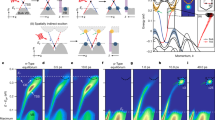
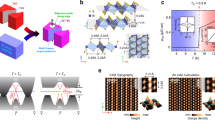
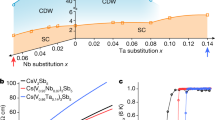
Abstract
In the past two decades, various classes of topological materials have been discovered, yet the deliberate control of topology in a single material remains largely unexplored. Here we demonstrate full experimental control over the topological nodal loop in the square-net material LaSbxTe2−x by chemical substitution and electron doping. Using angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy, we show that changing the antimony concentration x from 0.86 to 1.0 in the bulk opens a gap larger than 400 meV in the nodal loop. Symmetry analysis establishes that this effect originates from the breaking of n glide symmetry in the square-net layer. The same topological phase transition can also be driven reversibly on the surface of LaSbxTe2−x by in situ chemical gating via potassium deposition, enabling on-demand switching of topology. The control parameter for both the bulk and surface transition is the electron concentration, providing a pathway towards applications based on switching topology by electrostatic gating.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$32.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data needed to evaluate the conclusions in this study are available in the article and its Supplementary Information. The raw ARPES data acquired in this study are available via Zenodo at https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.17059971 (ref. 44). All other data are available from the corresponding authors upon request.
References
Zhang, H. et al. Topological insulators in Bi2Se3, Bi2Te3 and Sb2Te3 with a single Dirac cone on the surface. Nat. Phys. 5, 438–442 (2009).
Hasan, M. Z. & Kane, C. L. Colloquium: Topological insulators. Rev. Mod. Phys. 82, 3045–3067 (2010).
Ando, Y. & Fu, L. Topological crystalline insulators and topological superconductors: from concepts to materials. Annu. Rev. Condens. Matter Phys. 6, 361–381 (2015).
Bernevig, B. A., Hughes, T. L. & Zhang, S.-C. Quantum spin Hall effect and topological phase transition in HgTe quantum wells. Science 314, 1757–1761 (2006).
König, M. et al. Quantum spin Hall insulator state in HgTe quantum wells. Science 318, 766–770 (2007).
Wu, S. et al. Observation of the quantum spin Hall effect up to 100 kelvin in a monolayer crystal. Science 359, 76–79 (2018).
Chang, C.-Z. et al. Experimental observation of the quantum anomalous Hall effect in a magnetic topological insulator. Science 340, 167–170 (2013).
Liang, T. et al. Ultrahigh mobility and giant magnetoresistance in the Dirac semimetal Cd3As2. Nat. Mater. 14, 280–284 (2014).
Chen, Y. L. et al. Massive Dirac fermion on the surface of a magnetically doped topological insulator. Science 329, 659–662 (2010).
Zhang, J. et al. Topology-driven magnetic quantum phase transition in topological insulators. Science 340, 1582–1586 (2013).
Zeljkovic, I. et al. Dirac mass generation from crystal symmetry breaking on the surfaces of topological crystalline insulators. Nat. Mater. 14, 318–324 (2015).
Xu, S.-Y. et al. Topological phase transition and texture inversion in a tunable topological insulator. Science 332, 560–564 (2011).
Xu, S.-Y. et al. Observation of a topological crystalline insulator phase and topological phase transition in Pb1−xSnxTe. Nat. Commun. 3, 1192 (2012).
Wojek, B. M. et al. Direct observation and temperature control of the surface Dirac gap in a topological crystalline insulator. Nat. Commun. 6, 8463 (2015).
Collins, J. L. et al. Electric-field-tuned topological phase transition in ultrathin Na3Bi. Nature 564, 390–394 (2018).
Wang, Y. et al. Spectroscopic evidence for the realization of a genuine topological nodal-line semimetal in LaSbTe. Phys. Rev. B 103, 125131 (2021).
Deng, J. et al. Twisted nodal wires and three-dimensional quantum spin Hall effect in distorted square-net compounds. Phys. Rev. B 105, 224103 (2022).
Klemenz, S., Lei, S. & Schoop, L. M. Topological semimetals in square-net materials. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 49, 185–206 (2019).
DiMasi, E., Foran, B., Aronson, M. C. & Lee, S. Stability of charge-density waves under continuous variation of band filling in LaTe2−xSbx (0 ≤ x ≤ 1). Phys. Rev. B 54, 13587–13596 (1996).
Singha, R. et al. Evolving devil’s staircase magnetization from tunable charge density waves in nonsymmorphic Dirac semimetals. Adv. Mater. 33, 2103476 (2021).
Lei, S. et al. Charge density waves and magnetism in topological semimetal candidates GdSbxTe2−x−δ. Adv. Quantum Technol. 2, 1900045 (2019).
Pandey, K., Basnet, R., Wang, J., Da, B. & Hu, J. Evolution of electronic and magnetic properties in the topological semimetal SmSbxTe2−x. Phys. Rev. B 105, 155139 (2022).
Qian, Y. et al. Layer construction of topological crystalline insulator LaSbTe. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 63, 107011 (2020).
Brouet, V. et al. Fermi surface reconstruction in the CDW state of CeTe3 observed by photoemission. Phys. Rev. Lett. 93, 126405 (2004).
Brouet, V. et al. Angle-resolved photoemission study of the evolution of band structure and charge density wave properties in RTe3 (R = Y, La, Ce, Sm, Gd, Tb, and Dy). Phys. Rev. B 77, 235104 (2008).
Leonhardt, A. et al. Symmetry-enforced topological band crossings in orthorhombic crystals: classification and materials discovery. Phys. Rev. Mater. 5, 124202 (2021).
Hirschmann, M. M., Leonhardt, A., Kilic, B., Fabini, D. H. & Schnyder, A. P. Symmetry-enforced band crossings in tetragonal materials: Dirac and Weyl degeneracies on points, lines, and planes. Phys. Rev. Mater. 5, 054202 (2021).
Shin, K. Y., Brouet, V., Ru, N., Shen, Z. X. & Fisher, I. R. Electronic structure and charge-density wave formation in LaTe1.95 and CeTe2.00. Phys. Rev. B 72, 085132 (2005).
Malliakas, C. D. & Kanatzidis, M. G. Divergence in the behavior of the charge density wave in RETe3 (RE = rare-earth element) with temperature and RE element. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 128, 12612–12613 (2006).
Johannes, M. D. & Mazin, I. I. Fermi surface nesting and the origin of charge density waves in metals. Phys. Rev. B 77, 165135 (2008).
Yan, J.-Q., Sales, B. C., Susner, M. A. & McGuire, M. A. Flux growth in a horizontal configuration: an analog to vapor transport growth. Phys. Rev. Mater. 1, 023402 (2017).
Momma, K. & Izumi, F. VESTA 3 for three-dimensional visualization of crystal, volumetric and morphology data. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 44, 1272–1276 (2011).
Blaha, P. et al. WIEN2k: an APW+lo program for calculating the properties of solids. J. Chem. Phys. 152, 074101 (2020).
Blaha, P. et al. WIEN2k, An Augmented Plane Wave + Local Orbitals Program for Calculating Crystal Properties (Karlheinz Schwarz, Vienna University of Technology, 2021).
Perdew, J. P., Burke, K. & Ernzerhof, M. Generalized gradient approximation made simple. Phys. Rev. Lett. 77, 3865–3868 (1996).
Giannozzi, P. et al. QUANTUM ESPRESSO: a modular and open-source software project for quantum simulations of materials. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 21, 395502 (2009).
Giannozzi, P. et al. Advanced capabilities for materials modelling with QUANTUM ESPRESSO. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 29, 465901 (2017).
Pacilè, D. et al. Narrowing of d bands of FeCo layers intercalated under graphene. Appl. Phys. Lett. 118, 121602 (2021).
Kresse, G. & Furthmüller, J. Efficiency of ab-initio total energy calculations for metals and semiconductors using a plane-wave basis set. Comput. Mater. Sci. 6, 15–50 (1996).
Kresse, G. & Furthmüller, J. Efficient iterative schemes for ab initio total-energy calculations using a plane-wave basis set. Phys. Rev. B 54, 11169–11186 (1996).
Kresse, G. & Joubert, D. From ultrasoft pseudopotentials to the projector augmented-wave method. Phys. Rev. B 59, 1758–1775 (1999).
Blöchl, P. E. Projector augmented-wave method. Phys. Rev. B 50, 17953–17979 (1994).
Togo, A. First-principles phonon calculations with phonopy and phono3py. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn 92, 012001 (2023).
Bannies, J. Datasets of the manuscript ‘Electronic switching of topology in LaSbTe’. Zenodo https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.17059971 (2025).
Acknowledgements
We thank A. von der Handt (UBC Earth Sciences) for assistance with the wavelength-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy measurements. This research was undertaken thanks in part to funding from the Max Planck-UBC-UTokyo Centre for Quantum Materials and the Canada First Research Excellence Fund, Quantum Materials and Future Technologies Program. This project is also funded by the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC); the Canada Foundation for Innovation (CFI); the British Columbia Knowledge Development Fund (BCKDF); the Department of National Defence (DND); the Mitacs Accelerate Program; the Moore EPiQS Program (A.D.); the Canada Research Chairs Program (A.D.); and the CIFAR Quantum Materials Program (A.D.). This research is funded in part by a QuantEmX grant from ICAM and the Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation through Grant GBMF9616 to M.M. and H.-H.K. In addition, J.B. and H.-H.K. acknowledge the receipt of support from the CLSI Student Travel Support Program. J.W.S. was supported in part by a Provost’s Research Fellowship from Farmingdale State College. Use of the Canadian Light Source (QMSC), a national research facility of the University of Saskatchewan, is supported by CFI, the NSERC, the National Research Council, the Canadian Institutes of Health Research, the Government of Saskatchewan and the University of Saskatchewan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
J.B. grew the single crystals and characterized them. J.W.S. performed the single-crystal XRD and solved the crystal structures. J.B., M.M. and H.-H.K. conducted the ARPES experiments with help from M.Z., S. Gorovikov and S.Z. The ARPES data were analysed by J.B. with input from M.M., H.-H.K. and A.D. The core-level spectra were analysed by S. Godin, and J.B. and I.S.E. performed the DFT calculations. J.B., M.M., H.-H.K., M.O., A.D. and M.C.A. discussed the results. J.B., M.M., H.-H.K., A.D. and M.C.A. wrote the paper, with contributions from all authors.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Materials thanks the anonymous reviewers for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Discussion, Figs. 1–7 and Tables 1 and 2.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bannies, J., Michiardi, M., Kung, HH. et al. Electronic switching of topology in LaSbTe. Nat. Mater. (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41563-025-02396-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41563-025-02396-3