Abstract
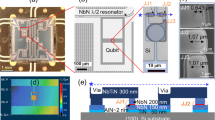
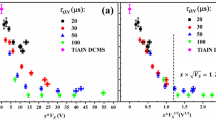
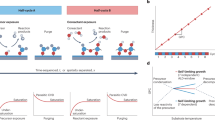
The development of large-scale quantum processors benefits from superconducting qubits that can operate at elevated temperatures and be fabricated with scalable, foundry-compatible processes. Atomic layer deposition (ALD) is increasingly being adopted as an industrial standard for thin-film growth, particularly in applications requiring precise control over layer thickness and composition. Here we report superconducting qubits based on NbN/AlN/NbN trilayers deposited entirely by ALD. By varying the number of ALD cycles used to form the AlN barrier, we achieve Josephson tunnelling through barriers of different thicknesses, with critical current density spanning seven orders of magnitude, demonstrating the uniformity and versatility of the process. Owing to the high critical temperature of NbN, transmon qubits based on these all-nitride trilayers exhibit microsecond-scale relaxation times, even at temperatures above 300 mK. These results establish ALD as a viable low-temperature deposition technique for superconducting quantum circuits and position all-nitride ALD qubits as a promising platform for operation at elevated temperatures.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$32.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data supporting this study are included in the Article and its Supplementary Information. Source data are provided with this paper.
References
Nakamura, Y., Pashkin, Y. A. & Tsai, J. S. Coherent control of macroscopic quantum states in a single-Cooper-pair box. Nature 398, 786–788 (1999).
Koch, J. et al. Charge-insensitive qubit design derived from the Cooper pair box. Phys. Rev. A 76, 042319 (2007).
Siddiqi, I. Engineering high-coherence superconducting qubits. Nat. Rev. Mater. 6, 875–891 (2021).
Google Quantum AI and Collaborators. Quantum error correction below the surface code threshold. Nature 638, 920–926 (2025).
Van Damme, J. et al. Advanced CMOS manufacturing of superconducting qubits on 300 mm wafers. Nature 634, 74–79 (2024).
Krinner, S. et al. Engineering cryogenic setups for 100-qubit scale superconducting circuit systems. EPJ Quantum Technol. 6, 2 (2019).
Martin, M. J. et al. Energy use in quantum data centers: scaling the impact of computer architecture, qubit performance, size, and thermal parameters. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Comput. 7, 864–874 (2022).
Yang, C. H. et al. Operation of a silicon quantum processor unit cell above one kelvin. Nature 580, 350–354 (2020).
Anferov, A., Lee, K.-H., Zhao, F., Simon, J. & Schuster, D. I. Improved coherence in optically defined niobium trilayer-junction qubits. Phys. Rev. Appl. 21, 024047 (2024).
Anferov, A. et al. Superconducting qubits above 20 GHz operating over 200 mK. PRX Quantum 5, 020336 (2024).
Anferov, A., Wan, F., Harvey, S. P., Simon, J. & Schuster, D. I. Millimeter-wave superconducting qubit. PRX Quantum 6, 020336 (2025).
Nakamura, Y. et al. Superconducting qubits consisting of epitaxially grown NbN/AlN/NbN Josephson junctions. Appl. Phys. Lett. 99, 212502 (2011).
Kim, S. et al. Enhanced coherence of all-nitride superconducting qubits epitaxially grown on silicon substrate. Commun. Mater. 2, 21 (2021).
Tinkham, M. Introduction to Superconductivity 2nd edn (Dover Publications, 2004).
Wang, Z., Shinozaki, K., Murooka, Y., & Kuzmin, L. S. High-quality epitaxial NbN/AlN/NbN tunnel junctions with a wide range of current density. Appl. Phys. Lett. 102, 102601 (2013).
Makise, K., Terai, H. & Uzawa, Y. NbN/AlN/NbN/TiN tunnel junctions on Si (100) substrate for superconducting devices. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 26, 1100403 (2016).
Qiu, W. & Terai, H. Fabrication of deep-sub-micrometer NbN/AlN/NbN epitaxial junctions on a Si-substrate. Appl. Phys. Express 13, 126501 (2020).
George, S. M. Atomic layer deposition: an overview. Chem. Rev. 110, 111–131 (2010).
Deyu, G. K. et al. Recent advances in atomic layer deposition of superconducting thin films: a review. Mater. Horiz. 12, 5594–5626 (2025).
Zhao, C. & Xiang, J. Atomic layer deposition (ALD) of metal gates for CMOS. Appl. Sci. 9, 2388 (2019).
Sheng, J. et al. Review article: atomic layer deposition for oxide semiconductor thin film transistors: advances in research and development. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 36, 060801 (2018).
Waechtler, T. et al. ALD-grown seed layers for electrochemical copper deposition integrated with different diffusion barrier systems. Microelectron. Eng. 88, 684–689 (2011).
Chen, R. et al. Atomic layer deposition in advanced display technologies: from photoluminescence to encapsulation. Int. J. Extrem. Manuf. 6, 022003 (2024).
Sowa, M. J. et al. Plasma-enhanced atomic layer deposition of superconducting niobium nitride. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 35, 01B143 (2017).
Cheng, R., Wang, S. & Tang, H. X. Superconducting nanowire single-photon detectors fabricated from atomic-layer-deposited NbN. Appl. Phys. Lett. 115, 241101 (2019).
Wilt, J. et al. Atomically thin Al2O3 films for tunnel junctions. Phys. Rev. Appl. 7, 064022 (2017).
Jhabvala, C. A., Nagler, P. C. & Stevenson, T. R. Atomic layer deposition Josephson junctions for cryogenic circuit applications. J. Low. Temp. Phys. 200, 331–335 (2020).
Rosenberg, D. et al. 3D integrated superconducting qubits. npj Quantum Inf. 3, 42 (2017).
Alevli, M., Ozgit, C., Donmez, I. & Biyikli, N. The influence of N2/H2 and ammonia N source materials on optical and structural properties of AlN films grown by plasma enhanced atomic layer deposition. J. Cryst. Growth 335, 51–57 (2011).
Goerke, S. et al. Atomic layer deposition of AlN for thin membranes using trimethylaluminum and H2/N2 plasma. Appl. Surf. Sci. 338, 35–41 (2015).
Shibalov, M. V. et al. Ultrathin epitaxial NbNx film deposited by PEALD method on C-plane sapphire: growth, structure and superconducting properties. Appl. Surf. Sci. 612, 155697 (2023).
Dang, P. et al. An all-epitaxial nitride heterostructure with concurrent quantum hall effect and superconductivity. Sci. Adv. 7, eabf1388 (2021).
Yaddanapudi, K. First-principles study of structural phase transformation and dynamical stability of cubic AlN semiconductors. AIP Adv. 8, 125006 (2018).
Chen, Z., Holec, D., Bartosik, M., Mayrhofer, P. H. & Zhang, Z. Crystallographic orientation dependent maximum layer thickness of cubic AlN in CrN/AlN multilayers. Acta Mater. 168, 190–202 (2019).
Shih, H.-Y. et al. Low-temperature atomic layer epitaxy of AlN ultrathin films by layer-by-layer, in-situ atomic layer annealing. Sci. Rep. 7, 17307 (2017).
Grönberg, L. et al. Side-wall spacer passivated sub-μm Josephson junction fabrication process. Supercond. Sci. Technol. 30, 125016 (2017).
Higurashi, E., Okumura, K., Kunimune, Y., Suga, T. & Hagiwara, K. Room-temperature bonding of wafers with smooth Au thin films in ambient air using a surface-activated bonding method. IEICE Trans. Electron. E100.C, 156–160 (2017).
Zhao, R. et al. Merged-element transmon. Phys. Rev. Appl. 14, 064006 (2020).
Mamin, H. J. et al. Merged-element transmons: design and qubit performance. Phys. Rev. Appl. 16, 034035 (2021).
Blais, A., Grimsmo, A. L., Girvin, S. M., & Wallraff, A. Circuit quantum electrodynamics. Rev. Mod. Phys. 93, 025005 (2021).
Place, A. P. M. et al. New material platform for superconducting transmon qubits with coherence times exceeding 0.3 milliseconds. Nat. Commun. 12, 1779 (2021).
Krantz, P. et al. A quantum engineer’s guide to superconducting qubits. Appl. Phys. Rev. 6, 021318 (2019).
Gao, Y. Y., Rol, M. A., Touzard, S., & Wang, C. Practical guide for building superconducting quantum devices. PRX Quantum 2, 047001 (2021).
Paik, H. et al. Observation of high coherence in Josephson junction qubits measured in a three-dimensional circuit QED architecture. Phys. Rev. Lett. 107, 240501 (2011).
Catelani, G., Schoelkopf, R. J., Devoret, M. H. & Glazman, L. I. Relaxation and frequency shifts induced by quasiparticles in superconducting qubits. Phys. Rev. B 84, 064517 (2011).
Serniak, K. et al. Hot nonequilibrium quasiparticles in transmon qubits. Phys. Rev. Lett. 121, 157701 (2018).
Jin, X. Y. et al. Thermal and residual excited-state population in a 3D transmon qubit. Phys. Rev. Lett. 114, 240501 (2015).
Lisenfeld, J., Lukashenko, A., Ansmann, M., Martinis, J. M. & Ustinov, A. V. Temperature dependence of coherent oscillations in Josephson phase qubits. Phys. Rev. Lett. 99, 170504 (2007).
Lvov, D. S., Lemziakov, S. A., Ankerhold, E., Peltonen, J. T. & Pekola, J. P. Thermometry based on a superconducting qubit. Phys. Rev. Appl. 23, 054079 (2025).
Ganjam, S. et al. Surpassing millisecond coherence in on chip superconducting quantum memories by optimizing materials and circuit design. Nat. Commun. 15, 3687 (2024).
Huang, S. et al. Microwave package design for superconducting quantum processors. PRX Quantum 2, 047003 (2021).
Tang, F. et al. Practical issues for atom probe tomography analysis of III-nitride semiconductor materials. Microsc. Microanal. 21, 544–556 (2015).
Acknowledgements
We thank D. Jena, H. G. Xing, V. Fatemi, F. Rana, C. E. Dreyer, P. L. McMahon, A. Ithepalli and M. Verma for helpful and inspirational discussions. We also thank Y. Sun, M. Rooks, L. McCabe, Y. Shin, K. Woods and S. Sohn for their assistance and guidance in device fabrications. This work was supported by the Air Force Office of Sponsored Research under grant number FA9550-23-1-0688 and by the Army Research Office under grant number W911NF-24-2-0240. H.X.T. acknowledges support from the Office of Naval Research under grant number N00014-23-1-2021. The use of the fabrication facilities was supported by the Yale Institute for Nanoscience and Quantum Engineering (YINQE) and the Yale SEAS Cleanroom. The TWPA used in this experiment was provided by IARPA and MIT Lincoln Laboratory. The work on STEM made use of the electron microscopy facility of the Cornell Center for Materials Research (CCMR) with support from the National Science Foundation Materials Research Science and Engineering Centers (MRSEC) program (DMR1719875). The Thermo Fisher Spectra 300 X-CFEG device was acquired with support from PARADIM, an NSF MIP (DMR-2039380) and Cornell University. N.P. acknowledges support from the National Science Foundation Graduate Research Fellowship under grant number DGE2139899. P.G. and B.M. acknowledge support from the Air Force Office of Sponsored Research under grant number 162023-22608.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
H.X.T. and D.W. conceived the research and designed the experiments. D.W. deposited the ALD films and fabricated the devices with contributions from M.C.C.P. D.W. performed the d.c. measurement with contributions from C.G.L.B. Y.W. constructed the RF measurement setup and Y.W. and D.W. performed the RF measurement. D.W., C.G.L.B. and M.C.C.P. provided the theoretical analysis. N.P. performed the STEM characterization. P.G. conducted the APT characterization. H.X.T., D.A.M. and B.M. supervised the project. D.W., N.P., P.G. and H.X.T. wrote the manuscript with input from all authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Materials thanks Cameron Kopas and the other, anonymous, reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Figs. S1–S4, Sections I–VI and Tables S1 and S2.
Source data
Source Data Fig. 1
Statistical source data for Fig. 1b.
Source Data Fig. 2
Statistical source data for Fig. 2b.
Source Data Fig. 3
Statistical source data for Fig. 3a–c,e,f.
Source Data Fig. 4
Statistical source data for Fig. 4a,b.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, D., Wu, Y., Pieczulewski, N. et al. All-nitride superconducting qubits based on atomic layer deposition. Nat. Mater. (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41563-025-02448-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41563-025-02448-8