Abstract
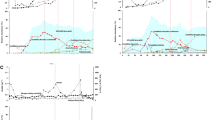
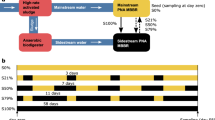
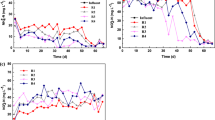
The synergistically optimized nitrogen removal strategy emerges from the co-treatment of municipal wastewater with the effluent from partial nitrification (PN) of high-ammonia wastewater through a partial denitrification-anaerobic ammonium oxidation (PDA) process. However, maximizing PDA efficiency remains a critical challenge. In this study, a two-stage partial nitrification-partial denitrification-anaerobic ammonium oxidation (PN-PDA) integrated system was developed to regulate synergistic granule-biofilm architecture in the second stage to enhance PDA. After 160-day operation, the system showed excellent nitrogen removal, with effluent nitrogen at 5.6 ± 2.9 and 5.2 ± 2.0 mg/L in two phases. In-situ activity assays revealed that anammox rate in granular sludge (9.6 mg N/(L·h)) was significantly higher than that in biofilms (1.8 mg N/(L·h)). Fluorescence in-situ hybridization analysis demonstrated a distinct spatial distribution, with PD functional bacteria Thauera dominating granule outer layer, while Ca. Brocadia was enriched in the inner layer. Metagenomic sequencing further confirmed that Ca. Brocadia accounted for 9.8% and 4.1% in granules and biofilms, respectively. Anammox-related genes (hzs, hdh) showed significantly higher abundance in the granules. This study offers a novel framework for concurrent high-strength and municipal wastewater treatment while providing critical insights into granule-biofilm engineering for nitrogen removal intensification.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data generated in this study are provided within the article and its Supplementary Information. Raw sequencing data have been archived in the NCBI Sequence Read Archive with the accession number PRJNA1250609. Source data are provided with this paper.
References
Yu, X.-L. et al. Mapping research on carbon neutrality in WWTPs between 2001 and 2021: a scientometric and visualization analysis. Sustain. Horiz. 3, 100022 (2022).
Miao, Y. et al. Application of intermittent aeration in nitrogen removal process: development, advantages and mechanisms. Chem. Eng. J. 430, 133184 (2022).
Yang, J. & Chen, B. Energy efficiency evaluation of wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs) based on data envelopment analysis. Appl. Energy 289, 116680 (2021).
Liu, S. C. et al. Advanced nitrogen removal of landfill leachate treatment with anammox process: a critical review. J. Water Process Eng. 58, 104756 (2024).
Kartal, B., Kuenen, J. G. & van Loosdrecht, M. C. M. Sewage treatment with anammox. Science 328, 702–703 (2010).
Feng, Y., Wang, B., Peng, Y., Li, X. & Zhang, Q. Enhanced nitrogen removal from low COD/TIN mainstream wastewater in a continuous plug-flow reactor via partial nitrification, simultaneous anammox and endogenous denitrification (PN-SAED) process. Bioresour. Technol. 345, 126539 (2022).
Li, J. et al. Highly enriched anammox within anoxic biofilms by reducing suspended sludge biomass in a real-sewage A2/O process. Water Res. 194, 116906 (2021).
Wang, Z. Y., Zheng, M., Duan, H. R., Yuan, Z. G. & Hu, S. H. A 20-year journey of partial nitritation and anammox (PN/A): from sidestream toward mainstream. Environ. Sci. Technol. 56, 7522–7531 (2022).
Yang, Q. et al. Start up of deammonification process in one single SBR system. Water Sci. Technol. 50, 1–8 (2004).
Wang, B. et al. Recovering partial nitritation in a PN/A system during mainstream wastewater treatment by reviving AOB activity after thoroughly inhibiting AOB and NOB with free nitrous acid. Environ. Int. 139, 105684 (2020).
Lackner, S. et al. Full-scale partial nitritation/anammox experiences—an application survey. Water Res 55, 292–303 (2014).
Pérez, J., Lotti, T., Kleerebezem, R., Picioreanu, C. & van Loosdrecht, M. C. M. Outcompeting nitrite-oxidizing bacteria in single-stage nitrogen removal in sewage treatment plants: a model-based study. Water Res. 66, 208–218 (2014).
Ma, B., Qian, W., Yuan, C., Yuan, Z. & Peng, Y. Achieving mainstream nitrogen removal through coupling anammox with denitratation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 51, 8405–8413 (2017).
Du, R. et al. Synergy of partial-denitrification and anammox in continuously fed upflow sludge blanket reactor for simultaneous nitrate and ammonia removal at room temperature. Bioresour. Technol. 274, 386–394 (2019).
Zhang, W., Peng, Y., Zhang, L., Li, X. & Zhang, Q. Simultaneous partial nitritation and denitritation coupled with polished anammox for advanced nitrogen removal from low C/N domestic wastewater at low dissolved oxygen conditions. Bioresour. Technol. 305, 123045 (2020).
Ji, J. T., Peng, Y. Z., Li, X. Y., Zhang, Q. & Liu, X. P. A novel partial nitrification-synchronous anammox and endogenous partial denitrification (PN-SAEPD) process for advanced nitrogen removal from municipal wastewater at ambient temperatures. Water Res. 175, 115690 (2020).
Xiong, L. et al. Efficient nitrogen removal from real municipal wastewater and mature landfill leachate using partial nitrification-simultaneous anammox and partial denitrification process. Water Res. 251, 121088 (2024).
Ma, Y. et al. Enrichment of anammox biomass during mainstream wastewater treatment driven by achievement of partial denitrification through the addition of bio-carriers. J. Environ. Sci. 137, 181–194 (2024).
Li, Z., Xu, X., Shao, B., Zhang, S. & Yang, F. Anammox granules formation and performance in a submerged anaerobic membrane bioreactor. Chem. Eng. J. 254, 9–16 (2014).
Zhang, K. et al. A rapid and effective way to cultivate anammox granular sludge through vibration. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 143, 104704 (2019).
Kosgey, K. et al. Critical analysis of biomass retention strategies in mainstream and sidestream ANAMMOX-mediated nitrogen removal systems. Environ. Sci. Technol. 55, 9–24 (2021).
Zheng, Y. F. et al. Microbial community structure and nitrogen conversion rate of size-fractionated granules in partial denitrification and anammox reactor. J. Clean. Prod. 414, 137714 (2023).
Zhang, L. & Okabe, S. Ecological niche differentiation among anammox bacteria. Water Res. 171, 115468 (2020).
Naufal, M. & Wu, J. H. Chemomixoautotrophy and stress adaptation of anammox bacteria: a review. Water Res. 257, 121663 (2024).
Zhao, Q. et al. Carbon-restricted anoxic zone as an overlooked anammox hotspot in municipal wastewater treatment plants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 57, 21767–21778 (2023).
van Niftrik, L. & Jetten, M. S. M. Anaerobic ammonium-oxidizing bacteria: unique microorganisms with exceptional properties. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 76, 585–596 (2012).
Kończak, B., Karcz, J. & Miksch, K. Influence of calcium, magnesium, and iron ions on aerobic granulation. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 174, 2910–2918 (2014).
Ma, H. T. et al. Calcium ions affect sludge digestion performance via changing extracellular polymeric substances in anaerobic bioreactor. Biomass Bioenergy 137, 105548 (2020).
Kimkes, T. E. P. & Heinemann, M. How bacteria recognise and respond to surface contact. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 44, 106–122 (2020).
Okabe, S. et al. Salinity tolerance and osmoadaptation strategies in four genera of anammox bacteria: Brocadia, Jettenia, Kuenenia, and Scalindua. Environ. Sci. Technol. 58, 5357–5371 (2024).
Gao, M. et al. Deciphering the role of granular activated carbon (GAC) in anammox: effects on microbial succession and communication. Water Res. 233, 119753 (2023).
Wang, B., Gong, X. & Peng, Y. Simultaneous anammox-denitrification process and its emerging extensions. Chem. Eng. J. 415, 128380 (2021).
Liu, B., Mao, Y., Bergaust, L., Bakken, L. R. & Frostegård, Å Strains in the genus Thauera exhibit remarkably different denitrification regulatory phenotypes. Environ. Microbiol. 15, 2816–2828 (2013).
Nagashima, S. et al. Complete genome sequence of phototrophic betaproteobacterium Rubrivivax gelatinosus IL144. J. Bacteriol. 194, 3541–3542 (2012).
Hassani, B. K. et al. Adaptation to oxygen. J. Biol. Chem. 285, 19891–19899 (2010).
Xing, Y. et al. Rapid initiation of partial denitrification with different seeding sludge and carriers: responses of wastewater treatment performance, microbial composition, and functional genes. J. Water Process Eng. 75, 107915 (2025).
Zhao, Q. et al. From hybrid process to pure biofilm anammox process: suspended sludge biomass management contributing to high-level anammox enrichment in biofilms. Water Res. 236, 119959 (2023).
Wang, K. C. et al. How to provide nitrite robustly for anaerobic ammonium oxidation in mainstream nitrogen removal. Environ. Sci. Technol. 57, 21503–21526 (2023).
Ran, X. C. et al. A novel perspective on the instability of mainstream partial nitrification: the niche differentiation of nitrifying guilds. Environ. Sci. Technol. 59, 8922–8938 (2025).
Xu, D. et al. A novel SAD process: match of anammox and denitrification. Water Res. 193, 116874 (2021).
Xu, R. H. et al. Combination of sequencing batch operation and A/O process to achieve partial mainstream anammox: pilot-scale demonstration and microbial ecological mechanism. Environ. Sci. Technol. 57, 13887–13900 (2023).
Du, R. et al. Spatiotemporal assembly and immigration of heterotrophic and anammox bacteria allow a robust synergy for high-rate nitrogen removal. Environ. Sci. Technol. 57, 9075–9085 (2023).
Del Nery, V., Pozzi, E., Damianovic, M. H. R. Z., Domingues, M. R. & Zaiat, M. Granules characteristics in the vertical profile of a full-scale upflow anaerobic sludge blanket reactor treating poultry slaughterhouse wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 99, 2018–2024 (2008).
Li, B. et al. The symbiosis of anaerobic ammonium oxidation bacteria and heterotrophic denitrification bacteria in a size-fractioned single-stage partial nitrification/anammox reactor. Biochem. Eng. J. 151, 107353 (2019).
Zhao, Y. et al. Advanced nitrogen elimination from domestic sewage through two stage partial nitrification and denitrification (PND) coupled with simultaneous anaerobic ammonia oxidation and denitrification (SAD). Bioresour. Technol. 343, 125986 (2022).
APHA. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater (American Public Health Association (APHA), 2012).
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 22176007, 22476005), the Project of Cultivation for young top-motch Talents of Beijing Municipal Institutions (BPHR202203009).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
B.W. and W.W. conceived the project. W.W., M.B., and B.W. visualized the data. B.W. acquired funding. B.W. and M.B. prepared the original draft of the manuscript, while B.W. and M.B. also handled the writing and review process. X.H., Y.Z., and Y.X. checked the manuscript. W.Z. and Y.P. supervised this work. All the authors discussed the results and commented on the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Bai, M., Wang, B., Wang, W. et al. Synergistic granule-biofilm PDA process enables ultra-efficient nitrogen removal in co-treating high-strength and municipal wastewater. npj Clean Water (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41545-025-00549-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41545-025-00549-0