Abstract
Plasmodium vivax is the most widespread of the different Plasmodium species able to infect humans and is responsible for most malaria cases outside Africa. An effective, strain-transcending vaccine that alleviates or suppresses erythrocyte invasion would be a game-changer in eliminating vivax malaria. Recently, the binding of P. vivax Reticulocyte Binding Protein 2b (PvRBP2b) to human Transferrin receptor (TfR1) has been described as essential for reticulocyte invasion, making this parasite protein an appealing vaccine candidate. Here, using P. vivax Cambodian clinical isolates in robust ex vivo invasion assays, we show that anti-PvRBP2b polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies that inhibit binding of PvRBP2b to TfR1 do not block P. vivax invasion into reticulocytes even at high concentrations. Anti-TfR1 antibodies do not inhibit P. vivax invasion either. Combinations at high concentrations of human monoclonal antibodies targeting different PvRBP2b epitopes do not inhibit invasion. Combinations of anti-PvRBP2b with anti-PvDBP do not enhance invasion inhibition caused by anti-PvDBP alone. We also show that the invasion of Cambodian P. vivax is trypsin-resistant while TfR1 is trypsin-sensitive, and we demonstrate that TfR1 is not recycled following trypsin treatment. We determined the PvRBP2b sequence of all isolates used in the invasion assays and analyzed polymorphism within epitopes recognized by anti-PvRBP2b antibodies. We show that polymorphism does not explain the absence of neutralization. Anti-PvRBP2b polyclonal antibodies recognized all four isolates tested in immunofluorescence assays while not inhibiting P. vivax invasion. Overall, our results demonstrate that PvRBP2b binding to TfR1 is not essential for invasion into reticulocytes of P. vivax Cambodian strains questioning the relevance of PvRBP2b as vaccine candidate.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Plasmodium vivax has the widest geographic distribution of human infective malaria species, and more than three billion people live within the P. vivax transmission limits1. Considered benign for decades, it is now clear that P. vivax malaria is a significant cause of morbidity and mortality in endemic populations2,3,4.
P. vivax elimination is particularly challenging because of parasite biology differences compared to Plasmodium falciparum, especially the dormant liver-stage causing relapses which facilitates transmission5. This hinders most control and elimination strategies mainly designed for P. falciparum. Tools specifically adapted for P. vivax elimination, such as an effective strain-transcending blood-stage vaccine, are needed6. Blood-stage vaccines aim to produce neutralizing antibodies (Abs) against parasite ligands to prevent reticulocyte invasion and the onset of malaria clinical symptoms7. Compared to P. falciparum, much fewer vaccine candidates have been identified for P. vivax due to the absence of a long-term in vitro culture system for this parasite8,9.
For the past decades, only P. vivax Duffy Binding Protein (PvDBP) was known as a critical blood-stage vaccine candidate10,11. However, P. vivax natural polymorphism has so far impeded the development of a strain-transcending vaccine, although recent developments are promising12,13,14,15,16.
Additional parasite targets are required to serve as vaccine candidates, individually or in combination with PvDBP.
Recently, P. vivax Reticulocyte Binding Protein 2b (PvRBP2b) has gained great interest following its identification as a parasite ligand binding the transferrin receptor 1 (TfR1 or CD71) on the surface of reticulocytes, the erythrocytes invaded by P. vivax17. Abs targeting either PvRBP2b or TfR1 can block this interaction17. Mouse monoclonal and rabbit polyclonal anti-PvRBP2b Abs inhibited PvRBP2b-TfR1 binding and the ex vivo invasion of a small number of P. vivax clinical isolates from Brazil and Thailand17. Naturally acquired human monoclonal antibodies (humAbs) targeting PvRBP2b were isolated from two Cambodian donors and could strongly inhibit PvRBP2b binding to reticulocytes18. Some of these humAbs and their epitopes have been characterized structurally18, but their capacity to neutralize P. vivax invasion to reticulocytes has not been evaluated yet.
Here, using a robust ex vivo flow cytometry-based assay, we aim to determine if these same anti-PvRBP2b Abs can inhibit the invasion of P. vivax isolates collected in Cambodia.
Results
Mouse or rabbit anti-PvRBP2b and anti-TfR1 antibodies do not inhibit P. vivax reticulocyte invasion
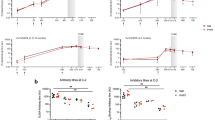
To examine whether anti-PvRBP2b or anti-TfR1 antibodies could inhibit P. vivax invasion into human reticulocytes we applied a flow cytometry-based invasion assay. In a first experiment using three different clinical isolates, we evaluated the impact on reticulocyte invasion of 3E9 mouse monoclonal anti-PvRBP2b Abs previously shown to inhibit both the binding of PvRBP2b to TfR1 and the invasion of a few Thai and Brazilian isolates17. As negative inhibition control, we included the 8G7 anti-PvRBP2b mouse monoclonal Abs (mAbs), shown not to affect either the binding of PvRBP2b to TfR1 or invasion into reticulocytes, as well as 043038, a humAbs specific of tetanus toxin C terminal fragment. An anti-Duffy mouse mAbs, 2C3, was used as positive inhibition control19. All mAbs were tested at 100 μg/ml. As expected, both negative inhibition controls did not inhibit reticulocyte invasion, however we observed only a modest (mean 17.4% ± 1.73 SEM), non-significant invasion inhibition by 3E9 (p = 0.2683) compared to the 043038 control (Fig. 1A, raw invasion data are provided in Supplementary Data 1).
The mean percentage (± SEM) of reticulocyte invasion by P. vivax clinical isolates in the presence of different anti-PvRBP2b antibodies tested at 100, 250, and 500 μg/ml is represented. All invasions are normalized to no-antibody controls. HumAbs 043038 specific of tetanus toxin C terminal fragment and the anti-Duffy mouse mAbs 2C3 were used as negative and positive invasion inhibition controls for each experiment. Each dot represents the invasion for a different clinical isolate with a single technical replicate per isolate. Differences are assessed by the Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn’s post-hoc correction (*p < 0.05; ***p = 0.0007; ****p < 0.0001). A Invasion of P. vivax in presence of 100 μg/ml of mouse anti-PvRBP2b mAbs 3E9 and 8G7. B Invasion of P. vivax in presence of 500 μg/ml (100 μg/ml for the 2C3 control) mouse anti-PvRBP2b mAbs 8G7, 3E9, 6H1, 10B12, mAbs pool (each mAb at one-third of the final concentration) and rabbit polyclonal mAbs (1527). C Invasion of P. vivax in presence of 100 μg/ml of anti-PvRBP2b humAbs 239229 and 241242. D Invasion inhibition of P. vivax in presence of 500 μg/ml (100 μg/ml for the 2C3 control) of humAbs 237235, 239229, 241242, 253245, 258259, 260261, 326327. E Invasion inhibition of P. vivax in the presence of 500 μg/ml (100 μg/ml for the 2C3 control) anti-PvRBP2b humAbs combinations (250 μg/ml each huAbs). F Invasion inhibition of P. vivax in presence of anti-PvRBP2b humAbs (2392209 or 241242 each at 250 μg/ml) or 043038 control in combination with anti-PvDBP 099100 at 250 μg/ml (final concentration of humAbs of 500 μg/ml) compared to invasion in presence of 099100 alone at 250 μg/ml or 2C3 control at 100 μg/ml.
We then increased the concentration of mAbs to 500 μg/ml and evaluated two additional anti-PvRBP2b mouse monoclonal (6H1, 10B12) and a rabbit polyclonal Abs (1527), all previously shown to inhibit binding and invasion17. Overall, using 19 different clinical isolates, we show that none of the anti-PvRBP2b mAbs or the 1527 polyclonal Abs significantly inhibited invasion into reticulocytes compared to the 043038 control (p > 0.9999 for all comparisons) (Fig. 1B). The highest average inhibition was of 17.8% (±2.69 SEM) and was observed for the 8G7 negative control mAbs. We also evaluated the combination of the three mAbs 3E9, 6H1 and 10B12 together (mAbs pool) each added at a third of 500 μg/ml and again, we failed to observe any significant invasion inhibition (p > 0.9999). Targeting TfR1 by the addition of 500 μg/ml of OKT9 mAb, previously shown to inhibit the binding of PvRBP2b to TfR1, did not lead to significant invasion inhibition (p > 0.9999) (Fig. 1B).
Naturally acquired human monoclonal anti-PvRBP2b antibodies do not inhibit P. vivax reticulocyte invasion
We determined whether naturally acquired anti-PvRBP2b humAbs isolated from Cambodian donors could inhibit reticulocyte invasion by Cambodian P. vivax isolates. These humAbs have previously been characterized with their PvRBP2b binding sites determined and have been shown to inhibit the binding of PvRBP2b to TfR1 and to reticulocytes18.
We first evaluated two different humAbs at 100 μg/ml, a concentration at which we previously showed that anti-PvDBP humAbs inhibit P. vivax invasion12. These two humAbs, 239229 and 241242 bind to non-overlapping epitopes on PvRBP2b. Using 15 different clinical isolates, we show that none of these two humAbs inhibit the invasion of P. vivax in reticulocytes compared to the 043038 control (p > 0.7905) (Fig. 1C).
We then increased the concentration to 500 μg/ml and evaluated five additional blocking humAbs. We also included the humAb 099100 as an additional positive inhibition control targeting PvDBP12,20,21. Using 25 different clinical isolates, no significant inhibition was observed for any of the seven anti-PvRBP2b humAbs (Fig. 1D). The highest average inhibition measured was 18.4% (±2.97 SEM) for the humAb 260261 and was not significantly different from the 043038 control (p > 0.999).
The results we obtained here contrast with those previously reported, so we investigated whether our invasion assay readout could affect the results. Our assay relies on flow cytometry to measure P. vivax invasion, while previous work showing anti-PvRBP2b activity used microscopy readout17. We tested the activity of 500 μg/ml of two humAbs (239229 and 241242) and the 1527 polyclonal anti-PvRBP2b using three to eight different clinical isolates and measured invasion by microscopy side-by-side with flow cytometry for most isolates. No significant difference was observed comparing the invasion rates obtained with flow cytometry or microscopy and regardless of the readout, no invasion inhibition was observed (Supplementary Fig. S2).
Combination of anti-PvRBP2b humAbs together or with anti-PvDBP humAbs does not increase P. vivax invasion inhibition
As some anti-PvRBP2b humAbs have different inhibitory mechanisms, it was previously proposed that some combinations of humAbs could act synergistically or additively18. We therefore evaluated the combination of 241242 targeting the N-terminal domain of PvRBP2b and leading to steric hindrance with TfR1with (i) 239229 binding to the C-terminal domain of PvRBP2b, (ii) 237235 believed to disturb PvRBP2b binding to transferrin allosterically, (iii) 326327 causing steric hindrance with the reticulocyte membrane18. We also evaluated the combination of 237235 with 326327. All combinations used 250 μg/ml for each humAb (500 μg/ml in total) and were tested with three different clinical isolates. None of the combinations tested showed invasion inhibition, with the highest average inhibition measured being 5.26% (±7.70 SEM) (Fig. 1E).
Finally, we performed a series of invasion assays to determine if adding 239229 or 241242 anti-PvRBP2b humAbs (binding respectively to the C and N-terminal of PvRBP2b) would enhance invasion inhibition caused by 099100 anti-PvDBP humAb. All combinations were done using 250 μg/ml for each humAb (500 μg/ml) and tested with four to five different clinical isolates. There was no significant difference in invasion inhibition between the combination of anti-PvDBP 099100 with 239229 (average inhibition 53.8% ± 7.1) or with 241242 (average inhibition 55.1% ± 4.5) compared to the combination of 043038 non-specific control with 099100 (average of 51.9% ± 3.2, p > 0.999) (Fig. 1F). The invasion inhibition was also not different between 099100 alone tested at 250 μg/ml (average inhibition 47.1% ± 4.8) and the combination of 043038 with 099100 (p > 0.999).
Sequence polymorphism of PvRBP2b among P. vivax clinical isolates does not affect inhibition caused by most anti-PvRBP2b Abs
To determine whether PvRBP2b polymorphism could explain the lack of inhibition by anti-PvRBP2b Abs, the PvRBP2b gene was sequenced to cover amino acid positions from 100 to 600 from all 50 clinical isolates used in the invasion assays.
Overall, the gene was highly polymorphic, with 44 different protein haplotypes identified among the 50 isolates sequenced, all of which differed from the Sal1 reference (Supplementary Data 2).
We stratified the invasion data by assessing the impact of PvRPB2b polymorphism within known epitopes recognized by the Abs tested. For each known epitope, we determined whether invasion in the presence of Abs was affected by polymorphism. The three mouse mAbs 3E9, 6H1 and 10B12 bind respectively to residues 330-343, 212-232 and 405-423 (Fig. 2A)18,22. All isolates tested with 3E9 at 500 μg/ml were WT in the residues 330-343 and were not inhibited by the mAbs (Fig. 2B). Of the four isolates tested against 6H1, one was WT in the residues 212-232 and the three others had all the same two mutations (T220K and T224K) and none were inhibited by these mAbs (Fig. 2B). Among the four isolates tested with 10B12 at 500 μg/ml, one was WT in the residues 405-423 and three others had the same single mutation (K412N) and none were inhibited by this mAbs. (Fig. 2B). These results indicate that P. vivax invasion is not inhibited by 3E9, 6H1 and 10B12, regardless of mutations in their respective epitopes.
A Epitopes recognized by anti-PvRBP2b mAbs18,22. B Invasion in the presence of 500 μg/ml of mouse anti-PvRBP2b mAbs is not affected by mutations in residues recognized by 6H1, 3E9, and 10B12 compared to the wild-type (WT). C Invasion in the presence of 500 μg/ml of humAbs is not affected by mutations in residues recognized by 237235, 239229, 253245, 258259 and 260261 compared to WT. For 241242 and 326327, all isolates had at least one mutation in the epitopes recognized by these humAbs. HumAbs 043038 specific of tetanus toxin C terminal fragment and the anti-Duffy mouse mAbs 2C3 were used as negative and positive invasion inhibition controls for each experiment. All invasions are normalized to no-antibody controls.
We similarly determined the impact of polymorphism in known epitopes18 of humAbs on their capacity to inhibit invasion. For 5 of the 7 humAbs (237235, 239229, 253245, 258259, and 260261), isolates WT in the epitopes were evaluated for their response to these humAbs and none showed significant invasion inhibition against these compared to the 043038 control (Fig. 2C). Similarly to mouse mAbs, these results indicate that P. vivax invasion is not inhibited by 237235, 239229, 253245, or 258259 regardless of mutations in their respective epitopes. For two humAbs (241242 and 326327), all isolates tested had at least one mutation in the epitopes, so the impact of polymorphism could not be determined for these (Fig. 2C).
Finally, to evaluate whether polymorphism would explain the absence of invasion inhibition by the rabbit polyclonal anti-PvRPB2b 1527, we performed IFA experiments on segmented schizonts from 4 different clinical isolates each having a different PvRBP2b haplotype. The polyclonal Abs recognized each of the isolates evaluated demonstrating that natural polymorphism does not prevent binding of the 1527 Abs to PvRBP2b (Fig. 3)
TfR1 is not recycled following trypsin treatment
We verified that reticulocyte invasion of P. vivax isolates from Cambodia displays the same sensitivity to enzymes as previously described23,24. As expected, reticulocytes treated with neuraminidase or trypsin were permissive to P. vivax invasion while chymotrypsin treatment abolished invasion (Fig. 4A). As TfR1 is trypsin sensitive, these results indicate that cleaving TfR1 from the reticulocytes does not prevent invasion by P. vivax. We determined if an intracellular pool of TfR1 could be recycled on the reticulocyte surface following trypsin treatment by flow cytometry. We confirmed that trypsin treatment removed over 80% of TfR1 as seen by the reduced percentage of reticulocytes expressing TfR1. The percentage of reticulocytes expressing TfR1 continues to decrease due to the maturation in vitro of reticulocytes into normocytes (which are TfR1 negative) (Fig. 4B). This indicated that after surface removal by trypsin treatment, there is no internal pool of TfR1 that can be recycled to the surface.
A Inhibition of P. vivax invasion after chymotrypsin, neuraminidase or trypsin treatment of reticulocytes. Only chymotrypsin treatment inhibits P. vivax merozoite invasion. B The absence of recycling of TfR1/CD71 on trypsin-treated reticulocytes. Trypsin treatment removed > 80% of TfR1 molecules on the surface of reticulocytes and the TfR1 levels remain below 10% to the original level. Data expressed are the % of the control (% of non-treated TfR1+ reticulocytes at Time 0). This experiment is representative of 4 separate experiments with 4 different batches of cord blood reticulocytes. All invasions are normalized to no-antibody controls.
Discussion
In this work, using a substantial quantity of P. vivax clinical isolates for invasion assays, none of the anti-PvRPB2b Abs previously shown to inhibit binding to and/or invasion in reticulocytes by P. vivax17,18 significantly reduced invasion even at high concentrations (500 μg/ml). Targeting the TfR1 with the binding inhibitory OKT9 Abs17 did not inhibit P. vivax invasion either. The mAbs we used in this work were extensively structurally characterized with epitopes identified and mechanisms of PvRBP2b-TfR1 inhibition described18,22. We leveraged this information to evaluate combinations of anti-PvRBP2b humAbs with a distinct mode of action expected to enhance invasion inhibition. Nonetheless, none of the combinations tested here led to significant invasion inhibition. Further tests combining humAbs targeting PvDBP and PvRBP2b were conducted, yet there was no observed variation in the invasion inhibition compared to the anti-PvDBP humAbs tested alone. Altogether, our results indicate that targeting PvRBP2b does not prevent reticulocyte invasion by P. vivax Cambodian isolates.
We verified that the absence of invasion inhibition caused by anti-PvRBP2b, which contrasts with what was previously reported, did not originate from methodological biases in our invasion assay readout performed by flow cytometry. Our assay scores an invasion event as a Far-Red labelled reticulocyte positive for Hoechst DNA staining. In theory, such event could also derive from a reticulocyte with a merozoite attached to it but with the invasion process further blocked. Our assay however allows to observe invasion inhibition caused by anti-PvDBP and anti-DARC Abs unambiguously. We nevertheless evaluated the response to anti-PvRBP2b Abs side-by-side using our flow cytometry readout with microscopy counting of ring stages. We did not observe any difference between the two methods indicating again the robustness of our approach.
The most likely explanation for the failure of anti-PvRBP2b and anti-TfR1 to block invasion in our work is the natural variations in pathways used by P. vivax parasites from different geographical regions. A previous study has shown a large variation in response of P. vivax to anti-TfR1 Abs OKT9 in reticulocyte invasion using isolates from India25. In P. falciparum, multiple invasion pathways are described, and variations in the pathways used are well characterized26,27. For P. vivax, so far, only the PvDBP-DARC pathway has been extensively shown to be critical for invasion, and evidence from recent work suggests that even in Duffy-negative individuals, P. vivax uses the same pathway for reticulocyte invasion28,29. Multiple RBPs are present in the genome of P. vivax. While PvRBP1a does not seem to be critical for invasion30, PvRBP2a interaction with CD98 was recently shown to be involved in reticulocyte invasion, although demonstration of the absolute requirement of this interaction was not made31. Redundancy in the function of RBPs assumed to allow reticulocyte tropism needs to be addressed and could signify the need to target multiple ligands together for invasion inhibition.
We show here that reticulocyte invasion by P. vivax isolates from Cambodia has similar enzymatic sensitivity to what was reported using isolates from Thailand23 and Brazil24 (although for this country only one strain was tested) with invasion being trypsin-resistant. This indicates a universal phenotype for P. vivax and further questions the critical requirement of the PvRBP2b-TfR1 interaction for P. vivax invasion as TfR1 is trypsin sensitive. Ultimately, one would need to demonstrate that a blood-stage vaccine candidate overcomes ligand redundancies and be universally critical for invasion to be of interest for P. vivax control and elimination.
Methods
Samples collection and ex vivo invasion inhibition assay
Sample collection and ex vivo invasion assays were performed with slight modifications as described12. Invasion assays performed here used either cryopreserved P. vivax isolates or freshly collected ones. Cryopreservation was performed immediately after blood collection using glycerolyte 57 solution as previously described12. Cryopreserved parasites were thawed using a NaCl step-wise process using established protocol12. P. vivax samples used fresh were collected in 2022 and 2023 from infected individuals in Kampong Speu, Western Cambodia. To ensure mono-infection, P. vivax was determined using rapid diagnostic testing (CareStart Malaria Pf/pan RDTs, Accesbio) or microscopy and species-specific PCR32. Venous blood was collected in lithium heparin tubes and immediately sent on ice to the Malaria Research Unit at Institut Pasteur of Cambodia. There, erythrocytes were separated from the plasma and re-suspended in warm RPMI medium before leukocyte depletion using a non-woven fabric filter33. The work presented here was approved by the National Ethics Committee for Health Research of Cambodia (192NECHR of July 11, 2022). All patients and/or their parents/guardians provided informed written consent.
Infected erythrocytes were enriched using a KCl-Percoll density gradient34 and then transferred into culture in supplemented IMDM medium (Gibco) (with 0.5% Albumax II (Gibco), 2.5% heat-inactivated human serum, 25 mM HEPES (Gibco), 20 μg/ml gentamicin (Sigma) and 0.2 mM hypoxanthine (C-C Pro)). The stage of the parasite culture was then assessed via thick blood smears. Parasites were cultured until most reached the schizont stages (~24–45 h, depending on their initial stage). The enriched schizonts were mixed 1:1 with reticulocytes (previously enriched from cord or adult peripheral blood from malaria-naive donors) and pre-labelled with Celltrace Far Red Dye. The cultures were incubated for ~10 h in the presence of test antibodies and the mouse monoclonal anti-Duffy 2C319 or, in a few experiments, heparin, was used as positive invasion inhibition control. Cells were stained with DNA stain Hoechst 33342 post-invasion and parasitemia was quantified by flow cytometry. Reticulocytes, which were Hoechst 3342 and Far-Red positive, were scored as new invasion events (Supplementary Figure S1). For quantification, data were normalized against invasion without antibodies and analyzed with FlowJo (V10.8.1) software. Invasion of reticulocytes in the absence of antibodies ranged from 0.4% to 13.8%. Antibodies used in this study were either purchased from commercial supplier (anti-TfR1 OKT9) or generated as previously described17,18.
To determine the enzymatic sensitivity of the invasion of P. vivax isolates, the invasion was performed as described above using reticulocytes pre-treated with either trypsin (1 mg/ml), chymotrypsin (1 mg/ml) or neuraminidase (100 mU/mL) for 1 h at 37 °C35. Invasion rates were compared to mock-treated reticulocytes. Of note, all enzymatic treatments did not affect reticulocyte viability since the number of cells stained with Thiazole orange (a specific reticulocyte stain) remained constant over at least 40 h post-treatment (data not shown).
Assessment of transferrin/TfR1 recycling after enzymatic treatment
Twenty ml of human cord blood was collected in lithium heparin (Sigma) and tested by protocols approved by the University of Oxford Tropical Research Ethics Committee (OXTREC 17-11) and the Ethics Committee of the Faculty of Tropical Medicine at Mahidol University (MUTM 2008-215). After plasma removal, the packed red cells were washed in McCoy’s 5 A medium (Gibco, Singapore). Host leukocytes and platelets were depleted from the cord red blood cells using CF11 column filtration36. Red cells were then adjusted to a 50% haematocrit using McCoy’s 5 A medium, and the mixture split into 5 ml aliquots that were each carefully layered on a 6 ml 80% Isotonic Percoll cushion (Thermofisher Scientific, Singapore). Following centrifugation for 15 min at 1200 g, the resulting fine band of concentrated reticulocytes formed on the Percoll interface was removed and washed in McCoy’s 5 A medium. The enriched reticulocyte populations were treated with trypsin (2.5 mg/ml) (0.25% bovine trypsin- EDTA solution, Sigma, Singapore) for 1 h at 37 °C, as previously described23,24. They were washed in McCoy’s 5 A medium containing 10% Fetal calf serum to inactivate and remove trypsin. Reticulocyte preparations were then kept at 37 °C for different lengths of time. The proportions of TfR1+ reticulocytes were determined by flow cytometry using the mouse monoclonal antibody IgG2a against human TfR1 tagged with APC (clone M-A172, Pharmingen) as described before37. The experiment was repeated with 4 different batches of cord blood reticulocytes.
Genomic DNA extraction, amplification, and sequencing of PvRBP2b
Genomic DNA from P. vivax infected peripheral blood was extracted using the QIAamp DNA Blood Minit Kit (QUIAGEN), according to manufacturer’s instructions. PvRPB2b sequences were determined by PCR and Sanger sequencing (Macrogen, Seoul, South Korea) using the following conditions. The PCR was conducted in 20 µL reaction consisting of 2 µL of DNA, 0.25 µM of primers (amino acid from 100 to 400, forward: 5′-AGAGGGGACATATATACACACAGT-3′ and reverse: 5′-GGTTTAACCCCGTCGGACAA-3′; from amino acid 398 to 630, forward: 5′-TCCATTGATCAAGTGACAGCA-3′ and reverse: 5′-TTCTTCCACATGTTGTTGGT-3′) and 1× HOT FirePol Blend MasterMix (Solis BioDyne, Tartu, Estonia) under the following conditions: 95°C for 12 min, followed by 34 cycles 95 °C for 20 s, 63.8 °C for 30 sec, 72 °C for 2 min and a final extension at 72 °C for 5 min. Nucleotides and corresponding amino acids were analyzed using MEGA 11 software. The sequences generated were compared to the reference strain Sal1 (PVX_094255). Shared amino acids between any isolate and Sal1 is referred to as wild type (WT).
Immunofluorescence assay
Enriched schizont parasites from P. vivax clinical isolates re-suspended at 1% hematocrit in PBS 1X were applied on IFA slides, air-dried and fixed in ice-cold acetone (90%)/methanol (10%). After blocking with 1% BSA, rabbit anti-PvRBP2b 1527 polyclonal antibody was added at 500 μg/ml and incubated for 1 h at 37 °C. After washes, Alexa Fluor 488 goat anti-rabbit IgG (H + L) antibody (1:500) mixed with Hoechst dye (1 μg/ml) were added on slides and incubated for 1 h at 37 °C. After being washed, the slides were visualized using a fluorescence microscope (Leica DM2500 MicroSystems CMS GmbH, Germany) equipped with 10×, 40× dry, and 60×, 100× oil objectives. Images were captured using the LAS V4.12 viewer software. Images were analyzed by ImageJ.
Statistical analyses
Multiple comparisons of mean of non-Gaussian data were compared by Kruskal-Wallis test and Dunn’s post-hoc tests and of normally distributed data by ANOVA and Dunnett’s post-hoc tests. All analyses were performed using GraphPad Prism (V10.1.0). A P value < 0.05 was considered significant.
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are present in this published article (and its supplementary information files). Resources or data supporting this study’s findings are available from the corresponding author upon request.
References
Battle, K. E. et al. Mapping the global endemicity and clinical burden of Plasmodium vivax, 2000–17: a spatial and temporal modelling study. Lancet 394, 332–343 (2019).
Baird, J. K. Evidence and implications of mortality associated with acute Plasmodium vivax malaria. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 26, 36–57 (2013).
Douglas, N. M. et al. Major burden of severe anemia from non-falciparum malaria species in Southern Papua: a hospital-based surveillance study. PLos Med. 10, e1001575 (2013).
Douglas, N. et al. Mortality attributable to Plasmodium vivax malaria: a clinical audit from Papua, Indonesia. BMC Med. 12, 217 (2014).
Mueller, I. et al. Key gaps in the knowledge of Plasmodium vivax, a neglected human malaria parasite. Lancet Infect. Dis. 9, 555–566 (2009).
Lover, A. A., Baird, J. K., Gosling, R. & Price, R. N. Malaria elimination: time to target all species. Am. J. Tropical Med. Hyg. 99, 17–23 (2018).
De, S. L., Ntumngia, F. B., Nicholas, J. & Adams, J. H. Progress towards the development of a P. vivax vaccine. Expert Rev. vaccines 20, 97–112 (2021).
Tham, W. H., Beeson, J. G. & Rayner, J. C. Plasmodium vivax vaccine research - we’ve only just begun. Int J. Parasitol. 47, 111–118 (2017).
Mueller, I., Shakri, A. R. & Chitnis, C. E. Development of vaccines for Plasmodium vivax malaria. Vaccine 33, 7489–7495 (2015).
Wertheimer, S. P. & Barnwell, J. W. Plasmodium vivax interaction with the human Duffy blood group glycoprotein: identification of a parasite receptor-like protein. Exp. Parasitol. 69, 340–350 (1989).
Chitnis, C. & Miller, L. H. Identification of the erythrocyte binding domains ofPlasmodium vivax and Plasmodium knowlesi proteins involved in erythrocyte invasion. J. Exp. Med. 180, 497–506 (1994).
Popovici, J. et al. Amplification of Duffy binding protein-encoding gene allows Plasmodium vivax to evade host anti-DBP humoral immunity. Nat. Commun. 11, 953 (2020).
Kar, S. & Sinha, A. Plasmodium vivax duffy binding protein-based vaccine: a distant dream. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 12, 916702 (2022).
Singh, K. et al. Malaria vaccine candidate based on Duffy-binding protein elicits strain transcending functional antibodies in a Phase I trial. NPJ vaccines 3, 48–48 (2018).
Hou, M. M. et al. Vaccination with Plasmodium vivax Duffy-binding protein inhibits parasite growth during controlled human malaria infection. Sci. Transl. Med. 15, eadf1782 (2023).
Martinez, F. J. et al. PvDBPII elicits multiple antibody-mediated mechanisms that reduce growth in a Plasmodium vivax challenge trial. NPJ Vaccines 9, 10 (2024).
Gruszczyk, J. et al. Transferrin receptor 1 is a reticulocyte-specific receptor for Plasmodium vivax. Sci. (N. Y., N. Y.) 359, 48–55 (2018).
Chan, L. J. et al. Naturally acquired blocking human monoclonal antibodies to Plasmodium vivax reticulocyte binding protein 2b. Nat. Commun. 12, 1538 (2021).
Russell, B. et al. A reliable ex vivo invasion assay of human reticulocytes by Plasmodium vivax. Blood 118, e74–e81 (2011).
Carias, L. L. et al. Identification and characterization of functional human monoclonal antibodies to Plasmodium vivax duffy-binding protein. J. Immunol. 202, 2648–2660 (2019).
Urusova, D. et al. Structural basis for neutralization of Plasmodium vivax by naturally acquired human antibodies that target DBP. Nat. Microbiol. 4, 1486–1496 (2019).
Gruszczyk, J. et al. Cryo-EM structure of an essential Plasmodium vivax invasion complex. Nature 559, 135–139 (2018).
Malleret, B., Rénia, L. & Russell, B. The unhealthy attraction of Plasmodium vivax to reticulocytes expressing transferrin receptor 1 (CD71). Int. J. Parasit. 47, 379–383 (2017).
Barnwell, J. W., Nichols, M. E. & Rubinstein, P. In vitro evaluation of the role of the Duffy blood group in erythrocyte invasion by Plasmodium vivax. J. Exp. Med. 169, 1795–1802 (1989).
Kanjee, U. et al. Plasmodium vivax strains use alternative pathways for invasion. J. Infect. Dis. 223, 1817–1821 (2020).
Dolan, S. A., Miller, L. H. & Wellems, T. E. Evidence for a switching mechanism in the invasion of erythrocytes by Plasmodium falciparum. J. Clin. Investig. 86, 618–624 (1990).
Stubbs, J. et al. Molecular mechanism for switching of P. falciparum invasion pathways into human erythrocytes. Science 309, 1384–1387 (2005).
Bouyssou, I. et al. Unveiling P. vivax invasion pathways in Duffy-negative individuals. Cell Host Microbe 31, 2080–2092.e2085 (2023).
Dechavanne, C. et al. Duffy antigen is expressed during erythropoiesis in Duffy-negative individuals. Cell Host Microbe 31, 2093–2106.e2097 (2023).
Gupta, S. et al. Targeting a Reticulocyte Binding Protein and Duffy Binding Protein to Inhibit Reticulocyte Invasion by Plasmodium vivax. Scientific reports 8, 10511–10511 (2018).
Malleret, B. et al. Plasmodium vivax binds host CD98hc (SLC3A2) to enter immature red blood cells. Nat. Microbiol 6, 991–999 (2021).
Canier, L. et al. An innovative tool for moving malaria PCR detection of parasite reservoir into the field. Malar. J. 12, 405 (2013).
Li, J. et al. Further evaluation of the NWF filter for the purification of Plasmodium vivax-infected erythrocytes. Malar. J. 16, 201 (2017).
Rangel, G. W. et al. Enhanced ex vivo plasmodium vivax intraerythrocytic enrichment and maturation for rapid and sensitive parasite growth assays. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 62, e02519–02517 (2018).
Cho, J.-S. et al. Unambiguous determination of Plasmodium vivax reticulocyte invasion by flow cytometry. Int. J. Parasit. 46, 31–39 (2016).
Sriprawat, K. et al. Effective and cheap removal of leukocytes and platelets from Plasmodium vivax infected blood. Malar. J. 8, 115 (2009).
Malleret, B. et al. Significant biochemical, biophysical and metabolic diversity in circulating human cord blood reticulocytes. PLoS ONE 8, e76062 (2013).
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to all the patients who agreed to participate in the study. We are also indebted to the Mae Sot Malaria Clinic staff and the clinics associated with the Shoklo Malaria Research Unit. We are grateful to Wai-Hong Tham for providing all mouse, rabbit and human anti-PvRBP2b antibodies used in this study. J.P. is supported by NIAID/NIH (grants R01AI175134 and R01AI173171). BW and JP are supported by the Pasteur International Unit PvESMEE. This work was supported by core funding from the Agency for Science, Technology and Research to A*STAR Infectious Diseases Labs, by a Start-up University Grant from the Ministry of Education–Singapore (022388-00001), and by Temasek Foundation (grant “Temasek Foundation Infectious Diseases Programme for Surveillance and Diseases X Resilience”) to L.R.; by the Singapore National Medical Research Council IRG Grant (NMRC/OFIRG/0065/2018) to L.R.; by a Marsden Grant Award (RGUOO180301 to L.R. and B.R.); by The Wellcome Trust of Great Britain, as part of the Oxford Tropical Medicine Research Programme of Wellcome Trust–Mahidol University, to the Shoklo Malaria Research Unit (FN); by Veterans Affairs Merit Award I01 BX001350 and R01AI143694 to C.L.K.; by NIAID/NIH (R01AI162947A) to E.L.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
L.B.F.-D., B.W., B.R. L.R. and J.P. conceived the study. L.B.F.-D., L.B., C.R., B.T., A.O., D.S., J.S., N.K., L.C., A.S.M.O., and H.M. were responsible for data collection. L.B.F.-D., B.R., L.R., and J.P. analyzed the data. Funding acquisition: C.L.K., L.R., B.R., F.N., E.L., and J.P. L.B.F.-D. and J.P. wrote the first draft. All authors have read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Feufack-Donfack, L.B., Baldor, L., Roesch, C. et al. The PvRBP2b-TfR1 interaction is not essential for reticulocytes invasion by Plasmodium vivax isolates from Cambodia. npj Vaccines 9, 232 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41541-024-01031-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41541-024-01031-7