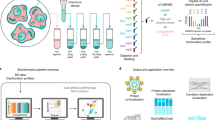
Abstract
Affinity purification coupled with mass spectrometry (AP–MS) and proximity-dependent biotinylation identification (BioID) methods have made substantial contributions to interaction proteomics studies. Whereas AP−MS results in the identification of proteins that are in a stable complex, BioID labels and identifies proteins that are in close proximity to the bait, resulting in overlapping yet distinct protein identifications. Integration of AP–MS and BioID data has been shown to comprehensively characterize a protein’s molecular context, but interactome analysis using both methods in parallel is still labor and resource intense with respect to cell line generation and protein purification. Therefore, we developed the Multiple Approaches Combined (MAC)-tag workflow, which allows for both AP–MS and BioID analysis with a single construct and with almost identical protein purification and mass spectrometry (MS) identification procedures. We have applied the MAC-tag workflow to a selection of subcellular markers to provide a global view of the cellular protein interactome landscape. This localization database is accessible via our online platform (http://proteomics.fi) to predict the cellular localization of a protein of interest (POI) depending on its identified interactors. In this protocol, we present the detailed three-stage procedure for the MAC-tag workflow: (1) cell line generation for the MAC-tagged POI; (2) parallel AP–MS and BioID protein purification followed by MS analysis; and (3) protein interaction data analysis, data filtration and visualization with our localization visualization platform. The entire procedure can be completed within 25 d.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$32.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All the relevant files and testing examples can be downloaded from our website (http://proteomics.fi/). Other data that support this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Code availability
MS-microscopy Python code as well as R code for Shiny server are freely available on GitHub at https://github.com/kamms/ms-microscopy.
References
Fields, S. & Song, O. A novel genetic system to detect protein–protein interactions. Nature 340, 245–246 (1989).
Yachie, N. et al. Pooled-matrix protein interaction screens using Barcode Fusion Genetics. Mol. Syst. Biol. 12, 863 (2016).
Rajagopala, S. V., Sikorski, P., Caufield, J. H., Tovchigrechko, A. & Uetz, P. Studying protein complexes by the yeast two-hybrid system. Methods 58, 392–399 (2012).
Rolland, T. et al. A proteome-scale map of the human interactome network. Cell 159, 1212–1226 (2014).
Varjosalo, M. et al. Interlaboratory reproducibility of large-scale human protein-complex analysis by standardized AP–MS. Nat. Methods 10, 307–314 (2013).
Roux, K. J., Kim, D. I., Raida, M. & Burke, B. A promiscuous biotin ligase fusion protein identifies proximal and interacting proteins in mammalian cells. J. Cell Biol. 196, 801–810 (2012).
Kim, D. I. et al. Probing nuclear pore complex architecture with proximity-dependent biotinylation. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 111, E2453–E2461 (2014).
Yadav, L. et al. Systematic analysis of human protein phosphatase interactions and dynamics. Cell Syst. 4, 430–444 (2017).
Liu, X. et al. An AP–MS- and BioID-compatible MAC-tag enables comprehensive mapping of protein interactions and subcellular localizations. Nat. Commun. 9, 1188 (2018).
Lambert, J. P., Tucholska, M., Go, C., Knight, J. D. & Gingras, A. C. Proximity biotinylation and affinity purification are complementary approaches for the interactome mapping of chromatin-associated protein complexes. J. Proteom. 118, 81–94 (2015).
Abbasi, S. & Schild-Poulter, C. Mapping the Ku interactome using proximity-dependent biotin identification in human cells. J. Proteome Res. 18, 1064–1077 (2019).
Couzens, A. L. et al. Protein interaction network of the mammalian Hippo pathway reveals mechanisms of kinase–phosphatase interactions. Sci. Signal. 6, rs15 (2013).
Lundberg, E. & Borner, G. H. H. Spatial proteomics: a powerful discovery tool for cell biology. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 20, 285–302 (2019).
van Vliet, A. R. et al. The ER stress sensor PERK coordinates ER-plasma membrane contact site formation through interaction with filamin-A and F-actin remodeling. Mol. Cell 65, 885–899 (2017).
Glatter, T., Wepf, A., Aebersold, R. & Gstaiger, M. An integrated workflow for charting the human interaction proteome: insights into the PP2A system. Mol. Syst. Biol. 5, 237 (2009).
Ortiz, D. A., Glassbrook, J. E. & Pellett, P. E. Protein–protein interactions suggest novel activities of human cytomegalovirus tegument protein pUL103. J. Virol. 90, 7798–7810 (2016).
Varjosalo, M. et al. The protein interaction landscape of the human CMGC kinase group. Cell Rep. 3, 1306–1320 (2013).
Hauri, S. et al. Interaction proteome of human Hippo signaling: modular control of the co-activator YAP1. Mol. Syst. Biol. 9, 713 (2013).
St-Denis, N. et al. Phenotypic and interaction profiling of the human phosphatases identifies diverse mitotic regulators. Cell Rep. 17, 2488–2501 (2016).
Ward, R. J., Alvarez-Curto, E. & Milligan, G. Using the Flp-In T-Rex system to regulate GPCR expression. Methods Mol. Biol. 746, 21–37 (2011).
Hesketh, G. G., Youn, J. Y., Samavarchi-Tehrani, P., Raught, B. & Gingras, A. C. Parallel exploration of interaction space by BioID and affinity purification coupled to mass spectrometry. Methods Mol. Biol. 1550, 115–136 (2017).
Schmidt, T. G. & Skerra, A. The Strep-tag system for one-step purification and high-affinity detection or capturing of proteins. Nat. Protoc. 2, 1528–1535 (2007).
Keskitalo, S. et al. Novel TMEM173 mutation and the role of disease modifying alleles. Front. Immunol. 10, 2770 (2019).
Yellapragada, V. et al. MKRN3 interacts with several proteins implicated in puberty timing but does not influence GNRH1 expression. Front. Endocrinol. 10, 48 (2019).
Kondelin, J. et al. Comprehensive evaluation of coding region point mutations in microsatellite-unstable colorectal cancer. EMBO Mol. Med. 10, e8552 (2018).
Go, C. D. et al. A proximity biotinylation map of a human cell. Preprint at https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/796391v1 (2019).
Johar, S. S. & Talbert, J. N. Strep-tag II fusion technology for the modification and immobilization of lipase B from Candida antarctica (CALB). J. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol. 15, 359–367 (2017).
Schmidt, T. G. et al. Development of the Twin-Strep-tag and its application for purification of recombinant proteins from cell culture supernatants. Protein Expr. Purif. 92, 54–61 (2013).
Einhauer, A. & Jungbauer, A. Affinity of the monoclonal antibody M1 directed against the FLAG peptide. J. Chromatogr. A 921, 25–30 (2001).
Domanski, M. et al. Improved methodology for the affinity isolation of human protein complexes expressed at near endogenous levels. BioTechniques 0, 1–6 (2012).
Lee, S.-Y. et al. APEX fingerprinting reveals the subcellular localization of proteins of interest. Cell Rep. 15, 1837–1847 (2016).
Chojnowski, A. et al. 2C-BioID: an advanced two component BioID system for precision mapping of protein interactomes. iScience 10, 40–52 (2018).
Trinkle-Mulcahy, L. Recent advances in proximity-based labeling methods for interactome mapping. F1000Research https://doi.org/10.12688/f1000research.16903.1 (2019).
Kim, D. I. et al. An improved smaller biotin ligase for BioID proximity labeling. Mol. Biol. Cell 27, 1188–1196 (2016).
Branon, T. C. et al. Efficient proximity labeling in living cells and organisms with TurboID. Nat. Biotechnol. 36, 880–887 (2018).
Waller, J. R., Anderson, J. K. & Ulmer, D. C. Use of avidin to prepare biotin-free culture media. Anal. Biochem. 141, 189–193 (1984).
Dakshinamurti, K., Chalifour, L. & Bhullar, R. P. Requirement for biotin and the function of biotin in cells in culture. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 447, 38–55 (1985).
May, D. G., Scott, K. L., Campos, A. R. & Roux, K. J. Comparative application of BioID and TurboID for protein-proximity biotinylation. Cells https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9051070 (2020).
Gupta, G. D. et al. A dynamic protein interaction landscape of the human centrosome–cilium interface. Cell 163, 1484–1499 (2015).
Zhang, L., Pan, X. & Hershey, J. W. Individual overexpression of five subunits of human translation initiation factor eIF3 promotes malignant transformation of immortal fibroblast cells. J. Biol. Chem. 282, 5790–5800 (2007).
Vaux, D. L., Fidler, F. & Cumming, G. Replicates and repeats-what is the difference and is it significant? A brief discussion of statistics and experimental design. EMBO Rep. 13, 291–296 (2012).
De Rivoyre, M. et al. Human receptors patched and smoothened partially transduce hedgehog signal when expressed in Drosophila cells. J. Biol. Chem. 281, 28584–28595 (2006).
Tu, C. et al. Optimization of search engines and postprocessing approaches to maximize peptide and protein identification for high-resolution mass data. J. Proteome Res. 14, 4662–4673 (2015).
Paulo, J. A. Practical and efficient searching in proteomics: a cross engine comparison. WebmedCentral https://doi.org/10.9754/journal.wplus.2013.0052 (2013).
Choi, H. et al. SAINT: probabilistic scoring of affinity purification-mass spectrometry data. Nat. Methods 8, 70–73 (2011).
Teo, G. et al. SAINTexpress: improvements and additional features in significance analysis of INTeractome software. J. Proteom. 100, 37–43 (2014).
Choi, H. et al. Analyzing protein–protein interactions from affinity purification–mass spectrometry data with SAINT. Curr. Protoc. 39, 8.15.11–18.15.23 (2012).
Acknowledgements
We thank S. Miettinen for technical assistance and T. Öhman and E. Niemelä for critical reading and comments on the manuscript. We thank D. A. Yohannes for technical support of the MAC-tag online platform. Imaging was performed at the Light Microscopy Unit, Institute of Biotechnology. This study was supported by grants from the Academy of Finland (nos. 288475 and 294173), the Sigrid Jusélius Foundation, the Finnish Cancer Foundation, the University of Helsinki Three-year Research Grant, Biocentrum Helsinki, Biocentrum Finland, HiLIFE and the Instrumentarium Research Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
M.V. and X.L. conceived the study and designed experiments. M.V., X.L., K.S., R.W. and G.L. performed experiments and data analysis. M.V., X.L., K.S., R.W. and G.L. participated in manuscript preparation. M.V. and X.L. wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Related links
Key references using this protocol
Liu, X. et al. Nat. Commun. 9, 1188 (2018): https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-018-03523-2
Kondelin, J. et al. EMBO Mol. Med. 10, e8552 (2018): https://www.embopress.org/doi/full/10.15252/emmm.201708552
Paakkola, T. et al. Hum. Mol. Genet. 27, 4288–4302 (2018): https://academic.oup.com/hmg/article/27/24/4288/5102903
Yellapragada, V. et al. Front. Endocrinol. 10, 48 (2019): https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fendo.2019.00048/full
Keskitalo, S. et al. Front. Immunol. 10, 2770 (2019): https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2019.02770/full.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Tables
Supplementary Tables 1 and 2.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, X., Salokas, K., Weldatsadik, R.G. et al. Combined proximity labeling and affinity purification−mass spectrometry workflow for mapping and visualizing protein interaction networks. Nat Protoc 15, 3182–3211 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41596-020-0365-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41596-020-0365-x
This article is cited by
-
Characterizing host-microbe interactions with bacterial effector proteins using proximity-dependent biotin identification (BioID)
Communications Biology (2025)
-
An enzymatic cascade enables sensitive and specific proximity labeling proteomics in challenging biological systems
Nature Communications (2025)
-
SUMOylation inhibition potentiates the glucocorticoid receptor to program growth arrest of acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells
Oncogene (2025)
-
Mechanisms and Research Methods of Protein Modification in Virus Entry
Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology (2025)
-
Functional omics of ORP7 in primary endothelial cells
BMC Biology (2024)