluated by the average accuracy of the two tasks, is 95.8%.
For classical learning, we use a three-layer feedforward neural network with 241 variational parameters as the classical classifier (Fig. 4b, right). In each learning stage, the ten-dimensional vector is directly taken as the input data of the classical classifier. We present the numerical results in Fig. 4d. We find that the classical classifier struggles to achieve good performance on both tasks simultaneously, as \({{\mathcal{T}}}_{1}^{{\prime} }\) and \({{\mathcal{T}}}_{2}^{{\prime} }\) largely interfere with each other. The dominance of each task depends on the regularization strength λc used in EWC. For small values of λc, the classical classifier achieves high accuracy on \({{\mathcal{T}}}_{2}^{{\prime} }\) but performs poorly on \({{\mathcal{T}}}_{1}^{{\prime} }\), indicating catastrophic forgetting. As λc increases, the classical classifier places more weight on preserving old memories for \({{\mathcal{T}}}_{1}^{{\prime} }\). This leads to an improvement in performance on \({{\mathcal{T}}}_{1}^{{\prime} }\) and a drop in performance on \({{\mathcal{T}}}_{2}^{{\prime} }\). When λc is increased to a large value (λc = 100), the classical classifier almost completely loses its learning plasticity for \({{\mathcal{T}}}_{2}^{{\prime} }\) in the second learning stage. The best overall performance that can be achieved by the classical classifier is 81.3%. In addition, we implement a classical convolutional neural network (CNN) with 181 variational parameters. The simulation results (Fig. S10) show that the CNN classifier achieves an overall performance of up to 81.1%.
The comparison between quantum and classical models shows that quantum models can outperform classical models in certain continual learning scenarios, despite containing fewer variational parameters. This agrees with the theoretical predictions that quantum neural networks in general possess larger expressive power42 and effective dimension43 than classical ones with a comparable number of parameters, thus would better accommodate distribution differences among multiple tasks and lead to superior overall performance in continual learning scenarios.
Discussion
In classical continual learning, a variety of strategies other than the EWC method, such as orthogonal gradient projection44 and parameter allocation45, have been proposed to overcome catastrophic forgetting. These strategies might also be adapted to quantum continual learning scenarios, and their experimental demonstrations would be interesting and important. Our work focuses on a representative approach–EWC–as a proof-of-concept demonstration of quantum continual learning on near-term quantum hardware. Along this direction, it is, however, worthwhile to mention a subtle distinction between quantum and classical continual learning. In the quantum domain, due to the no-cloning theorem46 and the difficulty in building long-lived quantum memories47, one cannot duplicate unknown quantum data and store them for a long time. As a result, replay-based strategies that rely on recovering the old data distributions48,49 require either (currently unavailable) fault-tolerant quantum random access memories50 or the training of quantum generative models for each task. The latter would then need to be re-executed on hardware to synthesize past samples, introducing substantial overhead. By contrast, EWC only stores a classical representation of the Fisher information matrix (or its diagonal) for old tasks. This avoids quantum data storage and makes EWC a more viable strategy for realizing quantum continual learning on near-term quantum devices. In addition, this work primarily focuses on classification tasks in the framework of supervised learning. The extension of quantum continual learning to unsupervised and reinforcement learning presents more technical difficulties and has yet to be achieved in both theory and experiment. The use of classical learning surrogates51,52 is a promising approach to reduce the training cost of variational quantum circuits and may thus assist the development of quantum continual learning.
We note that our quantum continual learning strategy against catastrophic forgetting shares a conceptual similarity with quantum error mitigation techniques designed to combat environmental noise. Combining them at the current stage is highly non-trivial. Quantum error mitigation techniques such as zero-noise extrapolation53 typically introduce significant overhead, often requiring multiple circuit executions with modified parameters or deeper circuits. When combined with the already-intensive cost of estimating the Fisher information matrix for EWC, the total burden can become impractical on current hardware. We expect the future integration of hardware-level error mitigation techniques with algorithm-level continual learning strategies, potentially further enhancing quantum continual learning performance in real quantum devices.
Enabling quantum learning models to accommodate a dynamic stream of tasks demands long-term research. Our work makes a primary step in this direction by demonstrating the issue of catastrophic forgetting and the effectiveness of the EWC method for quantum continual learning in experiments. We note that while variational quantum classifiers offer a flexible framework for encoding and processing classical and quantum data, they face scalability limitations. In particular, training deep and high-dimensional variational quantum classifiers beyond classical simulability would be hindered by issues such as barren plateaus54,55,56,57. Beyond this general limitation, the barren plateaus issue may pose a unique challenge specifically to EWC itself. If an old task’s landscape is a barren plateau, its gradients (and thus the Fisher information matrix, which measures the landscape’s curvature) decay exponentially with the qubit number. The EWC penalty term would consequently vanish, leading to a plausible conclusion that no parameters are important for that task and thus EWC would fail to protect the old task’s knowledge. Despite these limitations, our work provides a proof-of-principle experimental demonstration of quantum continual learning on existing quantum hardware, motivating future development of quantum continual learning strategies not only for variational quantum classifiers but also for more robust and scalable quantum machine learning architectures in the future.
Methods
Variational quantum classifiers
We build the quantum classifiers with multiple blocks of operations, as illustrated in Figs. 2 and 5. Each block contains three layers of single-qubit gates with programmable rotation angles and ends with two layers of entangling gates for leveraging the exponentially large Hilbert space and establishing quantum correlations among the qubits. For classification tasks, the quantum classifier assigns a label to each input data based on the measured expectation value of the Pauli-Z operator on the m-th qubit, \(\langle {\widehat{\sigma }}_{m}^{z}\rangle\): a label for one class is assigned when \(\langle {\widehat{\sigma }}_{m}^{z}\rangle \ge 0\), while a label for the other class is assigned when \(\langle {\widehat{\sigma }}_{m}^{z}\rangle < 0\). In the experiment for learning \({{\mathcal{T}}}_{1}\), \({{\mathcal{T}}}_{2}\) and \({{\mathcal{T}}}_{3}\), we use 18 qubits with four blocks to construct the quantum classifier with a total of 216 variational parameters, where the entangling gates are selected as CNOT gates, and m = 9. In the experiment for learning \({{\mathcal{T}}}_{1}^{{\prime} }\) and \({{\mathcal{T}}}_{2}^{{\prime} }\), we construct a ten-qubit quantum classifier with three blocks containing a total of 90 variational parameters, where the entangling gates are selected as CZ gates, and m = 1.
Each ten-dimensional input vector is first embedded into a quantum state via the quantum feature encoding (Fig. S2b). A variational circuit with randomly chosen parameters is then applied to the state. The ground true label of each input image vector is generated based on the local observable \(\langle {\widehat{\sigma }}_{1}^{z}\rangle\).
Dataset generation
The datasets for \({{\mathcal{T}}}_{1}\) and \({{\mathcal{T}}}_{2}\) are composed of images randomly selected from the Fashion-MNIST dataset35 and the MRI dataset36, respectively. The quantum dataset for \({{\mathcal{T}}}_{3}\) is composed of ground states of the cluster-Ising Hamiltonian58 in the ATF and SPT phases. We prepare approximate ground states in our experiments by executing a variational circuit. We first train the variational circuit on a classical computer with the aim of minimizing the energy expectation value for the output states. We then experimentally implement the variational circuit using the parameters obtained in the classical simulation. To characterize our quantum state preparation, we measure the string order parameter for these prepared states. In Supplementary Sec. IIB, we provide a detailed discussion about the quantum state preparation. For each of \({{\mathcal{T}}}_{1}\), \({{\mathcal{T}}}_{2}\), and \({{\mathcal{T}}}_{3}\), we construct a training set with 500 data samples and a test set with 100 data samples.
To construct the dataset for \({{\mathcal{T}}}_{1}^{{\prime} }\), we use the input data sourced from the Fashion-MNIST dataset. Specifically, we randomly select 1200 images labeled as “T-shirt” and “ankle boot”. We first perform PCA to compress these images to ten-dimensional vectors. Subsequently, each feature of these ten-dimensional vectors is further normalized to have a mean value of 0 and a standard deviation of 1. As depicted in Fig. 5, we generate the label g(x) for each data sample x using functions generated by a quantum model. To this end, we first use the feature encoding proposed in ref.39 to encode x into a quantum state. We show the quantum circuit for the feature encoding in Fig. S2b. We then experimentally implement the quantum circuit model with three blocks of operations. The variational parameters θ for the circuit are randomly generated within the range of [0, 2π]90. The ground true label g(x) is determined by the local observable \(\langle {\widehat{\sigma }}_{1}^{z}\rangle\) evolved under the above circuit model: g(x) = 0 if \(\langle {\widehat{\sigma }}_{1}^{z}\rangle > 0.2\) and g(x) = 1 if \(\langle {\widehat{\sigma }}_{1}^{z}\rangle < -0.2\). In our experiment, we obtain a total of 667 data samples with g(x) being 0 and 1. We select 556 of them as the training dataset and the other 111 of them as the test dataset.
To construct the dataset for \({{\mathcal{T}}}_{2}^{{\prime} }\), we use the data from the MRI dataset. We randomly select 600 images labeled as “hand” and “breast”. We also employ PCA to compress these images to ten-dimensional vectors. The ground true label of each ten-dimensional vector is just the label of the corresponding original image. We divide 600 samples into a training dataset of size 500 and a test dataset of size 100.
Data encoding
In our experiments, we utilize different strategies to encode different types of data. We use the interleaved block encoding strategy59 to encode classical images in the dataset for \({{\mathcal{T}}}_{1}\) and \({{\mathcal{T}}}_{2}\). For each classical image, we first reduce its size to 16 × 16 grayscale pixels and flatten it into a 256-dimensional vector. We then normalize the vector and add up the adjacent entries to obtain a 128-dimensional vector x. As shown in Fig. 2, we assign each single-qubit rotation gate with an angle of 2xi + θi, where θi is a variational parameter. We choose 128 rotation gates and assign the corresponding xi with an entry of x. For the remaining 88 rotation gates, we set the corresponding xi to zero. We note that other constant values could also be used for padding; however, this choice has no impact on performance in our setting. Since the variational parameters θi are randomly initialized, adding any constant value as padding simply results in an equally random initialization. Consequently, the specific padding value does not affect the model’s expressivity or optimization behavior. For the quantum data in \({{\mathcal{T}}}_{3}\), the quantum classifier can naturally handle these quantum states as input after their preparation on quantum devices.
For \({{\mathcal{T}}}_{1}^{{\prime} }\), we adopt the feature encoding approach proposed in Ref.39, with the circuit structure shown in Fig. S2b. This feature encoding is assumed to yield a kernel that is computationally hard to estimate on classical computers. For \({{\mathcal{T}}}_{2}^{{\prime} }\), we use a conventional rotation encoding approach in which the data vectors are encoded into a single layer of single-qubit rotation gates, with the circuit structure depicted in Fig. S2c.
Gradients and Fisher information
We minimize the loss function in Equation (1) by adapting the gradient descent method. Based on the chain rule, the derivatives of L with respect to the j-th parameter θj can be expressed as:
In our experiment, \({{\bf{g}}}_{k,i}^{0}\) and \({{\bf{g}}}_{k,i}^{1}\) are determined by the local observable \(\left|0\right\rangle {\left\langle 0\right|}_{m}\) and \(\left|1\right\rangle {\left\langle 1\right|}_{m}\) on the m-th qubit, respectively.
As all variational parameters in the quantum classifier take the form of \(\exp (-\frac{i}{2}\theta {P}_{n})\) (Pn belongs to the Pauli group), the derivatives of \({{\bf{g}}}_{k,i}^{l}\) can be computed via the “parameter-shift rule”37,60:
where l = 0, 1, and \({({{\bf{g}}}_{k,i}^{l})}^{\pm }\) denotes the expectation values of the local observables with parameter θj being \({\theta }_{j}\pm \frac{\pi }{2}\).
We directly measure \({({{\bf{g}}}_{k,i}^{l})}^{\pm }\) in experiments to obtain the quantum gradients, based on which we adapt the gradient descent method assisted by the Nadam optimizer61 to optimize the quantum classifier. The learning rate is set as 0.05 in experiments.
After learning the k-th task, we need to obtain the Fisher information Fk,j for measuring the importance of each variational parameter θj. Based on the derivatives of the loss function at \({{\boldsymbol{\theta }}}_{k}^{\star }\), we estimate Fk,j as:
The notations here follow those in Equation (1) and Equation (2). The detailed derivation of Fk,j is provided in Supplementary Sec. I.B. We provide the derivation of Fk,j in Supplementary Sec. I.B.
Training with EWC
To sequentially learn multiple tasks without catastrophic forgetting, we adapt the EWC method. The learning process consists of multiple stages. Initially, each variational parameter in the quantum classifier is randomly chosen within the range of [− π, π]. In the k-th stage, the quantum classifier is trained with the modified loss function LEWC as defined in Equation (2). At each training epoch, we calculate the gradients of LEWC on 25 data samples randomly selected from the training dataset, and evaluate the learning performance on all data samples in the test dataset. After the k-th stage, we obtain the Fisher information Fk,i for all variational parameters, which is used in the subsequent learning stage (see Supplementary Sec. IB for detailed algorithms).
In the experiment for learning \({{\mathcal{T}}}_{1}\), \({{\mathcal{T}}}_{2}\) and \({{\mathcal{T}}}_{3}\), we set λ2,1 = 60 in the second stage, and λ3,1 = 0 and λ3,2 = 60 in the third stage. We cancel the regularization term for \({{\mathcal{T}}}_{1}\) (λ3,1 = 0) in the third stage for two reasons. First, we expect the model to have fewer restrictions and thus more flexibility in adjusting parameters to learn \({{\mathcal{T}}}_{3}\).
Second, after the second stage, the obtained parameters \({{\boldsymbol{\theta }}}_{2}^{\star }\) can maintain knowledge for \({{\mathcal{T}}}_{1}\) since the regularization term for \({{\mathcal{T}}}_{1}\) is added during the second stage. Thus, by only adding the regularization term for \({{\mathcal{T}}}_{2}\), we can still preserve the learned knowledge from \({{\mathcal{T}}}_{1}\), as evidenced by the experimental results. Although the information from \({{\mathcal{T}}}_{1}\) will decay as we sequentially learn more tasks, considering there are only three tasks in total, it is reasonable to set λ3,1 = 0 for simplicity.
In addition, we simulate an idealized scenario in which \({{\mathcal{T}}}_{1}\), \({{\mathcal{T}}}_{2}\), and \({{\mathcal{T}}}_{3}\) are trained simultaneously, providing a best-case baseline for quantum continual learning. As shown in Fig. S11, this idealized setting achieves near-perfect performance.
Statistical analysis
In our experiments, we evaluated the prediction accuracies on 10 independent test datasets after sequential training. Each test set contains 50 data samples, and for each sample, 1200 repeated executions of the quantum circuit are performed to reliably determine the classification outcome.
The mean prediction accuracies, along with corresponding error bars, are presented in Fig. 6, clearly demonstrating the statistical robustness of the observed performance improvements when using the EWC method.
a, b,Cumulative distributions of prediction accuracy measured on 10 test datasets, each containing 50 randomly selected test samples, after sequentially learning three tasks: \({{\mathcal{T}}}_{1}\), \({{\mathcal{T}}}_{2}\) and \({{\mathcal{T}}}_{3}\). c, d Cumulative distributions of prediction accuracy for sequential learning of tasks \({{\mathcal{T}}}_{1}^{{\prime} }\) and \({{\mathcal{T}}}_{2}^{{\prime} }\).
Classical learning models for comparison
We specify classical feedforward networks used in numerical simulations for comparison. For quantum learning, we use the quantum circuit classifier belonging to the same variational family as those employed for relabeling data for \({{\mathcal{T}}}_{1}^{{\prime}}\), but initialized with different parameters randomly generated from [0, 2π]90. This quantum classifier contains a total of 90 variational parameters. For classical learning, we use a three-layer FFNN with ten neurons in the input layer, 20 neurons in the hidden layer, and one neuron in the output layer. The activation function used is the sigmoid function. This FFNN contains a total of 241 variational parameters. The ten neurons in the input layer encode the ten-dimensional input data vectors for the two tasks. The neuron in the output layer determines the prediction outcome for the input data: if the output value is greater than 0.5, the input data is assigned to class 0; if the output value is less than 0.5, it is assigned to class 1. The CNN first applies a one-dimensional convolutional layer with a kernel size of 3. This layer maps the single input channel to 20 output channels. The ReLU activation function is used, and padding (pad = 1) is used to ensure that the output length remains 10. Next, a max pooling layer with a pooling window of size two is applied, reducing the length of the signal from 10 to 5. The resulting feature map, which has dimensions 100, is flattened into a vector and fed into a fully connected layer with one neuron. A sigmoid activation function is used in this final layer to produce the output. In total, the CNN model contains a total of 181 trainable parameters.
Data availability
All data and codes needed to evaluate the conclusions in the paper are archived in Zenodo: https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.17669105.
Code availability
All codes needed to evaluate the conclusions in the paper are archived in Zenodo: https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.17669105.
References
Wang, L., Zhang, X., Su, H. & Zhu, J. A Comprehensive Survey of Continual Learning: Theory, Method and Application. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 46, 5362 (2024).
Ditzler, G., Roveri, M., Alippi, C. & Polikar, R. Learning in Nonstationary Environments: A Survey. IEEE Comput. Intell. Mag. 10, 12 (2015).
Chen, Z. & Liu, B. Lifelong Machine Learning, 2nd ed. (Springer Nature, Switzerland, 2022).
McCloskey, M. and Cohen, N. J. Catastrophic Interference in Connectionist Networks: The Sequential Learning Problem. Psychology of Learning and Motivation, Vol. 24, edited by Bower, G. H. (Academic Press, 1989) pp. 109–165.
Goodfellow, I. J., Mirza, M., Xiao, D., Courville, A. & Bengio, Y. An Empirical Investigation of Catastrophic Forgetting in Gradient-Based Neural Networks, arXiv:1312.6211 (2015).
Wang, L. et al. Incorporating neuro-inspired adaptability for continual learning in artificial intelligence. Nat. Mach. Intell. 5, 1356 (2023).
van de Ven, G. M., Tuytelaars, T. & Tolias, A. S. Three types of incremental learning. Nat. Mach. Intell. 4, 1185 (2022).
Zeng, G., Chen, Y., Cui, B. & Yu, S. Continual learning of context-dependent processing in neural networks. Nat. Mach. Intell. 1, 364 (2019).
Perkonigg, M. et al. Dynamic memory to alleviate catastrophic forgetting in continual learning with medical imaging. Nat. Commun. 12, 5678 (2021).
Soltoggio, A. et al. A collective AI via lifelong learning and sharing at the edge. Nat. Mach. Intell. 6, 251 (2024).
Lee, C. S. & Lee, A. Y. Clinical applications of continual learning machine learning. Lancet Digit. Health 2, e279 (2020).
Shaheen, K., Hanif, M. A., Hasan, O. & Shafique, M. Continual Learning for Real-World Autonomous Systems: Algorithms, Challenges and Frameworks. J. Intell. Rob. Syst. 105, 9 (2022).
Philps, D., Weyde, T., d’Avila Garcez, A. & Batchelor, R. Continual Learning Augmented Investment Decisions. arXiv:1812.02340 (2019).
Arute, F. et al. Quantum supremacy using a programmable superconducting processor. Nature 574, 505 (2019).
Zhong, H.-S. et al. Quantum computational advantage using photons. Science 370, 1460 (2020).
Wu, Y. et al. Strong Quantum Computational Advantage Using a Superconducting Quantum Processor. Phys. Rev. Lett. 127, 180501 (2021).
Google Quantum AI Suppressing quantum errors by scaling a surface code logical qubit. Nature 614, 676 (2023).
Bluvstein, D. et al. Logical quantum processor based on reconfigurable atom arrays. Nature 626, 58 (2024).
Paetznick, A. et al. Demonstration of logical qubits and repeated error correction with better-than-physical error rates. arXiv:2404.02280 (2024).
Google Quantum AI and Collaborators Quantum error correction below the surface code threshold. Nature 638, 920 (2025).
Biamonte, J. et al. Quantum machine learning. Nature 549, 195 (2017).
Dunjko, V. & Briegel, H. J. Machine learning & artificial intelligence in the quantum domain: A review of recent progress. Rep. Prog. Phys. 81, 074001 (2018).
Das Sarma, S., Deng, D.-L. & Duan, L.-M. Machine learning meets quantum physics. Phys. Today 72, 48 (2019).
Cerezo, M., Verdon, G., Huang, H.-Y., Cincio, L. & Coles, P. J. Challenges and opportunities in quantum machine learning. Nat. Comput. Sci. 2, 567 (2022).
Harrow, A. W., Hassidim, A. & Lloyd, S. Quantum Algorithm for Linear Systems of Equations. Phys. Rev. Lett. 103, 150502 (2009).
Lloyd, S., Mohseni, M. & Rebentrost, P. Quantum principal component analysis. Nat. Phys. 10, 631 (2014).
Lloyd, S. & Weedbrook, C. Quantum Generative Adversarial Learning. Phys. Rev. Lett. 121, 040502 (2018).
Hu, L. et al. Quantum generative adversarial learning in a superconducting quantum circuit. Sci. Adv. 5, eaav2761 (2019).
Gao, X., Zhang, Z.-Y. & Duan, L.-M. A quantum machine learning algorithm based on generative models. Sci. Adv. 4, eaat9004 (2018).
Liu, Y., Arunachalam, S. & Temme, K. A rigorous and robust quantum speed-up in supervised machine learning. Nat. Phys. 17, 1013 (2021).
Preskill, J. Quantum Computing in the NISQ era and beyond. Quantum 2, 79 (2018).
Bharti, K. et al. Noisy intermediate-scale quantum algorithms. Rev. Mod. Phys. 94, 015004 (2022).
Jiang, W., Lu, Z. & Deng, D.-L. Quantum Continual Learning Overcoming Catastrophic Forgetting. Chin. Phys. Lett. 39, 50303 (2022).
Kirkpatrick, J. et al. Overcoming catastrophic forgetting in neural networks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 114, 3521 (2017).
Xiao, H., Rasul, K. & Vollgraf, R. Fashion-MNIST: A Novel Image Dataset for Benchmarking Machine Learning Algorithms arXiv:1708.07747 (2017).
Clark, K. et al. The Cancer Imaging Archive (TCIA): Maintaining and Operating a Public Information Repository. J. Digital Imaging 26, 1045 (2013).
Mitarai, K., Negoro, M., Kitagawa, M. & Fujii, K. Quantum circuit learning. Phys. Rev. A 98, 032309 (2018).
Knoblauch, J., Husain, H. & Diethe, T. Optimal Continual Learning has Perfect Memory and is NP-hard. in Proc. 37th Int. Conf. Mach. Learn. (PMLR, 2020) pp. 5327–5337.
Havlíček, V. et al. Supervised learning with quantum-enhanced feature spaces. Nature 567, 209 (2019).
Huang, H.-Y. et al. Power of data in quantum machine learning. Nat. Commun. 12, 2631 (2021).
Jerbi, S. et al. Quantum machine learning beyond kernel methods. Nat. Commun. 14, 517 (2023).
Du, Y., Hsieh, M.-H., Liu, T. & Tao, D. Expressive power of parametrized quantum circuits. Phys. Rev. Res. 2, 033125 (2020).
Abbas, A. et al. The power of quantum neural networks. Nat. Comput. Sci. 1, 403 (2021).
Farajtabar, M., Azizan, N., Mott, A. & Li, A. Orthogonal Gradient Descent for Continual Learning. in Proc. Twenty Third Int. Conf. Artif. Intell. Stat. (PMLR, 2020) pp. 3762–3773.
Mallya, A., Davis, D. & Lazebnik, S. Piggyback: Adapting a Single Network to Multiple Tasks by Learning to Mask Weights in Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV) (2018) pp. 67–82.
Wootters, W. K. & Zurek, W. H. A single quantum cannot be cloned. Nature 299, 802 (1982).
Terhal, B. M. Quantum error correction for quantum memories. Rev. Mod. Phys. 87, 307 (2015).
Isele, D. & Cosgun, A. Selective Experience Replay for Lifelong Learning. Proc. AAAI Conf. Artif. Intell. 32, 1 (2018).
Rolnick, D., Ahuja, A., Schwarz, J., Lillicrap, T. & Wayne, G. Experience Replay for Continual Learning, in Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst., Vol. 32 (Curran Associates, Inc., 2019).
Giovannetti, V., Lloyd, S. & Maccone, L. Quantum Random Access Memory. Phys. Rev. Lett. 100, 160501 (2008).
Schreiber, F. J., Eisert, J. & Meyer, J. J. Classical Surrogates for Quantum Learning Models. Phys. Rev. Lett. 131, 100803 (2023).
Du, Y., Hsieh, M.-H. & Tao, D. Efficient learning for linear properties of bounded-gate quantum circuits. Nat Commun 16, 3790 (2025).
Temme, K., Sergey, B. & Gambetta, J. M. Error Mitigation for Short-Depth Quantum Circuits. Phys. Rev. Lett. 119, 180509 (2017).
McClean, J. R., Boixo, S., Smelyanskiy, V. N., Babbush, R. & Neven, H. Barren plateaus in quantum neural network training landscapes. Nat. Commun. 9, 4812 (2018).
Ragone, M. et al. A Lie algebraic theory of barren plateaus for deep parameterized quantum circuits. Nat. Commun. 15, 7172 (2024).
García-Martín, D., Larocca, & Cerezo, M. Quantum neural networks form Gaussian processes. Nat. Phys. 21, 1153-1159 (2025).
Larocca, M. et al. Barren plateaus in variational quantum computing. Nat. Rev. Phys. 7, 174 (2025).
Smacchia, P. et al. Statistical mechanics of the cluster Ising model. Phys. Rev. A 84, 022304 (2011).
Ren, W. et al. Experimental quantum adversarial learning with programmable superconducting qubits. Nat. Comput. Sci. 2, 711 (2022).
Li, J., Yang, X., Peng, X. & Sun, C.-P. Hybrid Quantum-Classical Approach to Quantum Optimal Control. Phys. Rev. Lett. 118, 150503 (2017).
Dozat, T. Incorporating Nesterov Momentum into Adam. in Proc. 13th Int. Conf. Learn. Represent. (2016).
Acknowledgements
We thank J. Eisert, M. Hafezi, D. Yuan, and S. Jiang for helpful discussions. The device was fabricated at the Micro-Nano Fabrication Center of Zhejiang University. We acknowledge support from the Quantum Science and Technology-National Science and Technology Major Project (Grant Nos. 2021ZD0300200 and 2021ZD0302203), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 12174342, 92365301, 12274367, 12322414, 12274368, 12075128, and T2225008), the National Key R&D Program of China (Grant No. 2023YFB4502600), and the Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. LDQ23A040001, LR24A040002). Z.L., W.L., W.J., Z.-Z.S., and D.-L.D. are supported in addition by Tsinghua University Dushi Program, and the Shanghai Qi Zhi Institute Innovation Program (Grant No. SQZ202318). C.S. is supported by the Xiaomi Young Scholars Program. P.-X.S. acknowledges support from the European Union's Horizon Europe research and innovation programme under the Marie Skłodowska-Curie Grant Agreement No. 101180589 (SymPhysAI), the National Science Centre (Poland) OPUS Grant No. 2021/41/B/ST3/04475, and the Foundation for Polish Science project MagTop (No. FENG.02.01-IP.05-0028/23) co-financed by the European Union from the funds of Priority 2 of the European Funds for a Smart Economy Program 2021–2027 (FENG). Views and opinions expressed are however those of the author(s) only and do not necessarily reflect those of the European Union or the European Research Executive Agency. Neither the European Union nor the granting authority can be held responsible for them.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
C.Z. carried out the experiments and analyzed the data with the assistance of S.X., K.W., J.C., Y.W., F.J., X.Z., Y.G., Z.T., Z.C., A.Z., N.W., Y.Z., T.L., F.S., J.Z., Z.B., Z.Z., Z.S., J.D., H.D., P.Z., H.L., Q.G., Z.W.; C.S. and H.W. directed the experiments; Z.L. formalized the theoretical framework and performed the numerical simulations under the supervision of D.-L.D.; W.L., W.J., Z.-Z.S. and P.-X.S. provided theoretical support; J.C. and X.Z. designed the device; H.L. fabricated the device, supervised by H.W.; L.Z. and J.H. provided further experimental support; C.Z., Z.L., J.H., H.W., D.-L.D., and C.S. wrote the manuscript with feedback from all authors.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, C., Lu, Z., Zhao, L. et al. Experimental demonstration of quantum continual learning with superconducting qubits. npj Quantum Inf 12, 28 (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41534-025-01174-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41534-025-01174-y