Abstract
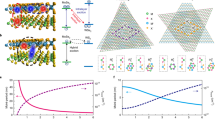
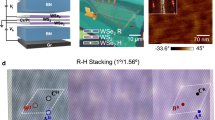
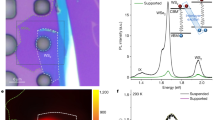
Spontaneous symmetry breaking, driven by competing interactions and quantum fluctuations, is fundamental to understanding ordered electronic phases. Although electrically neutral, optical excitations like excitons can interact through their dipole moment, raising the possibility of optically active ordered phases. The effects of spontaneous ordering on optical properties remains underexplored. The excitonic Mott insulating state recently observed in semiconducting moiré crystals may help clarify this question. Here we present evidence for an in-plane ferroelectric phase of dipolar moiré excitons driven by strong exciton–exciton interactions. We reveal a speed-up of photon emission at late times and low densities in excitonic decay. This counterintuitive behaviour is attributed to collective radiance, linked to the transition between disordered and symmetry-broken ferroelectric phases of moiré excitons. Our findings provide evidence for strong dipolar intersite interactions in moiré lattices, demonstrate collective photon emission as a probe for moiré quantum materials and a path for exploring cooperative optical phenomena in strongly correlated systems.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$32.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All the data that support the findings of this study are reported in the Article and its Supplementary Information. Source data are provided with this paper.
Change history
05 February 2026
In the version of the article initially published, Zach Hadjri, Runtong Li and Weijie Li were listed with affiliation 1 but should have been listed with affiliation 2 (Department of Physics, Emory University, Atlanta, USA) and Daniel Suárez-Forero, Klevis Domi, Bosai Lyu, Ludivine Fausten, Valeria Vento and Nicolas Ubrig were listed with affiliation 2 but should have been listed with affiliation 1 (Department of Quantum Matter Physics, University of Geneva, Geneva, Geneva, Switzerland). These errors have been corrected in the HTML and PDF versions of the article.
References
Cai, J. et al. Signatures of fractional quantum anomalous Hall states in twisted MoTe2. Nature 622, 63–68 (2023).
Park, H. et al. Observation of fractionally quantized anomalous Hall effect. Nature 622, 74–79 (2023).
Zeng, Y. et al. Thermodynamic evidence of fractional Chern insulator in moiré MoTe2. Nature 622, 69–73 (2023).
Xu, Y. et al. Correlated insulating states at fractional fillings of moiré superlattices. Nature 587, 214–218 (2020).
Regan, E. C. et al. Mott and generalized Wigner crystal states in WSe2/WS2 moiré superlattices. Nature 579, 359–363 (2020).
Tang, Y. et al. Simulation of Hubbard model physics in WSe2/WS2 moiré superlattices. Nature 579, 353–358 (2020).
Shimazaki, Y. et al. Strongly correlated electrons and hybrid excitons in a moiré heterostructure. Nature 580, 472–477 (2020).
Smoleński, T. et al. Signatures of Wigner crystal of electrons in a monolayer semiconductor. Nature 595, 53–57 (2021).
Zhou, Y. et al. Bilayer Wigner crystals in a transition metal dichalcogenide heterostructure. Nature 595, 48–52 (2021).
Jin, C. et al. Observation of moiré excitons in WSe2/WS2 heterostructure superlattices. Nature 567, 76–80 (2019).
Tran, K. et al. Evidence for moiré excitons in van der Waals heterostructures. Nature 567, 71–75 (2019).
Karni, O. et al. Structure of the moiré exciton captured by imaging its electron and hole. Nature 603, 247–252 (2022).
Lagoin, C., Suffit, S., Baldwin, K., Pfeiffer, L. & Dubin, F. Mott insulator of strongly interacting two-dimensional semiconductor excitons. Nat. Phys. 18, 149–153 (2022).
Xiong, R. et al. Correlated insulator of excitons in WSe2/WS2 moiré superlattices. Science 380, 860–864 (2023).
Park, H. et al. Dipole ladders with large Hubbard interaction in a moiré exciton lattice. Nat. Phys. 19, 1286–1292 (2023).
Wang, X. et al. Intercell moiré exciton complexes in electron lattices. Nat. Mater. 22, 599–604 (2023).
Gao, B. et al. Excitonic Mott insulator in a Bose-Fermi-Hubbard system of moiré WS2/WSe2 heterobilayer. Nat. Commun. 15, 2305 (2024).
Lian, Z. et al. Valley-polarized excitonic mott insulator in WS2/WSe2 moiré superlattice. Nat. Phys. 20, 34–39 (2024).
Rivera, P. et al. Valley-polarized exciton dynamics in a 2D semiconductor heterostructure. Science 351, 688–691 (2016).
Li, W., Lu, X., Dubey, S., Devenica, L. & Srivastava, A. Dipolar interactions between localized interlayer excitons in van der Waals heterostructures. Nat. Mater. 19, 624–629 (2020).
Kremser, M. et al. Discrete interactions between a few interlayer excitons trapped at a MoSe2-WSe2 heterointerface. npj 2DMater. Appl. 4, 39 (2020).
Lagoin, C. et al. Extended Bose–Hubbard model with dipolar excitons. Nature 609, 485–489 (2022).
Lagoin, C., Baldwin, K., Pfeiffer, L. & Dubin, F. Superlattice quantum solid of dipolar excitons. Phys. Rev. Lett. 132, 176001 (2024).
Kumlin, J., Srivastava, A. & Pohl, T. Superradiance of strongly interacting dipolar excitons in moiré quantum materials (2024). Phys. Rev. Lett. 134, 126901 (2025).
Huang, T.-S. et al. Collective optical properties of moiré‚ excitons. Phys. Rev. Lett. 134, 176901 (2025).
Lagoin, C., Morin, C., Baldwin, K., Pfeiffer, L. & Dubin, F. Evidence for a lattice supersolid of subradiant dipolar excitons. Preprint at http://arxiv.org/abs/2410.17162 (2024).
Li, H. et al. Imaging two-dimensional generalized Wigner crystals. Nature 597, 650–654 (2021).
Montblanch, A. R.-P. et al. Confinement of long-lived interlayer excitons in WS2/WSe2 heterostructures. Commun. Phys. 4, 119 (2021).
Miller, B. et al. Long-lived direct and indirect interlayer excitons in van der Waals heterostructures. Nano Lett. 17, 5229–5237 (2017).
Jauregui, L. A. et al. Electrical control of interlayer exciton dynamics in atomically thin heterostructures. Science 366, 870–875 (2019).
Choi, J. et al. Twist angle-dependent interlayer exciton lifetimes in van der Waals heterostructures. Phys. Rev. Lett. 126, 047401 (2021).
Moody, G., Schaibley, J. & Xu, X. Exciton dynamics in monolayer transition metal dichalcogenides. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 33, C39–C49 (2016).
Zhang, X.-X., You, Y., Zhao, S. Y. F. & Heinz, T. F. Experimental evidence for dark excitons in monolayer WSe2. Phys. Rev. Lett. 115, 257403 (2015).
Wu, F., Lovorn, T., Tutuc, E. & MacDonald, A. H. Hubbard model physics in transition metal dichalcogenide moiré bands. Phys. Rev. Lett. 121, 026402 (2018).
Shabani, S. et al. Deep moiré potentials in twisted transition metal dichalcogenide bilayers. Nat. Phys. 17, 720–725 (2021).
Wilson, N. R. et al. Determination of band offsets, hybridization, and exciton binding in 2D semiconductor heterostructures. Sci. Adv. 3, e1601832 (2017).
Zhang, D., Schoenherr, P., Sharma, P. & Seidel, J. Ferroelectric order in van der Waals layered materials. Nat. Rev. Mater. 8, 25–40 (2023).
de Paz, A. et al. Nonequilibrium quantum magnetism in a dipolar lattice gas. Phys. Rev. Lett. 111, 185305 (2013).
Zhang, C., Safavi-Naini, A., Rey, A. M. & Capogrosso-Sansone, B. Equilibrium phases of tilted dipolar lattice bosons. New J. Phys. 17, 123014 (2015).
Huber, J., Kirton, P. & Rabl, P. Nonequilibrium magnetic phases in spin lattices with gain and loss. Phys. Rev. A 102, 012219 (2020).
Su, L. et al. Dipolar quantum solids emerging in a Hubbard quantum simulator. Nature 622, 724–729 (2023).
Rui, J. et al. A subradiant optical mirror formed by a single structured atomic layer. Nature 583, 369–374 (2020).
Wu, F. Y. The Potts model. Rev. Mod. Phys. 54, 235–268 (1982).
Park, H. Three-state Potts model on a triangular lattice. Phys. Rev. B 49, 12881–12887 (1994).
de Vega, I., Cirac, J. I. & Porras, D. Detection of spin correlations in optical lattices by light scattering. Phys. Rev. A 77, 051804 (2008).
Pizzi, A., Gorlach, A., Rivera, N., Nunnenkamp, A. & Kaminer, I. Light emission from strongly driven many-body systems. Nat. Phys. 19, 551–561 (2023).
Zomer, P., Guimarães, M., Brant, J., Tombros, N. & Van Wees, B. Fast pick up technique for high quality heterostructures of bilayer graphene and hexagonal boron nitride. Appl. Phys. Lett. 105, 013101 (2014).
Kim, K. et al. Van der Waals heterostructures with high accuracy rotational alignment. Nano Lett. 16, 1989–1995 (2016).
Acknowledgements
We thank L. Zhang, M. Hafezi, A. Imamoğlu, M. Claassen, T. Smoleński and M. Kroner for insightful discussions. A.S. acknowledges funding from the NSF Division of Materials Research (award number 1905809) and the State Secretariat for Education, Research and Innovation (SERI)-funded European Research Council Consolidator Grant TuneInt2Quantum (number 101043957). T.P. and J.K. acknowledge support from the European Union’s Horizon Europe research and innovation programme under the Marie Skłodowska-Curie grant agreement number 101106552 (QuLowD), from the Austrian Science Fund (grant number 10.55776/COE1) and the European Union (NextGenerationEU), and from the European Research Council through the ERC Synergy Grant SuperWave (grant number 101071882). Synthesis of WSe2 (S.L. and J.H.) was supported by the NSF MRSEC program through the Columbia University Center for Precision-Assembled Quantum Materials (DMR-2011738). K.W. and T.T. acknowledge support from the JSPS KAKENHI (grant numbers 21H05233 and 23H02052), the CREST (JPMJCR24A5), JST and World Premier International Research Center Initiative (WPI), MEXT, Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
A.S., T.P., L.M.D., Z.H. and D.S.-F. conceived the project. K.W. and T.T. provided the hBN crystals, and S.L. and J.H. provided the WSe2 crystals. L.M.D., B.L., W.L., Z.H. and L.F. prepared the samples. L.M.D., Z.H., R.L., D.S.-F., K.D., B.L., V.V., N.U. and L.F. carried out the measurements. J.K. and T.P. developed the theoretical model and conducted the Monte Carlo simulations. A.S. and T.P. supervised the project. All authors were involved in the analysis of the experimental data and contributed extensively.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Materials thanks the anonymous reviewers for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Figs. 1–17 and Notes 1–5.
Source data
Source Data Fig. 1
Statistical source data.
Source Data Fig. 2
Statistical source data.
Source Data Fig. 3
Statistical source data.
Source Data Fig. 4
Statistical source data.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Devenica, L.M., Hadjri, Z., Kumlin, J. et al. Collective photon emission and ferroelectric exciton ordering near Mott insulating state in WSe2/WS2 heterobilayers. Nat. Mater. (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41563-025-02476-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41563-025-02476-4