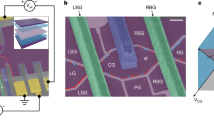
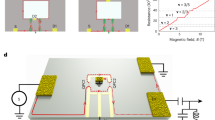
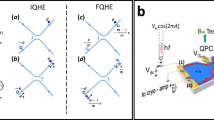
Abstract
Aharonov–Bohm interference of fractional quasiparticles in the quantum Hall effect generally reveals their elementary charge (e*)1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15. Recently, our interferometry experiments with several ‘particle states’ reported flux periods of ΔΦ = (e/e*)Φ0 (with Φ0 the flux quantum) at moderate temperatures16. Here we report interference measurements of ‘particle–hole conjugated’ states at filling factors ν = 2/3, 3/5 and 4/7, which revealed unexpected flux periodicities of ΔΦ = ν−1Φ0. The measured shot-noise Fano factor (F) of the partitioned quasiparticles in each of the quantum point contacts of the interferometer was F = ν (ref. 17) rather than that of the elementary charge F = e*/e (refs. 18,19). These observations indicate that the interference of bunched (clustered) elementary quasiparticles occurred for coherent pairs, triples and quadruplets, respectively. A small metallic gate (top gate), deposited in the centre of the interferometer bulk, formed an antidot (or a dot) when charged, thus introducing local quasiparticles at the perimeter of the (anti)dot. Surprisingly, such charging led to a dissociation of the ‘bunched quasiparticles’ and, thus, recovered the conventional flux periodicity set by the elementary charge of the quasiparticles. However, the shot-noise Fano factor (of each quantum point contact) consistently remained at F = ν, possibly due to the neutral modes accompanying the conjugated states. The two observations—bunching and debunching (or dissociation)—were not expected by current theories. Similar effects may arise in Jain’s ‘particle states’ (at lower temperatures) and at even denominator fractional quantum Hall states20.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$32.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the plots within this paper and other findings of this study are publicly available at https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.15395283 (ref. 39). Source data are provided with this paper.
References
Zhang, Y. M. et al. Distinct signatures for Coulomb blockade and Aharonov-Bohm interference in electronic Fabry-Perot interferometers. Phys. Rev. B 79, 241304 (2009).
Ofek, N. et al. Role of interactions in an electronic Fabry–Perot interferometer operating in the quantum Hall effect regime. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 107, 5276–5281 (2010).
Ronen, Y. et al. Aharonov-Bohm effect in graphene-based Fabry-Pérot quantum Hall interferometers. Nat. Nanotechnol. 16, 563–569 (2021).
Nakamura, J., Liang, S., Gardner, G. C. & Manfra, M. J. Direct observation of anyonic braiding statistics. Nat. Phys. 16, 931–936 (2020).
Kim, J. et al. Aharonov–Bohm interference and statistical phase-jump evolution in fractional quantum Hall states in bilayer graphene. Nat. Nanotechnol. 19, 1619–1626 (2024).
Nakamura, J. et al. Aharonov–Bohm interference of fractional quantum Hall edge modes. Nat. Phys. 15, 563–569 (2019).
Déprez, C. et al. A tunable Fabry-Pérot quantum Hall interferometer in graphene. Nat. Nanotechnol. 16, 555–562 (2021).
Samuelson, N. L. et al. Anyonic statistics and slow quasiparticle dynamics in a graphene fractional quantum Hall interferometer. Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/2403.19628 (2024).
Werkmeister, T. et al. Anyon braiding and telegraph noise in a graphene interferometer. Science 388, 730–735 (2024).
Chamon, C. D. C., Freed, D. E., Kivelson, S. A., Sondhi, S. L. & Wen, X. G. Two point-contact interferometer for quantum Hall systems. Phys. Rev. B 55, 2331–2343 (1997).
Willett, R. L. et al. Interference measurements of non-abelian e/4 & abelian e/2 quasiparticle braiding. Phys. Rev. 13, 011028 (2023).
Yang, W. et al. Evidence for correlated electron pairs and triplets in quantum Hall interferometers. Nat. Commun. 15, 10064 (2024).
Ji, Y. et al. An electronic Mach-Zehnder interferometer. Nature 422, 415–418 (2003).
Neder, I., Heiblum, M., Levinson, Y., Mahalu, D. & Umansky, V. Unexpected behavior in a two-path electron interferometer. Phys. Rev. Lett. 96, 016804 (2006).
Kundu, H. K., Biswas, S., Ofek, N., Umansky, V. & Heiblum, M. Anyonic interference and braiding phase in a Mach-Zehnder interferometer. Nat. Phys. 19, 515–521 (2023).
Ghosh, B. et al. Anyonic braiding in a chiral Mach–Zehnder interferometer. Nat. Phys. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41567-025-02960-3 (in the press).
Bhattacharyya, R., Banerjee, M., Heiblum, M., Mahalu, D. & Umansky, V. Melting of interference in the fractional quantum Hall effect: appearance of neutral modes. Phys. Rev. Lett. 122, 246801 (2019).
de-Picciotto, R. et al. Direct observation of a fractional charge. Phys. B: Condens. Matter 249–251, 395–400 (1998).
Reznikov, M., de Picciotto, R., Griffiths, T. G., Heiblum, M. & Umansky, V. Observation of quasiparticles with one-fifth of an electron’s charge. Nature 399, 238–241 (1999).
Chung, Y. C., Heiblum, M. & Umansky, V. Scattering of bunched fractionally charged quasiparticles. Phys. Rev. Lett. 91, 216804 (2003).
Schuster, R. et al. Phase measurement in a quantum dot via a double-slit interference experiment. Nature 385, 417–420 (1997).
Neder, I. et al. Interference between two indistinguishable electrons from independent sources. Nature 448, 333–337 (2007).
dePicciotto, R. et al. Direct observation of a fractional charge. Nature 389, 162–164 (1997).
Saminadayar, L., Glattli, D. C., Jin, Y. & Etienne, B. Observation of the e/3 fractionally charged Laughlin quasiparticle. Phys. Rev. Lett. 79, 2526–2529 (1997).
Simmons, J. A. et al. Resistance fluctuations in the integral-quantum-Hall-effect and fractional-quantum-Hall-effect regimes. Phys. Rev. B 44, 12933–12944 (1991).
Lee, J.-Y. M. et al. Partitioning of diluted anyons reveals their braiding statistics. Nature 617, 277–281 (2023).
Glidic, P. et al. Cross-correlation investigation of anyon statistics in the ν = 1/3 and 2/5 fractional quantum Hall states. Phys. Rev. 13, 011030 (2023).
Ruelle, M. et al. Comparing fractional quantum Hall Laughlin and Jain topological orders with the anyon collider. Phys. Rev. 13, 011031 (2023).
Bartolomei, H. et al. Fractional statistics in anyon collisions. Science 368, 173–177 (2020).
Biswas, S. et al. Shot noise does not always provide the quasiparticle charge. Nat. Phys. 18, 1476–1481 (2022).
Deviatov, E. V., Egorov, S. V., Biasiol, G. & Sorba, L. Quantum Hall Mach-Zehnder interferometer at fractional filling factors. Europhys. Lett. 100, 67009 (2012).
Batra, N., Wei, Z., Vishveshwara, S. & Feldman, D. E. Anyonic Mach-Zehnder interferometer on a single edge of a two-dimensional electron gas. Phys. Rev. B 108, L241302 (2023).
Bid, A., Ofek, N., Heiblum, M., Umansky, V. & Mahalu, D. Shot noise and charge at the 2/3 composite fractional quantum Hall state. Phys. Rev. Lett. 103, 236802 (2009).
Biswas, S., Kundu, H. K., Umansky, V. & Heiblum, M. Electron pairing of interfering interface-based edge modes. Phys. Rev. Lett. 131, 096302 (2023).
Choi, H. K. et al. Robust electron pairing in the integer quantum Hall effect regime. Nat. Commun. 6, 7435 (2015).
Frigeri, G. A., Scherer, D. D. & Rosenow, B. Sub-periods and apparent pairing in integer quantum Hall interferometers. Europhys. Lett. 126, 67007 (2019).
Kim, J. et al. Aharonov-Bohm interference in even-denominator fractional quantum Hall states. Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/2412.19886 (2024).
Moore, G. & Read, N. Nonabelions in the fractional quantum Hall effect. Nucl. Phys. B 360, 362–396 (1991).
Ghosh, B. Coherent bunching of anyons and their dissociation in interference experiments. Zenodo https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.15395283 (2025).
Acknowledgements
M.H. thanks Y. Ronen for fruitful discussions. D.F.M. acknowledges many illuminating conversations on quantum Hall interferometry with Y. Ronen. B.G. thanks A. K. Paul for his helpful comment that improved the device. M.L. thanks the Ariane de Rothschild Women Doctoral Program for their support. D.F.M. acknowledges the support of the Israel Science Foundation (Grant No. 2572/21) and the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG) within the CRC network TR 183 (Project Grant No. 277101999). M.H. acknowledges the support of the European Research Council under the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme (Grant Agreement No. 833078) and the support of the Israel Science Foundation (Grant No. 1510/22).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
B.G. fabricated the devices. B.G. and M.L. performed the measurements and analysed the data with the input from M.H. M.H. supervised the design, execution and data analysis in the experiment. D.F.M. worked on the theoretical aspects and data analysis. V.U. grew the GaAs heterostructures. All authors contributed to the writing of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature thanks the anonymous reviewers for their contribution to the peer review of this work. Peer reviewer reports are available.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Notes, methods, Figs. 1–11 and references.
Source data
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ghosh, B., Labendik, M., Umansky, V. et al. Coherent bunching of anyons and dissociation in an interference experiment. Nature 642, 922–927 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-025-09143-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-025-09143-3