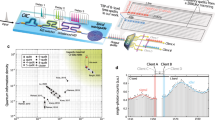
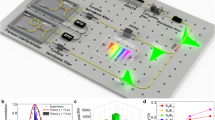
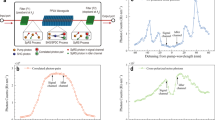
Abstract
Frequency-bin entangled photons can be efficiently produced on-chip which offers a scalable, robust and low-footprint platform for quantum communication, particularly well-suited for resource-constrained settings such as mobile or satellite-based systems. However, analyzing such entangled states typically requires active and lossy components, limiting scalability and multi-mode compatibility. We demonstrate a novel technique for processing frequency-encoded photons using linear interferometry and time-resolved detection. Our approach is fully passive and compatible with spatially multi-mode light, making it suitable for free-space and satellite-to-ground applications. As a proof-of-concept, we utilize frequency-bin entangled photons generated from a high-brightness multi-resonator source integrated on-chip to show the ability to perform arbitrary projective measurements over both single- and multi-mode channels. We report the first measurement of the joint temporal intensity between frequency-bin entangled photons, which allows us to certify entanglement by violating the Clauser-Horne-Shimony-Holt (CHSH) inequality, with a measured value of ∣S∣ = 2.32 ± 0.05 over multi-mode fiber. By combining time-resolved detection with energy-correlation measurements, we perform full quantum state tomography, yielding a state fidelity of up to 91%. We further assess our ability to produce non-classical states via a violation of time-energy entropic uncertainty relations and investigate the feasibility of a quantum key distribution protocol. Our work establishes a resource-efficient and scalable approach toward the deployment of robust frequency-bin entanglement over free-space and satellite-based links.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The analysis code is provided in ref. 61. The data sets used and analyzed in the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Olislager, L. et al. Frequency-bin entangled photons. Phys. Rev. A 82, 013804 (2010).
Lu, H.-H., Liscidini, M., Gaeta, A. L., Weiner, A. M. & Lukens, J. M. Frequency-bin photonic quantum information. Optica 10, 1655–1671 (2023).
Reimer, C. et al. Generation of multiphoton entangled quantum states by means of integrated frequency combs. Science 351, 1176–1180 (2016).
Clementi, M. et al. Programmable frequency-bin quantum states in a nano-engineered silicon device. Nat. Commun. 14, 176 (2023).
Kues, M. et al. On-chip generation of high-dimensional entangled quantum states and their coherent control. Nature 546, 622–626 (2017).
Borghi, M. et al. Reconfigurable silicon photonic chip for the generation of frequency-bin-entangled qudits. Phys. Rev. Appl. 19, 064026 (2023).
Vinet, S., Wu, W., Zhang, Y. & Jennewein, T. Feasibility study of frequency-encoded photonic qubits over a free-space channel. Opt. Express 33, 40437–40449 (2025).
HYPER entanglement in SPACE (hyperspace) (2025). https://cordis.europa.eu/project/id/101070168. Grant-ID:101070168.
Kobayashi, T. et al. Frequency-domain Hong-Ou-Mandel interference. Nat. Photonics 10, 441–444 (2016).
Serino, L., Eigner, C., Brecht, B. & Silberhorn, C. Programmable time-frequency mode-sorting of single photons with a multi-output quantum pulse gate. Opt. Express 33, 5577–5586 (2025).
Serino, L. et al. Complementarity-based complementarity: The choice of mutually unbiased observables shapes quantum uncertainty relations. Phys. Rev. Res. 7, 033152 (2025).
Lukens, J. M. & Lougovski, P. Frequency-encoded photonic qubits for scalable quantum information processing. Optica 4, 8–16 (2017).
Lu, H.-H. et al. Electro-optic frequency beam splitters and tritters for high-fidelity photonic quantum information processing. Phys. Rev. Lett. 120, 030502 (2018).
Lu, H.-H. et al. Bayesian tomography of high-dimensional on-chip biphoton frequency combs with randomized measurements. Nat. Commun. 13, 4338 (2022).
Zhao, T.-M. et al. Entangling different-color photons via time-resolved measurement and active feed forward. Phys. Rev. Lett. 112, 103602 (2014).
Halder, M. et al. Entangling independent photons by time measurement. Nat. Phys. 3, 692–695 (2007).
Cui, C., Seshadreesan, K. P., Guha, S. & Fan, L. High-dimensional frequency-encoded quantum information processing with passive photonics and time-resolving detection. Phys. Rev. Lett. 124, 190502 (2020).
Guo, X., Mei, Y. & Du, S. Testing the bell inequality on frequency-bin entangled photon pairs using time-resolved detection. Optica 4, 388–392 (2017).
Jin, J. et al. Genuine time-bin-encoded quantum key distribution over a turbulent depolarizing free-space channel. Opt. Express 27, 37214–37223 (2019).
Vallone, G. et al. Interference at the single photon level along satellite-ground channels. Phys. Rev. Lett. 116, 253601 (2016).
Shepherd, G. G. et al. Wamdii: wide-angle michelson doppler imaging interferometer for spacelab. Appl. Opt. 24, 1571–1584 (1985).
Liu, D., Hostetler, C., Miller, I., Cook, A. & Hair, J. System analysis of a tilted field-widened Michelson interferometer for high spectral resolution lidar. Opt. Express 20, 1406–1420 (2012).
Liscidini, M. & Sipe, J. E. Scalable and efficient source of entangled frequency bins. Opt. Lett. 44, 2625 (2019).
Tagliavacche, N. et al. Frequency-bin entanglement-based quantum key distribution. npj Quantum Inf. 11, https://doi.org/10.1038/s41534-025-00991-5 (2025).
Pang, Y. et al. Versatile chip-scale platform for high-rate entanglement generation using an AlGaAs microresonator array. PRX Quantum 6, 010338 (2025).
Loudon, R. The Quantum Theory of Light (Oxford University Press, 2000).
Kuzucu, O., Wong, F. N. C., Kurimura, S. & Tovstonog, S. Joint temporal density measurements for two-photon state characterization. Phys. Rev. Lett. 101, https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.101.153602(2008).
Borghi, M., Pagano, P. L., Liscidini, M., Bajoni, D. & Galli, M. Uncorrelated photon pair generation from an integrated silicon nitride resonator measured by time-resolved coincidence detection. Opt. Lett. 49, 3966 (2024).
Freedman, S. J. & Clauser, J. F. Experimental test of local hidden-variable theories. Phys. Rev. Lett. 28, 938–941 (1972).
Franson, J. D. Bell inequality for position and time. Phys. Rev. Lett. 62, 2205–2208 (1989).
Clauser, J. F., Horne, M. A., Shimony, A. & Holt, R. A. Proposed experiment to test local hidden-variable theories. Phys. Rev. Lett. 23, 880–884 (1969).
Vanasse, G. A. Spectrometric Techniques Vol. 1 (Academic Press, 1977).
Jin, J. et al. Demonstration of analyzers for multimode photonic time-bin qubits. Phys. Rev. A 97, 043847 (2018).
Saunders, D. J., Jones, S. J., Wiseman, H. M. & Pryde, G. J. Experimental EPR-steering using Bell-local states. Nat. Phy. 6, 845–849 (2010).
Uola, R., Costa, A. C. S., Nguyen, H. C. & Gühne, O. Quantum steering. Rev. Mod. Phys. 92, 015001 (2020).
Maassen, H. & Uffink, J. B. M. Generalized entropic uncertainty relations. Phys. Rev. Lett. 60, 1103–1106 (1988).
Schneeloch, J., Broadbent, C. J., Walborn, S. P., Cavalcanti, E. G. & Howell, J. C. Einstein-Podolsky-Rosen steering inequalities from entropic uncertainty relations. Phys. Rev. A 87, 062103 (2013).
Reid, M. D. Demonstration of the Einstein-Podolsky-Rosen paradox using nondegenerate parametric amplification. Phys. Rev. A 40, 913–923 (1989).
Cavalcanti, E. G., Jones, S. J., Wiseman, H. M. & Reid, M. D. Experimental criteria for steering and the Einstein-Podolsky-Rosen paradox. Phys. Rev. A 80, 032112 (2009).
Cozzolino, D., Da Lio, B., Bacco, D. & Oxenløwe, L. K. High-dimensional quantum communication: benefits, progress, and future challenges. Adv. Quantum Technol. 2, https://doi.org/10.1002/qute.201900038 (2019).
Pennacchietti, M. et al. Oscillating photonic Bell state from a semiconductor quantum dot for quantum key distribution. Commun. Phys. 7, 62 (2024).
McSorley, S. M. et al. Free-space optical-frequency comparison over rapidly moving links. Phys. Rev. Appl. 23, L021003 (2025).
Tannous, R. et al. Demonstration of a 6 state-4 state reference frame independent channel for quantum key distribution. Appl. Phys. Lett. 115, 211103 (2019).
Tannous, R. et al. Towards fully passive time-bin quantum key distribution over moving free-space channels. Opt. Express 33, 35635–35648 (2025).
Clemmen, S., Farsi, A., Ramelow, S. & Gaeta, A. L. Ramsey interference with single photons. Phys. Rev. Lett. 117, 223601 (2016).
Dekkers, K. et al. Observing high-dimensional bell inequality violations using multi-outcome spectral measurements. https://arxiv.org/abs/2506.20796 (2025).
Collins, D., Gisin, N., Linden, N., Massar, S. & Popescu, S. Bell inequalities for arbitrarily high-dimensional systems. Phys. Rev. Lett. 88, 040404 (2002).
Imany, P. et al. 50-ghz-spaced comb of high-dimensional frequency-bin entangled photons from an on-chip silicon nitride microresonator. Opt. Express 26, 1825–1840 (2018).
Morrison, C. L. et al. Frequency-bin entanglement from domain-engineered down-conversion. APL Photonics 7, 066102 (2022).
Henry, A. et al. Parallelization of frequency domain quantum gates: manipulation and distribution of frequency-entangled photon pairs generated by a 21 Â GHz silicon microresonator. Adv. Photonics 6, 036003 (2024).
Herriott, D. R. & Schulte, H. J. Folded optical delay lines. Appl. Opt. 4, 883–889 (1965).
Pepper, B., Ghobadi, R., Jeffrey, E., Simon, C. & Bouwmeester, D. Optomechanical superpositions via nested interferometry. Phys. Rev. Lett. 109, 023601 (2012).
Lingaraju, N. B. et al. Bell state analyzer for spectrally distinct photons. Optica 9, 280–283 (2022).
Wang, F.-Y., Shi, B.-S. & Guo, G.-C. Observation of time correlation function of multimode two-photon pairs on a rubidium d2 line. Opt. Lett. 33, 2191–2193 (2008).
Yamazaki, T., Arizono, T., Kobayashi, T., Ikuta, R. & Yamamoto, T. Linear optical quantum computation with frequency-comb qubits and passive devices. Phys. Rev. Lett. 130, 200602 (2023).
Korzh, B. et al. Demonstration of sub-3 ps temporal resolution with a superconducting nanowire single-photon detector. Nat. Photonics 14, 250–255 (2020).
Esmaeil Zadeh, I. et al. Superconducting nanowire single-photon detectors: a perspective on evolution, state-of-the-art, future developments, and applications. Appl. Phys. Lett. 118, 190502 (2021).
Chang, J. et al. Multimode-fiber-coupled superconducting nanowire single-photon detectors with high detection efficiency and time resolution. Appl. Opt. 58, 9803–9807 (2019).
Matres, J. & Sorin, W. V. Simple model for ring resonators backscatter. Opt. Express 25, 3242–3251 (2017).
Martínez, N., Rodríguez-Ramos, L. F. & Sodnik, Z. Toward the uplink correction: application of adaptive optics techniques on free-space optical communications through the atmosphere. Opt. Eng. 57, 076106 (2018).
Vinet, S. et al. Frequency-bin entanglement analysis code. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.16576461 (2025).
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Micro Photon Devices for kindly providing the MPD PDM-IR detector. The authors thank Kaylee Sherk, Kimia Mohammadi, Paul Godin, Katanya Kuntz, and Giuseppe Vallone for helpful discussions. This work is co-funded by the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC) and the European Union (EU) under Grant no. 101070168 (HyperSpace). The authors further acknowledge support from the NRC Quantum Sensing Challenge Program (QSP-019), the Canada Excellence Research Chair program (CERC), the Canadian Foundation for Innovation (CFI), the Ontario Research Fund (ORF), and the Institute for Quantum Computing. S.V. thanks the NSERC CGS-D for personal funding. M.C. and M.B. acknowledge support by the Italian Ministry of Education (MUR) PNRR project PE0000023-NQSTI.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
S.V., Y.Z., M.B., M.Ga., D.B., and T.J. conceived the original idea. M.C. and Y.Z. developed the theoretical framework. M.C. and M.B. developed the frequency-bin entangled photon source. S.V. and M. Gi. engineered and fabricated the field-widened interferometers with the assistance of L.N. S.V., M.C., M.B., and M. Gi. performed the experimental measurements. P.V., M.Ga., D.B., and T.J. supervised the experiment. S.V. performed the data analysis with the assistance of M.C., Y.Z., and M.B. S.V., M.C., and Y.Z. wrote and revised the manuscript. All authors commented on the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Vinet, S., Clementi, M., Bacchi, M. et al. Time-resolved certification of frequency-bin entanglement over multi-mode channels. npj Quantum Inf (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41534-026-01183-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41534-026-01183-5