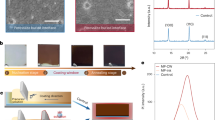
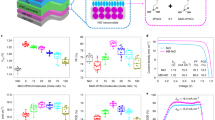
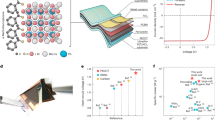
Abstract
Flexible perovskite solar cells hold promises for lightweight photovoltaics, yet their performance, durability and scalability lag behind rigid counterparts. Conventional efficiency-enhancing strategies, such as grain enlargement or lead iodide passivation, often degrade mechanical robustness. Here we combine data-driven machine learning with a passivation approach to overcome this trade-off. We design β-cyclodextrin derivatives that form in situ self-assembled amorphous grain boundaries, enhancing optoelectronic properties and mechanical resilience through coordination bonds, hydrogen bonds and host–guest interactions. We achieve flexible solar cells with an efficiency of 24.52% and enhanced durability: 92.5% efficiency retention after 10,000 bending cycles, 95% after 300 days in ambient air and 80% under 650 h of maximum power point tracking. We demonstrate modules with certified efficiencies of 21.09% (aperture area: 21.07 cm2) and 17.38% (aperture area: 0.5 m2, 86.9 W). Larger-area module (aperture area: 1.4725 m2) delivers 226 W power output and power per weight of 558 W kg−1. Our work addresses critical barriers in flexible perovskite photovoltaics.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$32.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available within the article and its Supplementary Information. Source data are provided with this paper.
References
Miyasaka, T. Toward printable sensitized mesoscopic solar cells: light-harvesting management with thin TiO2 films. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2, 262–269 (2011).
Li, Y. et al. High-efficiency robust perovskite solar cells on ultrathin flexible substrates. Nat. Commun. 7, 10214 (2016).
Meng, X. et al. Bio-inspired vertebral design for scalable and flexible perovskite solar cells. Nat. Commun. 11, 3016 (2020).
Kaltenbrunner, M. et al. Flexible high power-per-weight perovskite solar cells with chromium oxide-metal contacts for improved stability in air. Nat. Mater. 14, 1032–1039 (2015).
Li, L. et al. Flexible all-perovskite tandem solar cells approaching 25% efficiency with molecule-bridged hole-selective contact. Nat. Energy 7, 708–717 (2022).
Wang, Y. et al. Utilizing electrostatic dynamic bonds in zwitterion elastomer for self-curing of flexible perovskite solar cells. Joule 8, 1120–1141 (2024).
Zhang, C. et al. Occlusal architecture of the buried interface enables record-efficiency flexible perovskite photovoltaic modules with enhanced in-plane bending mechanical endurance. Adv. Funct. Mater. 34, 2313910 (2024).
Lee, D. S. et al. Overcoming stability limitations of efficient, flexible perovskite solar modules. Joule 8, 1380–1393 (2024).
Xu, X. et al. Multifunctional entinostat enhances the mechanical robustness and efficiency of flexible perovskite solar cells and minimodules. Nat. Photonics 18, 379–387 (2024).
Best research-cell efficiencies. NREL https://www.nrel.gov/pv/cell-efficiency (2024).
Luo, D. et al. Minimizing non-radiative recombination losses in perovskite solar cells. Nat. Rev. Mater. 5, 44–60 (2019).
Ni, N. et al. Resolving spatial and energetic distributions of trap states in metal halide perovskite solar cells. Science 367, 1352–1358 (2020).
Ball, J. M. & Petrozza, A. Defects in perovskite-halides and their effects in solar cells. Nat. Energy 1, 16149 (2016).
Chen, Q. et al. Controllable self-induced passivation of hybrid lead iodide perovskites toward high performance solar cells. Nano Lett. 14, 4158–4163 (2014).
Yang, W. S. et al. Iodide management in formamidinium-lead-halide-based perovskite layers for efficient solar cells. Science 356, 1376–1379 (2017).
Bi, D. et al. Efficient luminescent solar cells based on tailored mixed-cation perovskites. Sci. Adv. 2, e1501170 (2016).
Burschka, J. et al. Sequential deposition as a route to high-performance perovskite-sensitized solar cells. Nature 499, 316–319 (2013).
Yoo, J. J. et al. Efficient perovskite solar cells via improved carrier management. Nature 590, 587–593 (2021).
Rolston, N. et al. Effect of cation composition on the mechanical stability of perovskite solar cells. Adv. Energy Mater. 8, 1702116 (2017).
Azmi, R. et al. Damp heat-stable perovskite solar cells with tailored-dimensionality 2D/3D heterojunctions. Science 376, 73–77 (2022).
Chen, H. et al. Quantum-size-tuned heterostructures enable efficient and stable inverted perovskite solar cells. Nat. Photonics 16, 352–358 (2022).
Park, S. M. et al. Engineering ligand reactivity enables high-temperature operation of stable perovskite solar cells. Science 381, 209–215 (2023).
Azmi, R. et al. Double-side 2D/3D heterojunctions for inverted perovskite solar cells. Nature 628, 93–98 (2024).
Ma, K. et al. Holistic energy landscape management in 2D/3D heterojunction via molecular engineering for efficient perovskite solar cells. Sci. Adv. 9, eadg0032 (2023).
deQuilettes, D. W. et al. Reduced recombination via tunable surface fields in perovskite thin films. Nat. Energy 9, 457–466 (2024).
Wen, J. et al. Heterojunction formed via 3D-to-2D perovskite conversion for photostable wide-bandgap perovskite solar cells. Nat. Commun. 14, 7118 (2023).
Degani, M. et al. 23.7% Efficient inverted perovskite solar cells by dual interfacial modification. Sci. Adv. 7, eabj7930 (2021).
Ferdowsi, P. et al. Supramolecular interactions using β-cyclodextrin in controlling perovskite solar cell performance. J. Mater. Chem. A 12, 15837–15846 (2024).
Masi, S. et al. Connecting the solution chemistry of PbI2 and MAI: a cyclodextrin-based supramolecular approach to the formation of hybrid halide perovskites. Chem. Sci. 9, 3200–3208 (2018).
Nomura, K. et al. Room-temperature fabrication of transparent flexible thin-film transistors using amorphous oxide semiconductors. Nature 432, 488–492 (2004).
Ge, C. et al. Thermal dynamic self-healing supramolecular dopant towards efficient and stable flexible perovskite solar cells. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 61, e202116602 (2022).
Shi, P. et al. Oriented nucleation in formamidinium perovskite for photovoltaics. Nature 620, 323–327 (2023).
Liu, C. et al. Flexible indoor perovskite solar cells by in situ bottom-up crystallization modulation and interfacial passivation. Adv. Mater. 36, 2311562 (2024).
Chen, H. et al. Cyclodextrin-assisted supramolecular host-guest inclusion for durable and sustainable optoelectronics. Microstructures 4, 2024031 (2024).
Kondo, S. Spectral analysis of optical absorption near the fundamental edge in amorphous lead halides. Phys. Stat. Sol. A 153, 529–537 (1996).
Tian, T. et al. Large-area waterproof and durable perovskite luminescent textiles. Nat. Commun. 14, 234 (2023).
Kumar, M. H. et al. Flexible, low-temperature, solution processed zno-based perovskite solid state solar cells. Chem. Commun. 49, 11089–11091 (2013).
Liu, D. et al. Perovskite solar cells with a planar heterojunction structure prepared using room-temperature solution processing techniques. Nat. Photonics 8, 133–138 (2014).
Yang, D. et al. High efficiency flexible perovskite solar cells using superior low temperature TiO2. Energy Environ. Sci. 8, 3208–3214 (2015).
Kim, B. J. et al. Highly efficient and bending durable perovskite solar cells: toward a wearable power source. Energy Environ. Sci. 8, 916–921 (2015).
Yoon, J. et al. Superflexible, high-efficiency perovskite solar cells utilizing graphene electrodes: towards future foldable power sources. Energy Environ. Sci. 10, 337–345 (2017).
Bi, C. et al. Efficient flexible solar cell based on composition-tailored hybrid perovskite. Adv. Mater. 29, 1605900 (2017).
Feng, J. et al. Record efficiency stable flexible perovskite solar cell using effective additive assistant strategy. Adv. Mater. 30, 1801418 (2018).
Wang, Z. et al. Rational interface design and morphology control for blade-coating efficient flexible perovskite solar cells with a record fill factor of 81%. Adv. Funct. Mater. 30, 2001240 (2020).
Yang, L. et al. Artemisinin-passivated mixed-cation perovskite films for durable flexible perovskite solar cells with over 21% efficiency. J. Mater. Chem. A 9, 1574–1582 (2021).
Wu, S. et al. Low-bandgap organic bulk-heterojunction enabled efficient and flexible perovskite solar cells. Adv. Mater. 33, 2105539 (2021).
Wu, Y. et al. In situ crosslinking-assisted perovskite grain growth for mechanically robust flexible perovskite solar cells with 23.4% efficiency. Joule 7, 398–415 (2023).
Xie, L. et al. Molecular dipole engineering-assisted strain release for mechanically robust flexible perovskite solar cells. Energy Environ. Sci. 16, 5423–5433 (2023).
Wu, Y. et al. Stereoscopic polymer network for developing mechanically robust flexible perovskite solar cells with an efficiency approaching 25%. Adv. Mater. 36, 2403531 (2024).
Fukuda, K. et al. A bending test protocol for characterizing the mechanical performance of flexible photovoltaics. Nat. Energy 9, 1335–1343 (2024).
Sun, L. et al. A flexible photovoltaic fatigue factor for quantification of mechanical device performance. Adv. Funct. Mater. 35, 2422706 (2025).
Wang, H. et al. An in situ bifacial passivation strategy for flexible perovskite solar module with mechanical robustness by roll-to-roll fabrication. J. Mater. Chem. A 9, 5759–5768 (2021).
Xue, T. et al. Mechanically robust and flexible perovskite solar cells via a printable and gelatinous interface. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 13, 19959–19969 (2021).
Wang, Z. et al. An embedding 2D/3D heterostructure enables high-performance FA-alloyed flexible perovskite solar cells with efficiency over 20%. Adv. Sci. 8, 2101856 (2021).
Fan, B. et al. A bionic interface to suppress the coffee-ring effect for reliable and flexible perovskite modules with a near-90% yield rate. Adv. Mater. 34, 2201840 (2022).
Yang, X. et al. Scalable flexible perovskite solar cells based on a crystalline and printable template with intelligent temperature sensitivity. Sol. RRL 6, 2100991 (2022).
Park, M. et al. Scalable production of high performance flexible perovskite solar cells via film-growth-megasonic-spray-coating system. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. Green. Technol. 10, 1223–1234 (2023).
Zhang, R. et al. A self-assembled vertical-gradient and well-dispersed mxene structure for flexible large-area perovskite modules. Adv. Funct. Mater. 33, 2210063 (2023).
Xu, Y. et al. Uniform coverage functional layers enable high-efficient flexible perovskite solar modules with an outstanding fill factor. Sol. RRL 7, 2300283 (2023).
Kim, U. et al. Foldable perovskite solar cells and modules enabled by mechanically engineered ultrathin indium-tin-oxide electrodes. Adv. Energy Mater. 13, 2203198 (2023).
Tong, X. et al. Large orientation angle buried substrate enables efficient flexible perovskite solar cells and modules. Adv. Mater. 36, 2407032 (2024).
Gong, C. et al. An equalized flow velocity strategy for perovskite colloidal particles in flexible perovskite solar cells. Adv. Mater. 36, 2405572 (2024).
Tu, S. et al. Engineering a thermally robust hole-selective layer for stable flexible perovskite solar cells. Chem. Eng. J. 503, 158389 (2025).
Zhang, W. et al. Chemical passivation and grain-boundary manipulation via in situ cross-linking strategy for scalable flexible perovskite solar cells. Sci. Adv. 11, eadr2290 (2025).
Liu, C. et al. Dimensional regulation of organic n-type dopants for highly efficient perovskite solar cells and modules. Adv. Mater. 37, e2417251 (2025).
Du, J. et al. Face-on oriented self-assembled molecules with enhanced π-π stacking for highly efficient inverted perovskite solar cells on rough FTO substrate. Energy Environ. Sci. 18, 3196–3210 (2025).
Zhong, H. et al. Hydrophobic surface release and energy-level alignment of PTAA enabling stable flexible perovskite solar modules. J. Energy Chem. 109, 448–454 (2025).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (62475103,62005099), Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation (2021B1515120003). We sincerely thank our colleagues, Y. Deng from Chongqing University and R. Chen from Hubei University of Technology, for their valuable suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
S.W., J.F., L.H. and Y. Mai conceived the idea for the manuscript and designed the experiments. M.H., Y. Ma, L.L., H.Z., Y.J. Z.Z., W.M. and H.T. conducted sample preparation, device fabrication, optimization and characterization. Y. Ma conducted the in situ XRD and photoluminescence measurements. W.D. and J.F. performed the machine learning and calculations. M.H., H.L., H.T., Yanyan Gao, Yin Gao, C.Z. and C.L. assisted with solar cell and module fabrication and characterizations. M.H. and Y. Ma wrote the manuscript. S.W. and J.F. revised the manuscript. S.W., J.F., L.H. and Y. Mai led the project. All authors were involved in discussions of data analysis and commented on the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Energy thanks the anonymous reviewers for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary text, Figs. 1–35 and Tables 1–7.
Supplementary Data
Molecular structure of A\B\C.
Source data
Source Data Fig. 3
Source data of figure.
Source Data Fig. 4
Source data of figure.
Source Data Fig. 5
Source data of figure.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
He, M., Ma, Y., Wu, S. et al. Amorphous grain boundary engineering for scalable flexible perovskite photovoltaics with improved stability. Nat Energy (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41560-025-01932-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41560-025-01932-4