Abstract
Bright point-defect emitters in hexagonal boron nitride have potential applications in quantum sensing and other technologies. However, it can be difficult to correctly identify the microscopic nature of observed defects, creating challenges for further development. A class of bright emitters exhibiting optically detected magnetic resonance with no resolvable zero-field splitting has been observed in hexagonal boron nitride across a broad range of wavelengths. However, the microscopic structure of the defects and the physical origin of their optically detected magnetic resonance signal have still not been identified. Here we describe a model that accounts for and provides a physical explanation for all key experimental features of the spin-resolved photodynamics of ensembles and single emitters. The model, inspired by the radical-pair mechanism from spin chemistry, assumes a pair of nearby point defects, one of which is optically active. Using first-principles calculations, we show that simple defect pairs made of common carbon defects provide a plausible realization of our model. As well as addressing open questions about defects in hexagonal boron nitride, our model may also explain similar phenomena observed in other wide-bandgap semiconductors.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$32.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Source data are provided with this paper. All other data supporting the findings of this study are available within the paper and its Supplementary Information files.
References
Gottscholl, A. et al. Initialization and read-out of intrinsic spin defects in a van der Waals crystal at room temperature. Nat. Mater. 19, 540 (2020).
Gottscholl, A. et al. Room temperature coherent control of spin defects in hexagonal boron nitride. Sci. Adv. 7, eabf3630 (2021).
Liu, W. et al. Coherent dynamics of multi-spin \({\rm V_{\rm{B}}^{-}}\) center in hexagonal boron nitride. Nat. Commun. 13, 5713 (2022).
Gao, X. et al. Nuclear spin polarization and control in hexagonal boron nitride. Nat. Mater. 21, 1024 (2022).
Gong, R. et al. Coherent dynamics of strongly interacting electronic spin defects in hexagonal boron nitride. Nat. Commun. 14, 3299 (2023).
Healey, A. et al. Quantum microscopy with van der Waals heterostructures. Nat. Phys. 19, 87 (2023).
Ramsay, A. J. et al. Coherence protection of spin qubits in hexagonal boron nitride. Nat. Commun. 14, 461 (2023).
Rizzato, R. et al. Extending the coherence of spin defects in hBN enables advanced qubit control and quantum sensing. Nat. Commun. 14, 5089 (2023).
Atatüre, M., Englund, D., Vamivakas, N., Lee, S.-Y. & Wrachtrup, J. Material platforms for spin-based photonic quantum technologies. Nat. Rev. Mater. 3, 38 (2018).
Wolfowicz, G. et al. Quantum guidelines for solid-state spin defects. Nat. Rev. Mater. 6, 906 (2021).
Durand, A. et al. Optically active spin defects in few-layer thick hexagonal boron nitride. Phys. Rev. Lett. 131, 116902 (2023).
Robertson, I. O. et al. Detection of paramagnetic spins with an ultrathin van der Waals quantum sensor. ACS Nano 17, 13408 (2023).
Gao, X. et al. Quantum sensing of paramagnetic spins in liquids with spin qubits in hexagonal boron nitride. ACS Photonics 10, 2894 (2023).
Zhou, J. et al. Sensing spin wave excitations by spin defects in few-layer-thick hexagonal boron nitride. Sci. Adv. 10, eadk8495 (2024).
Yao, N. Y., Zaletel, M. P., Stamper-Kurn, D. M. & Vishwanath, A. A quantum dipolar spin liquid. Nat. Phys. 14, 405 (2018).
Davis, E. J. et al. Probing many-body dynamics in a two-dimensional dipolar spin ensemble. Nat. Phys. 19, 836 (2023).
Ivády, V. et al. Ab initio theory of the negatively charged boron vacancy qubit in hexagonal boron nitride. npj Comput. Mater. 6, 41 (2020).
Reimers, J. R. et al. Photoluminescence, photophysics, and photochemistry of the \({\rm V_{\rm{B}}^{-}}\) defect in hexagonal boron nitride. Phys. Rev. B 102, 144105 (2020).
Kianinia, M., White, S., Fröch, J. E., Bradac, C. & Aharonovich, I. Generation of spin defects in hexagonal boron nitride. ACS Photonics 7, 2147 (2020).
Gao, X. et al. High-contrast plasmonic-enhanced shallow spin defects in hexagonal boron nitride for quantum sensing. Nano Lett. 21, 7708 (2021).
Liu, W. et al. Temperature-dependent energy-level shifts of spin defects in hexagonal boron nitride. ACS Photonics 8, 1889 (2021).
Mathur, N. et al. Excited-state spin-resonance spectroscopy of \({\rm V_{\rm{B}}^{-}}\) defect centers in hexagonal boron nitride. Nat. Commun. 13, 3233 (2022).
Haykal, A. et al. Decoherence of \({\rm V_{\rm{B}}^{-}}\) spin defects in monoisotopic hexagonal boron nitride. Nat. Commun. 13, 4347 (2022).
Mendelson, N. et al. Identifying carbon as the source of visible single-photon emission from hexagonal boron nitride. Nat. Mater. 20, 321 (2021).
Chejanovsky, N. et al. Single-spin resonance in a van der Waals embedded paramagnetic defect. Nat. Mater. 20, 1079 (2021).
Stern, H. L. et al. Room-temperature optically detected magnetic resonance of single defects in hexagonal boron nitride. Nat. Commun. 13, 618 (2022).
Guo, N.-J. et al. Coherent control of an ultrabright single spin in hexagonal boron nitride at room temperature. Nat. Commun. 14, 2893 (2023).
Yang, Y.-Z. et al. Laser direct writing of visible spin defects in hexagonal boron nitride for applications in spin-based technologies. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 6, 6407 (2023).
Scholten, S. C. et al. Multi-species optically addressable spin defects in a van der Waals material. Nat. Commun. 15, 6727 (2024).
Patel, R. N. et al. Room temperature dynamics of an optically addressable single spin in hexagonal boron nitride. Nano Lett. 24, 7623 (2024).
Singh, P. et al. Violet to near-infrared optical addressing of spin pairs in hexagonal boron nitride. Adv. Mater. 37, 2414846 (2025).
Auburger, P. & Gali, A. Towards ab initio identification of paramagnetic substitutional carbon defects in hexagonal boron nitride acting as quantum bits. Phys. Rev. B 104, 075410 (2021).
Pinilla, F. et al. Spin-active single photon emitters in hexagonal boron nitride from carbon-based defects. Phys. Scr. 98, 095505 (2023).
Golami, O. et al. Ab initio and group theoretical study of properties of a carbon trimer defect in hexagonal boron nitride. Phys. Rev. B 105, 184101 (2022).
Tan, Q. et al. Donor-acceptor pair quantum emitters in hexagonal boron nitride. Nano Lett. 22, 1331 (2022).
Benedek, Z. et al. Symmetric carbon tetramers forming spin qubits in hexagonal boron nitride. npj Comput. Mater. 9, 187 (2023).
Hunter, D., Hoff, A. & Hore, P. Theoretical calculations of RYDMR effects in photosynthetic bacteria. Chem. Phys. Lett. 134, 6 (1987).
Steiner, U. E. & Ulrich, T. Magnetic field effects in chemical kinetics and related phenomena. Chem. Rev. 89, 51 (1989).
Woodward, J. R. Radical pairs in solution. Prog. React. Kinet. Mech. 27, 165 (2002).
Evans, E. W. et al. Magnetic field effects in flavoproteins and related systems. Interface Focus 3, 20130037 (2013).
Luo, J., Geng, Y., Rana, F. & Fuchs, G. D. Room temperature optically detected magnetic resonance of single spins in GaN. Nat. Mater. 23, 512 (2024).
McCamey, D. R. et al. Hyperfine-field-mediated spin beating in electrostatically bound charge carrier pairs. Phys. Rev. Lett. 104, 017601 (2010).
Lee, S.-Y. et al. Tuning hyperfine fields in conjugated polymers for coherent organic spintronics. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 133, 2019 (2011).
Kosugi, N., Matsuo, S., Konno, K. & Hatakenaka, N. Theory of damped Rabi oscillations. Phys. Rev. B 72, 172509 (2005).
Davies, J. Optically-detected magnetic resonance studies of II-VI compounds. J. Cryst. Growth 86, 599 (1988).
Boehme, C. & Lips, K. Theory of time-domain measurement of spin-dependent recombination with pulsed electrically detected magnetic resonance. Phys. Rev. B 68, 245105 (2003).
Dean, P. Inter-impurity recombinations in semiconductors. Prog. Solid State Chem. 8, 1–126 (1973).
Tran, T. T., Bray, K., Ford, M. J., Toth, M. & Aharonovich, I. Quantum emission from hexagonal boron nitride monolayers. Nat. Nanotechnol. 11, 37 (2016).
Kumar, A. et al. Localized creation of yellow single photon emitting carbon complexes in hexagonal boron nitride. APL Mater. 11, 071108 (2023).
Pelliciari, J. et al. Elementary excitations of single-photon emitters in hexagonal boron nitride. Nat. Mater. 23, 1230–1236 (2024).
Liu, W. et al. Experimental observation of spin defects in van der Waals material GeS2. Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/2410.18892 (2024).
Stern, H. L. et al. A quantum coherent spin in hexagonal boron nitride at ambient conditions. Nat. Mater. 23, 1379–1385 (2024).
Gao, X. et al. Single nuclear spin detection and control in a van der Waals material. Nature 643, 943–949 (2025).
Onodera, M. et al. Carbon-rich domain in hexagonal boron nitride: carrier mobility degradation and anomalous bending of the Landau fan diagram in adjacent graphene. Nano Lett. 19, 7282 (2019).
Jara, C. et al. First-principles identification of single photon emitters based on carbon clusters in hexagonal boron nitride. J. Phys. Chem. A 125, 1325 (2021).
Linderälv, C., Wieczorek, W. & Erhart, P. Vibrational signatures for the identification of single-photon emitters in hexagonal boron nitride. Phys. Rev. B 103, 115421 (2021).
Lillie, S. E. et al. Laser modulation of superconductivity in a cryogenic wide-field nitrogen-vacancy microscope. Nano Lett. 20, 1855 (2020).
Bluvstein, D., Zhang, Z. & Jayich, A. C. B. Identifying and mitigating charge instabilities in shallow diamond nitrogen-vacancy centers. Phys. Rev. Lett. 122, 076101 (2019).
Johnston, D. C. Stretched exponential relaxation arising from a continuous sum of exponential decays. Phys. Rev. B 74, 184430 (2006).
Campaioli, F., Cole, J. H. & Hapuarachchi, H. Quantum master equations: tips and tricks for quantum optics, quantum computing, and beyond. PRX Quantum 5, 020202 (2024).
Blöchl, P. E. Projector augmented-wave method. Phys. Rev. B 50, 17953 (1994).
Heyd, J., Scuseria, G. E. & Ernzerhof, M. Hybrid functionals based on a screened Coulomb potential. J. Chem. Phys. 118, 8207 (2003).
Weston, L., Wickramaratne, D., Mackoit, M., Alkauskas, A. & Van de Walle, C. G. Native point defects and impurities in hexagonal boron nitride. Phys. Rev. B 97, 214104 (2018).
Grimme, S., Ehrlich, S. & Goerigk, L. Effect of the damping function in dispersion corrected density functional theory. J. Comput. Chem. 32, 1456 (2011).
Kresse, G. & Furthmüller, J. Efficiency of ab-initio total energy calculations for metals and semiconductors using a plane-wave basis set. Comput. Mater. Sci. 6, 15 (1996).
Jones, R. O. & Gunnarsson, O. The density functional formalism, its applications and prospects. Rev. Mod. Phys. 61, 689 (1989).
Szász, K., Hornos, T., Marsman, M. & Gali, A. Hyperfine coupling of point defects in semiconductors by hybrid density functional calculations: the role of core spin polarization. Phys. Rev. B 88, 075202 (2013).
Runge, E. & Gross, E. K. Density-functional theory for time-dependent systems. Phys. Rev. Lett. 52, 997 (1984).
Casida, M. E. in Recent Advances in Density Functional Methods, Part I (ed. Chong, D. P.) 155–192 (World Scientific, 1995).
Dreuw, A. & Head-Gordon, M. Single-reference ab initio methods for the calculation of excited states of large molecules. Chem. Rev. 105, 4009 (2005).
Neese, F. Software update: the ORCA program system–version 5.0. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev.: Comput. Mol. Sci. 12, e1606 (2022).
Weigend, F. & Ahlrichs, R. Balanced basis sets of split valence, triple zeta valence and quadruple zeta valence quality for H to Rn: design and assessment of accuracy. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 7, 3297 (2005).
Perdew, J. P., Ernzerhof, M. & Burke, K. Rationale for mixing exact exchange with density functional approximations. J. Chem. Phys. 105, 9982 (1996).
Benedek, Z., Ganyecz, Á., Pershin, A., Ivády, V. & Barcza, G. Accurate and convergent energetics of color centers by wavefunction theory. Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/2406.05092 (2024).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Australian Research Council (grant nos. CE200100010, FT200100073, FT220100053, DE200100279, DP220100178, DE230100192 and DP250100973), the Office of Naval Research Global (grant no. N62909-22-1-2028) and the Air Force Office of Scientific Research (grant no. FA2386-25-1-4044). I.O.R. is supported by an Australian Government Research Training Program Scholarship. P.R. acknowledges support through an RMIT University Vice-Chancellor’s Research Fellowship. V.I. acknowledges support from the National Research, Development and Innovation Office of Hungary within the Quantum Information National Laboratory of Hungary (grant nos. 2022-2.1.1-NL-2022-00004 and FK145395). This project is funded by the European Union under Horizon Europe (projects 101156088 and 101129663). First-principles calculations were enabled by resources provided by the National Academic Infrastructure for Supercomputing in Sweden at the Swedish National Infrastructure for Computing at Tetralith, partially funded by the Swedish Research Council (grant agreement no. 2022-06725) and KIFÜ high-performance computation units in Hungary.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
I.O.R., I.A. and J.-P.T. conceived of the project. I.O.R. and B.W. prepared the samples with assistance from A.J.H. and P.S. I.O.R., B.W. and P.R. built and performed the experiments with assistance from S.C.S., A.J.H. and M.K. I.O.R., S.C.S. and J.-P.T. performed the numerical simulations. G.B. and V.I. performed the ab initio calculations. D.A.B., I.A. and J.-P.T. supervised the project. All authors analysed the results and contributed to the writing of the paper.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Physics thanks Yuan Ping, Chong Zu and the other, anonymous, reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Extended data
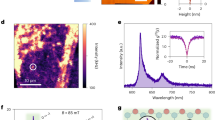
Extended Data Fig. 1 Example PL images.
(a) Widefield PL image of the dense powder sample used for ensemble measurements. (b) Confocal PL map of the dilute powder sample used for measurements of single emitters. Grey circle indicates a single emitter.
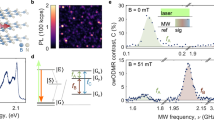
Extended Data Fig. 2 Spin dynamics measurements.
(a) Rabi measurement pulse sequence indicating the front (F1, F2) and back (B1, B2) gated regions for PL averaging. (b) F1, F2 and B1, B2 plotted against τ. (c) T1 pulse sequence similarly with F1, F2 and B1, B2 marked on the laser pulses which are plotted against τ in (d). (e) Hahn echo pulse sequence with F1, F2 and B1, B2 marked on the laser pulses which are plotted against τ in (f). Inset: Normalised Hahn echo data fit with a single exponential.
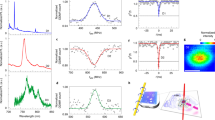
Extended Data Fig. 3 Stretched exponential function.
Distribution G(u) of the monoexponential components of a stretched exponential function for selected values of the stretch exponent β.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Figs. 1–22, Tables 1–7 and discussion.
Source data
Source Data Fig. 1
Data for all plots in Fig. 1.
Source Data Fig. 2
Data for all plots in Fig. 2.
Source Data Fig. 3
Data for all plots in Fig. 3.
Source Data Fig. 4
Data for all plots in Fig. 4.
Source Data Fig. 6
Data for all plots in Fig. 6.
Source Data Extended Data Fig. 1
Data for all plots in Extended Data Fig. 1.
Source Data Extended Data Fig. 2
Data for all plots in Extended Data Fig. 2.
Source Data Extended Data Fig. 3
Data for Extended Data Fig. 3.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Robertson, I.O., Whitefield, B., Scholten, S.C. et al. A charge transfer mechanism for optically addressable solid-state spin pairs. Nat. Phys. 21, 1981–1987 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41567-025-03091-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41567-025-03091-5
This article is cited by
-
Narrowband quantum emitters in hexagonal boron nitride with optically addressable spins
Nature Materials (2026)
-
Quantum sensing with spin defects in boron nitride nanotubes
Nature Communications (2025)
-
Raman signatures of single point defects in hexagonal boron nitride quantum emitters
npj Computational Materials (2025)