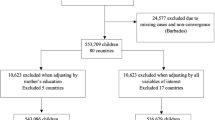
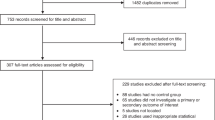
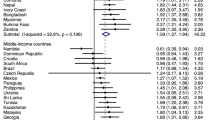
Abstract
Research from high-income countries has found negative outcomes associated with physical punishment. Yet, the extent to which such research evidence generalizes to children in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs) is largely unknown. The objective of the current pre-registered study (PROSPERO: CRD42022347346) was to conduct a meta-analysis of the associations between childhood physical punishment and individual outcomes in LMICs. We identified eligible articles by searching for keywords related to physical punishment in six languages across 11 databases, with search periods from April to August 2021 and June to July 2024. This process yielded 5,072 unique records, of which 189 studies, comprising 1,490 unique effect sizes and representing 92 LMICs, met our inclusion criteria. Findings from random-effects multilevel meta-analyses indicated that physical punishment was associated with detrimental outcomes, including mental health problems, worse parent–child relationships, substance use, impaired social–emotional development, negative academic outcomes and heightened externalizing behaviour problems, among others. Despite some variation by contextual and study-level characteristics, all subgroup estimates were consistent in direction. Sensitivity checks indicated that these findings were not typical of other non-violent methods of discipline but were specific to physical punishment and psychological aggression. The analysis confirmed that physical punishment is associated with detrimental outcomes for individuals in LMICs. Additional research is needed to inform the design, implementation, and evaluation of policies and interventions to prevent the physical punishment of children and adolescents worldwide.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$32.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
We compiled the data for this study on the basis of the studies identified in our systematic literature review. Our data are available via our projects’ Open Science Framework repository at https://osf.io/kysc8/?view_only=671a44c0b0e240049cdc0346fe5250a0 (ref. 238). In the systematic review, we searched the following databases: APA PsycInfo, PubMed, EMBASE, ERIC, Sociological Abstracts, EconLit, Global Health, CINAHL Plus with Full Text, Academic Search Premier, Bibliography of Asian Studies, and Education Source.
References
Cuartas, J. et al. Early childhood exposure to non-violent discipline and physical and psychological aggression in low- and middle-income countries: national, regional, and global prevalence estimates. Child Abuse Negl. 92, 93–105 (2019).
Heekes, S.-L., Kruger, C. B., Lester, S. N. & Ward, C. L. A systematic review of corporal punishment in schools: global prevalence and correlates. Trauma Violence Abuse 23, 52–72 (2022).
Heilmann, A. et al. Physical punishment and child outcomes: a narrative review of prospective studies. Lancet 398, 355–364 (2021).
Gershoff, E. T. Corporal punishment by parents and associated child behaviors and experiences: a meta-analytic and theoretical review. Psychol. Bull. 128, 539–579 (2002).
Gershoff, E. T. & Grogan-Kaylor, A. Spanking and child outcomes: old controversies and new meta-analyses. J. Fam. Psychol. 30, 453–469 (2016).
Ferguson, C. J. Spanking, corporal punishment and negative long-term outcomes: a meta-analytic review of longitudinal studies. Clin. Psychol. Rev. 33, 196–208 (2013).
Visser, L. N., van der Put, C. E. & Assink, M. The association between school corporal punishment and child developmental outcomes: a meta-analytic review. Children 9, 383 (2022).
Corporal Punishment and Health (World Health Organization, 2021); https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/corporal-punishment-and-health
UN Committee on the Rights of the Child. General Comment No. 8: The Right of the Child to Protection from Corporal Punishment and Other Cruel or Degrading Forms of Punishment (CRC/C/GC/8) (United Nations, 2007).
Countdown to Universal Prohibition (Global Initiative to End Corporal Punishment of Children, 2023); https://endcorporalpunishment.org/countdown/
World Bank Country and Lending Groups (World Bank, 2022); https://datahelpdesk.worldbank.org/knowledgebase/articles/906519-world-bank-country-and-lending-groups
Afifi, T. O. et al. Examining the relationships between parent experiences and youth self-reports of slapping/spanking: a population-based cross-sectional study. BMC Public Health 19, 1345 (2019).
Finkelhor, D., Turner, H., Wormuth, B. K., Vanderminden, J. & Hamby, S. Corporal punishment: current rates from a national survey. J. Child Fam. Stud. 28, 1991–1997 (2019).
Black, M. et al. Early childhood development coming of age: science through the life course. Lancet 389, 77–90 (2017).
Walker, S. et al. Inequality in early childhood: risk and protective factors for early child development. Lancet 378, 1325–1338 (2011).
Cuartas, J. Corporal punishment and child development in low- and- middle-income countries: progress, challenges, and directions. Child Psychiatry Hum. Dev. 54, 1607–1623 (2023).
Larzelere, R. E., Gunnoe, M. L. & Ferguson, C. J. Improving causal inferences in meta-analyses of longitudinal studies: spanking as an illustration. Child Dev. 89, 2038–2050 (2018).
Henrich, J., Heine, S. J. & Norenzayan, A. The weirdest people in the world? Behav. Brain Sci. 33, 61–83 (2010).
Nielsen, M., Haun, D., Kärtner, J. & Legare, C. H. The persistent sampling bias in developmental psychology: a call to action. J. Exp. Child Psychol. 162, 31–38 (2017).
Deater-Deckard, K. & Dodge, K. A. Externalizing behavior problems and discipline revisited: nonlinear effects and variation by culture, context, and gender. Psychol. Inq. 8, 161–175 (1997).
Bailey, D. H. et al. Causal inference on human behaviour. Nat. Hum. Behav. 8, 1448–1459 (2024).
Larzelere, R. E. & Kuhn, B. R. Comparing child outcomes of physical punishment and alternative disciplinary tactics: a meta-analysis. Clin. Child Fam. Psychol. Rev. 8, 1–37 (2005).
Duncan, G. J., Engel, M., Claessens, A. & Dowsett, C. J. Replication and robustness in developmental research. Dev. Psychol. 50, 2417–2425 (2014).
Cuartas, J., Gershoff, E. T., Bailey, D. & McCoy, D. C. Physical punishment and child, adolescent, and adult outcomes in low- and middle-income countries: protocol for systematic review and meta-analysis. Syst. Rev. 11, 276 (2022).
Sedgwick, P. Confidence intervals, P values, and statistical significance. BMJ 350, h1113 (2015).
Corboz, J., Hemat, O., Siddiq, W. & Jewkes, R. Children’s peer violence perpetration and victimization: prevalence and associated factors among school children in Afghanistan. PLoS ONE 13, e0192768 (2018).
Lansford, J. E. et al. Physical discipline and children’s adjustment: cultural normativeness as a moderator. Child Dev. 76, 1234–1246 (2005).
Wain, K. U. R. & Saeed, M. Effect of teacher and parent-related factors on Pakistani secondary grade students' achievement in physics. Int. J. Sci. Soc. 2, 51 (2011).
Madhlopa, Y., Qin, J. & Chen, C. The relationships between child maltreatment and child behavior problems. Comparative study of Malawi and China. Child. Youth Serv. Rev. 119, 105533 (2020).
Roopnarine, J., Jin, B. & Krishnakumar, A. Do Guyanese mothers’ levels of warmth moderate the association between harshness and justness of physical punishment and preschoolers’ prosocial behaviours and anger? Int. J. Psychol. 49, 271–279 (2014).
Roopnarine, J., Krishnakumar, A., Narine, L., Logie, C. & Lape, M. E. Relationships between parenting practices and preschoolers’ social skills in African, Indo, and mixed-ethnic families in Trinidad and Tobago: the mediating role of ethnic socialization. J. Cross Cult. Psychol. 45, 362–380 (2014).
Abolfotouh, M. A., El-Bourgy, M. D., El Din, A. G. S. & Mehanna, A. A. Corporal punishment: mother’s disciplinary behavior and child’s psychological profile in Alexandria, Egypt. J. Forensic Nurs. 5, 5–17 (2009).
Agudelo-Hernández, F., Vélez Botero, H. & Rojas-Andrade, R. Identification of factors associated with suicidal behavior in Colombian indigenous children and adolescents. Int. J. Ment. Health https://doi.org/10.1080/00207411.2024.2334479 (2024).
Ahmad, I. & Smetana, J. Palestinian refugee youth in Jordan: parental practices, neighborhood cohesion and assistance, and adolescent wellbeing. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 18, 3649 (2021).
Alampay, L. P. et al. Severity and justness do not moderate the relation between corporal punishment and negative child outcomes: a multicultural and longitudinal study. Int. J. Behav. Dev. 41, 491–502 (2017).
Ali, A., Malik, M. A. & Khan, I. Psychological trauma and corporal punishment. Glob. Soc. Sci. Rev. IV, 102–109 (2019).
Alvarenga, P., Magalhães, M. D. O. & Gomes, Q. D. S. Relações entre práticas educativas maternas e problemas de externalização em pré-escolares. Estud. Psicol. 29, 33–42 (2012).
Amirshamsi, E., Fazel, A. & Hosseini, S. M. Forecast welfare psychological wellbeing of children based on child rearing methods by parents and family communication patterns. Ind. J. Posit. Psychol. 7, 5–8 (2016).
Anih, A. S., Söderberg, P. A. & Björkqvist, K. The effect of exposure to armed conflict on depression as mediated by physical punishment: a study among Nigerian adolescents. J. Aggress. Confl. Peace Res. 15, 360–371 (2023).
Araujo, M. F. M., Silva, E. P. & Ludermir, A. B. Maternal educational practices and mental health disorders of school-age children. J. Pediatr. 99, 193–202 (2023).
Aydin, Y. E., Altindag, A. & Ozkan, M. Childhood traumatic events and dissociation in university students. Int. J. Psychiatry Clin. Pract. 13, 25–30 (2009).
Bérgamo, L. P. D. & Bazon, M. R. Experiências infantis e risco de abuso físico: mecanismos envolvidos na repetição da violência. Psicol. Reflex. Crít. 24, 710–719 (2011).
Baker-Henningham, H., Meeks-Gardner, J., Chang, S. & Walker, S. Experiences of violence and deficits in academic achievement among urban primary school children in Jamaica. Child Abuse Negl. 33, 296–306 (2009).
Bakoula, C., Kolaitis, G., Veltsista, A., Gika, A. & Chrousos, G. P. Parental stress affects the emotions and behaviour of children up to adolescence: a Greek prospective, longitudinal study. Stress 12, 486–498 (2009).
Balan, R., Dobrean, A., Roman, G. & Balazsi, R. Indirect effects of parenting practices on internalizing problems among adolescents: the role of expressive suppression. J. Child Fam. Stud. 26, 40–47 (2017).
Bansal, V., Goyal, S. & Srivastava, K. Study of prevalence of depression in adolescent students of a public school. Ind. Psychiatry J. 18, 43–46 (2009).
Becirovic, E., Avdibegović, E., Softic, R., Mirković Hajdukov, M. & Bećirović, A. Adverse childhood experiences as risk factor for combat-related PTSD. Acta Med. Sal. https://doi.org/10.5457/10.5457/400 (2017).
Bieliauskaitė, R., Garckija, R. & Jusienė, R. Bronchine astma sergančių ikimokyklinio amžiaus vaikų psichologinio prisitaikymo, tėvų konfliktiškumo ir auklėjimo būdų sąsajos. Psichologija 40, 37–52 (2009).
Bo, H., Gengli, Z., Wenkun, Z. & Lijun, C. The influence of parents’ health education on children’s behavioral problems. Chin. J. Ment. Health 20, 284–287 (2006).
Bordin, I. A., Handegård, B. H., Paula, C. S., Duarte, C. S. & Rønning, J. A. Home, school, and community violence exposure and emotional and conduct problems among low-income adolescents: the moderating role of age and sex. Soc. Psychiatry Psychiatr. Epidemiol. 57, 95–110 (2022).
Bordin, I. A., Paula, C. S., do Nascimento, R. & Duarte, C. S. Severe physical punishment and mental health problems in an economically disadvantaged population of children and adolescents. Braz. J. Psychiatry 28, 290–296 (2006).
Brajović, M. et al. Impact of adverse childhood experiences on alcohol use in emerging adults in Montenegro and Romania. Zdr. Varst. 58, 129–138 (2019).
Bucheli, M. & Rossi, M. Transmisión intergeneracional del castigo físico en la niñez. Rev. Econ. Rosario 24, 1–15 (2021).
Burela, A., Piazza, M., Alvarado, G. F., Gushiken, A. & Fiestas, F. [Acceptability of physical punishment in child rearing by people who were victims of physical violence during childhood in Peru]. Rev. Peru Med. Exp. Salud Publica 31, 669–675 (2014).
Burlaka, V. Externalizing behaviors of Ukrainian children: the role of parenting. Child Abuse Negl. 54, 23–32 (2016).
Burlaka, V. et al. The role of adverse childhood experiences and corporal punishment in early adulthood depression and substance use among Ukrainian college students. J. Fam. Violence 35, 285–295 (2020).
Burlaka, V. et al. Parenting practices, bullying perpetration, and conduct problems among Ukrainian children. Child Abuse Negl. 161, 106508 (2025).
Burlaka, V. et al. Bullying victimization among Ukrainian college students: the role of family communication and satisfaction, corporal punishment and child abuse. J. Fam. Issues 44, 1129–1148 (2023).
Cai, Z., Wang, M. & Wang, F. Actor–partner analyses of the associations between harsh discipline and parent–child relationships in China. J. Interpers. Violence 36, 9691–9708 (2021).
Castro, R., Cerellino, L. & Rivera, R. Risk factors of violence against women in Peru. J. Fam. Violence 32, 807–815 (2017).
Chen, J. Q. et al. [A retrospective survey of childhood corporal punishment by school teachers in students]. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi 44, 26–30 (2006).
Chen, J. & Liao, W. Childhood non-contact corporal punishment revealed in the questionnaire survey of technical secondary school students. Chin. Ment. Health J. 19, 243–246 (2005).
Cheng, H. G., Anthony, J. C. & Huang, Y. Harsh physical punishment as a specific childhood adversity linked to adult drinking consequences: evidence from China. Addiction 105, 2097–2105 (2010).
Cheng, H. G. et al. Childhood physical punishment and the onset of drinking problems: evidence from metropolitan China. Drug Alcohol Depend. 118, 31–39 (2011).
Cheng, H. G., Huang, Y. & Anthony, J. C. Childhood physical punishment and later alcohol drinking consequences: evidence from a Chinese context. J. Stud. Alcohol Drugs 72, 24–33 (2011).
Csémy, L., Hrachovinová, T., Čáp, P. & Starostová, O. Agresivní chování dospívajících: prevalence a analýza vlivu faktorů z oblasti rodiny, vrstevnických vztahů a školy. Česk. Psychol. 58, 242–252 (2014).
Cuartas, J. Neighborhood crime undermines parenting: violence in the vicinity of households as a predictor of aggressive discipline. Child Abuse Negl. 76, 388–399 (2018).
Cuartas, J. Corporal punishment and early childhood development in 49 low- and middle-income countries. Child Abuse Negl. 120, 105205 (2021).
Cuartas, J., Grogan-Kaylor, A., Ma, J. & Castillo, B. Civil conflict, domestic violence, and poverty as predictors of corporal punishment in Colombia. Child Abuse Negl. 90, 108–119 (2019).
Cuartas, J., McCoy, D. C., Grogan-Kaylor, A. & Gershoff, E. Physical punishment as a predictor of early cognitive development: evidence from econometric approaches. Dev. Psychol. 56, 2013–2026 (2020).
Cuartas, J., Ward, K. P., Ma, J. & Grogan-Kaylor, A. Physical punishment and Colombian children and adolescents’ cognitive and behavioral outcomes. J. Appl. Dev. Psychol. 68, 101140 (2020).
Cuartas, J. The effect of spanking on early social-emotional skills. Child Dev. 93, 180–193 (2022).
Cuartas, J. The effect of maternal education on parenting and early childhood development: an instrumental variables approach. J. Fam. Psychol. 36, 280–290 (2022).
Daryanavard, A. et al. Prevalence of depression among high school students and its relation to family structure. Am. J. Appl. Sci. 8, 39–44 (2011).
Deb, S., Kumar, A., Holden, G. W. & Simpson Rowe, L. School corporal punishment, family tension, and students’ internalizing problems: evidence from India. Sch. Psychol. Int. 38, 60–77 (2016).
Dede Yildirim, E. & Roopnarine, J. Positive discipline, harsh physical discipline, physical discipline and psychological aggression in five Caribbean countries: associations with preschoolers’ early literacy skills. Int. J. Psychol. 54, 342–350 (2019).
Dede Yildirim, E., Roopnarine, J. & Abolhassani, A. Maternal use of physical and non-physical forms of discipline and preschoolers’ social and literacy skills in 25 African countries. Child Abuse Negl. 106, 104513 (2020).
Dilbaz, N. & Aytekin, Y. Alkol bağimlilarinda intihar düşüncesi, davranişi ve niyeti. J. Depend. 4, 1–9 (2003).
Dominiak-Kochanek, M. & Frączek, A. Retrospektywna ocena doświadczania kar fizycznych w dzieciństwie a wzorce gotowości do agresji u młodych dorosłych. Psychol. Roz. 19, 69–84 (2014).
Dominiak-Kochanek, M., Konopka, K., Rutkowska, M., Frączek, A. & Ramirez, J. M. Direct and indirect effects of parenting practices on socio-moral approval of aggression in Polish young adults. Do all practices matter? Int. J. Psychol. 53, 200–209 (2018).
Dong, S., Dong, Q. & Chen, M. The relationship between grandparents’ violent discipline and school bullying behavior among left-behind children. J. Interpers. Violence 40, 177–203 (2025).
Duc, N. H. Developmental risk factors in Vietnamese preschool-age children: cross-sectional survey. Pediatr. Int. 58, 14–21 (2016).
Eisenberg, N., Chang, L., Ma, Y. & Huang, X. Relations of parenting style to Chinese children’s effortful control, ego resilience, and maladjustment. Dev. Psychopathol. 21, 455–477 (2009).
Erkman, F. & Rohner, R. P. Youths’ perceptions of corporal punishment, parental acceptance, and psychological adjustment in a Turkish metropolis. Cross Cult. Res. 40, 250–267 (2006).
Fu, C. & Wang, M. Parental corporal punishment and girls’ self-esteem: the moderating effects of girls’ agency and communion in China. Sex Roles 84, 392–403 (2021).
Fu, C., Niu, H. & Wang, M. Parental corporal punishment and children’s problem behaviors: the moderating effects of parental inductive reasoning in China. Child. Youth Serv. Rev. 99, 1–9 (2019).
Gülseven, Z. et al. Longitudinal relations among parenting daily hassles, child rearing, and prosocial and aggressive behaviors in Turkish children. Soc. Dev. 27, 45–57 (2018).
Gage, A. J. & Silvestre, E. A. Maternal violence, victimization, and child physical punishment in Peru. Child Abuse Negl. 34, 523–533 (2010).
Gershoff, E. T. et al. Parent discipline practices in an international sample: associations with child behaviors and moderation by perceived normativeness. Child Dev. 81, 487–502 (2010).
Goodman, A., Fleitlich-Bilyk, B., Patel, V. & Goodman, R. Child, family, school and community risk factors for poor mental health in Brazilian schoolchildren. J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 46, 448–456 (2007).
Grogan-Kaylor, A. et al. Global perspectives on physical and nonphysical discipline: a Bayesian multilevel analysis. Int. J. Behav. Dev. 45, 216–225 (2021).
Gundersen, S. & McKay, M. Reward or punishment? An examination of the relationship between teacher and parent behavior and test scores in the Gambia. Int. J. Educ. Dev. 68, 20–34 (2019).
Halgunseth, L. et al. Parenting and adolescent adjustment in Mexico: initial evidence of validity for the Mexican Parenting Questionnaire for Adolescents (MPQ-A). J. Child Fam. Stud. 26, 471–481 (2017).
Hardt, P. D. J., Kreutzberger, C., Schier, K. & Laubach, W. Kindheitsbelastungen und Symptome der Sozialen Phobie und Agoraphobie im Erwachsenenalter. Z. Psychosom. Med. Psychother. 64, 144–157 (2018).
He, G.-H. et al. Interpersonal conflict, school connectedness and depressive symptoms in Chinese adolescents: moderation effect of gender and grade level. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 16, 2182 (2019).
Hecker, T., Hermenau, K., Isele, D. & Elbert, T. Corporal punishment and children’s externalizing problems: a cross-sectional study of Tanzanian primary school aged children. Child Abuse Negl. 38, 884–892 (2014).
Hensels, I. S. et al. Do not forget the boys - gender differences in children living in high HIV-affected communities in South Africa and Malawi in a longitudinal, community-based study. AIDS Care 28, 100–109 (2016).
Hesketh, T. et al. Behaviour problems in Chinese primary school children. Soc. Psychiatry Psychiatr. Epidemiol. 46, 733–741 (2011).
Huang, Y. et al. Association between violent discipline at home and risk of illness and injury in children: findings from a cross-sectional study in rural western China. J. Interpers. Violence 37, NP11413–NP11435 (2022).
Illachura, V. C., Montesinos-Malpartida, M. I., Bellido-Boza, L., Puyén, Z. M. & Blitchtein-Winicki, D. Physical punishment and effective verbal communication in children aged 9–36 months, according to sex: secondary analysis of a national survey. BMC Pediatr. 24, 134 (2024).
Islam, M. M., Khan, J. R., Kabir, A., Khan, M. Z. R. & Islam, M. M. Associations of socio-demographic and environmental factors with the early development of young children in Bangladesh. Int. J. Early Child. 53, 175–196 (2021).
Islam, S. & Akhter, T. Magnitude and effect of punishment on psychosocial development of urban and rural school children in Bangladesh. Ind. J. Posit. Psychol. 6, 326–330 (2015).
Jeyaseelan, L. et al. Physical spousal violence against women in India: some risk factors. J. Biosoc. Sci. 39, 657–670 (2007).
Jeyaseelan, L. et al. World studies of abuse in the family environment–risk factors for physical intimate partner violence. Inj. Control Saf. Promot. 11, 117–124 (2004).
Jiang, S., Jiang, C., Cheng, Y. & Hu, W. Understanding the relationship between corporal punishment and adolescent externalizing problems: the roles of psychological distress and parent–child relationship. Curr. Psychol. 42, 27668–27677 (2023).
Kamran, Z. & Kazi, A. Association between harsh disciplinary methods and child functioning in children aged 7–14 years in Punjab, Pakistan. J. Interpers. Violence 39, 4549–14572 (2024).
Khatab, K., Raheem, M. A., Sartorius, B. & Ismail, M. Prevalence and risk factors for child labour and violence against children in Egypt using Bayesian geospatial modelling with multiple imputation. PLoS ONE 14, e0212715 (2019).
Khayyer, M. Perceived locus of control as a function of parental physical punishment among a group of Iranian children. Psychol. Rep. 93, 288–290 (2003).
Khuwaja, H. M. A. et al. The intersection of school corporal punishment and associated factors: baseline results from a randomized controlled trial in Pakistan. PLoS ONE 13, e0206032 (2018).
Kohrt, H. E., Kohrt, B. A., Waldman, I., Saltzman, K. & Carrion, V. G. An ecological–transactional model of significant risk factors for child psychopathology in Outer Mongolia. Child Psychiatry Hum. Dev. 35, 163–181 (2004).
Krishnakumar, A., Narine, L., Roopnarine, J. & Logie, C. Multilevel and cross-level effects of neighborhood and family influences on children’s behavioral outcomes in Trinidad and Tobago: the intervening role of parental control. J. Abnorm. Child Psychol. 42, 1057–1068 (2014).
Lansford, J. E. et al. Reward sensitivity, impulse control, and social cognition as mediators of the link between childhood family adversity and externalizing behavior in eight countries. Dev. Psychopathol. 29, 1675–1688 (2017).
Lansford, J. E. et al. Children’s perceptions of maternal hostility as a mediator of the link between discipline and children’s adjustment in four countries. Int. J. Behav. Dev. 34, 452–461 (2010).
Lansford, J. E. et al. Corporal punishment, maternal warmth, and child adjustment: a longitudinal study in eight countries. J. Clin. Child Adolesc. Psychol. 43, 670–685 (2014).
Lastrić, G. & Torlak, B. Povezanost fizičkog kažnjavanja i dječije agresivnosti. Med. Glas. 5, 115–120 (2008).
Lau, J. T. et al. Psychological distress among adolescents in Chengdu, Sichuan at 1 month after the 2008 Sichuan earthquake. J. Urban Health 87, 504–523 (2010).
Laurenzi, C. A. et al. Associations between young children’s exposure to household violence and behavioural problems: evidence from a rural Kenyan sample. Glob. Public Health 15, 173–184 (2020).
Le, K. & Nguyen, M. ‘Bad Apple’ peer effects in elementary classrooms: the case of corporal punishment in the home. Educ. Econ. 27, 557–572 (2019).
Leto, I. V., Petrenko, E. N. & Slobodskaya, H. R. Life satisfaction in Russian primary schoolchildren: links with personality and family environment. J. Happiness Stud. 20, 1893–1912 (2019).
Li, J., Wang, M., Liu, X. & Zhang, H. Developmental cascades of preschoolers’ effortful control, externalizing behaviors, and parental corporal punishment in China. J. Interpers. Violence 37, NP1322–NP1347 (2020).
Li, W. et al. Prevalence, correlates of major depression: a mental health survey among undergraduates at a mainland Chinese university. Asia Pac. Psychiatry 8, 206–214 (2016).
Li, Z., Yu, C., Nie, Y. & Liu, Q. Parental corporal punishment, peer victimization, and aggressive adolescent behavior: the moderating effect of parent–adolescent relationship. J. Child Fam. Stud. 31, 949–961 (2022).
Li, Z., Xu, X. & Xing, X. The intergenerational transmission of executive function: the mediating effect of parental harsh discipline. Child Abuse Negl. 136, 106019 (2023).
Lin, X. et al. Family risk factors associated with oppositional defiant disorder symptoms, depressive symptoms, and aggressive behaviors among Chinese children with oppositional defiant disorder. Front. Psychol. 10, 2062 (2019).
Liu, B., Wei, Z.-m., Xing, X.-p. & Wang, M.-f. Relations between paternal and maternal harsh disciplines and junior middle school students' externalizing problem behaviors. Chin. J. Clin. Psychol. 20, 842–845 (2012).
Liu, L. & Wang, M. Parental harsh discipline and adolescent problem behavior in China: perceived normativeness as a moderator. Child Abuse Negl. 86, 1–9 (2018).
Liu, L. & Wang, M. Parental corporal punishment and child anxiety in China: the moderating role of HPA-axis activity. J. Affect. Disord. 273, 500–507 (2020).
Liu, L., Zhai, P. & Wang, M. Parental harsh discipline and migrant children’s anxiety in China: the moderating role of parental warmth and gender. J. Interpers. Violence 37, NP18761–NP18783 (2021).
Liu, R. X. Physical discipline and verbal punishment: an assessment of domain and gender-specific effects on delinquency among Chinese adolescents. Youth Soc. 50, 871–890 (2018).
Liu, R. X. The relative effects of physical and verbal discipline and gender variations on adolescents’ bonds to parents: a case of urban China. J. Fam. Stud. 28, 529–550 (2022).
Liu, W., Guo, S., Qiu, G. & Zhang, S. X. Corporal punishment and adolescent aggression: an examination of multiple intervening mechanisms and the moderating effects of parental responsiveness and demandingness. Child Abuse Negl. 115, 105027 (2021).
Liu, X., Sun, Z. & Yang, Y. Parent-reported suicidal behavior and correlates among adolescents in China. J. Affect. Disord. 105, 73–80 (2008).
Liu, L., Wang, Y., Zhao, J. & Wang, M. Parental reports of stress and anxiety in their migrant children in China: the mediating role of parental psychological aggression and corporal punishment. Child Abuse Negl. 131, 105695 (2022).
Liu, W., Qiu, G., Zhang, S. X. & Fan, Q. Corporal punishment, self-control, parenting style, and school bullying among chinese adolescents: a conditional process analysiS. J. Sch. Violence 21, 4–18 (2022).
Logan, M. W., Pare, P.-P. & Dulisse, B. Parental discipline and child psychosocial outcomes in Iraq and Kurdistan: evidence from a nationally representative sample. J. Interpers. Violence 37, 1223–12471 (2022).
Lopez Boo, F., Mateus, M. C. & Duryea, S. Analysis of socioeconomic gradients in the development of children aged 0–3 years in Fortaleza, Northeastern Brazil. Rev. Saude Publica 52, 84 (2018).
Ma, J. et al. Family correlates of emotional and behavioral problems in Nepali school children. PLoS ONE 17, e0262690 (2022).
Ma, J., Grogan-Kaylor, A. & Delva, J. Behavior problems among adolescents exposed to family and community violence in Chile. Fam. Rel. 65, 502–516 (2016).
Ma, J., Han, Y., Grogan-Kaylor, A., Delva, J. & Castillo, M. Corporal punishment and youth externalizing behavior in Santiago, Chile. Child Abuse Negl. 36, 481–490 (2012).
Ma, J., Grogan-Kaylor, A. C., Pace, G. T., Ward, K. P. & Lee, S. J. The association between spanking and physical abuse of young children in 56 low- and middle-income countries. Child Abuse Negl. 129, 105662 (2022).
Macedo, A., Sherr, L., Tomlinson, M., Skeen, S. & Roberts, K. Parental bereavement in young children living in South Africa and Malawi: understanding mental health resilience. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 78, 390–398 (2018).
Maciel, M. et al. Children working on the streets in Brazil: predictors of mental health problems. Eur. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 22, 165–175 (2013).
Maiti, A. Effect of corporal punishment on young children’s educational outcomes. Educ. Econ. 29, 411–423 (2021).
Malhi, P. & Ray, M. Prevalence and correlates of corporal punishment among adolescents. Stud. Psychol. 46, 219–228 (2004).
Meeks Gardner, J. M., Powell, C. A. & Grantham-McGregor, S. M. Determinants of aggressive and prosocial behaviour among Jamaican schoolboys. West Indian Med. J. 56, 34–41 (2007).
Mello, A. F. et al. Factors related to the cortisol awakening response of children working on the streets and siblings, before and after 2 years of a psychosocial intervention. Psychiatry Res. 225, 625–630 (2015).
Mello, A. F. et al. Exposure to maltreatment and urban violence in children working on the streets in São Paulo, Brazil: factors associated with street work. Rev. Bras. Psiquiatr. 36, 191–198 (2014).
Miller-Graff, L. E., Scheid, C. R., Guzmán, D. B. & Grein, K. Caregiver and family factors promoting child resilience in at-risk families living in Lima, Peru. Child Abuse Negl. 108, 104639 (2020).
Morales, A. & Singh, P. The effects of child physical maltreatment on nutritional outcomes: evidence from Peru. J. Dev. Stud. 51, 826–850 (2015).
Navaitis, G., Kairienė, B. & Gaidys, V. Fizinių bausmių vaikystėje sąsajos su laimingumu suaugus. Pedagogika 120, 116–129 (2015).
Niu, H., Liu, L. & Wang, M. Intergenerational transmission of harsh discipline: the moderating role of parenting stress and parent gender. Child Abuse Negl. 79, 1–10 (2018).
Nkuba, M., Hermenau, K. & Hecker, T. The association of maltreatment and socially deviant behavior—findings from a national study with adolescent students and their parents. Ment. Health Prev. 13, 159–168 (2019).
Nkuba, M., Hermenau, K., Goessmann, K. & Hecker, T. Mental health problems and their association to violence and maltreatment in a nationally representative sample of Tanzanian secondary school students. Soc. Psychiatry Psychiatr. Epidemiol. 53, 699–707 (2018).
Noreen, F. et al. Relationship between corporal punishment on academic performance and wellbeing of school students: a study of Gojal, Hunza, Pakistan. Elem. Educ. Online 20, 1920–1926 (2021).
Nyarko, K. Corporal punishment, academic performance and self-esteem among junior high school students in GHANA. IFE PsychologIA 25, 120–132 (2017).
Oliveira, W. A. D. et al. Interações familiares de estudantes em situações de bullying. J. Bras. Psiquiatr. 67, 151–158 (2018).
Pace, G. T., Lee, S. J. & Grogan-Kaylor, A. Spanking and young children’s socioemotional development in low- and middle-income countries. Child Abuse Negl. 88, 84–95 (2019).
Pandey, A. R. et al. Factors associated with physical and sexual violence among school-going adolescents in Nepal: findings from global school-based student health survey. PLoS ONE16, e0248566 (2021).
Peets, K., Hodges, E. V. & Kikas, E. Unravelling the parent–child contexts in which corporal punishment predicts increases vs. decreases in children’s aggression. J. Clin. Child Adolesc. Psychol. 51, 183–194 (2022).
Peltonen, K., Gredebäck, G., Pollak, S. D., Lindskog, M. & Hall, J. The role of maternal trauma and discipline types in emotional processing among Syrian refugee children. Eur. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 32, 1487–1495 (2023).
Rafique, S. & Ahmed, K. F. Gender differences in corporal punishment, academic self-efficacy and drop-out in secondary school students. Int. J. Psychol. Educ. Stud. 6, 73–79 (2019).
Ramos de Oliveira, C. V. et al. Association of exposure to intimate partner violence with maternal depressive symptoms and early childhood socioemotional development among mothers and children in rural Tanzania. JAMA Netw. Open 5, e2248836 (2022).
Ranjitkar, S. et al. Determinants of cognitive development in the early life of children in Bhaktapur, Nepal. Front. Psychol. 10, 2739 (2019).
Rao, J. et al. Cyberbullying perpetration and victimisation among junior and senior high school students in Guangzhou, China. Inj. Prev. 25, 13–19 (2019).
Rey-Anacona, C. A., Redondo-Pacheco, J. & Moreno-Méndez, J. H. Predictores de la perpetración de violencia en el noviazgo en adolescentes: diferencias en función del sexo. Rev. Psicopatol. Psicol. Clín. 26, 95–108 (2021).
Salhi, C. et al. Physical discipline, deprivation, and differential risk of developmental delay across 17 countries. J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 60, 296–306 (2021).
Seleem, M. A., Amer, R. A., Romeh, A. H. & Hamoda, H. M. Demographic and clinical characteristics of children seeking psychiatric services in the Nile Delta region: an observational retrospective study. Int. J. Ment. Health Syst. 13, 66 (2019).
Shamu, S. et al. Prevalence and risk factors for intimate partner violence among Grade 8 learners in urban South Africa: baseline analysis from the Skhokho Supporting Success cluster randomised controlled trial. Int. Health 8, 18–26 (2016).
Sherr, L. et al. Exposure to violence predicts poor educational outcomes in young children in South Africa and Malawi. Int. Health 8, 36–43 (2015).
Silva, J. L. D. et al. Vitimização por bullying em estudantes brasileiros: resultados da Pesquisa Nacional de Saúde do Escolar (PENSE). Texto Contexto Enferm. https://doi.org/10.1590/0104-07072018000310017 (2018).
Skeen, S., Macedo, A., Tomlinson, M., Hensels, I. S. & Sherr, L. Exposure to violence and psychological well-being over time in children affected by HIV/AIDS in South Africa and Malawi. AIDS Care 28, 16–25 (2016).
Skinner, A. T., Oburu, P., Lansford, J. E. & Bacchini, D. Childrearing violence and child adjustment following exposure to Kenyan post-election violence. Psychol. Violence 4, 37–50 (2014).
Smith, D., Springer, C. & Barrett, S. Physical discipline and socioemotional adjustment among Jamaican adolescents. J. Fam. Violence 26, 51–61 (2011).
Sorsdahl, K., Stein, D., Williams, D., Anthony, J. & Myers, B. Childhood punishment and risk for alcohol use disorders: data from South Africa. Int. J. Ment. Health Addict. 13, 103–114 (2015).
Speizer, I. S., Goodwin, M. M., Samandari, G., Kim, S. Y. & Clyde, M. Dimensions of child punishment in two Central American countries: Guatemala and El Salvador. Rev. Panam. Salud Publica 23, 247–256 (2008).
Steely, A. C. & Rohner, R. P. Relations among corporal punishment, perceived parental acceptance, and psychological adjustment in Jamaican youths. Cross Cult. Res. 40, 268–286 (2006).
Stelko-Pereira, A. C., Santini, P. M. & Williams, L. C. d. A. Punição corporal aplicada por funçionarios de duas escolas públicas Brasileiras. [Corporal punishment by school staff in Brazil: prevalence in two public schools.]. Psicol. Estud. 16, 581–591 (2011).
Sun, X. Child maltreatment and quality of life among urban Chinese children. J. Interpers. Violence 36, NP13077–NP13093 (2021).
Sun, Z. et al. Why am I always lonely? The lasting impact of childhood harsh parental discipline on adolescents’ loneliness. Fam. Rel. 73, 1933–1948 (2024).
Tao, Z. et al. Parental corporal punishment and adolescent drinking: the protective role of personal growth initiative and gender difference. Front. Psychol. 14, 1199285 (2024).
Tian, W., Wang, F. & Wang, M. Parental marital quality and children’s depression in China: the different mediating roles of parental psychological aggression and corporal punishment. J. Fam. Violence 38, 275–285 (2023).
Tripković, M. et al. Family factors associated with auto-aggressiveness in adolescents in Croatia. Coll. Antropol. 37, 1081–1088 (2013).
Urke, H. B. & Mittelmark, M. B. Associations between intimate partner violence, childcare practices and infant health: findings from demographic and health surveys in Bolivia, Colombia and Peru. BMC Public Health 15, 819 (2015).
Uwemedimo, O. T., Howlader, A. & Pierret, G. Parenting practices and associations with development delays among young children in Dominican Republic. Ann. Glob. Health 83, 568–576 (2017).
Vargas-Fernández, R., Visconti-Lopez, F. J. & Hernández-Vásquez, A. Physical abuse in childhood and intimate partner violence in Peruvian women: a population-based survey, 2019. Prev. Med. 164, 107278 (2022).
Vieira, M. A., Rønning, J. A., de J Mari, J. & Bordin, I. A. Does cyberbullying occur simultaneously with other types of violence exposure? Braz. J. Psychiatry 41, 234–237 (2019).
Vitolo, Y. L., Fleitlich-Bilyk, B., Goodman, R. & Bordin, I. A. [Parental beliefs and child-rearing attitudes and mental health problems among schoolchildren]. Rev. Saude Publica 39, 716–724 (2005).
Wang, F., Wang, M. & Xing, X. Attitudes mediate the intergenerational transmission of corporal punishment in China. Child Abuse Negl. 76, 34–43 (2018).
Wang, F., Wang, M., Wang, T. & Wang, Z. Harsh parental discipline, parent–child attachment, and peer attachment in late childhood and early adolescence. J. Child Fam. Stud. 30, 196–205 (2021).
Wang, M. & Liu, L. Reciprocal relations between harsh discipline and children’s externalizing behavior in China: a 5-year longitudinal study. Child Dev. 89, 174–187 (2018).
Wang, M. & Xing, X. Intergenerational transmission of parental corporal punishment in China: the moderating role of spouse’s corporal punishment. J. Fam. Violence 29, 119–128 (2014).
Wang, M., Li, J. & Liu, L. Perceived appropriateness as a moderator of the association between corporal punishment and Chinese adolescents’ externalizing behaviors. J. Child Fam. Stud. 28, 2867–2875 (2019).
Wang, M., Niu, H. & Liu, L. Intergenerational transmission of corporal punishment: the independent and interactive moderating role of children’s negative affectivity and effortful control. J. Interpers. Violence 36, NP4588–NP4610 (2021).
Wang, M., Wang, X. & Liu, L. Paternal and maternal psychological and physical aggression and children’s anxiety in China. Child Abuse Negl. 51, 12–20 (2016).
Wang, M., Wang, Y., Wang, F. & Xing, X. Parental corporal punishment and child temperament: independent and interactive predictors of child emotion regulation in China. J. Interpers. Violence 36, NP6680–NP6698 (2021).
Wang, M., Xing, X. & Zhao, J. Intergenerational transmission of corporal punishment in China: the moderating role of marital satisfaction and gender. J. Abnorm. Child Psychol. 42, 1263–1274 (2014).
Wang, Z. et al. The time sensitive and dose-responsive association between parental corporal punishment and sleep disturbances in preschoolers: a prospective cohort study. Child Abuse Negl. 154, 106866 (2024).
Wang, X. & Wang, M. Developmental cascades of marital quality, harsh discipline, and child externalizing behavior in China. J. Interpers. Violence 37, NP11009–NP11033 (2022).
Wang, Y., Fu, C. & Wang, M. The additive and interactive effects of parental harsh discipline and boys’ gender-related traits on boys’ externalizing problem behaviors. Child. Youth Serv. Rev. 122, 105908 (2021).
Wang, Y., Wang, M. & Xing, X. Parental harsh discipline and child emotion regulation: the moderating role of parental warmth in China. Child. Youth Serv. Rev. 93, 283–290 (2018).
Watakakosol, R., Suttiwan, P., Wongcharee, H., Kish, A. & Newcombe, P. A. Parent discipline in Thailand: corporal punishment use and associations with myths and psychological outcomes. Child Abuse Negl. 88, 298–306 (2019).
Wei, Q., Zhang, C., Zhang, J., Luo, S. & Wang, X. Caregiver’s depressive symptoms and young children’s socioemotional development delays: a cross-sectional study in poor areas of China. Infant Ment. Health J. 39, 209–219 (2018).
Wolf, S. & Suntheimer, N. M. Predictors of parental disciplinary practices and associations with child outcomes among Ghanaian preschoolers. Child. Youth Serv. Rev. 112, 104518 (2020).
Xing, X. & Wang, M. Sex differences in the reciprocal relationships between mild and severe corporal punishment and children’s internalizing problem behavior in a Chinese sample. J. Appl. Dev. Psychol. 34, 9–16 (2013).
Xing, X. & Wang, M. Gender differences in the moderating effects of parental warmth and hostility on the association between corporal punishment and child externalizing behaviors in China. J. Child Fam. Stud. 26, 928–938 (2017).
Xing, X. & Wang, M. The moderating role of HPA activity in the relations between parental corporal punishment and executive function in Chinese school-aged children. Psychol. Violence 8, 418–426 (2018).
Xing, X., Wang, M. & Wang, Z. Parental corporal punishment in relation to children’s executive function and externalizing behavior problems in China. Soc. Neurosci. 13, 184–189 (2018).
Xing, X., Wang, M., Zhang, Q., He, X. & Zhang, W. Gender differences in the reciprocal relationships between parental physical aggression and children’s externalizing problem behavior in China. J. Fam. Psychol. 25, 699–708 (2011).
Xing, X., Yin, T. & Wang, M. Cortisol stress reactivity moderates the effects of parental corporal punishment on Chinese preschoolers’ executive function. Child Abuse Negl. 88, 288–297 (2019).
Xing, X., Zhang, H., Shao, S. & Wang, M. Child negative emotionality and parental harsh discipline in Chinese preschoolers: the different mediating roles of maternal and paternal anxiety. Front. Psychol. 8, 339 (2017).
Xing, X., Zhang, L., Wei, Y. & Wang, Z. Parental harsh discipline and preschooler’s inhibitory control in China: bidirectional relations and gender differences. J. Interpers. Violence 36, NP9109–NP9129 (2021).
Yang, L., Liu, S., Wang, M. & Fu, C. Mediating effect of parental harsh discipline on the relationship between parental marital satisfaction and children’s life satisfaction in China. Curr. Psychol. 42, 2229–2242 (2023).
Yang, Q.-F., Xie, R.-B., Zhang, R. & Ding, W. Harsh childhood discipline and developmental changes in adolescent aggressive behavior: the mediating role of self-compassion. Behav. Sci. 13, 725 (2023).
Yonas, B. Association of harsh physical disciplining and the mental and behavioral health problems among pre-school children in Ethiopia. Ethiop. J. Health Dev. https://doi.org/10.20372/ejhd.v38i1.6023 (2024).
Yu, X.-n et al. Posttraumatic growth and reduced suicidal ideation among adolescents at month 1 after the Sichuan Earthquake. J. Affect. Disord. 123, 327–331 (2010).
Zacarías Salinas, X., Aguilar Villalobos, E. J. & Andrade Palos, P. Efectos de las prácticas parentales en la empatía y la conducta prosocial de preadolescentes. Inf. Psicol. 17, 71–86 (2017).
Zequinão, M. A. et al. Physical punishment at home and grade retention related to bullying. J. Hum. Growth Dev. 30, 434–442 (2020).
Zhang, N., Cheng, F., Wu, X. & Wang, Y. Mothers’ negative expressivity and children’s emotion dysregulation: mediating effect of discipline. Child. Youth Serv. Rev. 155, 107158 (2023).
Zhu, J. et al. Deviant peer affiliation as an explanatory mechanism in the association between corporal punishment and physical aggression: a longitudinal study among Chinese adolescents. J. Abnorm. Child Psychol. 45, 1537–1551 (2017).
Zottis, G. A., Salum, G. A., Isolan, L. R., Manfro, G. G. & Heldt, E. Associations between child disciplinary practices and bullying behavior in adolescents. J. Pediatr. 90, 408–414 (2014).
Egger, M., Smith, G. D., Schneider, M. & Minder, C. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ 315, 629–634 (1997).
Stanley, T. D. & Doucouliagos, H. Meta-regression approximations to reduce publication selection bias. Res. Synth. Methods 5, 60–78 (2014).
Straus, M. A. Beating the Devil Out of Them: Corporal Punishment in American Families (Lexington Books, 1994).
Baumrind, D., Larzelere, R. E. & Cowan, P. A. Ordinary physical punishment: is it harmful? Comment on Gershoff (2002). Psychol. Bull. 128, 580–589 (2002).
Cuartas, J. Physical punishment against the early childhood in Colombia: national and regional prevalence, sociodemographic gaps, and ten-year trends. Child. Youth Serv. Rev. 93, 428–440 (2018).
A Familiar Face: Violence in the Lives of Children and Adolescents (UNICEF, 2017).
Dekkers, O. M. et al. COSMOS-E: guidance on conducting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of observational studies of etiology. PLoS Med. 16, e1002742 (2019).
Paolucci, E. O. & Violato, C. A meta-analysis of the published research on the affective, cognitive, and behavioral effects of corporal punishment. J. Psychol. 138, 197–221 (2004).
Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences (Academic, 2013).
Lüdecke, D. esc: effect size computation for meta analysis. https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=esc (2019).
Borenstein, M., Hedges, L. V., Higgins, J. P. T. & Rothstein, H. R. Introduction to Meta-Analysis (Wiley, 2011).
Wilson, D. B. Formulas Used by the “Practical Meta-Analysis Effect Size Calculator” (George Mason Univ., 2016); https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&source=web&rct=j&opi=89978449&url=https://mason.gmu.edu/~dwilsonb/downloads/esformulas.pdf
Gelman, A. Scaling regression inputs by dividing by two standard deviations. Stat. Med. 27, 2865–2873 (2008).
Cheung, M. W. L. A guide to conducting a meta-analysis with non-independent effect sizes. Neuropsychol. Rev. 29, 387–396 (2019).
Van den Noortgate, W., López-López, J. A., Marín-Martínez, F. & Sánchez-Meca, J. Three-level meta-analysis of dependent effect sizes. Behav. Res. Methods 45, 576–594 (2013).
Harrer, M., Cuijpers, P., Furukawa, T. & Ebert, D. Doing Meta-analysis with R: A Hands-on Guide (Chapman and Hall/CRC, 2021).
Viechtbauer, W. Conducting meta-analyses in R with the metafor package. J. Stat. Softw. 36, 1–48 (2010).
Cuartas, J., Gershoff, E. T., Bailey, D. H., Gutierrez, M. A. & McCoy, D. Physical punishment and lifelong outcomes in low‑ and middle‑income countries: a systematic review and multi-level meta-analysis. OSF https://osf.io/kysc8/?view_only=671a44c0b0e240049cdc0346fe5250a0 (2025).
Acknowledgements
We thank all authors who provided data for the systematic review and meta-analysis, six Harvard librarians who supported the search strategy, and research assistants who supported study screening. J.C. was supported by the National Academy of Education/Spencer Dissertation Fellowship, a fellowship from the American Psychological Foundation, and the Patrice L. Engle Dissertation Grant in Global Early Child Development from the Society for Research in Child Development (SRCD) to conduct this project. E.T.G. was supported by grant P2CHD042849 awarded to the Population Research Center at The University of Texas at Austin by the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development (NICHD) (PI: Gershoff). The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish or preparation of the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
J.C. conceptualized the original study, defined the search strategy, preregistered the study, conducted data extraction and verified the underlying data, designed the methodology, conducted formal statistical analysis, wrote the original draft, and provided critical review and editing. E.T.G. conceptualized the original study, designed the methodology, wrote the original draft, and provided critical review and editing. D.H.B. designed the methodology, conducted formal statistical analysis, and provided critical review and editing. M.A.G. conducted data extraction, verified the underlying data, and provided critical review and editing. D.C.M. designed the methodology and provided critical review and editing. All authors approved the final paper as submitted and agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Human Behaviour thanks Will Schneider, Catherine Ward and the other, anonymous, reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work. Peer reviewer reports are available.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Appendices 1–20 and reference list for the Appendices.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Cuartas, J., Gershoff, E.T., Bailey, D.H. et al. Physical punishment and lifelong outcomes in low‑ and middle‑income countries: a systematic review and multilevel meta-analysis. Nat Hum Behav 9, 1365–1379 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41562-025-02164-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41562-025-02164-y
This article is cited by
-
How to prevent physical punishment that harms children
Nature Mental Health (2025)