Abstract
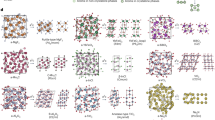
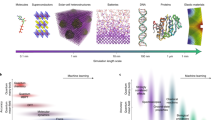
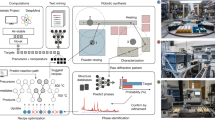
One of the grand challenges in the physical sciences is to ‘design’ a material before it is ever synthesized. There has been fast progress in predicting new solid-state compounds with the help of quantum-mechanical computations and supervised machine learning, and yet such progress has largely been limited to materials with ordered crystal structures. In this Perspective, we argue that the computational design of entirely non-crystalline, amorphous solids is an emerging and rewarding frontier in materials research. We show how recent advances in computational modelling and artificial intelligence can provide the previously missing links among atomic-scale structure, microscopic properties and macroscopic functionality of amorphous solids. Accordingly, we argue that the combination of physics-based modelling and artificial intelligence is now bringing amorphous functional materials ‘by design’ within reach. We discuss new implications for laboratory synthesis, and we outline our vision for the development of the field in the years ahead.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$32.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nayak, P. K., Mahesh, S., Snaith, H. J. & Cahen, D. Photovoltaic solar cell technologies: analysing the state of the art. Nat. Rev. Mater. 4, 269–285 (2019).
Kuzum, D., Jeyasingh, R. G. D., Lee, B. & Wong, H.-S. P. Nanoelectronic programmable synapses based on phase change materials for brain-inspired computing. Nano Lett. 12, 2179–2186 (2012).
van de Burgt, Y., Melianas, A., Keene, S. T., Malliaras, G. & Salleo, A. Organic electronics for neuromorphic computing. Nat. Electron. 1, 386–397 (2018).
Zhang, W., Mazzarello, R., Wuttig, M. & Ma, E. Designing crystallization in phase-change materials for universal memory and neuro-inspired computing. Nat. Rev. Mater. 4, 150–168 (2019).
Mannsfeld, S. C. B. et al. Highly sensitive flexible pressure sensors with microstructured rubber dielectric layers. Nat. Mater. 9, 859–864 (2010).
Laurila, T., Sainio, S. & Caro, M. A. Hybrid carbon based nanomaterials for electrochemical detection of biomolecules. Prog. Mater. Sci. 88, 499–594 (2017).
Kaspar, C., Ravoo, B. J., van der Wiel, W. G., Wegner, S. V. & Pernice, W. H. P. The rise of intelligent matter. Nature 594, 345–355 (2021).
Keen, D. A. & Goodwin, A. L. The crystallography of correlated disorder. Nature 521, 303–309 (2015).
Simonov, A. & Goodwin, A. L. Designing disorder into crystalline materials. Nat. Rev. Chem. 4, 657–673 (2020).
Elliott, S. R. Medium-range structural order in covalent amorphous solids. Nature 354, 445–452 (1991).
Wright, A. C. The great crystallite versus random network controversy: a personal perspective. Int. J. Appl. Glass Sci. 5, 31–56 (2014).
Tanaka, H., Tong, H., Shi, R. & Russo, J. Revealing key structural features hidden in liquids and glasses. Nat. Rev. Phys. 1, 333–348 (2019).
Savoie, B. M. et al. Mesoscale molecular network formation in amorphous organic materials. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 111, 10055–10060 (2014).
Kim, S., Agarwala, A. & Chowdhury, D. Fractionalization and topology in amorphous electronic solids. Phys. Rev. Lett. 130, 026202 (2023).
Nomura, K. et al. Room-temperature fabrication of transparent flexible thin-film transistors using amorphous oxide semiconductors. Nature 432, 488–492 (2004).
Smith, R. D. L. et al. Photochemical route for accessing amorphous metal oxide materials for water oxidation catalysis. Science 340, 60–63 (2013).
Han, F. et al. High electronic conductivity as the origin of lithium dendrite formation within solid electrolytes. Nat. Energy 4, 187–196 (2019).
Hong, S. et al. Ultralow-dielectric-constant amorphous boron nitride. Nature 582, 511–514 (2020).
Heo, J. et al. Amorphous iron fluorosulfate as a high-capacity cathode utilizing combined intercalation and conversion reactions with unexpectedly high reversibility. Nat. Energy 8, 30–39 (2022).
Hautier, G., Jain, A. & Ong, S. P. From the computer to the laboratory: materials discovery and design using first-principles calculations. J. Mater. Sci. 47, 7317–7340 (2012).
Saal, J. E., Kirklin, S., Aykol, M., Meredig, B. & Wolverton, C. Materials design and discovery with high-throughput density functional theory: the Open Quantum Materials Database (OQMD). JOM 65, 1501–1509 (2013).
Butler, T. et al. Computational materials design of crystalline solids. Chem. Soc. Rev. 45, 6138–6146 (2016).
Jain, A., Shin, Y. & Persson, K. A. Computational predictions of energy materials using density functional theory. Nat. Rev. Mater. 1, 15004 (2016).
Gorai, P., Stevanović, V. & Toberer, E. S. Computationally guided discovery of thermoelectric materials. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2, 17053 (2017).
Therrien, F., Jones, E. B. & Stevanović, V. Metastable materials discovery in the age of large-scale computation. Appl. Phys. Rev. 8, 031310 (2021).
Merchant, A. et al. Scaling deep learning for materials discovery. Nature 624, 80–85 (2023).
Szymanski, N. J. et al. An autonomous laboratory for the accelerated synthesis of novel materials. Nature 624, 86–91 (2023).
Burger, B. et al. A mobile robotic chemist. Nature 583, 237–241 (2020).
Miao, J., Ercius, P. & Billinge, S. J. L. Atomic electron tomography: 3D structures without crystals. Science 353, aaf2157 (2016).
Yang, Y. et al. Determining the three-dimensional atomic structure of an amorphous solid. Nature 592, 60–64 (2021).
Yuan, Y. et al. Three-dimensional atomic packing in amorphous solids with liquid-like structure. Nat. Mater. 21, 95–102 (2022).
Chang, C., Deringer, V. L., Katti, K. S., Van Speybroeck, V. & Wolverton, C. M. Simulations in the era of exascale computing. Nat. Rev. Mater. 8, 309–313 (2023).
Erhard, L. C., Rohrer, J., Albe, K. & Deringer, V. L. Modelling atomic and nanoscale structure in the silicon–oxygen system through active machine learning. Nat. Commun. 15, 1927 (2024).
Yabuuchi, N., Kubota, K., Dahbi, M. & Komaba, S. Research development on sodium-ion batteries. Chem. Rev. 114, 11636–11682 (2014).
Janek, J. & Zeier, W. G. A solid future for battery development. Nat. Energy 1, 16141 (2016).
Choi, J. W. & Aurbach, D. Promise and reality of post-lithium-ion batteries with high energy densities. Nat. Rev. Mater. 1, 16013 (2016).
Li, M., Lu, J., Chen, Z. & Amine, K. 30 years of lithium-ion batteries. Adv. Mater. 30, 1800561 (2018).
Vaalma, C., Buchholz, D., Weil, M. & Passerini, S. A cost and resource analysis of sodium-ion batteries. Nat. Rev. Mater. 3, 18013 (2018).
Nayak, P. K., Yang, L., Brehm, W. & Adelhelm, P. From lithium-ion to sodium-ion batteries: advantages, challenges, and surprises. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 57, 102–120 (2018).
Grey, C. P. & Hall, D. S. Prospects for lithium-ion batteries and beyond — a 2030 vision. Nat. Commun. 11, 6279 (2020).
Guo, T., Hu, P., Li, L., Wang, Z. & Guo, L. Amorphous materials emerging as prospective electrodes for electrochemical energy storage and conversion. Chem 9, 1080–1093 (2023).
Jiang, Y. et al. Amorphous Fe2O3 as a high-capacity, high-rate and long-life anode material for lithium ion batteries. Nano Energy 4, 23–30 (2014).
Lin, L., Xu, X., Chu, C., Majeed, M. K. & Yang, J. Mesoporous amorphous silicon: a simple synthesis of a high-rate and long-life anode material for lithium-ion batteries. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 128, 14269–14272 (2016).
Ding, J., Ji, D., Yue, Y. & Smedskjaer, M. M. Amorphous materials for lithium-ion and post-lithium-ion batteries. Small 20, 2304270 (2024).
Wang, X. et al. Glassy Li metal anode for high-performance rechargeable Li batteries. Nat. Mater. 19, 1339–1345 (2020).
Stevens, D. A. & Dahn, J. R. High capacity anode materials for rechargeable sodium‐ion batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 147, 1271 (2000).
Stevens, D. A. & Dahn, J. R. The mechanisms of lithium and sodium insertion in carbon materials. J. Electrochem. Soc. 148, A803 (2001).
Zhao, R., Sun, N. & Xu, B. Recent advances in heterostructured carbon materials as anodes for sodium-ion batteries. Small Struct. 2, 2100132 (2021).
Kudu, Ö. U. et al. A review of structural properties and synthesis methods of solid electrolyte materials in the Li2S−P2S5 binary system. J. Power Sources 407, 31–43 (2018).
Hu, Y. et al. Superionic amorphous NaTaCl6 halide electrolyte for highly reversible all-solid-state Na-ion batteries. Matter 7, 1018–1034 (2024).
Ridley, P. et al. Amorphous and nanocrystalline halide solid electrolytes with enhanced sodium-ion conductivity. Matter 7, 485–499 (2024).
Wuttig, M. & Yamada, N. Phase-change materials for rewriteable data storage. Nat. Mater. 6, 824–832 (2007).
Akola, J. & Jones, R. O. Structure of amorphous Ge8Sb2Te11: GeTe-Sb2Te3 alloys and optical storage. Phys. Rev. B 79, 134118 (2009).
Kang, D.-H., Young Kim, N., Jeong, H. & Cheong, B. Understanding on the current-induced crystallization process and faster set write operation thereof in non-volatile phase change memory. Appl. Phys. Lett. 100, 063508 (2012).
Ambrogio, S. et al. An analog-AI chip for energy-efficient speech recognition and transcription. Nature 620, 768–775 (2023).
Rao, F. et al. Reducing the stochasticity of crystal nucleation to enable subnanosecond memory writing. Science 358, 1423–1427 (2017).
Liu, B. et al. Y-doped Sb2Te3 phase-change materials: toward a universal memory. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 12, 20672–20679 (2020).
Zhang, Y. et al. Characteristics of Si-doped Sb2Te3 thin films for phase-change random access memory. Appl. Surf. Sci. 254, 5602–5606 (2008).
Yang, J., Wang, D., Han, H. & Li, C. Roles of cocatalysts in photocatalysis and photoelectrocatalysis. Acc. Chem. Res. 46, 1900–1909 (2013).
Zhang, L. et al. Photoelectrocatalytic arene C–H amination. Nat. Catal. 2, 366–373 (2019).
Shan, B. et al. Binary molecular-semiconductor p–n junctions for photoelectrocatalytic CO2 reduction. Nat. Energy 4, 290–299 (2019).
Wang, B. M., Biesold, G., Zhang, M. & Lin, Z. Amorphous inorganic semiconductors for the development of solar cell, photoelectrocatalytic and photocatalytic applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 50, 6914–6949 (2021).
Anantharaj, S. & Noda, S. Amorphous catalysts and electrochemical water splitting: an untold story of harmony. Small 16, 1905779 (2020).
Chemelewski, W. D., Lee, H.-C., Lin, J.-F., Bard, A. J. & Mullins, C. B. Amorphous FeOOH oxygen evolution reaction catalyst for photoelectrochemical water splitting. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 136, 2843–2850 (2014).
Duan, Y. et al. Scaled-up synthesis of amorphous NiFeMo oxides and their rapid surface reconstruction for superior oxygen evolution catalysis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 58, 15772–15777 (2019).
Morales-Guio, C. G., Tilley, S. D., Vrubel, H., Grätzel, M. & Hu, X. Hydrogen evolution from a copper(I) oxide photocathode coated with an amorphous molybdenum sulphide catalyst. Nat. Commun. 5, 3059 (2014).
Wu, L. et al. The origin of high activity of amorphous MoS2 in the hydrogen evolution reaction. ChemSusChem 12, 4383–4389 (2019).
Yu, L. et al. Amorphous NiFe layered double hydroxide nanosheets decorated on 3D nickel phosphide nanoarrays: a hierarchical core–shell electrocatalyst for efficient oxygen evolution. J. Mater. Chem. A 6, 13619–13623 (2018).
Hu, Y. et al. Single Ru atoms stabilized by hybrid amorphous/crystalline FeCoNi layered double hydroxide for ultraefficient oxygen evolution. Adv. Energy Mater. 11, 2002816 (2021).
Tang, C. W. & VanSlyke, S. A. Organic electroluminescent diodes. Appl. Phys. Lett. 51, 913–915 (1987).
Noguchi, Y., Tanaka, Y., Ishii, H. & Brütting, W. Understanding spontaneous orientation polarization of amorphous organic semiconducting films and its application to devices. Synth. Met. 288, 117101 (2022).
Ito, E. et al. Spontaneous buildup of giant surface potential by vacuum deposition of Alq3 and its removal by visible light irradiation. J. Appl. Phys. 92, 7306–7310 (2002).
Tanaka, M., Auffray, M., Nakanotani, H. & Adachi, C. Spontaneous formation of metastable orientation with well-organized permanent dipole moment in organic glassy films. Nat. Mater. 21, 819–825 (2022).
Street, R. A. Thin-film transistors. Adv. Mater. 21, 2007–2022 (2009).
Nolas, G. S. & Goldsmid, H. J. The figure of merit in amorphous thermoelectrics. Phys. Stat. Sol. 194, 271–276 (2002).
Liang, H. et al. Flexible X-ray detectors based on amorphous Ga2O3 thin films. ACS Photon. 6, 351–359 (2019).
Clarke, D. R. & Phillpot, S. R. Thermal barrier coating materials. Mater. Today 8, 22–29 (2005).
Croissant, J. G., Fatieiev, Y., Almalik, A. & Khashab, N. M. Mesoporous silica and organosilica nanoparticles: physical chemistry, biosafety, delivery strategies, and biomedical applications. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 7, 1700831 (2018).
He, S. et al. Semiconductor glass with superior flexibility and high room temperature thermoelectric performance. Sci. Adv. 6, eaaz8423 (2020).
Fu, Y. et al. Superflexible inorganic Ag2Te0.6S0.4 fiber with high thermoelectric performance. Adv. Sci. 10, 2207642 (2023).
Croissant, J. G., Butler, K. S., Zink, J. I. & Brinker, C. J. Synthetic amorphous silica nanoparticles: toxicity, biomedical and environmental implications. Nat. Rev. Mater. 5, 886–909 (2020).
Toh, C.-T. et al. Synthesis and properties of free-standing monolayer amorphous carbon. Nature 577, 199–203 (2020).
Tian, H. et al. Disorder-tuned conductivity in amorphous monolayer carbon. Nature 615, 56–61 (2023).
Wang, W. H., Dong, C. & Shek, C. H. Bulk metallic glasses. Mater. Sci. Eng. R. Rep. 44, 45–89 (2004).
Štich, I., Car, R. & Parrinello, M. Amorphous silicon studied by ab initio molecular dynamics: preparation, structure, and properties. Phys. Rev. B 44, 11092–11104 (1991).
McCulloch, D. G., McKenzie, D. R. & Goringe, C. M. Ab initio simulations of the structure of amorphous carbon. Phys. Rev. B 61, 2349–2355 (2000).
Akola, J. & Jones, R. O. Structural phase transitions on the nanoscale: the crucial pattern in the phase-change materials Ge2Sb2Te5 and GeTe. Phys. Rev. B 76, 235201 (2007).
Hegedüs, J. & Elliott, S. R. Microscopic origin of the fast crystallization ability of Ge–Sb–Te phase-change memory materials. Nat. Mater. 7, 399–405 (2008).
Aykol, M., Dwaraknath, S. S., Sun, W. & Persson, K. A. Thermodynamic limit for synthesis of metastable inorganic materials. Sci. Adv. 4, eaaq0148 (2018).
Behler, J. First principles neural network potentials for reactive simulations of large molecular and condensed systems. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 56, 12828–12840 (2017).
Deringer, V. L., Caro, M. A. & Csányi, G. Machine learning interatomic potentials as emerging tools for materials science. Adv. Mater. 31, 1902765 (2019).
Friederich, P., Häse, F., Proppe, J. & Aspuru-Guzik, A. Machine-learned potentials for next-generation matter simulations. Nat. Mater. 20, 750–761 (2021).
Cheng, B., Mazzola, G., Pickard, C. J. & Ceriotti, M. Evidence for supercritical behaviour of high-pressure liquid hydrogen. Nature 585, 217–220 (2020).
Muhli, H. et al. Machine learning force fields based on local parametrization of dispersion interactions: application to the phase diagram of C60. Phys. Rev. B 104, 054106 (2021).
Zhou, Y., Kirkpatrick, W. & Deringer, V. L. Cluster fragments in amorphous phosphorus and their evolution under pressure. Adv. Mater. 34, 2107515 (2022).
Fan, Z. & Tanaka, H. Microscopic mechanisms of pressure-induced amorphous–amorphous transitions and crystallisation in silicon. Nat. Commun. 15, 368 (2024).
Zhou, Y., Zhang, W., Ma, E. & Deringer, V. L. Device-scale atomistic modelling of phase-change memory materials. Nat. Electron. 6, 746–754 (2023).
Deringer, V. L. & Csányi, G. Machine learning based interatomic potential for amorphous carbon. Phys. Rev. B 95, 094203 (2017).
Sosso, G. C., Miceli, G., Caravati, S., Behler, J. & Bernasconi, M. Neural network interatomic potential for the phase change material GeTe. Phys. Rev. B 85, 174103 (2012).
Mocanu, F. C. et al. Modeling the phase-change memory material, Ge2Sb2Te5, with a machine-learned interatomic potential. J. Phys. Chem. B 122, 8998–9006 (2018).
Deringer, V. L. et al. Realistic atomistic structure of amorphous silicon from machine-learning-driven molecular dynamics. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 9, 2879–2885 (2018).
Konstantinou, K., Mocanu, F. C., Lee, T.-H. & Elliott, S. R. Revealing the intrinsic nature of the mid-gap defects in amorphous Ge2Sb2Te5. Nat. Commun. 10, 3065 (2019).
Simoncelli, M., Mauri, F. & Marzari, N. Thermal conductivity of glasses: first-principles theory and applications. npj Comput. Mater. 9, 106 (2023).
Caro, M. A., Deringer, V. L., Koskinen, J., Laurila, T. & Csányi, G. Growth mechanism and origin of high sp3 content in tetrahedral amorphous carbon. Phys. Rev. Lett. 120, 166101 (2018).
Caro, M. A., Csányi, G., Laurila, T. & Deringer, V. L. Machine learning driven simulated deposition of carbon films: from low-density to diamond-like amorphous carbon. Phys. Rev. B 102, 174201 (2020).
Choy, K. L. Chemical vapour deposition of coatings. Prog. Mater. Sci. 48, 57–170 (2003).
Yang, H.-S. et al. Anomalously high thermal conductivity of amorphous Si deposited by hot-wire chemical vapor deposition. Phys. Rev. B 81, 104203 (2010).
Maita, J. M., Song, G., Colby, M. & Lee, S.-W. Atomic arrangement and mechanical properties of chemical-vapor-deposited amorphous boron. Mater. Des. 193, 108856 (2020).
Sun, L. et al. Chemical vapour deposition. Nat. Rev. Methods Primers 1, 5 (2021).
Wang, H. et al. Efficient screening framework for organic solar cells with deep learning and ensemble learning. npj Comput. Mater. 9, 200 (2023).
Basha, B. et al. Designing of novel organic semiconductors materials for organic solar cells: a machine learning assisted proficient pipeline. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 153, 110818 (2023).
Yoo, P. et al. Deep learning workflow for the inverse design of molecules with specific optoelectronic properties. Sci. Rep. 13, 20031 (2023).
Kilgour, M., Gastellu, N., Hui, D. Y. T., Bengio, Y. & Simine, L. Generating multiscale amorphous molecular structures using deep learning: a study in 2D. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 11, 8532–8537 (2020).
Kwon, H. et al. Spectroscopy-guided discovery of three-dimensional structures of disordered materials with diffusion models. Mach. Learn. Sci. Technol. 5, 045037 (2024).
Madanchi, A., Kilgour, M., Zysk, F., Kühne, T. D. & Simine, L. Simulations of disordered matter in 3D with the morphological autoregressive protocol (MAP) and convolutional neural networks. J. Chem. Phys. 160, 024101 (2024).
Barkema, G. T. & Mousseau, N. Event-based relaxation of continuous disordered systems. Phys. Rev. Lett. 77, 4358–4361 (1996).
Mousseau, N. & Barkema, G. T. Traveling through potential energy landscapes of disordered materials: the activation–relaxation technique. Phys. Rev. E 57, 2419–2424 (1998).
Madanchi, A. et al. Is the future of materials amorphous? Challenges and opportunities in simulations of amorphous materials. Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/2410.05035 (2024).
Opletal, G. et al. Hybrid approach for generating realistic amorphous carbon structure using metropolis and reverse Monte Carlo. Mol. Simul. 28, 927–938 (2002).
Nicholas, T. C. et al. Geometrically frustrated interactions drive structural complexity in amorphous calcium carbonate. Nat. Chem. 16, 36–41 (2024).
Leist, C., He, M., Liu, X., Kaiser, U. & Qi, H. Deep-learning pipeline for statistical quantification of amorphous two-dimensional materials. ACS Nano 16, 20488–20496 (2022).
Zarrouk, T., Ibragimova, R., Bartók, A. P. & Caro, M. A. Experiment-driven atomistic materials modeling: a case study combining X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and machine learning potentials to infer the structure of oxygen-rich amorphous carbon. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 146, 14645–14659 (2024).
Anker, A. S., Butler, K. T., Le, M. D., Perring, T. G. & Thiyagalingam, J. Using generative adversarial networks to match experimental and simulated inelastic neutron scattering data. Digit. Discov. 2, 578–590 (2023).
Khan, A., Lee, C.-H., Huang, P. Y. & Clark, B. K. Leveraging generative adversarial networks to create realistic scanning transmission electron microscopy images. npj Comput. Mater. 9, 85 (2023).
Sosso, G. C., Donadio, D., Caravati, S., Behler, J. & Bernasconi, M. Thermal transport in phase-change materials from atomistic simulations. Phys. Rev. B 86, 104301 (2012).
Aryana, K. et al. Tuning network topology and vibrational mode localization to achieve ultralow thermal conductivity in amorphous chalcogenides. Nat. Commun. 12, 2817 (2021).
Liu, Y. et al. Unraveling thermal transport correlated with atomistic structures in amorphous gallium oxide via machine learning combined with experiments. Adv. Mater. 35, 2210873 (2023).
Ramprasad, R., Batra, R., Pilania, G., Mannodi-Kanakkithodi, A. & Kim, C. Machine learning in materials informatics: recent applications and prospects. npj Comput. Mater. 3, 54 (2017).
Schmidt, J., Marques, M. R. G., Botti, S. & Marques, M. A. L. Recent advances and applications of machine learning in solid-state materials science. npj Comput. Mater. 5, 83 (2019).
Raty, J. Y. et al. Aging mechanisms in amorphous phase-change materials. Nat. Commun. 6, 7467 (2015).
Behler, J. & Parrinello, M. Generalized neural-network representation of high-dimensional potential-energy surfaces. Phys. Rev. Lett. 98, 146401 (2007).
Li, W., Ando, Y., Minamitani, E. & Watanabe, S. Study of Li atom diffusion in amorphous Li3PO4 with neural network potential. J. Chem. Phys. 147, 214106 (2017).
Chen, C. & Ong, S. P. A universal graph deep learning interatomic potential for the periodic table. Nat. Comput. Sci. 2, 718–728 (2022).
Deng, B. et al. CHGNet as a pretrained universal neural network potential for charge-informed atomistic modelling. Nat. Mach. Intell. 5, 1031–1041 (2023).
Zheng, H. et al. The ab initio amorphous materials database: empowering machine learning to decode diffusivity. Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/2402.00177 (2024).
Abou El Kheir, O., Bonati, L., Parrinello, M. & Bernasconi, M. Unraveling the crystallization kinetics of the Ge2Sb2Te5 phase change compound with a machine-learned interatomic potential. npj Comput. Mater. 10, 33 (2024).
Orava, J., Greer, A. L., Gholipour, B., Hewak, D. W. & Smith, C. E. Characterization of supercooled liquid Ge2Sb2Te5 and its crystallization by ultrafast-heating calorimetry. Nat. Mater. 11, 279–283 (2012).
Wilson, H. W. On the velocity of solidification and viscosity of super-cooled liquids. Philos. Mag. 50, 238–250 (1900).
Niefind, F., Shivhare, R., Mannsfeld, S. C. B., Abel, B. & Hambsch, M. Investigating the morphology of bulk heterojunctions by laser photoemission electron microscopy. Polym. Test. 116, 107791 (2022).
Yi, Y., Coropceanu, V. & Brédas, J.-L. Exciton-dissociation and charge-recombination processes in pentacene/C60 solar cells: theoretical insight into the impact of interface geometry. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 131, 15777–15783 (2009).
Vandervelden, C. A., Khan, S. A., Scott, S. L. & Peters, B. Site-averaged kinetics for catalysts on amorphous supports: an importance learning algorithm. React. Chem. Eng. 5, 77–86 (2019).
Zhang, J., Hu, P. & Wang, H. Amorphous catalysis: machine learning driven high-throughput screening of superior active site for hydrogen evolution reaction. J. Phys. Chem. C 124, 10483–10494 (2020).
Zhang, D. et al. Unlocking the performance of ternary metal (hydro)oxide amorphous catalysts via data-driven active-site engineering. Energy Environ. Sci. 16, 5065–5075 (2023).
Zhang, X., Li, K., Wen, B., Ma, J. & Diao, D. Machine learning accelerated DFT research on platinum-modified amorphous alloy surface catalysts. Chin. Chem. Lett. 34, 107833 (2023).
Noh, J. et al. Inverse design of solid-state materials via a continuous representation. Matter 1, 1370–1384 (2019).
Ren, Z. et al. An invertible crystallographic representation for general inverse design of inorganic crystals with targeted properties. Matter 5, 314–335 (2022).
Ben Mahmoud, C., Gardner, J. L. A. & Deringer, V. L. Data as the next challenge in atomistic machine learning. Nat. Comput. Sci. 4, 384–387 (2024).
Jain, A. et al. Commentary: the materials project: a materials genome approach to accelerating materials innovation. APL Mater. 1, 011002 (2013).
Zakutayev, A. et al. An open experimental database for exploring inorganic materials. Sci. Data 5, 180053 (2018).
Mocanu, F. C., Konstantinou, K. & Elliott, S. R. Quench-rate and size-dependent behaviour in glassy Ge2Sb2Te5 models simulated with a machine-learned Gaussian approximation potential. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 53, 244002 (2020).
Cole, J. M. A design-to-device pipeline for data-driven materials discovery. Acc. Chem. Res. 53, 599–610 (2020).
Mikolov, T., Chen, K., Corrado, G. & Dean, J. Efficient estimation of word representations in vector space. Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/1301.3781 (2013).
Pennington, J., Socher, R. & Manning, C. GloVe: global vectors for word representation. In Proc. 2014 Conf. Empir. Methods Nat. Lang. Process. (eds Moschitti, A., Pang, B. & Daelemans, W.) 1532–1543 (Association for Computational Linguistics, 2014).
Peters, M. E. et al. Deep contextualized word representations. In Proc. 2018 Conf. North Am. Chapter Assoc. Comput. Linguist. (eds Walker, M., Ji, H. & Stent, A.) 2227–2237 (ACL, 2018).
Bojanowski, P., Grave, E., Joulin, A. & Mikolov, T. Enriching word vectors with subword information. Trans. Assoc. Comput. Linguist. 5, 135–146 (2017).
Tshitoyan, V. et al. Unsupervised word embeddings capture latent knowledge from materials science literature. Nature 571, 95–98 (2019).
Devlin, J., Chang, M.-W., Lee, K. & Toutanova, K. BERT: pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. In Proc. 2019 Conf. North Am. Chapter Assoc. Comput. Linguist. (eds Burstein, J., Doran, C. & Solorio, T.) 4171–4186 (ACL, 2019).
Brown, T. B. et al. Language models are few-shot learners. In Proc. 34th Int. Conf. Neural Inform. Process. Syst. (eds Larochelle, H., Ranzato, M., Hadsell, R., Balcan, M. F. & Lin, H.) 1877–1901 (Curran Associates, 2020).
Lee, J. et al. BioBERT: a pre-trained biomedical language representation model for biomedical text mining. Bioinformatics 36, 1234–1240 (2020).
Court, C. J. & Cole, J. M. Magnetic and superconducting phase diagrams and transition temperatures predicted using text mining and machine learning. npj Comput. Mater. 6, 18 (2020).
Kononova, O. et al. Opportunities and challenges of text mining in materials research. iScience 24, 102155 (2021).
Gupta, T., Zaki, M., Krishnan, N. M. A. & Mausam MatSciBERT: a materials domain language model for text mining and information extraction. npj Comput. Mater. 8, 102 (2022).
Dagdelen, J. et al. Structured information extraction from scientific text with large language models. Nat. Commun. 15, 1418 (2024).
Raccuglia, P. et al. Machine-learning-assisted materials discovery using failed experiments. Nature 533, 73–76 (2016).
Chang, Y. et al. A survey on evaluation of large language models. ACM Trans. Intell. Syst. Technol. 15, 39:1–39:45 (2024).
Sun, W. & David, N. A critical reflection on attempts to machine-learn materials synthesis insights from text-mined literature recipes. Faraday Discuss. https://doi.org/10.1039/D4FD00112E (2024).
Boström, H. L. B. et al. How reproducible is the synthesis of Zr–porphyrin metal–organic frameworks? An interlaboratory study. Adv. Mater. 36, 2304832 (2024).
Shields, B. J. et al. Bayesian reaction optimization as a tool for chemical synthesis. Nature 590, 89–96 (2021).
Colliandre, L. & Muller, C. in High Performance Computing for Drug Discovery and Biomedicine (ed. Heifetz, A.) 101–136 (Springer, 2024).
Häse, F., Roch, L. M., Kreisbeck, C. & Aspuru-Guzik, A. Phoenics: a Bayesian optimizer for chemistry. ACS Cent. Sci. 4, 1134–1145 (2018).
Braconi, E. & Godineau, E. Bayesian optimization as a sustainable strategy for early-stage process development? A case study of Cu-catalyzed C–N coupling of sterically hindered pyrazines. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 11, 10545–10554 (2023).
Liu, C. et al. Understanding causalities in organic photovoltaics device degradation in a machine-learning-driven high-throughput platform. Adv. Mater. 36, 2300259 (2024).
Coli, G. M., Boattini, E., Filion, L. & Dijkstra, M. Inverse design of soft materials via a deep learning-based evolutionary strategy. Sci. Adv. 8, eabj6731 (2022).
Zhou, Z., Li, X. & Zare, R. N. Optimizing chemical reactions with deep reinforcement learning. ACS Cent. Sci. 3, 1337–1344 (2017).
Sanchez-Lengeling, B. & Aspuru-Guzik, A. Inverse molecular design using machine learning: generative models for matter engineering. Science 361, 360–365 (2018).
Valleti, M., Vasudevan, R. K., Ziatdinov, M. A. & Kalinin, S. V. Bayesian optimization in continuous spaces via virtual process embeddings. Digit. Discov. 1, 910–925 (2022).
Anker, A. S. et al. Characterising the atomic structure of mono-metallic nanoparticles from X-ray scattering data using conditional generative models. Preprint at https://chemrxiv.org/abs/12662222.v1 (2020).
Kjær, E. T. S. et al. DeepStruc: towards structure solution from pair distribution function data using deep generative models. Digit. Discov. 2, 69–80 (2023).
Anstine, D. M. & Isayev, O. Generative models as an emerging paradigm in the chemical sciences. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 145, 8736–8750 (2023).
Groom, C. R., Bruno, I. J., Lightfoot, M. P. & Ward, S. C. The Cambridge structural database. Acta Crystallogr. B Struct. Sci. Cryst. Eng. Mater. 72, 171–179 (2016).
Belsky, A., Hellenbrandt, M., Karen, V. L. & Luksch, P. New developments in the Inorganic Crystal Structure Database (ICSD): accessibility in support of materials research and design. Acta Crystallogr. B 58, 364–369 (2002).
Zunger, A., Wei, S.-H., Ferreira, L. G. & Bernard, J. E. Special quasirandom structures. Phys. Rev. Lett. 65, 353–356 (1990).
Thyagarajan, R. & Sholl, D. S. A database of porous rigid amorphous materials. Chem. Mater. 32, 8020–8033 (2020).
Cheng, J., Fong, K. D. & Persson, K. A. Materials design principles of amorphous cathode coatings for lithium-ion battery applications. J. Mater. Chem. A 10, 22245–22256 (2022).
Batatia, I. et al. A foundation model for atomistic materials chemistry. Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/2401.00096 (2023).
Zhang, D. et al. DPA-2: a large atomic model as a multi-task learner. Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/2312.15492 (2024).
Gardner, J. L. A., Baker, K. T. & Deringer, V. L. Synthetic pre-training for neural-network interatomic potentials. Mach. Learn. Sci. Technol. 5, 015003 (2024).
Kaur, H. et al. Data-efficient fine-tuning of foundational models for first-principles quality sublimation enthalpies. Faraday Discuss. https://doi.org/10.1039/D4FD00107A (2024).
Lunt, A. M. et al. Modular, multi-robot integration of laboratories: an autonomous workflow for solid-state chemistry. Chem. Sci. 15, 2456–2463 (2024).
Pithan, L. et al. Closing the loop: autonomous experiments enabled by machine-learning-based online data analysis in synchrotron beamline environments. J. Synchrotron Radiat. 30, 1064–1075 (2023).
Huang, J.-X., Csányi, G., Zhao, J.-B., Cheng, J. & Deringer, V. L. First-principles study of alkali-metal intercalation in disordered carbon anode materials. J. Mater. Chem. A 7, 19070–19080 (2019).
Deringer, V. L. et al. Towards an atomistic understanding of disordered carbon electrode materials. Chem. Commun. 54, 5988–5991 (2018).
Ke, G. et al. LightGBM: a highly efficient gradient boosting decision tree. In 31st Conf. Advances Neural Inform. Process. Syst. (eds Guyon, I. et al.) (Curran Associates, 2017).
El-Machachi, Z. et al. Accelerated first-principles exploration of structure and reactivity in graphene oxide. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202410088 (2024).
Spöri, C., Kwan, J. T. H., Bonakdarpour, A., Wilkinson, D. P. & Strasser, P. The stability challenges of oxygen evolving catalysts: towards a common fundamental understanding and mitigation of catalyst degradation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 56, 5994–6021 (2017).
Wu, G. et al. A general synthesis approach for amorphous noble metal nanosheets. Nat. Commun. 10, 4855 (2019).
Cheng, H., Yang, N., Lu, Q., Zhang, Z. & Zhang, H. Syntheses and properties of metal nanomaterials with novel crystal phases. Adv. Mater. 30, 1707189 (2018).
Griffin, J. M. et al. In situ NMR and electrochemical quartz crystal microbalance techniques reveal the structure of the electrical double layer in supercapacitors. Nat. Mater. 14, 812–819 (2015).
Pecher, O., Carretero-González, J., Griffith, K. J. & Grey, C. P. Materials’ methods: NMR in battery research. Chem. Mater. 29, 213–242 (2017).
Cao, C., Li, Z.-B., Wang, X.-L., Zhao, X.-B. & Han, W.-Q. Recent advances in inorganic solid electrolytes for lithium batteries. Front. Energy Res. 2, 388–416 (2014).
Xu, Z. & Xia, Y. Progress, challenges and perspectives of computational studies on glassy superionic conductors for solid-state batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A 10, 11854–11880 (2022).
Schulmeister, K. & Mader, W. TEM investigation on the structure of amorphous silicon monoxide. J. Non Cryst. Solids 320, 143–150 (2003).
Hirata, A. et al. Atomic-scale disproportionation in amorphous silicon monoxide. Nat. Commun. 7, 11591 (2016).
Heremans, P. et al. Mechanical and electronic properties of thin-film transistors on plastic, and their integration in flexible electronic applications. Adv. Mater. 28, 4266–4282 (2016).
Liu, L. & Zhang, C. Fe-based amorphous coatings: structures and properties. Thin Solid Films 561, 70–86 (2014).
Calin, M. et al. Designing biocompatible Ti-based metallic glasses for implant applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 33, 875–883 (2013).
Zhong, L., Wang, J., Sheng, H., Zhang, Z. & Mao, S. X. Formation of monatomic metallic glasses through ultrafast liquid quenching. Nature 512, 177–180 (2014).
Sohrabi, N., Jhabvala, J. & Logé, R. E. Additive manufacturing of bulk metallic glasses — process, challenges and properties: a review. Metals 11, 1279 (2021).
Cheng, H. et al. Ligand-exchange-induced amorphization of Pd nanomaterials for highly efficient electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution reaction. Adv. Mater. 32, 1902964 (2020).
Billinge, S. J. L. & Levin, I. The problem with determining atomic structure at the nanoscale. Science 316, 561–565 (2007).
Momma, K. & Izumi, F. VESTA 3 for three-dimensional visualization of crystal, volumetric and morphology data. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 44, 1272–1276 (2011).
Stukowski, A. Visualization and analysis of atomistic simulation data with OVITO — the open visualization tool. Model. Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng. 18, 015012 (2010).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Y.L. and V.L.D. prepared the initial draft. All authors contributed to the writing of the paper.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Reviews Materials thanks Kedar Hippalgaonkar, Kiran Prasai and the other, anonymous, reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Madanchi, A., Anker, A.S. et al. The amorphous state as a frontier in computational materials design. Nat Rev Mater 10, 228–241 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41578-024-00754-2
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41578-024-00754-2
This article is cited by
-
Full-cycle device-scale simulations of memory materials with a tailored atomic-cluster-expansion potential
Nature Communications (2025)
-
Boosting crystal structure prediction via symmetry
Nature Computational Science (2025)
-
Amorphous chalcogenides in two dimensions
Nature Materials (2025)
-
A generative diffusion model for amorphous materials
npj Computational Materials (2025)
-
OpenPoly: A Polymer Database Empowering Benchmarking and Multi-property Predictions
Chinese Journal of Polymer Science (2025)