Abstract
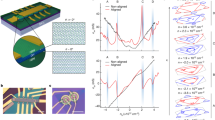
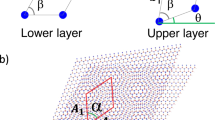
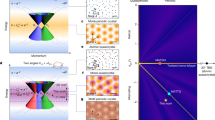
Stacking two atomic crystals with a twist between their crystal axes produces moiré potentials that modify the electronic properties. Here we show that double-moiré potentials generated by superposing three atomic crystals create a unique class of tunable quasiperiodic structures that alter the symmetry and spatial distribution of the electronic wavefunctions. By using scanning tunnelling microscopy and scanning tunnelling spectroscopy to study twisted bilayer graphene on hexagonal boron nitride, we unveil a moiré phase diagram defined by the lattice constants of the two moiré lattices (graphene-on-graphene and graphene-on-hexagonal boron nitride), comprising both commensurate periodic and incommensurate quasiperiodic crystals. Remarkably, the 1:1 commensurate crystals, which should theoretically exist at only one point on this phase diagram, are observed over a wide range, demonstrating an unexpected self-alignment mechanism. The incommensurate crystals include quasicrystals, which are quasiperiodic and feature a Bravais-forbidden dodecagonal symmetry, and intercrystals, which are also quasiperiodic but lack forbidden symmetries. This rich variety of tunable double-moiré structures offers a synthetic platform for exploring the unique electronic properties of quasiperiodic crystals, which are rarely found in nature.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$32.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data are available in the article and its Supplementary Information.
References
Lopes dos Santos, J. M., Peres, N. M. R. & Castro Neto, A. H. Graphene bilayer with a twist: electronic structure. Phys. Rev. Lett. 99, 256802 (2007).
Li, G. et al. Observation of Van Hove singularities in twisted graphene layers. Nat. Phys. 6, 109–113 (2010).
Suárez Morell, E., Vargas, P., Chico, L. & Brey, L. Charge redistribution and interlayer coupling in twisted bilayer graphene under electric fields. Phys. Rev. B 84, 195421 (2011).
Bistritzer, R. & MacDonald, A. H. Moiré bands in twisted double-layer graphene. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 108, 12233–12237 (2011).
San–Jose, P., Gonz´alez, J. & Guinea, F. Non-Abelian gauge potentials in graphene bilayers. Phys. Rev. Lett. 108, 216802 (2012).
Andrei, E. Y. & MacDonald, A. H. Graphene bilayers with a twist. Nat. Mater. 19, 1265–1275 (2020).
Andrei, E. Y. et al. The marvels of moiré materials. Nat. Rev. Mater. 6, 201–206 (2021).
Cao, Y. et al. Correlated insulator behaviour at half-filling in magic-angle graphene superlattices. Nature 556, 80–84 (2018).
Cao, Y. et al. Unconventional superconductivity in magic-angle graphene superlattices. Nature 556, 43–50 (2018).
Zhu, Z. Y., Carr, S., Massatt, D., Luskin, M. & Kaxiras, E. Twisted trilayer graphene: a precisely tunable platform for correlated electrons. Phys. Rev. Lett. 125, 11640 (2020).
Li, Y. W. et al. Observation of coexisting Dirac bands and moiré flat bands in magic-angle twisted trilayer graphene. Adv. Mater. 34, 2205996 (2022).
Uri, A. et al. Superconductivity and strong interactions in a tunable moiré quasicrystal. Nature 620, 762–767 (2023).
Christos, M., Sachdev, S. & Scheurer, M. S. Nodal band-off-diagonal superconductivity in twisted graphene superlattices. Nat. Commun. 14, 7134 (2023).
Chen-Yue Hao, Z. Z. et al. Robust flat bands in twisted trilayer graphene quasicrystals. Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/2401.09010 (2024).
Sharpe, A. L. et al. Emergent ferromagnetism near three-quarters filling in twisted bilayer graphene. Science 365, 605–608 (2019).
Serlin, M. et al. Intrinsic quantized anomalous Hall effect in a moiré heterostructure. Science 367, 900–903 (2020).
Nuckolls, K. P. et al. Strongly correlated Chern insulators in magic-angle twisted bilayer graphene. Nature 588, 610–615 (2020).
Xie, Y. et al. Fractional Chern insulators in magic-angle twisted bilayer graphene. Nature 600, 439–443 (2021).
Wu, S., Zhang, Z., Watanabe, K., Taniguchi, T. & Andrei, E. Y. Chern insulators, Van Hove singularities and topological flat bands in magic-angle twisted bilayer graphene. Nat. Mater. 20, 488–494 (2021).
Das, I. et al. Symmetry-broken Chern insulators and Rashba-like Landau-level crossings in magic-angle bilayer graphene. Nat. Phys. 17, 710–714 (2021).
Saito, Y. et al. Hofstadter subband ferromagnetism and symmetry-broken Chern insulators in twisted bilayer graphene. Nat. Phys. 17, 478–481 (2021).
Cea, T., Pantaleon, P. A. & Guinea, F. Band structure of twisted bilayer graphene on hexagonal boron nitride. Phys. Rev. B 102, 155136 (2020).
Lin, X. Q. & Ni, J. Symmetry breaking in the double moiré superlattices of relaxed twisted bilayer graphene on hexagonal boron nitride. Phys. Rev. B 102, 035441 (2020).
Shi, J. T., Zhu, J. H. & MacDonald, A. H. Moiré commensurability and the quantum anomalous Hall effect in twisted bilayer graphene on hexagonal boron nitride. Phys. Rev. B 103, 075122 (2021).
Lin, X. Q., Su, K. L. & Ni, J. Misalignment instability in magic-angle twisted bilayer graphene on hexagonal boron nitride. 2D Mater. 8, 025025 (2021).
Kim, K. et al. van der Waals heterostructures with high accuracy rotational alignment. Nano Lett. 16, 1989–1995 (2016).
Li, G. & Andrei, E. Y. Observation of Landau levels of Dirac fermions in graphite. Nat. Phys. 3, 623–627 (2007).
Li, G., Luican, A. & Andrei, E. Y. Self-navigation of a scanning tunneling microscope tip toward a micron-sized graphene sample. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 82, 073701 (2011).
Shechtman, D., Blech, I., Gratias, D. & Cahn, J. W. Metallic phase with long-range orientational order and no translational symmetry. Phys. Rev. Lett. 53, 1951–1953 (1984).
Levine, D. & Steinhardt, P. J. Quasicrystals—a new class of ordered structures. Phys. Rev. Lett. 53, 2477–2480 (1984).
Levine, D. & Steinhardt, P. J. Quasi-crystals. I. Definition and structure. Phys. Rev. B 34, 596–616 (1986).
Janssen, T., Chapuis, G. & Boissieu, M. D. Aperiodic Crystals: From Modulated Phases to Quasicrystals (Oxford Univ. Press, 2007).
Lifshitz, R., Schmid, S. & Withers, R. L. 286 Pages 144 Illustrations, 295 Illustrations in Color (Springer, 2013).
Ahn, S. J. et al. Dirac electrons in a dodecagonal graphene quasicrystal. Science 361, 782–786 (2018).
van Wijk, M. M., Schuring, A., Katsnelson, M. I. & Fasolino, A. Moiré patterns as a probe of interplanar interactions for graphene on h-BN. Phys. Rev. Lett. 113, 135504 (2014).
Gargiulo, F. & Yazyev, O. V. Structural and electronic transformation in low-angle twisted bilayer graphene. 2D Mater. 5, 015019 (2018).
Li, H. Y. et al. Imaging moiré flat bands in three-dimensional reconstructed WSe/WS superlattices. Nat. Mater. 20, 945–950 (2021).
Molino, L. et al. Influence of atomic relaxations on the moiré flat band wave functions in antiparallel twisted bilayer WS2. Nano Lett. 23, 11778–11784 (2023).
Nakatsuji, N., Kawakami, T. & Koshino, M. Multiscale lattice relaxation in general twisted trilayer graphenes. Phys. Rev. X 13, 041007 (2023).
Kazmierczak, N. P. et al. Strain fields in twisted bilayer graphene. Nat. Mater. 20, 956 (2021).
Jiang, Y. H. et al. Charge order and broken rotational symmetry in magic-angle twisted bilayer graphene. Nature 573, 91–95 (2019).
Xie, Y. L. et al. Spectroscopic signatures of many-body correlations in magic-angle twisted bilayer graphene. Nature 572, 101–105 (2019).
Devakul, T. & Huse, D. A. Anderson localization transitions with and without random potentials. Phys. Rev. B 96, 214201 (2017).
Fu, Y., Wilson, J. H. & Pixley, J. H. Flat topological bands and eigenstate criticality in a quasiperiodic insulator. Phys. Rev. B 104, L041106 (2021).
Mao, D. & Senthil, T. Quasiperiodicity, band topology, and moiré graphene. Phys. Rev. B 103, 115110 (2021).
Jagannathan, A. The Fibonacci quasicrystal: case study of hidden dimensions and multifractality. Rev. Mod. Phys. 93, 045001 (2021).
Morison, D., Murphy, N. B., Cherkaev, E. & Golden, K. M. Order to disorder in quasiperiodic composites. Commun. Phys. 5, 148 (2022).
Deguchi, K. et al. Quantum critical state in a magnetic quasicrystal. Nat. Mater. 11, 1013–1016 (2012).
Agrawal, U., Gopalakrishnan, S. & Vasseur, R. Quantum criticality in the 2D quasiperiodic Potts model. Phys. Rev. Lett. 125, 265702 (2020).
Wu, A.-K. et al. Aubry-André Anderson model: magnetic impurities coupled to a fractal spectrum. Phys. Rev. B 106, 165123 (2022).
Ticea, N. S., May-Mann, J., Xiao, J. W., Berg, E. & Devakul, T. Stability of quasiperiodic superconductors. Phys. Rev. B 110, L060501 (2024).
Lu, C.-P. et al. Local, global, and nonlinear screening in twisted double-layer graphene. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 113, 6623 (2016).
Li, B. W. et al. Fabricating ultra-sharp tungsten STM tips with high yield: double-electrolyte etching method and machine learning. SN Appl. Sci. 2, 1246 (2020).
Coe, A. M., Li, G. & Andrei, E. Y. Cryogen-free modular scanning tunneling microscope operating at 4-K in high magnetic field on a compact ultra-high vacuum platform. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 95, 083702 (2024).
Acknowledgements
We thank P. Steinhardt, E. Kaxiris and Z. Zhang for insightful discussions, E. Kim and K. Mallayya for help with machine learning tools, N. Tilak for help with the sample fabrication, D. Guerci and J. Wilson for collaborations on related topics and S. Fang for discussions at the early stages of this work. Funding for this project was provided by the Department of Energy grant no. DOE-FG02-99ER45742 (X.L., A.M.C. and E.Y.A.); Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation EPiQS initiative grant GBMF9453 (X.L., A.M.C. and E.Y.A.); Rutgers University, SAS (G.L.); NSF CAREER grant no. DMR-1941569 (J.H.P.) and Sloan Research Fellowship through the Alfred P. Sloan Foundation (J.H.P.); Aspen Center for Physics at which part of this work was performed, which is supported by the National Science Foundation grant no. PHY-1607611 (J.H.P.); and Kavli Institute of Theoretical Physics supported in part by NSF under Grants NSF PHY-1748958 and PHY-2309135 (J.H.P. and E.Y.A.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
E.Y.A. conceived and supervised the project. X.L. fabricated, characterized the samples and performed the STM measurements with input from G.L., A.M.C. and E.Y.A. X.L., G.L., J.H.P. and E.Y.A. analysed and interpreted the results. T.T. and K.W. synthesized the hBN crystals. X.L., G.L. and E.Y.A. wrote the paper with input from all authors. All authors discussed the results.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Materials thanks Xiaohui Qiu and the other, anonymous, reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Extended data
Extended Data Fig. 1 Classification of 2D moiré periodic and quasiperiodic crystals.
A representative FFT and the corresponding topography (insets) of moiré crystal, MIC and MQC is shown on the right of the table. The right panel schematically illustrates the different moiré structures in GG/GBN. The scale bars are 0.16 nm-1 for the FFTs and 16 nm for the topographies.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Figs. 1–21, Tables 1–3 and Discussion.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lai, X., Li, G., Coe, A.M. et al. Moiré periodic and quasiperiodic crystals in heterostructures of twisted bilayer graphene on hexagonal boron nitride. Nat. Mater. 24, 1019–1026 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41563-025-02222-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41563-025-02222-w
This article is cited by
-
Synthesis of incommensurate moiré structures with short-range-ordered charge density modulation
Nature Communications (2025)