Abstract
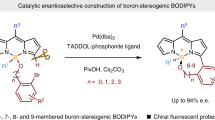
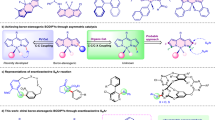
Boron dipyrromethenes (BODIPYs) are some of the most popular and indispensable tetracoordinate boron compounds and have found widespread applications owing to their excellent spectroscopic and photophysical properties. BODIPYs possessing boron-stereogenic centres are scarce, and strategies for the synthesis of enantioenriched boron-stereogenic BODIPYs with structural diversity remain underdeveloped. In theory, the BODIPY core skeleton has several sites that could be decorated with different substituents. However, due to the lack of general and efficient asymmetric synthetic methods, this potential diversity of chiral BODIPYs has not been exploited. Here we demonstrate a modular enantioselective assembly of multi-substituted boron-stereogenic BODIPYs in high efficiency with excellent enantioselectivities. Key to the success is the Pd-catalysed desymmetric Suzuki cross-coupling, enabling the precise discrimination of the two α C–Cl bonds of the designed prochiral BODIPY scaffold, giving access to a wide range of highly functionalized boron-stereogenic BODIPYs. Derivatizations, photophysical properties and applications in chiral recognition of the obtained optical BODIPYs are further explored.

This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$32.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available within the Article and its Supplementary Information. Details about materials and methods, experimental procedures, characterization data, 1H, 13C, 19F, 11B NMR spectra and mass spectrometry data are available in Supplementary Information. Crystallographic data for the structures reported in this Article have been deposited at the Cambridge Crystallographic Data Centre, under deposition numbers CCDC 2278973 (3a), 2278972 (4a) and 2278967 (4l). Copies of the data can be obtained free of charge via https://www.ccdc.cam.ac.uk/structures/. Source data are provided with this paper.
References
Treibs, A. & Kreuzer, F.-H. Difluorboryl-komplexe von di- und tripyrrylmethenen. Justus Liebigs Ann. Chem. 718, 208–223 (1968).
Bin-Kai, L., Kun-Xu, T., Li-Ya, N. & Qing-Zheng, Y. Progress in the synthesis of boron dipyrromethene (BODIPY) fluorescent dyes. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 42, 1265–1285 (2022).
Loudet, A. & Burgess, K. BODIPY dyes and their derivatives: syntheses and spectroscopic properties. Chem. Rev. 107, 4891–4932 (2007).
Ulrich, G., Ziessel, R. & Harriman, A. The chemistry of fluorescent BODIPY dyes: versatility unsurpassed. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 47, 1184–1201 (2008).
Boens, N., Verbelen, B., Ortiz, M. J., Jiao, L. & Dehaen, W. Synthesis of BODIPY dyes through postfunctionalization of the boron dipyrromethene core. Coord. Chem. Rev. 399, 213024–213108 (2019).
Bañuelos, J. BODIPY dye, the most versatile fluorophore ever? Chem. Rec. 16, 335–348 (2016).
Poddar, M. & Misra, R. Recent advances of BODIPY based derivatives for optoelectronic applications. Coord. Chem. Rev. 421, 213462–213483 (2020).
Nguyen, V.-N. et al. Recent developments of BODIPY-based colorimetric and fluorescent probes for the detection of reactive oxygen/nitrogen species and cancer diagnosis. Coord. Chem. Rev. 439, 213936–213952 (2021).
Yuan, L., Su, Y., Cong, H., Yu, B. & Shen, Y. Application of multifunctional small molecule fluorescent probe BODIPY in life science. Dyes Pigm. 208, 110851–110869 (2023).
Zhang, J. et al. BODIPY-based fluorescent probes for biothiols. Chem. Eur. J. 26, 4172–4192 (2020).
Boens, N., Leen, V. & Dehaen, W. Fluorescent indicators based on BODIPY. Chem. Soc. Rev. 41, 1130–1172 (2012).
Kolemen, S. & Akkaya, E. U. Reaction-based BODIPY probes for selective bio-imaging. Coord. Chem. Rev. 354, 121–134 (2018).
De Bonfils, P., Péault, L., Nun, P. & Coeffard, V. State of the art of BODIPY-based photocatalysts in organic synthesis. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2021, 1809–1824 (2021).
Singh, P. K., Majumdar, P. & Singh, S. P. Advances in BODIPY photocleavable protecting groups. Coord. Chem. Rev. 449, 214193–214248 (2021).
Zhang, W. et al. Application of multifunctional BODIPY in photodynamic therapy. Dyes Pigm. 185, 108937–108950 (2021).
Kamkaew, A. et al. BODIPY dyes in photodynamic therapy. Chem. Soc. Rev. 42, 77–88 (2013).
Kowada, T., Maeda, H. & Kikuchi, K. BODIPY-based probes for the fluorescence imaging of biomolecules in living cells. Chem. Soc. Rev. 44, 4953–4972 (2015).
Pu, L. Simultaneous determination of concentration and enantiomeric composition in fluorescent sensing. Acc. Chem. Res. 50, 1032–1040 (2017).
Pop, F., Zigon, N. & Avarvari, N. Main-group-based electro- and photoactive chiral materials. Chem. Rev. 119, 8435–8478 (2019).
Zu, B., Guo, Y. & He, C. Catalytic enantioselective construction of chiroptical boron-stereogenic compounds. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 143, 16302–16310 (2021).
Zhang, G. et al. Construction of boron-stereogenic compounds via enantioselective Cu-catalyzed desymmetric B–H bond insertion reaction. Nat. Commun. 13, 2624 (2022).
Zhang, G. et al. Cu(I)-catalyzed highly diastereo- and enantioselective constructions of boron/carbon vicinal stereogenic centers via insertion reaction. ACS Catal. 13, 9502–9508 (2023).
Zu, B., Guo, Y., Ren, L.-Q., Li, Y. & He, C. Catalytic enantioselective synthesis of boron-stereogenic BODIPYs. Nat. Synth. 2, 564–571 (2023).
Haefele, A., Zedde, C., Retailleau, P., Ulrich, G. & Ziessel, R. Boron asymmetry in a BODIPY derivative. Org. Lett. 12, 1672–1675 (2010).
Gobo, Y., Matsuoka, R., Chiba, Y., Nakamura, T. & Nabeshima, T. Synthesis and chiroptical properties of phenanthrene-fused N2O-type BODIPYs. Tetrahedron Lett. 59, 4149–4152 (2018).
Ray, C. et al. Dissimilar-at-boron N-BODIPYs: from light-harvesting multichromophoric arrays to CPL-bright chiral-at-boron BODIPYs. Org. Chem. Front. 10, 5834–5842 (2023).
Lu, H., Mack, J., Nyokong, T., Kobayashi, N. & Shen, Z. Optically active BODIPYs. Coord. Chem. Rev. 318, 1–15 (2016).
Li, X., Zhang, G. & Song, Q. Recent advances in the construction of tetracoordinate boron compounds. Chem. Commun. 59, 3812–3820 (2023).
Abdou-Mohamed, A. et al. Stereoselective formation of boron-stereogenic organoboron derivatives. Chem. Soc. Rev. 52, 4381–4391 (2023).
Vedejs, E. et al. Asymmetric memory at labile, stereogenic boron: enolate alkylation of oxazaborolidinones. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 121, 2460–2470 (1999).
Charoy, L. et al. Synthesis of benzylcyanoborane adducts of amines and separation of their enantiomers; S2 substitution at boron atom. Chem. Commun. 2275–2276 (2000).
Imamoto, T. & Morishita, H. An enantiomerically pure tetracoordinate boron compound: stereochemistry of substitution reactions at the chirogenic boron atom. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 122, 6329–6330 (2000).
Toyota, S., Ito, F., Nitta, N. & Hakamata, T. Substituent effects on configurational stabilities at tetrahedral boron atoms in intramolecular borane–amine complexes: structures, enantiomeric resolution, and rates of enantiomerization of [2-(dimethylaminomethyl)phenyl]phenylboranes. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 77, 2081–2088 (2004).
Braun, M., Schlecht, S., Engelmann, M., Frank, W. & Grimme, S. Boron-based diastereomerism and enantiomerism in imine complexes—determination of the absolute configuration at boron by CD spectroscopy. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2008, 5221–5225 (2008).
Kaiser, P. F., White, J. M. & Hutton, C. A. Enantioselective preparation of a stable boronate complex stereogenic only at boron. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 130, 16450–16451 (2008).
Schlecht, S., Frank, W. & Braun, M. Stereogenic boron in 2-amino-1,1-diphenylethanol-based boronate-imine and amine complexes. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 7, 615–621 (2011).
Jiménez, V. G. et al. Circularly polarized luminescence of boronic acid-derived salicylidenehydrazone complexes containing chiral boron as stereogenic unit. J. Org. Chem. 83, 14057–14062 (2018).
Aupic, C. et al. Highly diastereoselective preparation of chiral NHC-boranes stereogenic at the boron atom. Chem. Sci. 10, 6524–6530 (2019).
Stöckl, Y. et al. Enantioenriched boron C,N-chelates via chirality transfer. Chem. Eur. J. 29, e202301324 (2023).
Braun, M. Boron-based enantiomerism. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 27, e202400052 (2024).
Guo, Y., Zu, B., Chen, C. D. & He, C. Boron-stereogenic compounds: synthetic developments and opportunities. Chin. J. Chem. https://doi.org/10.1002/cjoc.202400130 (2024).
Suzuki, S., Segawa, Y., Itami, K. & Yamaguchi, J. Synthesis and characterization of hexaarylbenzenes with five or six different substituents enabled by programmed synthesis. Nat. Chem. 7, 227–233 (2015).
Aiken, S. G. et al. Iterative synthesis of 1,3-polyboronic esters with high stereocontrol and application to the synthesis of bahamaolide A. Nat. Chem. 15, 248–256 (2023).
Lyu, H. et al. Modular synthesis of 1,2-azaborines via ring-opening BN-isostere benzannulation. Nat. Chem. 16, 269–276 (2024).
Rohand, T., Dolusic, E., Ngo, T. H., Maes, W. & Dehaen, W. Efficient synthesis of aryldipyrromethanes in water and their application in the synthesis of corroles and dipyrromethenes. Arkivoc 307–324 (2007).
Willis, M. C., Powell, L. H. W., Claverie, C. K. & Watson, S. J. Enantioselective Suzuki reactions: catalytic asymmetric synthesis of compounds containing quaternary carbon centers. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 43, 1249–1251 (2004).
Urbaneja, X., Mercier, A., Besnard, C. & Kündig, E. P. Highly efficient desymmetrisation of a tricarbonylchromium 1,4-dibromonaphthalene complex by asymmetric Suzuki–Miyaura coupling. Chem. Commun. 47, 3739–3741 (2011).
Hedouin, G., Hazra, S., Gallou, F. & Handa, S. The catalytic formation of atropisomers and stereocenters via asymmetric Suzuki–Miyaura couplings. ACS Catal. 12, 4918–4937 (2022).
Lou, Y., Wei, J., Li, M. & Zhu, Y. Distal ionic substrate–catalyst interactions enable long-range stereocontrol: Access to remote quaternary stereocenters through a desymmetrizing Suzuki–Miyaura reaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 144, 123–129 (2022).
Pearce-Higgins, R. et al. An enantioselective Suzuki–Miyaura coupling to form axially chiral biphenols. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 144, 15026–15032 (2022).
Zhang, M., Lee, P. S., Allais, C., Singer, R. A. & Morken, J. P. Desymmetrization of vicinal bis(boronic) esters by enantioselective Suzuki–Miyaura cross-coupling reaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 145, 8308–8313 (2023).
Höpfl, H. The tetrahedral character of the boron atom newly defined—a useful tool to evaluate the N→B bond. J. Organomet. Chem. 581, 129–149 (1999).
Satyanarayana, T., Abraham, S. & Kagan, H. B. Nonlinear effects in asymmetric catalysis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 48, 456–494 (2009).
Imbos, R., Minnaard, A. J. & Feringa, B. L. Monodentate phosphoramidites; versatile ligands in catalytic asymmetric intramolecular heck reactions. Dalton Trans. 2017–2023 (2003).
Barder, T. E., Walker, S. D., Martinelli, J. R. & Buchwald, S. L. Catalysts for Suzuki–Miyaura coupling processes: scope and studies of the effect of ligand structure. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 127, 4685–4696 (2005).
Bodio, E. & Goze, C. Investigation of B-F substitution on BODIPY and aza-BODIPY dyes: development of B-O and B-C BODIPYs. Dyes Pigm. 160, 700–710 (2019).
Lu, H., Mack, J., Yang, Y. & Shen, Z. Structural modification strategies for the rational design of red/NIR region BODIPYs. Chem. Soc. Rev. 43, 4778–4823 (2014).
Teng, K.-X., Niu, L.-Y., Li, J., Jia, L. & Yang, Q.-Z. An unexpected coupling–reduction tandem reaction for the synthesis of alkenyl-substituted BODIPYs. Chem. Commun. 55, 13761–13764 (2019).
Wang, Z. et al. Organotrifluoroborate salts as complexation reagents for synthesizing BODIPY dyes containing both fluoride and an organo substituent at the boron center. J. Org. Chem. 84, 2732–2740 (2019).
Niu, L.-Y. et al. BODIPY-based ratiometric fluorescent sensor for highly selective detection of glutathione over cysteine and homocysteine. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 134, 18928–18931 (2012).
Wang, S.-Y., Niu, L.-Y. & Yang, Q.-Z. Fluorescent probes for detection of bioactive molecules based on ‘aromatic nucleophilic substitution-rearrangement’ mechanism. Sci. Sin. Chim. 52, 893–912 (2022).
Acknowledgements
We are grateful for financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (22122102, 22101120 and 22271134), Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Catalysis (2020B121201002), Guangdong Pearl River Talent Program (2019QN01Y628) and Shenzhen Science and Technology Innovation Committee (RCJC20221008092723013 and JCYJ20230807093104009). We acknowledge the assistance of SUSTech Core Research Facilities (SUSTech CRF) for obtaining photophysical properties and chiral recognition data.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
C.H. and L.-Q.R. conceived the project. L.-Q.R., B.Zhan, J.Z., Y.G. and B.Zu designed and performed the synthetic experiments. Y.L. performed the computational studies. C.H. and L.-Q.R. prepared the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Chemistry thanks Olivier Chuzel, Erhong Hao and the other, anonymous, reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary figures, discussion and tables.
Supplementary Data 1
Crystallographic data for compound 3a; CCDC reference 2278973.
Supplementary Data 2
Crystallographic data for compound 4a; CCDC reference 2278972.
Supplementary Data 3
Crystallographic data for compound 4l; CCDC reference 2278967.
Source data
Source Data Fig. 4
Excel file for Fig. 4.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ren, LQ., Zhan, B., Zhao, J. et al. Modular enantioselective assembly of multi-substituted boron-stereogenic BODIPYs. Nat. Chem. 17, 83–91 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41557-024-01649-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41557-024-01649-z
This article is cited by
-
Organocatalytic iminium-assisted asymmetric B(sp²)-to-B(sp³) transformation
Nature Communications (2025)
-
Enantioselective construction of inherently chiral pillar[5]arenes via palladium-catalysed Suzuki–Miyaura cross-coupling
Nature Communications (2025)
-
Streamlined construction of boron-stereogenic BODIPY library for near-infrared bioimaging
Nature Communications (2025)
-
Accessing carbon, boron and germanium spiro stereocentres in a unified catalytic enantioselective approach
Nature Catalysis (2025)
-
Rhodium-catalyzed construction of boron-based point and axial chirality via asymmetric annulation of alkynylborons
Nature Communications (2025)