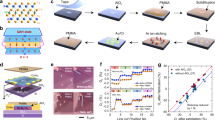
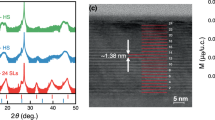
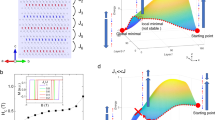
Abstract
The interplay between nontrivial band topology and layered antiferromagnetism in MnBi2Te4 has opened a new avenue for exploring topological phases of matter1,2,3,4. The quantum anomalous Hall effect5 and axion insulator state6 have been observed in odd and even number layers of MnBi2Te4, and the quantum metric nonlinear Hall effect7,8 has been shown to exist in this topological antiferromagnet. The rich and complex antiferromagnetic spin dynamics in MnBi2Te4 is expected to generate new quantum anomalous Hall phenomena that are absent in conventional ferromagnetic topological insulators, but experimental observations are still unknown. Here we fabricate a device of 7-septuple-layer MnBi2Te4 covered with an AlOx capping layer, which enables the investigation of antiferromagnetic quantum anomalous Hall effect over wide parameter spaces. By tuning the gate voltage and perpendicular magnetic field, we uncover a cascade of quantum phase transitions that can be attributed to the influence of complex spin configurations on edge state transport. Furthermore, we find that an in-plane magnetic field enhances both the coercive field and the exchange gap of the surface state, in contrast to that in the ferromagnetic quantum anomalous Hall state. Combined with numerical simulations, we propose that these peculiar features arise from the spin flip and flop transitions that are inherent to a van der Waals antiferromagnet. The versatile tunability of the quantum anomalous Hall effect in MnBi2Te4 paves the way for potential applications in topological antiferromagnetic spintronics9,10.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$32.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All raw and derived data used to support the findings of this work are available from the authors on request.
References
Otrokov, M. M. et al. Prediction and observation of an antiferromagnetic topological insulator. Nature 576, 416–422 (2019).
Gong, Y. et al. Experimental realization of an intrinsic magnetic topological insulator. Chin. Phys. Lett. 36, 076801 (2019).
Li, J. et al. Intrinsic magnetic topological insulators in van der Waals layered MnBi2Te4-family materials. Sci. Adv. 5, eaaw5685 (2019).
Zhang, D. et al. Topological axion states in the magnetic insulator MnBi2Te4 with the quantized magnetoelectric effect. Phys. Rev. Lett. 122, 206401 (2019).
Deng, Y. et al. Quantum anomalous Hall effect in intrinsic magnetic topological insulator MnBi2Te4. Science 367, 895–900 (2020).
Liu, C. et al. Robust axion insulator and Chern insulator phases in a two-dimensional antiferromagnetic topological insulator. Nat. Mater. 19, 522–527 (2020).
Wang, N. et al. Quantum-metric-induced nonlinear transport in a topological antiferromagnet. Nature 621, 487–492 (2023).
Gao, A. et al. Quantum metric nonlinear Hall effect in a topological antiferromagnetic heterostructure. Science 381, 181–186 (2023).
Šmejkal, L., Mokrousov, Y., Yan, B. & MacDonald, A. H. Topological antiferromagnetic spintronics. Nat. Phys. 14, 242–251 (2018).
He, Q. L., Hughes, T. L., Armitage, N. P., Tokura, Y. & Wang, K. L. Topological spintronics and magnetoelectronics. Nat. Mater. 21, 15–23 (2022).
Chang, C.-Z. et al. Experimental observation of the quantum anomalous Hall effect in a magnetic topological insulator. Science 340, 167–170 (2013).
Serlin, M. et al. Intrinsic quantized anomalous Hall effect in a moiré heterostructure. Science 367, 900–903 (2020).
Sharpe, A. L. et al. Emergent ferromagnetism near three-quarters filling in twisted bilayer graphene. Science 365, 605–608 (2019).
Chen, G. et al. Tunable correlated Chern insulator and ferromagnetism in a moiré superlattice. Nature 579, 56–61 (2020).
Li, T. et al. Quantum anomalous Hall effect from intertwined moiré bands. Nature 600, 641–646 (2021).
Park, H. et al. Observation of fractionally quantized anomalous Hall effect. Nature 622, 74–79 (2023).
Xu, F. et al. Observation of integer and fractional quantum anomalous Hall effects in twisted bilayer MoTe2. Phys. Rev. 13, 031037 (2023).
Lu, Z. et al. Fractional quantum anomalous Hall effect in multilayer graphene. Nature 626, 759–764 (2024).
Han, T. et al. Large quantum anomalous Hall effect in spin-orbit proximitized rhombohedral graphene. Science 384, 647–651 (2024).
Ge, J. et al. High-Chern-number and high-temperature quantum Hall effect without Landau levels. Natl Sci. Rev. 7, 1280–1287 (2020).
Ying, Z. et al. Experimental evidence for dissipationless transport of the chiral edge state of the high-field Chern insulator in MnBi2Te4 nanodevices. Phys. Rev. B 105, 085412 (2022).
Cai, J. et al. Electric control of a canted-antiferromagnetic Chern insulator. Nat. Commun. 13, 1668 (2022).
Bai, Y. et al. Quantized anomalous Hall resistivity achieved in molecular beam epitaxy-grown MnBi2Te4 thin films. Natl Sci. Rev. 11, nwad189 (2024).
Gao, A. et al. Layer Hall effect in a 2D topological axion antiferromagnet. Nature 595, 521–525 (2021).
Zhang, R.-X., Wu, F. & Das Sarma, S. Möbius Insulator and Higher-Order Topology in MnBi2nTe3n+1. Phys. Rev. Lett. 124, 136407 (2020).
Lei, C., Heinonen, O., MacDonald, A. H. & McQueeney, R. J. Metamagnetism of few-layer topological antiferromagnets. Phys. Rev. Mater. 5, 064201 (2021).
Li, Z. et al. Tunable interlayer magnetism and band topology in van der Waals heterostructures of MnBi2Te4-family materials. Phys. Rev. B 102, 081107 (2020).
Sun, H.-P. et al. Analytical solution for the surface states of the antiferromagnetic topological insulator MnBi2Te4. Phys. Rev. B 102, 241406 (2020).
Yang, S. et al. Odd-even layer-number effect and layer-dependent magnetic phase diagrams in MnBi2Te4. Phys. Rev. 11, 011003 (2021).
Sass, P. M., Kim, J., Vanderbilt, D., Yan, J. & Wu, W. Robust A-type order and spin-flop transition on the surface of the antiferromagnetic topological insulator MnBi2Te4. Phys. Rev. Lett. 125, 037201 (2020).
Ovchinnikov, D. et al. Intertwined topological and magnetic orders in atomically thin Chern insulator MnBi2Te4. Nano Lett. 21, 2544–2550 (2021).
Garnica, M. et al. Native point defects and their implications for the Dirac point gap at MnBi2Te4(0001). npj Quantum Mater. 7, 7 (2022).
Tan, H. & Yan, B. Distinct magnetic gaps between antiferromagnetic and ferromagnetic orders driven by surface defects in the topological magnet MnBi2Te4. Phys. Rev. Lett. 130, 126702 (2023).
Lai, Y., Ke, L., Yan, J., McDonald, R. D. & McQueeney, R. J. Defect-driven ferrimagnetism and hidden magnetization in MnBi2Te4. Phys. Rev. B 103, 184429 (2021).
Du, M.-H., Yan, J., Cooper, V. R. & Eisenbach, M. Tuning Fermi levels in intrinsic antiferromagnetic topological insulators MnBi2Te4 and MnBi4Te7 by defect engineering and chemical doping. Adv. Funct. Mater. 31, 2006516 (2021).
Hou, F. et al. Te-vacancy-induced surface collapse and reconstruction in antiferromagnetic topological insulator MnBi2Te4. ACS Nano 14, 11262–11272 (2020).
Huang, Z., Du, M.-H., Yan, J. & Wu, W. Native defects in antiferromagnetic topological insulator MnBi2Te4. Phys. Rev. Mater. 4, 121202 (2020).
Zeugner, A. et al. Chemical aspects of the candidate antiferromagnetic topological insulator MnBi2Te4. Chem. Mater. 31, 2795–2806 (2019).
Li, H. et al. Antiferromagnetic topological insulator MnBi2Te4: synthesis and magnetic properties. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 22, 556–563 (2020).
Li, Y. et al. Fabrication-induced even-odd discrepancy of magnetotransport in few-layer MnBi2Te4. Nat. Commun. 15, 3399 (2024).
Zhang, Z. et al. Controlled large non-reciprocal charge transport in an intrinsic magnetic topological insulator MnBi2Te4. Nat. Commun. 13, 6191 (2022).
Liu, S. et al. Gate-tunable intrinsic anomalous Hall effect in epitaxial MnBi2Te4 films. Nano Lett. 24, 16–25 (2024).
Li, Y. et al. Reentrant quantum anomalous Hall effect in molecular beam epitaxy-grown MnBi2Te4 thin films. Preprint at arxiv.org/abs/2401.11450 (2024).
Wang, Y. et al. Towards the quantized anomalous Hall effect in AlOx-capped MnBi2Te4. Nat. Commun. 16, 1727 (2025).
Dieny, B. & Chshiev, M. Perpendicular magnetic anisotropy at transition metal/oxide interfaces and applications. Rev. Mod. Phys. 89, 025008 (2017).
Monso, S. et al. Crossover from in-plane to perpendicular anisotropy in Pt/CoFe/AlOx sandwiches as a function of Al oxidation: a very accurate control of the oxidation of tunnel barriers. Appl. Phys. Lett. 80, 4157–4159 (2002).
Rodmacq, B., Auffret, S., Dieny, B., Monso, S. & Boyer, P. Crossovers from in-plane to perpendicular anisotropy in magnetic tunnel junctions as a function of the barrier degree of oxidation. J. Appl. Phys. 93, 7513–7515 (2003).
Chang, C.-Z. et al. High-precision realization of robust quantum anomalous Hall state in a hard ferromagnetic topological insulator. Nat. Mater. 14, 473–477 (2015).
Checkelsky, J. G. et al. Trajectory of the anomalous Hall effect towards the quantized state in a ferromagnetic topological insulator. Nat. Phys. 10, 731–736 (2014).
Kou, X. et al. Scale-invariant quantum anomalous Hall effect in magnetic topological insulators beyond the two-dimensional limit. Phys. Rev. Lett. 113, 137201 (2014).
Mills, D. L. Surface spin-flop state in a simple antiferromagnet. Phys. Rev. Lett. 20, 18–21 (1968).
Bac, S.-K. et al. Topological response of the anomalous Hall effect in MnBi2Te4 due to magnetic canting. npj Quantum Mater. 7, 46 (2022).
Chong, S. K. et al. Intrinsic exchange biased anomalous Hall effect in an uncompensated antiferromagnet MnBi2Te4. Nat. Commun. 15, 2881 (2024).
Bartram, F. M. et al. Real-time observation of magnetization and magnon dynamics in a two-dimensional topological antiferromagnet MnBi2Te4. Sci. Bull. 68, 2734–2742 (2023).
Liu, C. et al. Magnetic-field-induced robust zero Hall plateau state in MnBi2Te4 Chern insulator. Nat. Commun. 12, 4647 (2021).
Luan, J. et al. Controlling the zero Hall plateau in a quantum anomalous Hall insulator by in-plane magnetic field. Phys. Rev. Lett. 130, 186201 (2023).
Coey, J. M. D. Magnetism and Magnetic Materials (Cambridge Univ. Press, 2010).
Chikazumi, S. & Graham, C. D. Physics of Ferromagnetism (Oxford Univ. Press, 1997).
Silevitch, D. M., Aeppli, G. & Rosenbaum, T. F. Switchable hardening of a ferromagnet at fixed temperature. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 107, 2797–2800 (2010).
Brooke, J., Rosenbaum, T. F. & Aeppli, G. Tunable quantum tunnelling of magnetic domain walls. Nature 413, 610–613 (2001).
Kresse, G. & Furthmüller, J. Efficient iterative schemes for ab initio total-energy calculations using a plane-wave basis set. Phys. Rev. B 54, 11169–11186 (1996).
Perdew, J. P., Burke, K. & Ernzerhof, M. Generalized gradient approximation made simple. Phys. Rev. Lett. 77, 3865–3868 (1996).
Grimme, S., Antony, J., Ehrlich, S. & Krieg, H. A consistent and accurate ab initio parametrization of density functional dispersion correction (DFT-D) for the 94 elements H-Pu. J. Chem. Phys. 132, 154104 (2010).
Acknowledgements
Yayu Wang was supported the Basic Science Center Project of Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 52388201), the Innovation program for Quantum Science and Technology (grant no. 2021ZD0302502) and the New Cornerstone Science Foundation through the New Cornerstone Investigator Program and the XPLORER PRIZE. C.L. was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 12274453), Beijing Nova Program (grant no. 20240484574), and the Open Research Fund Program of the State Key Laboratory of Low-Dimensional Quantum Physics (grant no. KF202204). J.Z. was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant nos. 12274252 and 12350404) and the National Key Research and Development Program of China (grant no. 2024YFA1409100). We thank W. Wang, S. Yang and H. Yang for their discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yayu Wang, C.L. and J.Z. supervised the research. Z.L., Yongchao Wang, Yongqian Wang, Yaoxin Li, Y.F., B.F. and S.Y. fabricated the devices and performed the transport measurements. Yongchao Wang, L.X. and Yuetan Li grew the MnBi2Te4 crystals. Z.D. performed the TEM measurements. Z.L., M.M. and W.J. performed the simulation of the spin configurations. W.-H.D. and Y.X. performed the first-principles calculation. Z.L., C.L., J.Z. and Yayu Wang prepared the paper with comments from all authors.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature thanks Haijun Zhang and the other, anonymous, reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Extended data figures and tables
Extended Data Fig. 1 Transport data of the 7SL MnBi2Te4 device at T = 0.02 K.
a, Photograph of the measured device. The scale bar is 10 μm. b, Colour map of ρyx as a function of Hz and Vg at T = 0.02 K. c, The μ0Hz dependent ρxx (blue) and ρyx (red) curves at the CNP measured by using the Keithley 6221-2182 in the delta mode with a current of 10 nA and a delay of 0.027 s, which demonstrates ρxx = 0.012 h/e2 and ρyx = 0.988 h/e2 at μ0Hz = 0 T. d, The evolution of ρxx and ρyx as a function of Vg at μ0Hz = 0, 1, and 2 T.
Extended Data Fig. 2 Individual Hz-dependent ρxx and ρyx curves for varied Ts at Vg = 30 V.
The upper and lower panels are the ρyx (red) and ρxx (blue) curves, respectively, from T = 0.02 K to T = 23 K. The one-step transition in the ground state is replaced by much more complex variations at higher T.
Extended Data Fig. 3 Colour map of σxx as a function of T and Vg at various μ0Hz.
The Vg dependent transport data are measured at fixed μ0Hz and selected Ts (T = 0.02, 0.05, 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.5, 0.7, 1, 1.5, 2, 3, 4, 5, 7, 9, 11, 13, 15, 17 and 20 K). The thermal activation gap size Δ is extracted using the Arrhenius formula lnσxx = −Δ/2kBT, where kB represents the Boltzmann constant.
Extended Data Fig. 4 Complete data of μ0Hz dependent ρyx at varied Ts and μ0Hx.
The measurements were conducted by sweeping Hz at different Hx at fixed T. The measuring sequence is from 0.01 K to 22 K. All data taken at Vg = 30 V.
Extended Data Fig. 5 The hysteresis manipulated by in-plane magnetic field at different Ts.
a-f, The ρyx versus Hz loops show that the coercivity increases with the application of Hx at T ≤ 18 K. g-h, Near the Néel temperature (T = 20 and 22 K), the trend is reversed and the coercivity decreases with the application of Hx. All data taken at Vg = 30 V.
Extended Data Fig. 6 Colour map of σxx in the parameter space of μ0Hz and Vg at T = 0.2 K with increasing μ0Hx.
The measurements were conducted by fixing μ0Hx and sweeping Vg with μ0Hz varied from +2.5 T to −1.5 T. As μ0Hx increases, the QAH region indicated by blue colour is enlarged and the sudden gap increase at μ0Hz ≈ 2.2 T becomes smoother. When μ0Hx is increased to 2 T, the AFM to SSF transition nearly disappears.
Extended Data Fig. 7 The μ0Hz dependence of ρxx and ρyx at varied μ0Hx.
The application of Hx smears out the transition at H2 in both ρxx (upper panel) and ρyx (lower panel). Meanwhile, the hysteresis is increased, accompanied by a sharper transition at H1. All data taken at Vg = 30 V.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
This file contains Supplementary Information sections A–D, including Supplementary Figs. 1–10, Supplementary Table 1 and Supplementary References.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lian, Z., Wang, Y., Wang, Y. et al. Antiferromagnetic quantum anomalous Hall effect under spin flips and flops. Nature 641, 70–75 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-025-08860-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-025-08860-z
This article is cited by
-
Half-quantized layer hall effect as a probe of quantized axion field
Nature Communications (2026)
-
Ferroelectric switching of quantum anomalous Hall effects in MnBi2Te4 films
npj Quantum Materials (2025)
-
Zero-field chiral edge transport in an intrinsic magnetic topological insulator MnBi2Te4
Nature Communications (2025)
-
Intrinsic magnetic topological insulators of the MnBi2Te4 family
Communications Materials (2025)
-
Dynamic magnetic behaviors of the MBene Cr2B2 monolayer in a time-dependent magnetic field
Applied Physics A (2025)