Abstract
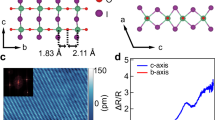
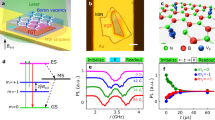
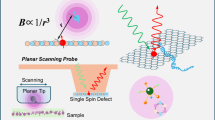
The exfoliation and stacking of two-dimensional van der Waals crystals have created unprecedented opportunities in the discovery of quantum phases. A major obstacle to the advancement of this field is the limited spectroscopic access due to a mismatch in the sample sizes (10−6–10−5 m) and the wavelengths (10−4–10−3 m) of electromagnetic radiation relevant to their low-energy excitations. Here we introduce ferroelectric semiconductor NbOI2 as a two-dimensional van der Waals material capable of operating as a van der Waals terahertz emitter. We demonstrate intense and broadband terahertz generation from NbOI2 with an optical rectification efficiency that is more than one order of magnitude higher than that of ZnTe, the current standard terahertz emitter. Moreover, this NbOI2 terahertz emitter can be integrated into van der Waals heterostructures to enable on-chip near-field terahertz spectroscopy of a target van der Waals material and device. Our approach provides a general spectroscopic tool for two-dimensional van der Waals materials and quantum matter.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$32.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are presented in the article and its Supplementary Information. Further data are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Andrei, E. Y. et al. The marvels of moiré materials. Nat. Rev. Mater. 6, 201–206 (2021).
Cao, Y. et al. Correlated insulator behaviour at half-filling in magic-angle graphene superlattices. Nature 556, 80–84 (2018).
Tang, Y. et al. Simulation of Hubbard model physics in WSe2/WS2 moiré superlattices. Nature 579, 353–358 (2020).
Regan, E. C. et al. Mott and generalized Wigner crystal states in WSe2/WS2 moiré superlattices. Nature 579, 359–363 (2020).
Wang, L. et al. Correlated electronic phases in twisted bilayer transition metal dichalcogenides. Nat. Mater. 19, 861–866 (2020).
Cao, Y. et al. Unconventional superconductivity in magic-angle graphene superlattices. Nature 556, 43–50 (2018).
Lu, X. et al. Superconductors, orbital magnets and correlated states in magic-angle bilayer graphene. Nature 574, 653–657 (2019).
Cai, J. et al. Signatures of fractional quantum anomalous Hall states in twisted MoTe2. Nature 622, 63–68 (2023).
Park, H. et al. Observation of fractionally quantized anomalous Hall effect. Nature 622, 74–79 (2023).
Zeng, Y. et al. Thermodynamic evidence of fractional Chern insulator in moiré MoTe2. Nature 622, 69–73 (2023).
Lu, Z. et al. Fractional quantum anomalous Hall effect in multilayer graphene. Nature 626, 759–764 (2024).
Xu, F. et al. Observation of integer and fractional quantum anomalous Hall effects in twisted bilayer MoTe2. Phys. Rev. X 13, 031037 (2023).
Bistritzer, R. & MacDonald, A. H. Moiré bands in twisted double-layer graphene. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 108, 12233–12237 (2011).
Zhang, Y., Yuan, N. F. Q. & Fu, L. Moiré quantum chemistry: charge transfer in transition metal dichalcogenide superlattices. Phys. Rev. B 102, 201115 (2020).
Wu, F., Lovorn, T., Tutuc, E., Martin, I. & MacDonald, A. H. Topological insulators in twisted transition metal dichalcogenide homobilayers. Phys. Rev. Lett. 122, 086402 (2019).
Wang, C. et al. Fractional Chern insulator in twisted bilayer MoTe2. Phys. Rev. Lett. 132, 036501 (2024).
Li, H. et al. Mapping charge excitations in generalized Wigner crystals. Nat. Nanotechnol. 19, 618–623 (2024).
Kerelsky, A. et al. Maximized electron interactions at the magic angle in twisted bilayer graphene. Nature 572, 95–100 (2019).
Xie, Y. et al. Spectroscopic signatures of many-body correlations in magic-angle twisted bilayer graphene. Nature 572, 101–105 (2019).
Choi, Y. et al. Electronic correlations in twisted bilayer graphene near the magic angle. Nat. Phys. 15, 1174–1180 (2019).
Yang, J. et al. Spectroscopy signatures of electron correlations in a trilayer graphene/hBN moiré superlattice. Science 375, 1295–1299 (2022).
Stinson, H. T. et al. Imaging the nanoscale phase separation in vanadium dioxide thin films at terahertz frequencies. Nat. Commun. 9, 3604 (2018).
Gallagher, P. et al. Quantum-critical conductivity of the Dirac fluid in graphene. Science 364, 158–162 (2019).
Zhao, W. et al. Observation of hydrodynamic plasmons and energy waves in graphene. Nature 614, 688–693 (2023).
Potts, A. M. et al. On-chip time-domain terahertz spectroscopy of superconducting films below the diffraction limit. Nano. Lett. 23, 3835–3841 (2023).
Kipp, G. et al. Cavity electrodynamics of van der Waals heterostructures. Preprint at https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2403.19745 (2024).
Nahata, A., Weling, A. S. & Heinz, T. F. A wideband coherent terahertz spectroscopy system using optical rectification and electro‐optic sampling. Appl. Phys. Lett. 69, 2321–2323 (1996).
Blanchard, F. et al. Generation of 1.5 μJ single-cycle terahertz pulses by optical rectification from a large aperture ZnTe crystal. Opt. Express 15, 13212–13220 (2007).
Kaindl, R. A., Hägele, D., Carnahan, M. A. & Chemla, D. S. Transient terahertz spectroscopy of excitons and unbound carriers in quasi-two-dimensional electron-hole gases. Phys. Rev. B 79, 045320 (2009).
Bilbro, L. S. et al. Temporal correlations of superconductivity above the transition temperature in La2−xSrxCuO4 probed by terahertz spectroscopy. Nat. Phys. 7, 298–302 (2011).
Ulbricht, R., Hendry, E., Shan, J., Heinz, T. F. & Bonn, M. Carrier dynamics in semiconductors studied with time-resolved terahertz spectroscopy. Rev. Mod. Phys. 83, 543–586 (2011).
Adam, A. J. L. Review of near-field terahertz measurement methods and their applications. J. Infrared Millim. Terahertz Waves 32, 976–1019 (2011).
Rijnsdorp, J. & Jellinek, F. The crystal structure of niobium oxide diiodide NbOI2. J. Less Common Met. 61, 79–82 (1978).
Abdelwahab, I. et al. Giant second-harmonic generation in ferroelectric NbOI2. Nat. Photon. 16, 644–650 (2022).
Jia, Y., Zhao, M., Gou, G., Zeng, X. C. & Li, J. Niobium oxide dihalides NbOX2: a new family of two-dimensional van der Waals layered materials with intrinsic ferroelectricity and antiferroelectricity. Nanoscale Horiz. 4, 1113–1123 (2019).
Boyd, R. W. Nonlinear Optics (Academic Press, 2008).
Bao, Y. et al. Gate-tunable in-plane ferroelectricity in few-layer SnS. Nano Lett. 19, 5109–5117 (2019).
Li, Y. et al. Probing symmetry properties of few-layer MoS2 and h-BN by optical second-harmonic generation. Nano Lett. 13, 3329–3333 (2013).
Huang, C.-Y. et al. Coupling of electronic transition to ferroelectric order in a 2D semiconductor. Nat. Commun. 16, 1896 (2025).
Ma, E. Y. et al. Recording interfacial currents on the subnanometer length and femtosecond time scale by terahertz emission. Sci. Adv. 5, eaau0073 (2019).
Tong, M. et al. Ultraefficient terahertz emission mediated by shift-current photovoltaic effect in layered gallium telluride. ACS Nano 15, 17565–17572 (2021).
Pettine, J. et al. Light-driven nanoscale vectorial currents. Nature 626, 984–989 (2024).
Seifert, T. et al. Efficient metallic spintronic emitters of ultrabroadband terahertz radiation. Nat. Photon. 10, 483–488 (2016).
Vaitsi, A. et al. Rotating spintronic terahertz emitter optimized for microjoule pump-pulse energies and megahertz repetition rates. Appl. Phys. Lett. 125, 071107 (2024).
Löffler, T., Hahn, T., Thomson, M., Jacob, F. & Roskos, H. G. Large-area electro-optic ZnTe terahertz emitters. Opt. Express 13, 5353–5362 (2005).
Kampfrath, T. et al. Terahertz spin current pulses controlled by magnetic heterostructures. Nat. Nanotechnol. 8, 256–260 (2013).
Li, Y. et al. Coherent modulation of two-dimensional moiré states with on-chip THz waves. Nano Lett. 24, 12156–12162 (2024).
Yoon, Y. et al. Terahertz phonon engineering with van der Waals heterostructures. Nature 631, 771–776 (2024).
Dawlaty, J. M. et al. Measurement of the optical absorption spectra of epitaxial graphene from terahertz to visible. Appl. Phys. Lett. 93, 131905 (2008).
Soule, D. Magnetic field dependence of the Hall effect and magnetoresistance in graphite single crystals. Phys. Rev. 112, 698–707 (1958).
Barzola‐Quiquia, J., Yao, J., Rödiger, P., Schindler, K. & Esquinazi, P. Sample size effects on the transport characteristics of mesoscopic graphite samples. Phys. Status Solidi A 205, 2924–2933 (2008).
Zhang, Y., Small, J. P., Pontius, W. V. & Kim, P. Fabrication and electric-field-dependent transport measurements of mesoscopic graphite devices. Appl. Phys. Lett. 86, 073104 (2005).
Arsenault, E. A. et al. Two-dimensional moiré polaronic electron crystals. Phys. Rev. Lett. 132, 126501 (2024).
Arsenault, E. A. et al. Time-domain signatures of distinct correlated insulators in a moiré superlattice. Nat. Commun. 16, 549 (2025).
Handa, T. et al. Spontaneous exciton dissociation in transition metal dichalcogenide monolayers. Sci. Adv. 10, eadj4060 (2024).
Ding, Y. M., Yan, L., Wu, Y. & Zhou, L. Exciton-driven and layer-independent linear and nonlinear optical properties in NbOCl2. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 15, 7191–7198 (2024).
Planken, P. C. M., Nienhuys, H.-K., Bakker, H. J. & Wenckebach, T. Measurement and calculation of the orientation dependence of terahertz pulse detection in ZnTe. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 18, 313–317 (2001).
Acknowledgements
Experiments on the discovery of THz emission (Fig. 1) and implementation in near-field microscopy and spectroscopy (Fig. 3), as well as sample synthesis and characterization, were supported by the Materials Science and Engineering Research Center (MRSEC) through National Science Foundation (NSF) grant DMR-2011738. Experiments on thickness dependence and THz emission mechanisms (Fig. 2) were supported by the US Army Research Office, grant number W911NF-23-1-0056. J.W.M. acknowledges support by Programmable Quantum Materials, an Energy Frontier Research Center funded by the US Department of Energy (DOE), Office of Science, Basic Energy Sciences (BES), under award DE-SC0019443. X.Z. acknowledges support by the Max Planck – New York City Center for Non-Equilibrium Quantum Phenomena for fruitful collaborations, interactions and discussions with the Max Planck Institutes (MPIs), particularly M. Bonn of MPI-Mainz, and M. Fechner and H. M. Bretscher of MPI-Hamburg. T.H. acknowledges support by the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) Overseas Postdoctoral Research Fellowship programme. C.-Y.H. acknowledges support from the Taiwan–Columbia scholarship funded by the Ministry of Education of Taiwan and Columbia University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
T.H. and X.Z. conceived this work. T.H. and C.-Y.H. carried out the optical measurements. C.-Y.H., N.O. and F.S. prepared the exfoliated samples under the supervision of X.Z. and J.W.M.; Y.L. and D.D.X. fabricated the vdW heterostructures. D.G.C. synthesized the crystals under the supervision of X.R.; X.Z. supervised the project. The paper was prepared by T.H. and X.Z. in consultation with all other authors. All authors read and commented on the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Materials thanks Su-Yang Xu and the other, anonymous, reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Figs. 1–15, Notes 1–10 and References.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Handa, T., Huang, CY., Li, Y. et al. Terahertz emission from giant optical rectification in a van der Waals material. Nat. Mater. 24, 1203–1208 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41563-025-02201-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41563-025-02201-1
This article is cited by
-
Observation of an isolated flat band in the van der Waals crystal NbOCl2
Communications Materials (2026)
-
Imaging a terahertz superfluid plasmon in a two-dimensional superconductor
Nature (2026)
-
Ultrafast dynamics of ferroelectric polarization of NbOI2 captured with femtosecond electron diffraction
Nature Communications (2025)
-
A terahertz source for quantum physics
Nature Materials (2025)
-
Terahertz light confined to the nanoscale with hafnium dichalcogenides
Nature Materials (2025)