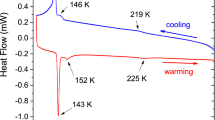
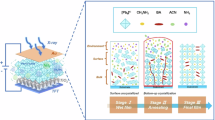
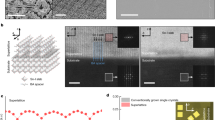
Abstract
Coherent heterojunctions, quantum wells and multiple quantum wells are needed for high-performance devices; these are generally grown via a dedicated vapour phase epitaxy process. Here we demonstrate the growth of coherent perovskite heterojunctions and quantum wells made of mixed-dimensional perovskites using a solution process. By exploiting the solubility difference of methylammonium (MA+) and 4-(aminomethyl)piperidinium (4AMP2+), we assemble layered perovskites with different layer numbers. The resulting 4AMP-MAn–1PbnI3n+1 materials each with different layer numbers or bandgaps form quantum wells. Heterojunctions and quantum wells made of 4AMP-MA2Pb3I10 (n = 3) and 4AMP-MAPb2I7 (n = 2) with various barrier thickness are tailored by the solution temperature profile during crystal growth. Multiple quantum wells have been formed by cycling temperature profiles. The planar heterojunction and quantum wells have lattice matching without interfacial defects, and exhibit strong thermal stability. Type I band alignment at the n = 2/n = 3 heterojunction is confirmed by both computation and optical studies. This study opens a new direction for the development of sophisticated perovskite heterojunction and quantum well devices.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$32.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in the article and its Supplementary Information. Source Data are provided with this paper.
References
Peng, J., Chen, Y., Zheng, K., Pullerits, T. & Liang, Z. Insights into charge carrier dynamics in organo-metal halide perovskites: from neat films to solar cells. Chem. Soc. Rev. 46, 5714–5729 (2017).
Dong, Q. et al. Electron-hole diffusion lengths >175 μm in solution-grown CH3NH3PbI3 single crystals. Science 347, 967–970 (2015).
De Wolf, S. et al. Organometallic halide perovskites: sharp optical absorption edge and its relation to photovoltaic performance. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 5, 1035–1039 (2014).
Fei, C. et al. Lead-chelating hole-transport layers for efficient and stable perovskite minimodules. Science 380, 823–829 (2023).
Huang, Z. et al. Anion–π interactions suppress phase impurities in FAPbI3 solar cells. Nature 623, 531–537 (2023).
Lin, K. et al. Perovskite light-emitting diodes with external quantum efficiency exceeding 20 per cent. Nature 562, 245–248 (2018).
Li, J. et al. Efficient all-thermally evaporated perovskite light-emitting diodes for active-matrix displays. Nat. Photon. 17, 435–441 (2023).
Zhao, L. et al. High-yield growth of FACsPbBr3 single crystals with low defect density from mixed solvents for gamma-ray spectroscopy. Nat. Photon. 17, 315–323 (2023).
He, Y. et al. CsPbBr3 perovskite detectors with 1.4% energy resolution for high-energy γ-rays. Nat. Photon. 15, 36–42 (2021).
Sakhatskyi, K. et al. Stable perovskite single-crystal X-ray imaging detectors with single-photon sensitivity. Nat. Photon. 17, 510–517 (2023).
Zhou, Y. et al. Self-powered perovskite photon-counting detectors. Nature 616, 712–718 (2023).
Szabó, G., Park, N.-G., De Angelis, F. & Kamat, P. V. Are perovskite solar cells reaching the efficiency and voltage limits? ACS Energy Lett. 8, 3829–3831 (2023).
Luo, L. et al. Stabilization of 3D/2D perovskite heterostructures via inhibition of ion diffusion by cross-linked polymers for solar cells with improved performance. Nat. Energy 8, 294–303 (2023).
Zhou, Y. et al. Heterojunction structures for reduced noise in large-area and sensitive perovskite X-ray detectors. Sci. Adv. 7, eabg6716 (2021).
Li, H. et al. 2D/3D Heterojunction engineering at the buried interface towards high-performance inverted methylammonium-free perovskite solar cells. Nat. Energy 8, 946–955 (2023).
Lei, Y. et al. A fabrication process for flexible single-crystal perovskite devices. Nature 583, 790–795 (2020).
Chen, Y. et al. Strain engineering and epitaxial stabilization of halide perovskites. Nature 577, 209–215 (2020).
Mali, S. S. et al. Phase-heterojunction all-inorganic perovskite solar cells surpassing 21.5% efficiency. Nat. Energy 8, 989–1001 (2023).
Pan, D. et al. Deterministic fabrication of arbitrary vertical heterostructures of two-dimensional Ruddlesden–Popper halide perovskites. Nat. Nanotechnol. 16, 159–165 (2021).
Akriti et al. Layer-by-layer anionic diffusion in two-dimensional halide perovskite vertical heterostructures. Nat. Nanotechnol. 16, 584–591 (2021).
Yi, M. & Shen, Z. A review on mechanical exfoliation for the scalable production of graphene. J. Mater. Chem. A 3, 11700–11715 (2015).
Shi, E. et al. Two-dimensional halide perovskite lateral epitaxial heterostructures. Nature 580, 614–620 (2020).
Luo, Y. et al. Photo-induced halide redistribution in 2D halide perovskite lateral heterostructures. Joule 7, 2376–2385 (2023).
Roy, C. R. et al. Anion exchange of Ruddlesden–Popper lead halide perovskites produces stable lateral heterostructures. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 143, 5212–5221 (2021).
Dou, L. et al. Spatially resolved multicolor CsPbX3 nanowire heterojunctions via anion exchange. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 114, 7216–7221 (2017).
Lai, M. et al. Intrinsic anion diffusivity in lead halide perovskites is facilitated by a soft lattice. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 115, 11929–11934 (2018).
Zhang, X. et al. Solution-grown large-sized single-crystalline 2D/3D perovskite heterostructure for self-powered photodetection. Adv Optical Mater. 8, 2000311 (2020).
Zhang, X., Zhu, T., Ji, C., Yao, Y. & Luo, J. In situ epitaxial growth of centimeter-sized lead-free (BA)2CsAgBiBr7/Cs2AgBiBr6 heterocrystals for self-driven X-ray detection. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 143, 20802–20810 (2021).
Cao M. et al. Perovskite heterojunction based on CH3NH3PbBr3 single crystal for high-sensitive self-powered photodetector. Appl. Phys. Lett. 109, (2016).
Pan, Y. et al. Visible elimination, ultraviolet and near-infrared dual-band photodetector based on single-crystal perovskite heterojunctions toward secure optical communication. ACS Photon. 11, 1252–1263 (2024).
Zhu, Z. et al. Room-temperature epitaxial welding of 3D and 2D perovskites. Nat. Mater. 21, 1042–1049 (2022).
Barker, A. J. et al. Defect-assisted photoinduced halide segregation in mixed-halide perovskite thin films. ACS Energy Lett. 2, 1416–1424 (2017).
Yoon, S. J., Kuno, M. & Kamat, P. V. Shift happens. How halide ion defects influence photoinduced segregation in mixed halide perovskites. ACS Energy Lett. 2, 1507–1514 (2017).
Panish, M. B. Molecular beam epitaxy. Science 208, 916–922 (1980).
Cho, A. Y. & Arthur, J. R. Molecular beam epitaxy. Prog. Solid State Chem. 10, 157–191 (1975).
Liu, Y., Yang, Z. & Liu, S. Recent progress in single-crystalline perovskite research including crystal preparation, property evaluation, and applications. Adv. Sci. 5, 1700471 (2018).
Shi, Z., Ni, Z. & Huang, J. Direct observation of fast carriers transport along out-of-plane direction in a Dion–Jacobson layered perovskite. ACS Energy Lett. 7, 984–987 (2022).
Lin, Y. et al. Unveiling the operation mechanism of layered perovskite solar cells. Nat. Commun. 10, 1008 (2019).
Mao, L. et al. Hybrid Dion–Jacobson 2D lead iodide perovskites. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 140, 3775–3783 (2018).
Mao, L. et al. Seven-layered 2D hybrid lead iodide perovskites. Chem 5, 2593–2604 (2019).
Ni, Z. et al. High grain boundary recombination velocity in polycrystalline metal halide perovskites. Sci. Adv. 8, eabq8345 (2022).
Ziffer, M. E., Mohammed, J. C. & Ginger, D. S. Electroabsorption spectroscopy measurements of the exciton binding energy, electron-hole reduced effective mass, and bandgap in the perovskite CH3NH3PbI3. ACS Photon. 3, 1060–1068 (2016).
Kresse, G. & Furthmüller, J. Efficiency of ab initio total energy calculations for metals and semiconductors using a plane-wave basis set. Comput. Mater. Sci. 6, 15–50 (1996).
Kresse, G. & Furthmüller, J. Efficient iterative schemes for ab initio total-energy calculations using a plane-wave basis set. Phys. Rev. B 54, 11169 (1996).
Blöchl, P. E. Projector augmented-wave method. Phys. Rev. B 50, 17953 (1994).
Perdew, J. P., Burke, K. & Ernzerhof, M. Generalized gradient approximation made simple. Phys. Rev. Lett. 77, 3865 (1996).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Center for Hybrid Organic Inorganic Semiconductors for Energy (CHOISE), an Energy Frontier Research Center funded by the Office of Basic Energy Sciences, Office of Science within the US Department of Energy. The WAXS measurements used resources of the Center for Functional Nanomaterials and the SMI beamline (12-ID) of the National Synchrotron Light Source II, both supported by US DOE Office of Science Facilities at Brookhaven National Laboratory under contract no. DE-SC0012704.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Z.S. and J.H. conceived the idea. Z.S. designed the experiments, synthesized heterojunction crystals, and performed XRD and PL related measurements. H.Z. and Y.Z. conducted the WAXS measurement and analysed related data. H.J. performed SEM measurements. Y.X., X.W. and Y.Y. performed the DFT band alignment calculations. Z.N. provided helpful suggestions about PL measurements. Z.S. and J.H. wrote the paper, and all authors reviewed the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Photonics thanks the anonymous reviewers for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Figs. 1–14 and Table 1.
Source data
Source Data Fig. 1
Source data.
Source Data Fig. 2
Source data.
Source Data Fig. 3
Source data.
Source Data Fig. 4
Source data.
Source Data Fig. 5
Source data.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, Z., Xian, Y., Wang, X. et al. Tunable coherent mixed-dimensional perovskite heterojunctions and quantum wells grown from solution. Nat. Photon. 19, 1056–1063 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41566-025-01723-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41566-025-01723-z