Abstract
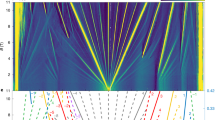
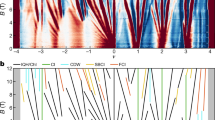
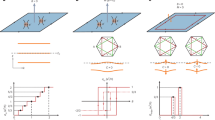
Magic-angle twisted bilayer graphene hosts a variety of strongly correlated states at partial fillings of its flat bands. In a magnetic field, these flat bands evolve into a Hofstadter spectrum renormalized by strong Coulomb interactions. Here we study the interacting Hofstadter states that spontaneously form within the topological magnetic sub-bands of an ultraclean magic-angle twisted bilayer graphene device, including symmetry-broken Chern insulator states and fractional quantum Hall states. The observed symmetry-broken Chern insulator states form a cascade, with their Chern numbers mimicking the main sequence of correlated Chern insulators. The fractional quantum Hall states form in a Jain sequence. However, they disappear at high magnetic field, in contrast to conventional fractional quantum Hall states that strengthen with increasing magnetic field. We reveal a magnetic-field-driven phase transition from composite fermion phases to a dissipative Fermi liquid. Our theoretical analysis of the magnetic sub-bands hosting the fractional quantum Hall states predicts non-uniform quantum geometric properties far from the lowest Landau level. This points towards a more natural interpretation of these states as in-field fractional Chern insulators of the magnetic sub-bands.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$32.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Source data are provided with this paper. All other data are available from the corresponding authors upon reasonable request.
Code availability
The code used for the data analysis in this study is available from the corresponding authors upon reasonable request.
References
Hofstadter, D. R. Energy levels and wave functions of Bloch electrons in rational and irrational magnetic fields. Phys. Rev. B 14, 2239–2249 (1976).
Wannier, G. H. A result not dependent on rationality for Bloch electrons in a magnetic field. Phys. Status Solidi B 88, 757–765 (1978).
Wang, L. et al. Evidence for a fractional fractal quantum Hall effect in graphene superlattices. Science 350, 1231–1234 (2015).
Spanton, E. M. et al. Observation of fractional Chern insulators in a van der Waals heterostructure. Science 360, 62–66 (2018).
Bistritzer, R. & MacDonald, A. H. Moiré bands in twisted double-layer graphene. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 108, 12233–12237 (2011).
Cao, Y. et al. Correlated insulator behaviour at half-filling in magic-angle graphene superlattices. Nature 556, 80–84 (2018).
Cao, Y. et al. Unconventional superconductivity in magic-angle graphene superlattices. Nature 556, 43–50 (2018).
Yankowitz, M. et al. Tuning superconductivity in twisted bilayer graphene. Science 363, eaav1910 (2019).
Lu, X. et al. Superconductors, orbital magnets and correlated states in magic-angle bilayer graphene. Nature 574, 653–657 (2019).
Sharpe, A. L. et al. Emergent ferromagnetism near three-quarters filling in twisted bilayer graphene. Science 365, 605–608 (2019).
Serlin, M. et al. Intrinsic quantized anomalous Hall effect in a moiré heterostructure. Science 367, 900–903 (2020).
Xie, Y. et al. Fractional Chern insulators in magic-angle twisted bilayer graphene. Nature 600, 439–443 (2021).
Saito, Y. et al. Hofstadter subband ferromagnetism and symmetry-broken Chern insulators in twisted bilayer graphene. Nat. Phys. 17, 478–481 (2021).
Yu, J. et al. Correlated Hofstadter spectrum and flavour phase diagram in magic-angle twisted bilayer graphene. Nat. Phys. 18, 825–831 (2022).
Polshyn, H. et al. Topological charge density waves at half-integer filling of a moiré superlattice. Nat. Phys. 18, 42–47 (2021).
He, M. et al. Symmetry-broken Chern insulators in twisted double bilayer graphene. Nano Lett. 23, 11066–11072 (2023).
Park, J. M., Cao, Y., Watanabe, K., Taniguchi, T. & Jarillo-Herrero, P. Flavour Hund’s coupling, Chern gaps and charge diffusivity in moiré graphene. Nature 592, 43–48 (2021).
Nuckolls, K. P. et al. Strongly correlated Chern insulators in magic-angle twisted bilayer graphene. Nature 588, 610–615 (2020).
Choi, Y. et al. Correlation-driven topological phases in magic-angle twisted bilayer graphene. Nature 589, 536–541 (2021).
Das, I. et al. Symmetry-broken Chern insulators and Rashba-like Landau-level crossings in magic-angle bilayer graphene. Nat. Phys. 17, 710–714 (2021).
Wu, S., Zhang, Z., Watanabe, K., Taniguchi, T. & Andrei, E. Y. Chern insulators, van Hove singularities and topological flat bands in magic-angle twisted bilayer graphene. Nat. Mater. 20, 488–494 (2021).
Wang, X. & Vafek, O. Theory of correlated Chern insulators in twisted bilayer graphene. Phys. Rev. X 14, 021042 (2023).
Jain, J. K. Composite-fermion approach for the fractional quantum Hall effect. Phys. Rev. Lett. 63, 199–202 (1989).
Polski, R. et al. Hierarchy of symmetry breaking correlated phases in twisted bilayer graphene. Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/2205.05225 (2022).
He, M. et al. Dynamically tunable moiré exciton Rydberg states in a monolayer semiconductor on twisted bilayer graphene. Nat. Mater. 23, 224–229 (2024).
Tschirhart, C. L. et al. Imaging orbital ferromagnetism in a moiré Chern insulator. Science 372, 1323–1327 (2021).
Arora, H. S. et al. Superconductivity in metallic twisted bilayer graphene stabilized by WSe2. Nature 583, 379–384 (2020).
Lin, J.-X. et al. Spin-orbit–driven ferromagnetism at half moiré filling in magic-angle twisted bilayer graphene. Science 375, 437–441 (2022).
Stepanov, P. et al. Competing zero-field Chern insulators in superconducting twisted bilayer graphene. Phys. Rev. Lett. 127, 197701 (2021).
Grover, S. et al. Chern mosaic and Berry-curvature magnetism in magic-angle graphene. Nat. Phys. 18, 885–892 (2022).
Tseng, C.-C. et al. Anomalous Hall effect at half filling in twisted bilayer graphene. Nat. Phys. 18, 1038–1042 (2022).
Streda, P. Quantised Hall effect in a two-dimensional periodic potential. J. Phys. C 15, L1299 (1982).
Kwan, Y. H. et al. Kekulé spiral order at all nonzero integer fillings in twisted bilayer graphene. Phys. Rev. X 11, 041063 (2021).
Nuckolls, K. P. et al. Quantum textures of the many-body wavefunctions in magic-angle graphene. Nature 620, 525–532 (2023).
Uri, A. et al. Mapping the twist-angle disorder and Landau levels in magic-angle graphene. Nature 581, 47–52 (2020).
Bolotin, K. I., Ghahari, F., Shulman, M. D., Stormer, H. L. & Kim, P. Observation of the fractional quantum Hall effect in graphene. Nature 462, 196–199 (2009).
Du, X., Skachko, I., Duerr, F., Luican, A. & Andrei, E. Y. Fractional quantum Hall effect and insulating phase of Dirac electrons in graphene. Nature 462, 192–195 (2009).
Ghahari, F., Zhao, Y., Cadden-Zimansky, P., Bolotin, K. & Kim, P. Measurement of the ν = 1/3 fractional quantum Hall energy gap in suspended graphene. Phys. Rev. Lett. 106, 046801 (2011).
Dean, C. R. et al. Multicomponent fractional quantum Hall effect in graphene. Nat. Phys. 7, 693–696 (2011).
Feldman, B. E., Krauss, B., Smet, J. H. & Yacoby, A. Unconventional sequence of fractional quantum Hall states in suspended graphene. Science 337, 1196–1199 (2012).
Kou, A. et al. Electron-hole asymmetric integer and fractional quantum Hall effect in bilayer graphene. Science 345, 55–57 (2014).
Maher, P. et al. Tunable fractional quantum Hall phases in bilayer graphene. Science 345, 61–64 (2014).
Li, J. I. A. et al. Even-denominator fractional quantum Hall states in bilayer graphene. Science 358, 648–652 (2017).
Zibrov, A. A. et al. Tunable interacting composite fermion phases in a half-filled bilayer-graphene Landau level. Nature 549, 360–364 (2017).
Huang, K. et al. Valley isospin controlled fractional quantum Hall states in bilayer graphene. Phys. Rev. X 12, 031019 (2022).
Haldane, F. D. M. Fractional quantization of the Hall effect: a hierarchy of incompressible quantum fluid states. Phys. Rev. Lett. 51, 605–608 (1983).
Roy, R. Band geometry of fractional topological insulators. Phys. Rev. B 90, 165139 (2014).
Parker, D. et al. Field-tuned and zero-field fractional Chern insulators in magic angle graphene. Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/2112.13837 (2021).
Wang, N. et al. Quantum-metric-induced nonlinear transport in a topological antiferromagnet. Nature 621, 487–492 (2023).
Gao, A. et al. Quantum metric nonlinear Hall effect in a topological antiferromagnetic heterostructure. Science 381, 181–186 (2023).
Luu, T. T. & Wörner, H. J. Measurement of the Berry curvature of solids using high-harmonic spectroscopy. Nat. Commun. 9, 916 (2018).
Schüler, M. et al. Local Berry curvature signatures in dichroic angle-resolved photoelectron spectroscopy from two-dimensional materials. Sci. Adv. 6, eaay2730 (2020).
de Juan, F., Grushin, A. G., Morimoto, T. & Moore, J. E. Quantized circular photogalvanic effect in Weyl semimetals. Nat. Commun. 8, 15995 (2017).
Acknowledgements
The work at UW is supported by NSF MRSEC DMR-2308979. M.H. acknowledges support from the Princeton quantum initiative. X.W. acknowledges support from the National High Magnetic Field Laboratory through NSF Grant No. DMR-2128556 and the State of Florida. B.A.B. was supported by Simons Investigator Grant No. 404513. B.A.B. and O.V. are supported by the Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation’s EPiQS Initiative (Grant No. GBMF11070). K.W. and T.T. acknowledge support from the JSPS KAKENHI (Grant Nos. 21H05233 and 23H02052) and the World Premier International Research Center Initiative, MEXT, Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
M.H. fabricated the devices. M.H. and J.C. performed the measurements and analysed the data supervised by M.Y. and X.X. X.W. performed the theoretical calculations supervised by O.V., with theory inputs from J.H.-A., R.P., A.S. and B.A.B. K.W. and T.T. grew the hBN crystals. M.H., X.W., M.Y., O.V. and X.X. wrote the paper with input from all authors.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Physics thanks the anonymous reviewers for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Figs. 1–18 and Notes 1–3.
Source data
Source Data Fig. 1
Source data for Fig. 1.
Source Data Fig. 2
Source data for Fig. 2.
Source Data Fig. 3
Source data for Fig. 3.
Source Data Fig. 4
Source data for Fig. 4.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
He, M., Wang, X., Cai, J. et al. Strongly interacting Hofstadter states in magic-angle twisted bilayer graphene. Nat. Phys. 21, 1380–1386 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41567-025-02997-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41567-025-02997-4
This article is cited by
-
Optical control of orbital magnetism in magic-angle twisted bilayer graphene
Nature Physics (2026)