Abstract
In magnetic topological insulators, spontaneous time-reversal symmetry breaking by intrinsic magnetic order can gap the topological surface spectrum, resulting in exotic properties like axion electrodynamics, the quantum anomalous Hall effect, and other topological magnetoelectric responses. Understanding the magnetic order and its coupling to topological states is essential to harness these properties. Here, we leverage near-resonant magnetic dipole optical second harmonic generation to probe magnetic fluctuations in the candidate axion insulator EuSn2(As,P)2 across its antiferromagnetic phase boundary. We observe a pronounced dimensional crossover in the quantum decoherence induced by magnetic fluctuations, whereby two-dimensional in-plane ferromagnetic correlations at high temperatures give way to three-dimensional long-range order at the Néel temperature. We also observe the breaking of rotational symmetry within the long-range-ordered antiferromagnetic state and map out the resulting spatial domain structure. More generally, we demonstrate the unique capabilities of nonlinear optical spectroscopy to study quantum coherence and fluctuations in magnetic quantum materials.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Magnetic topological insulators are a class of quantum materials that combine nontrivial electronic topology with magnetic order1. Spontaneous time-reversal symmetry breaking by magnetism, or by magnetic fluctuations sufficiently slower than the characteristic electronic timescale, can promote a range of novel phenomena, including axion electrodynamics2,3,4,5,6,7, the quantum anomalous Hall effect8,9,10,11, chiral topological superconductivity12, and the generation of ideal Weyl nodes13,14,15. These states have unique properties with potential applications in spintronics and other advanced technologies. The first experimental observation of such physics occurred in conventional topological insulators extrinsically doped with dilute magnetic ions9,10,11, but this necessarily introduces substantial disorder into the material. More recently, intrinsic magnetic topological insulators, which are stoichiometric compounds with native long-range magnetic order, have garnered interest as clean and tunable material platforms that may facilitate the observation and study of topological magnetoelectric phenomena at higher temperature scales.
A series of Eu-based intrinsic magnetic topological insulators, including EuCd2As2, EuSn2As2, and EuSn2P2, has emerged in recent years13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20. This family has a layered structure with Eu2+ ions forming a triangular lattice sandwiched between two covalently-bonded buckled honeycomb layers, such as (SnAs)\({}_{2}^{2-}\), from which the topological bands are derived. Magnetism arises from half-filled 4f7 subshells on the Eu2+ ions. These localized high-spin (S = 7/2) moments align ferromagnetically in the plane and antiferromagnetically out of the plane (Fig. 1a), resulting in long-range A-type antiferromagnetism below a Néel temperature TN that ranges from 10 to 30 K. The distinct spatial separation of magnetic and topological electronic states in these materials raises the possibility of precise magnetic control over the electronic topology, for example, through the direction of magnetization5.
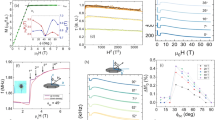
a Crystal structure showing half of the conventional magnetic unit cell. Red arrows depict Eu2+ local magnetic moments, which lie within the plane along the a axis. Moments are aligned within each plane and antialigned with neighboring planes, forming long-range A-type antiferromagnetism. The inset illustrates the local environment surrounding the Eu2+ ions, showing D3d site symmetry. b Orbital-resolved electronic band structure of EuSn2As2 from DFT. Vertical arrows highlight optical transitions near the M point contributing to near-resonant SHG. The irreducible representations of the states participating in the resonances are labeled. The right inset shows an energy level diagram of MD-SHG involving both ED and MD optical transitions. c Parallel polarization RA-SHG patterns for all three materials at 50 K. The top left panel defines the oblique-incidence scattering geometry. The top row shows Sin-Sout (SS) polarization patterns and the bottom row shows Pin-Pout (PP) polarization patterns.
In this work, we study fluctuations and symmetry breaking by the magnetic degrees of freedom in the Eu-based materials using near-resonant magnetic dipole optical second harmonic generation (SHG). We focus on the compounds EuSn2As2, EuSn2P2, and EuSn2AsP, referred to collectively as EuSn2(As,P)2, which have the highest reported TN (24 and 30 K for the As and P endmembers, respectively16,18). We measure the quantum decoherence induced by magnetic fluctuations across TN and find a dimensional crossover from short-range two-dimensional in-plane ferromagnetic correlations above TN to three-dimensional long-range antiferromagnetic order below it. Within the low-temperature antiferromagnetic phase, we detect broken rotational symmetry due to global alignment of the in-plane magnetic moments, and map out the corresponding spatial domain patterns. Our results shed light on the magnetism in this series of materials, paving the way for the potential control of topological magnetoelectric properties. More broadly, we showcase the capabilities of nonlinear optical spectroscopy to access the degree of quantum coherence of magnetic fluctuations in quantum materials.
Results
Single crystals of EuSn2As2, EuSn2P2, and the 1:1 alloy EuSn2AsP were prepared by a flux method similar to refs. 21,22. All three materials show similar nonlinear optical responses, and magnetic susceptibility measurements show clear signatures of antiferromagnetic transitions (Supplementary Note 1), with TN closely matching previously reported values16,18,19,21. Despite the similar intrinsic behavior of the three compounds, EuSn2As2 yielded the largest single crystals, and we focus on this material when mapping spatial domain patterns. Measuring the rotational anisotropy of optical SHG (RA-SHG) is a precise method to access the nonlinear optical susceptibility tensor and deduce the point group symmetries of a material. Using RA-SHG, tensor elements can be tracked across a wide temperature range to reveal minute changes in order, symmetry, dimensionality, and the strength of interactions in a sample23,24,25,26. The extreme sensitivity of SHG can be further enhanced near resonances, strengthening the SHG response by orders of magnitude and amplifying signatures of states involved in the resonant transition. As Fig. 1b demonstrates, 800 nm excitation (1.55 eV) is nearly resonant with several energy transitions involving Eu 4f and 5d orbitals at the M point, gaining us direct access to the magnetic degrees of freedom.
Figure 1c illustrates the RA-SHG experimental scattering geometry and corresponding data for all three samples. In the Sin-Sout channel, six equal lobes appear, while in the Pin-Pout channel, the underlying threefold rotational symmetry of the crystallographic point group D3d (\(\bar{3}m\)) is revealed through alternating large and small lobes. The measured SHG intensity is relatively strong, which is unusual because D3d is centrosymmetric and leading-order bulk electric dipole (ED) SHG—the usual source of strong nonlinear optical responses—is hence excluded by symmetry. Among the most likely higher-order nonlinear responses are surface ED, bulk magnetic dipole (MD), and bulk electric quadrupole (EQ) SHG24. Surface SHG typically arises from slight atomic distortions at the surface of a material and is therefore generally weakly dependent on temperature. We exclude this possibility based on the striking temperature dependence that we observe and discuss below. Thus, bulk MD-SHG or EQ-SHG is the primary nonlinear response channel in EuSn2(As,P)2.
MD-SHG and EQ-SHG are both described by a fourth-rank nonlinear optical susceptibility tensor χijkl that relates the induced nonlinear polarization density in a material Pi(2ω) to two powers of the incident electric field Ei(ω) via the equation Pi(2ω) = χijklEj(ω)∇kEl(ω)24. Within point group D3d and with additional permutation symmetries adapted from ref. 27, we may calculate the explicit angular dependence of the RA-SHG patterns. For the two parallel polarization channels shown in Fig. 1c, we obtain \({I}_{SS}(\phi )=| \alpha \sin (3\phi ){| }^{2}\) and \({I}_{PP}(\phi )=| \alpha \cos (3\phi )+\beta {| }^{2}\), where \(\alpha ={\chi }_{xxzx}\cos (\theta )\), \(\beta =({\chi }_{xxxx}-{\chi }_{xxzz})\sin (\theta )\), ϕ is the azimuthal angle of the scattering plane, and θ is the angle of incidence relative to the sample surface normal (Supplementary Note 2). Fits of the data to these functional forms show excellent agreement, as demonstrated in Fig. 1c.
A defining characteristic of MD-SHG and EQ-SHG is an optical transition between two states of the same parity, a good quantum number in centrosymmetric systems. Such excitations are forbidden for conventional ED transitions. With this symmetry condition in mind, we examine the irreducible representations of wavefunctions calculated by density functional theory (DFT) for EuSn2As2 and identify the M point as the likely source of near-resonant SHG at 800 nm. At this high-symmetry point, with little group C2h (2/m), we find both MD and EQ transitions are allowed, but the amplitude of one particular pathway involving an MD transition exceeds all others by an order of magnitude (Supplementary Note 3). Thus, we conclude that MD-SHG is the primary nonlinear response channel in EuSn2(As,P)2. An electron occupying a Eu fxyz, \({f}_{x{z}^{2}}\), or \({f}_{x({x}^{2}-3{y}^{2})}\) orbital (odd-parity au symmetry), can be excited to an unoccupied even-parity ag virtual state through resonant ED absorption at ~1.5 eV, further excited by a parity-preserving MD transition to a higher bg virtual state, and then return to its initial state through resonant ED emission at ~3 eV. While other k-points will contribute weakly to the nonlinear optical response, none possess the same combination of orbital symmetry and double resonance necessary for strong SHG. The overall resonant MD-SHG process is illustrated in Fig. 1b. The participating unoccupied virtual states have partial (~20%) Eu 5d character but a majority Sn and As p character. Thus, in real space, we may interpret the initial optical transition as a charge-transfer excitation in which an electron is removed from a tightly-bound Eu 4f orbital and added to the extended (SnAs)2 network. This leaves behind an Eu atom in a 4f6 configuration with a reduced spin. The reduced moment on the spin lattice represents a localized magnetic excitation that will propagate outward as it becomes entangled with neighboring spins. This process of magnetic decoherence of the virtual states is expected to be sensitive to the strength and nature of the magnetic order in the system, as we detail below.
Now that near-resonant MD-SHG has been established as the dominant nonlinear optical response, we turn to its temperature dependence. Figure 2 shows SHG intensity integrated over ϕ versus temperature for EuSn2P2 and EuSn2AsP, which share a similar TN. Data for EuSn2As2 is shown in Supplementary Note 7. Several remarkable features are apparent in the data for all three compounds. First, we observe a significant growth in SHG as the sample is cooled, more than doubling between room temperature and 100 K. Second, below ~100 K a broad high-intensity hump exists with large associated fluctuations. Third, upon traversing the magnetic transition temperature TN, an extremely sharp SHG peak occurs. Finally, as temperature is further lowered in the magnetically-ordered phase, the SHG intensity decreases again. Such behavior resembles a linear magnetic susceptibility, but we emphasize that we are here measuring a nonlinear optical susceptibility, not directly sensitive to the magnetic degrees of freedom. Generally, one may expect a slight change in the SHG intensity below the magnetic ordering temperature, but that is not what we observe. Instead, we appear to be sensitive to fluctuations of the magnetic order. In particular, we observe an increase in SHG likely associated with the growth of short-range two-dimensional ferromagnetic correlations within the individual Eu layers above TN, giving rise to a broad hump with large accompanying fluctuations. In EuSn2(As,P)2 and related materials, the in-plane ferromagnetic exchange is much stronger than the out-of-plane antiferromagnetic exchange because of the distances between Eu atoms, and it is therefore natural to expect in-plane correlations to emerge before out-of-plane order condenses13,28,29. Large fluctuations are expected in this regime, as neighboring planes are only weakly coupled. Indeed, in the limit of completely isolated planes, true long-range two-dimensional order is suppressed by fluctuations30. Strong in-plane ferromagnetic fluctuations below ~100 K have also been detected in the related material EuCd2As2 by muon spin relaxation, and it has been suggested that these short-range magnetic fluctuations are sufficient to induce topological properties even in the absence of long-range magnetic order13,31. At TN, we observe a dimensional crossover as the in-plane ferromagnetic correlations give rise to true long-range three-dimensional antiferromagnetic order. Here, critical fluctuations are expected to be largest, and this is reflected in a sharp SHG peak. Finally, upon further cooling, the long-range magnetic order grows in strength and fluctuations accordingly diminish, as does the SHG intensity. Thus, taken as a whole, our observations are consistent with a pronounced sensitivity of MD-SHG to fluctuations of the magnetic degrees of freedom, rather than the magnetic order itself.
Upon cooling from room temperature, the SHG intensity increases dramatically. Below ~100 K, a broad hump (most apparent in EuSn2AsP) and large fluctuations (most apparent in EuSn2P2) are observed. We identify these features with the emergence of fluctuating short-range ferromagnetic correlations within the Eu planes (blue). Within ~2 K of TN, a pronounced peak appears, which we attribute to critical slowing down at the magnetic phase transition. Below TN, the SHG intensity decreases as long-range three-dimensional antiferromagnetic order freezes in (green). The inset shows a close-up view of the low-temperature region.
To interpret this result, we examine the expression for the MD-SHG nonlinear optical susceptibility tensor derived from perturbation theory32:
where N is the electron density, m, v, and n label eigenstates, \({\rho }_{nm}^{{\rm{(eq)}}}\) is the equilibrium density matrix, \({\hat{\mu }}_{i}\) and \({\hat{Q}}_{ij}\) are components of the ED and MD operators, respectively, ωnm = (En − Em)/ℏ, and γnm is a phenomenological parameter introduced to account for environmental degrees of freedom that contribute to quantum decoherence but are not explicitly included in the density matrix. More precisely, the density matrix obeys the quantum master equation
showing that γnm parameterizes quantum coherence through the rate at which off-diagonal density matrix elements decay in time: \({\rho }_{nm}(t)\propto {e}^{-i{\omega }_{nm}t}{e}^{-{\gamma }_{nm}t}\). Here, the density matrix captures orbital (charge) eigenstates but not magnetism, so quantum decoherence primarily arises from interactions with the background magnetic environment. As shown above, the SHG signal is dominated by a near resonance at the M point, where both ωnm ≈ 2ω and ωvm ≈ ω. This significantly amplifies the effects of the γ parameters appearing in the denominator of the susceptibility expression. In fact, these are the only parameters that can appreciably influence the temperature dependence of SHG, as \({\rho }_{mm}^{{\rm{(eq)}}}-{\rho }_{vv}^{{\rm{(eq)}}}=1\) because m is occupied and v is unoccupied, and the ED and MD matrix elements in the numerator are not expected to change significantly with temperature. Thus, we see that near-resonant MD-SHG is acutely sensitive to the quantum decoherence induced by magnetic fluctuations in the system, as we have inferred from our temperature dependence measurements.
A hallmark of second-order phase transitions is “critical slowing down,” a significant increase in the time it takes for a system to respond to perturbations and return to equilibrium. Within the context of magnetic transitions, this occurs when locally fluctuating moments become entangled with their neighbors at increasingly long distances. Both the correlation length \(\xi \propto {\left\vert T-{T}_{c}\right\vert }^{-\nu }\) and time τ ∝ ξz diverge at TN, with critical exponents ν and z, respectively33. In Supplementary Note 4, we derive the relationship between the off-diagonal quantum decoherence rate γnm and the magnetic correlation time: \({\gamma }_{nm}^{-1}=2\tau\). This results in γnm → 0 at TN, which we propose as the likely origin for the sharp peak in SHG that we observe. We emphasize that within this picture, the growth of SHG approaching TN results from an increase in the lifetime of magnetic fluctuations, not their amplitude. We can place a rough upper bound on the coherence time τ of the 4f7 → 4f6 charge-transfer magnetic excitation. We observe an O(1) change in SHG over the measured temperature range, which implies that γ must be at least of the same order as Δω, the spectral width of the ultrafast laser. Thus, we calculate τ ~ 1/γ < 1/Δω ~ 16 fs. This value is comparable to the excitation lifetime of an isolated magnetic atom bound to a metallic substrate, as measured by inelastic tunneling spectroscopy, where it was suggested that the short lifetime was due to hybridization with metallic bands, leading to efficient electron-electron interactions that relax the magnetic state of the atom34. EuSn2(As,P)2 is also metallic, and it has been suggested that the magnetic exchange coupling in the material is mediated by conduction electrons via the Ruderman–Kittel–Kasuya–Yosida (RKKY) interaction16,35. Indeed, the electrical conductivity of each compound directly correlates with TN (Supplementary Note 1), supporting a picture of carrier-mediated exchange. Thus, we may also expect a similarly short magnetic excitation lifetime due to coupling to conduction electrons.
According to the fluctuation-dissipation theorem, there is a close relationship between the imaginary part of a linear susceptibility and the power spectral density of fluctuations of that susceptibility’s conjugate observable33. No such theorem exists for nonlinear susceptibilities, where the imaginary part does not represent dissipation36. It has been theoretically shown, however, that nonlinear responses are much more sensitive to semiclassical chaotic behavior through the interference of multiple dynamical Liouville-space trajectories37. The second-order susceptibility, for example, is directly related to the stability matrix of a system and its associated Lyapunov exponents, quantifying the system’s sensitivity to initial conditions. Our measurements largely affirm this notion, demonstrating that, at least near resonances, the nonlinear optical response of a material can be significantly influenced by the dynamics of fluctuations of some order parameter of the material, even when that order is not the conjugate observable. We expect that this principle is generally applicable, and that under resonant conditions the nonlinear optical response can be harnessed to study fluctuations, dynamics, and quantum coherence across many types of phase transitions. In the case of magnetic systems, this information is complementary to that of the conventional linear optical susceptibility, whose real and imaginary parts have already been shown to be sensitive to lifetimes and entanglement of spin excitations in exotic magnets38.
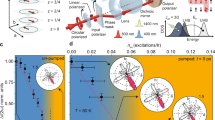
Below TN, the Eu2+ moments globally align, spontaneously breaking the \(\bar{3}\) symmetry axis of the crystal as they choose to orient along one of three equivalent crystallographic directions. Rotational symmetry breaking can be revealed through RA-SHG patterns, which are exceptionally sensitive to point group symmetries24. As Fig. 3a demonstrates, we indeed observe rotational symmetry breaking below TN, with a clear order parameter-like onset. We measure the unpolarized SHG output (Uout) because a fully isotropic response is expected in the high-symmetry phase, degenerating into a twofold “peanut-like” shape when the symmetry axis is lost (Supplementary Note 5). We attribute this observation to two possible mechanisms, both involving spin-orbit coupling. In the first, coupling of the globally-aligned spins to the initial-state f orbitals (fxyz, \({f}_{x{z}^{2}}\), and \({f}_{x({x}^{2}-3{y}^{2})}\)) shifts their energies, and this manifests as slight changes to the optical resonance condition for different polarization angles, and in the second, global alignment of moments influences the quantum coherence of different initial-state f orbitals. Accompanying spontaneous symmetry breaking is the formation of magnetic domains transforming into each other by the broken symmetry element. Optical imaging of antiferromagnetic domains is typically challenging because of the absence of a net magnetization, with SHG being one of the few known techniques for doing so39,40. Figure 3b shows a spatial RA-SHG mapping over a 300 × 300 μm area that reveals these domains. We find a roughly equal distribution of all three possible domain orientations, with a domain length scale of ~100 μm. Thermal cycling across TN generates new domain patterns (Supplementary Note 6), suggesting domain boundaries are not strongly pinned by disorder.
a Temperature dependence of the twofold rotational anisotropy that emerges at the antiferromagnetic phase transition. The inset shows Sin-Uout (SU) RA-SHG patterns for each temperature, and the main panel shows the corresponding 2-fold anisotropy versus temperature. The gray curve is a guide to the eye, showing an order parameter-like onset below TN. b Spatial map of rotational symmetry breaking. RA-SHG patterns were acquired on a 10 × 10 grid spanning a 300 × 300 μm area. At each grid point, the amplitude and direction of the twofold anisotropy was extracted (represented by the length and direction, respectively, of the double-headed arrows). The upper left inset shows a photograph of the sample with the mapped region identified, and the lower left inset shows a polar plot of the anisotropy sorted by direction into three symmetry-equivalent antiferromagnetic domains (red, green, and blue).
Discussion
In conclusion, we harnessed near-resonant MD-SHG to probe quantum decoherence by magnetic fluctuations in the candidate axion insulator EuSn2(As,P)2. We observed an unusually sharp SHG peak at the magnetic phase boundary that we attribute to critical slowing down, where the dynamics of the system become extremely slow and the correlation length and time diverge. The quantum coherence time of the charge-transfer 4f7 → 4f6 magnetic excitation is estimated to be no more than ~16 fs. We conjecture that such a short lifetime is due to efficient coupling between the localized magnetic moments and the conduction electrons, supporting a scenario whereby RKKY interactions mediate magnetic exchange16,35. This conclusion has important implications for the coupling strength between the magnetic order and the topological electronic states, where prior work has reported only a very weak hybridization19. We also uncovered evidence of strong short-range in-plane ferromagnetic correlations surviving far above TN, which in similar materials has been proposed to stabilize topological phases13 and has also been attributed to the possible formation of magnetic polarons41. Finally, we revealed the clear breaking of rotational symmetry within the antiferromagnetic phase and used it to map out the spatial domain structure. As a whole, our findings help to clarify the nature of the magnetic order in this class of materials and its interactions with topological surface states, which play a critical role in realizing topological magnetoelectric phenomena. More generally, our work shows that despite a lack of symmetry breaking enabling a direct coupling of the antiferromagnetic order parameter to SHG, resonant SHG can nevertheless still couple to magnetic fluctuations, providing access to antiferromagnetic order through an entirely different mechanism than considered by previous SHG studies of centrosymmetric antiferromagnets42. Ultimately, our work showcases the unique capabilities of nonlinear optical spectroscopy as a powerful tool for investigating quantum coherence, fluctuations, and symmetry breaking in magnetic quantum materials.
Methods
Optical experiments
SHG experiments were performed on freshly cleaved samples in an optical cryostat using a laser supplying 40 fs pulses at a 50 kHz repetition rate with a center wavelength of 800 nm and a fluence of ~1 mJ/cm2. The oblique-incidence experimental geometry is illustrated in the upper left panel of Fig. 1c. The incidence angle relative to the sample surface normal was ~10°. For the RA patterns shown in Fig. 1 and the temperature dependence shown in Fig. 2, the SHG signal was measured using a scientific CMOS camera. RA patterns were collected by directly rotating the sample, with the scattering plane remaining fixed. For the RA patterns and domain scans shown in Fig. 3, the SHG signal was measured using a silicon photomultiplier detector and a lock-in amplifier. For these measurements, normal incidence was used, and the polarization of the incident beam was rotated instead of the sample, which afforded a much higher spatial resolution for mapping.
Density functional theory calculations
DFT calculations were performed with the Vienna ab initio simulation package (VASP) using the supplied projector augmented wave potentials within the generalized gradient approximation, the experimental structural parameters16, a 400 eV energy cutoff, and a 6 × 6 × 6 k-point mesh. Following prior work, to match the experimental energy position of the Eu 4f bands, a Hubbard parameter U = 5.0 eV was employed19.
Sample synthesis and characterization
High-quality single crystals of EuSn2As2 were prepared by a flux method similar to ref. 21. Europium (99.9999%, Ames Lab) was cut up and combined with arsenic pieces (99.99%, Alfa Aesar) and Tin shot (99.9999%, Thermo Scientific) in a 1:3:20 molar ratio with a total mass of 4.0 g in an alumina crucible under a dry nitrogen glove box atmosphere. The crucible was sealed in a quartz ampoule under 300 Torr of argon without being exposed to air. The ampoule was heated in a box furnace from room temperature to 850 °C over 10 h, held for 24 h, then heated to 980 °C over 24 h, before soaking at 980 °C for 12 h. Finally, the ampoule was slowly cooled to 650 °C at 3.67 °C/hour, and spun in a centrifuge to remove excess tin flux. Shiny crystals in the form of hexagonal platelets with a typical diameter of 2 mm were obtained. Crystals of EuSn2P2 and EuSn2PAs were similarly prepared but with a different peak soaking temperature of 1000 °C and a centrifuging temperature of 700 °C, yielding crystals with a typical diameter of 1 mm. EuSn2As2 crystals grown without the heat soaks and the argon backfill pressure had notably smaller diameters, at around 200 μm. Both of these procedures have been used in previous growths of EuIn2As222 to help avoid any high vapor pressure of arsenic and increase the homogeneity of the flux solution before reaching the peak temperature. We also note that growth attempts which centrifuged a Eu-Sn-As mixture at 750 °C yielded Eu5Sn2As6, a black needle-like crystal with a width of 100 μm and a length of a few mm. The structure and quality of the crystals was verified using powder x-ray diffraction on a Rigaku Ultima-4 system as well as energy-dispersive x-ray spectroscopy (EDX/EDS) on a SCIOS 2 DualBeam system.
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Tokura, Y., Yasuda, K. & Tsukazaki, A. Magnetic topological insulators. Nat. Rev. Phys. 1, 126 (2019).
Essin, A. M., Moore, J. E. & Vanderbilt, D. Magnetoelectric polarizability and axion electrodynamics in crystalline insulators. Phys. Rev. Lett. 102, 146805 (2009).
Li, R., Wang, J., Qi, X.-L. & Zhang, S.-C. Dynamical axion field in topological magnetic insulators. Nat. Phys. 6, 284 (2010).
Mogi, M. et al. A magnetic heterostructure of topological insulators as a candidate for an axion insulator. Nat. Mater. 16, 516 (2017).
Xu, Y., Song, Z., Wang, Z., Weng, H. & Dai, X. Higher-order topology of the axion insulator EuIn2As2. Phys. Rev. Lett. 122, 256402 (2019).
Zhang, D., Shi, M., Zhu, T., Xing, D., Zhang, H. & Wang, J. Topological axion states in the magnetic insulator MnBi2Te4 with the quantized magnetoelectric effect. Phys. Rev. Lett. 122, 206401 (2019).
Sekine, A. & Nomura, K. Axion electrodynamics in topological materials. J. Appl. Phys. 129, 141101 (2021).
Mong, R. S. K., Essin, A. M. & Moore, J. E. Antiferromagnetic topological insulators. Phys. Rev. B 81, 245209 (2010).
Liu, C.-X., Qi, X.-L., Dai, X., Fang, Z. & Zhang, S.-C. Quantum anomalous Hall effect in Hg1−yMnyTe quantum wells. Phys. Rev. Lett. 101, 146802 (2008).
Yu, R. et al. Quantized anomalous Hall effect in magnetic topological insulators. Science 329, 61 (2010).
Chang, C.-Z. et al. Experimental observation of the quantum anomalous Hall effect in a magnetic topological insulator. Science 340, 167 (2013).
Qi, X.-L., Hughes, T. L. & Zhang, S.-C. Chiral topological superconductor from the quantum Hall state. Phys. Rev. B 82, 184516 (2010).
Ma, J.-Z. et al. Spin fluctuation induced Weyl semimetal state in the paramagnetic phase of EuCd2As2. Sci. Adv. 5, eaaw4718 (2019).
Soh, J.-R. et al. Ideal Weyl semimetal induced by magnetic exchange. Phys. Rev. B 100, 201102(R) (2019).
Jo, N. H. et al. Manipulating magnetism in the topological semimetal EuCd2As2. Phys. Rev. B 101, 140402(R) (2020).
Arguilla, M. Q. et al. EuSn2As2: an exfoliatable magnetic layered Zintl-Klemm phase. Inorg. Chem. Front. 4, 378 (2017).
Rahn, M. C. et al. Coupling of magnetic order and charge transport in the candidate Dirac semimetal EuCd2As2. Phys. Rev. B 97, 214422 (2018).
Gui, X. et al. A new magnetic topological quantum material candidate by design. ACS Cent. Sci. 5, 900 (2019).
Li, H. et al. Dirac surface states in intrinsic magnetic topological insulators EuSn2As2 and MnBi2nTe3n+1. Phys. Rev. X 9, 041039 (2019).
Pierantozzi, G. M. et al. Evidence of magnetism-induced topological protection in the axion insulator candidate EuSn2P2. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 119, e2116575119 (2022).
Pakhira, S., Tanatar, M. A., Heitmann, T., Vaknin, D. & Johnston, D. C. A-type antiferromagnetic order and magnetic phase diagram of the trigonal Eu spin-7/2 triangular-lattice compound EuSn2As2. Phys. Rev. B 104, 174427 (2021).
Riberolles, S. X. M. et al. Magnetic crystalline-symmetry-protected axion electrodynamics and field-tunable unpinned Dirac cones in EuIn2As2. Nat. Commun. 12, 999 (2021).
Harter, J. W., Zhao, Z. Y., Yan, J.-Q., Mandrus, D. G. & Hsieh, D. A parity-breaking electronic nematic phase transition in the spin-orbit coupled metal Cd2Re2O7. Science 356, 295 (2017).
Orenstein, J. et al. Topology and symmetry of quantum materials via nonlinear optical responses. Annu. Rev. Condens. Matter Phys. 12, 247 (2021).
Ron, A., Zoghlin, E., Balents, L., Wilson, S. D. & Hsieh, D. Dimensional crossover in a layered ferromagnet detected by spin correlation driven distortions. Nat. Commun. 10, 1654 (2019).
Ahn, Y. et al. Electric quadrupole second-harmonic generation revealing dual magnetic orders in a magnetic Weyl semimetal. Nat. Photonics 18, 26 (2024).
Yang, S. A., Li, X., Bristow, A. D. & Sipe, J. E. Second harmonic generation from tetragonal centrosymmetric crystals. Phys. Rev. B 80, 165303 (2009).
Sun, H. et al. Magnetism variation of the compressed antiferromagnetic topological insulator EuSn2As2. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 64, 118211 (2021).
Blawat, J. et al. Unusual electrical and magnetic properties in layered EuZn2As2. Adv. Quantum Technol. 5, 2200012 (2022).
Mermin, N. D. & Wagner, H. Absence of ferromagnetism or antiferromagnetism in one- or two-dimensional isotropic Heisenberg models. Phys. Rev. Lett. 17, 1133 (1966).
Yi, E. et al. Topological Hall effect driven by short-range magnetic order in EuZn2As2. Phys. Rev. B 107, 035142 (2023).
Boyd, R. W. Nonlinear Optics (Academic Press, 2020).
Sethna, J. P. Entropy, Order Parameters, and Complexity (Oxford Univ. Press, 2006).
Schuh, T. et al. Lifetimes of magnetic excitations in Fe and Co atoms and clusters on Pt(111). J. Appl. Phys. 107, 09E156 (2010).
Bi, W. et al. Drastic enhancement of magnetic critical temperature and amorphization in topological magnet EuSn2P2 under pressure. npj Quant. Mater. 7, 43 (2022).
Pershan, P. S. Nonlinear optical properties of solids: energy considerations. Phys. Rev. 130, 919 (1963).
Mukamel, S., Khidekel, V. & Chernyak, V. Classical chaos and fluctuation-dissipation relations for nonlinear response. Phys. Rev. E 53, 1(R) (1996).
Zhang, H., Kim, S., Kim, Y.-J., Kee, H.-Y. & Yang, L. Ultrafast spin dynamics in the proximate quantum spin liquid α–RuCl3. Phys. Rev. B 110, L081111 (2024).
Fiebig, M., Pavlov, V. V. & Pisarev, R. V. Second-harmonic generation as a tool for studying electronic and magnetic structures of crystals: review. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 22, 96 (2005).
Seyler, K. L. et al. Direct visualization and control of antiferromagnetic domains and spin reorientation in a parent cuprate. Phys. Rev. B 106, L140403 (2022).
Zhang, Y. et al. In-plane antiferromagnetic moments and magnetic polaron in the axion topological insulator candidate EuIn2As2. Phys. Rev. B 101, 205126 (2020).
Fiebig, M. et al. Second harmonic generation in the centrosymmetric antiferromagnet NiO. Phys. Rev. Lett. 87, 137202 (2001).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the US Air Force Office of Scientific Research (AFOSR) under Award No. FA9550-22-1-0270. The research reported here made use of the shared facilities of the Materials Research Science and Engineering Center (MRSEC) at UC Santa Barbara: NSF DMR–2308708. The UC Santa Barbara MRSEC is a member of the Materials Research Facilities Network (http://www.mrfn.org).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
R.S., S.D. and R.S.R. conducted the optical measurements and analyzed the data. K.Y. and J.G.A. synthesized and characterized the samples. J.W.H. conceived and designed the project. R.S. and J.W.H. wrote the manuscript, with input from all authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Saatjian, R., Dovrén, S., Yamakawa, K. et al. Quantum decoherence by magnetic fluctuations in a magnetic topological insulator. npj Quantum Mater. 10, 81 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41535-025-00795-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41535-025-00795-y