Abstract
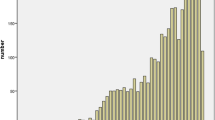
Research on metaphor has steadily increased over the last decades, as this phenomenon opens a window into a range of linguistic and cognitive processes. At the same time, the demand for rigorously constructed and extensively normed experimental materials increased as well. Here, we present the Figurative Archive, an open database of 996 metaphors in Italian enriched with ratings and corpus-based measures (from familiarity to semantic distance and preferred interpretations), derived by collecting stimuli used across 11 studies. It includes both everyday and literary metaphors, varying in structure and semantic domains, and is validated based on correlations between familiarity and other measures. The Archive has several aspects of novelty: it is increased in size compared to previous resources; it offers a measure of metaphor inclusiveness, to comply with recommendations for non-discriminatory language use; it is displayed in a web-based interface, with features for a customized consultation. We provide guidelines for using the Archive to source materials for studies investigating metaphor processing and the relationships between metaphor features in humans and computational models.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The Figurative Archive, including the main datasets and the datasets of the original studies, is available on Zenodo63 at https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.14924803.
Code availability
The codes to reproduce the Technical Validation and to locally access the interface are provided as R scripts in the Zenodo repository63 at https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.14924803.
References
Holyoak, K. J. & Stamenković, D. Metaphor comprehension: A critical review of theories and evidence. Psychol Bull 144, 641–671 (2018).
Rapp, A. M., Mutschler, D. E. & Erb, M. Where in the brain is nonliteral language? A coordinate-based meta-analysis of functional magnetic resonance imaging studies. Neuroimage 63, 600–610 (2012).
Huang, Y., Huang, J., Li, L., Lin, T. & Zou, L. Neural network of metaphor comprehension: an ALE meta-analysis and MACM analysis. Cerebral Cortex 33, 10918–10930 (2023).
Glucksberg, S. The psycholinguistics of metaphor. Trends Cogn Sci 7, 92–96 (2003).
Yuan, G. & Sun, Y. A bibliometric study of metaphor research and its implications (2010–2020). Southern African Linguistics and Applied Language Studies 41, 227–247 (2023).
Peng, Z. & Khatin-Zadeh, O. Research on metaphor processing during the past five decades: a bibliometric analysis. Humanit Soc Sci Commun 10, 928 (2023).
Zhao, X., Zheng, Y. & Zhao, X. Global bibliometric analysis of conceptual metaphor research over the recent two decades. Front Psychol 14, 1042121 (2023).
Coulson, S. Metaphor Comprehension and the Brain. in The Cambridge Handbook of Metaphor and Thought (ed. Gibbs, R. W. Jr.) 177–194 (Cambridge University Press, 2008).
Gonzalez-Marquez, M., Mittelberg, I., Coulson, S. & Spivey, M. J. (eds.) Methods in Cognitive Linguistics. https://doi.org/10.1075/hcp.18 (John Benjamins Publishing Company, 2007).
Noveck, I. Experimental Pragmatics: The Making of a Cognitive Science. (Cambridge University Press, 2018).
Canal, P. & Bambini, V. Pragmatics Electrified. in Language electrified. Principles, methods, and future perspectives of investigation (eds. Grimaldi, M., Brattico, E. & Shtyrov, Y.) 583–612, https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-3263-5_18 (Humana, 2023).
Bambini, V. & Domaneschi, F. Twenty years of experimental pragmatics. New advances in scalar implicature and metaphor processing. Cognition 244, 105708 (2024).
Bischetti, L., Frau, F. & Bambini, V. Neuropragmatics. in The Handbook of Clinical Linguistics, Second Edition (eds. Ball, M. J., Müller, N. & Spencer, E.) 41–54, https://doi.org/10.1002/9781119875949.ch4 (Wiley, 2024).
Cuccio, V. The figurative brain. in The Routledge Handbook of Semiosis and the Brain (eds. García, A. M. & Ibáñez, A.) 130–144, https://doi.org/10.4324/9781003051817-11 (Routledge, 2022).
Rossetti, I., Brambilla, P. & Papagno, C. Metaphor Comprehension in Schizophrenic Patients. Front Psychol 9, 670 (2018).
Bambini, V. et al. A leopard cannot change its spots: A novel pragmatic account of concretism in schizophrenia. Neuropsychologia 139, 107332 (2020).
Littlemore, J. & Low, G. Metaphoric Competence, Second Language Learning, and Communicative Language Ability. Appl Linguist 27, 268–294 (2006).
Werkmann Horvat, A., Bolognesi, M., Littlemore, J. & Barnden, J. Comprehension of different types of novel metaphors in monolinguals and multilinguals. Lang Cogn 14, 401–436 (2022).
Jacobs, A. M. (Neuro-)Cognitive poetics and computational stylistics. Sci Study Lit 8, 165–208 (2018).
Jacobs, A. M. Neurocognitive poetics: methods and models for investigating the neuronal and cognitive-affective bases of literature reception. Front Hum Neurosci 9, 186 (2015).
Bolognesi, M. & Werkmann Horvat, A. The Metaphor Compass, https://doi.org/10.4324/9781003041221 (Routledge, 2022).
Lai, V. T., Curran, T. & Menn, L. Comprehending conventional and novel metaphors: An ERP study. Brain Res 1284, 145–155 (2009).
Schmidt, G. L. & Seger, C. A. Neural correlates of metaphor processing: The roles of figurativeness, familiarity and difficulty. Brain Cogn 71, 375–386 (2009).
Bambini, V., Bertini, C., Schaeken, W., Stella, A. & Di Russo, F. Disentangling Metaphor from Context: An ERP Study. Front Psychol 7, 559 (2016).
Yang, J. & Shu, H. Involvement of the Motor System in Comprehension of Non-Literal Action Language: A Meta-Analysis Study. Brain Topogr 29, 94–107 (2016).
Lecce, S., Ronchi, L., Del Sette, P. & Bischetti, L. & Bambini, V. Interpreting physical and mental metaphors: Is Theory of Mind associated with pragmatics in middle childhood? J Child Lang 46, 393–407 (2019).
Canal, P. et al. N400 differences between physical and mental metaphors: The role of Theories of Mind. Brain Cogn 161, 105879 (2022).
Ceccato, I. et al. Aging and the Division of Labor of Theory of Mind Skills in Metaphor Comprehension. Top Cogn Sci https://doi.org/10.1111/tops.12785 (2025).
McQuire, M., McCollum, L. & Chatterjee, A. Aptness and beauty in metaphor. Lang Cogn 9, 316–331 (2017).
Jones, L. L. & Estes, Z. Roosters, robins, and alarm clocks: Aptness and conventionality in metaphor comprehension. J Mem Lang 55, 18–32 (2006).
Al-Azary, H. & Buchanan, L. Novel metaphor comprehension: Semantic neighbourhood density interacts with concreteness. Mem Cognit 45, 296–307 (2017).
Reid, N. J., Al-Azary, H. & Katz, A. N. Cognitive Factors Related to Metaphor Goodness in Poetic and Non-literary Metaphor. Metaphor Symb 38, 130–148 (2023).
Thibodeau, P. H., Sikos, L. & Durgin, F. H. Are subjective ratings of metaphors a red herring? The big two dimensions of metaphoric sentences. Behav Res Methods 50, 759–772 (2018).
Schmidt, G. L., Kranjec, A., Cardillo, E. R. & Chatterjee, A. Beyond Laterality: A Critical Assessment of Research on the Neural Basis of Metaphor. Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society 16, 1–5 (2010).
Katz, A. N., Paivio, A., Marschark, M. & Clark, J. M. Norms for 204 Literary and 260 Nonliterary Metaphors on 10 Psychological Dimensions. Metaphor and Symbolic Activity 3, 191–214 (1988).
Campbell, S. J. & Raney, G. E. A 25-year replication of Katz et al.’s (1988) metaphor norms. Behav Res Methods 48, 330–340 (2016).
Cardillo, E. R., Schmidt, G. L., Kranjec, A. & Chatterjee, A. Stimulus design is an obstacle course: 560 matched literal and metaphorical sentences for testing neural hypotheses about metaphor. Behav Res Methods 42, 651–664 (2010).
Cardillo, E. R., Watson, C. & Chatterjee, A. Stimulus needs are a moving target: 240 additional matched literal and metaphorical sentences for testing neural hypotheses about metaphor. Behav Res Methods 49, 471–483 (2017).
Roncero, C. & de Almeida, R. G. Semantic properties, aptness, familiarity, conventionality, and interpretive diversity scores for 84 metaphors and similes. Behav Res Methods 47, 800–812 (2015).
Citron, F. M. M., Lee, M. & Michaelis, N. Affective and psycholinguistic norms for German conceptual metaphors (COMETA). Behav Res Methods 52, 1056–1072 (2020).
Müller, N., Nagels, A. & Kauschke, C. Metaphorical expressions originating from human senses: Psycholinguistic and affective norms for German metaphors for internal state terms (MIST database). Behav Res Methods 54, 365–377 (2022).
Bambini, V., Resta, D. & Grimaldi, M. A Dataset of Metaphors from the Italian Literature: Exploring Psycholinguistic Variables and the Role of Context. PLoS One 9, e105634 (2014).
Krennmayr, T. & Steen, G. VU Amsterdam Metaphor Corpus. in Handbook of Linguistic Annotation (eds. Ide, N. & Pustejovsky, J.) 1053–1071, https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-024-0881-2_39 (Springer Netherlands, 2017).
Stamenković, D., Milenković, K. & Dinčić, J. Studija normiranјa knјiževnih i neknјiževnih metafora iz srpskog jezika [A norming study of Serbian literary and nonliterary metaphors]. Zbornik Matice srpske za filologiju i lingvistiku 62, 89–104 (2019).
Huang, J., Chen, L., Huang, Y., Chen, Y. & Zou, L. COGMED: a database for Chinese olfactory and gustatory metaphor. Humanit Soc Sci Commun 11, 1080 (2024).
Wang, X. Normed dataset for novel metaphors, novel similes, literal and anomalous sentences in Chinese. Front Psychol 13, 922722 (2022).
Neumann, C. Is Metaphor Universal? Cross-Language Evidence From German and Japanese. Metaphor Symb 16, 123–142 (2001).
Milenković, K., Tasić, M. & Stamenković, D. Influence of translation on perceived metaphor features: quality, aptness, metaphoricity, and familiarity. Linguistics Vanguard 10, 285–296 (2024).
Bambini, V., Gentili, C., Ricciardi, E., Bertinetto, P. M. & Pietrini, P. Decomposing metaphor processing at the cognitive and neural level through functional magnetic resonance imaging. Brain Res Bull 86, 203–216 (2011).
Poth, C. N. Fostering Equity and Diversity Through Essential Mixed Methods Research Inclusive Language Practices. J Mix Methods Res 18, 110–114 (2024).
Bischetti, L. et al. Assessment of pragmatic abilities and cognitive substrates (APACS) brief remote: a novel tool for the rapid and tele-evaluation of pragmatic skills in Italian. Lang Resour Eval 58, 951–979 (2024).
Bischetti, L. et al. Development and Validation of a Rapid Tool to Measure Pragmatic Abilities: The Brief Assessment of Pragmatic Abilities and Cognitive Substrates (APACS Brief). Behavioral Sciences 15, 107 (2025).
Barattieri di San Pietro, C., Frau, F., Mangiaterra, V. & Bambini, V. The pragmatic profile of ChatGPT: Assessing the communicative skills of a conversational agent. Sistemi intelligenti 35, 379–400 (2023).
Lombardi, A. & Lenci, A. Doing Things with Words: Rethinking Theory of Mind Simulation in Large Language Models. in Proceedings of the Eleventh Italian Conference on Computational Linguistics (CLiC-it 2025) (eds. C. Bosco, E. Jezek, M. Polignano & M. Sanguinetti) 613–624, https://aclanthology.org/2025.clicit-1.59/ (CEUR Workshop Proceedings, Cagliari, Italy, 2025).
Mangiaterra, V., Barattieri Di San Pietro, C., Frau, F., Bambini, V. & Al-Azary, H. On choosing the vehicles of metaphors without a body: evidence from Large Language Models. in Proceedings of the 2nd Workshop on Analogical Abstraction in Cognition, Perception, and Language (Analogy-Angle II) (eds. G. Rambelli, F. Ilievski, M. Bolognesi & P. Sommerauer) 37-44, https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/2025.analogyangle-1.4 (Association for Computational Linguistics, Vienna, Austria, 2025).
Pedinotti, P., Di Palma, E., Cerini, L. & Lenci, A. A howling success or a working sea? Testing what BERT knows about metaphors. in Proceedings of the Fourth BlackboxNLP Workshop on Analyzing and Interpreting Neural Networks for NLP (eds. J. Bastings, Y. Belinkov, E. Dupoux, M. Giulianelli, D. Hupkes, Y. Pinter & H. Sajjad) 192–204, https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/2021.blackboxnlp-1.13 (Association for Computational Linguistics, Punta Cana, Dominican Republic, 2021).
Ichien, N., Stamenković, D. & Holyoak, K. J. Large Language Model Displays Emergent Ability to Interpret Novel Literary Metaphors. Metaphor Symb 39, 296–309 (2024).
Suozzi, A., Capone, L., Lebani, G. E. & Lenci, A. BAMBI: Developing BAby language Models for Italian. Lingue e linguaggio 34, 83–102 (2025).
Attanasio, G. et al. CALAMITA: Challenge the Abilities of LAnguage Models in ITAlian. in Proceedings of the Tenth Italian Conference on Computational Linguistics (CLiC-it 2024) (eds. F. Dell’Orletta, A. Lenci, S. Montemagni & R. Sprugnoli) 1054–1063, https://aclanthology.org/2024.clicit-1.116/ (CEUR Workshop Proceedings, Pisa, Italy, 2024).
Blasi, D. E., Henrich, J., Adamou, E., Kemmerer, D. & Majid, A. Over-reliance on English hinders cognitive science. Trends Cogn Sci 26, 1153–1170 (2022).
Kövecses, Z. Metaphor in Culture. https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9780511614408 (Cambridge University Press, 2005).
Frau, F. et al. Testing motor grounding and somatotopic effects for literal and figurative action-language in Motor Neuron Diseases: a multiple-case analysis. Preprint at https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/mk9wh_v1 (2025).
IUSS Neurolinguistics and Experimental Pragmatics Laboratory (NEPLab). ERC_Cog PROMENADE - WP1: Figurative Archive. Zenodo https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.14924803 (2025).
Bambini, V., Ghio, M., Moro, A. & Schumacher, P. B. Differentiating among pragmatic uses of words through timed sensicality judgments. Front Psychol 4, 938 (2013).
Bertinetto, P. M. et al. Corpus e Lessico di Frequenza dell’Italiano Scritto (CoLFIS). (2005).
Lago, S., Zago, S., Bambini, V. & Arcara, G. Pre-Stimulus Activity of Left and Right TPJ in Linguistic Predictive Processing: A MEG Study. Brain Sci 14, 1014 (2024).
Baroni, M., Bernardini, S., Ferraresi, A. & Zanchetta, E. The WaCky wide web: a collection of very large linguistically processed web-crawled corpora. Lang Resour Eval 43, 209–226 (2009).
Marelli, M. Word-embeddings Italian semantic spaces: A semantic model for psycholinguistic research. Psihologija 50, 503–520 (2017).
Brysbaert, M., Warriner, A. B. & Kuperman, V. Concreteness ratings for 40 thousand generally known English word lemmas. Behav Res Methods 46, 904–911 (2014).
Battaglini, C. et al. Imagers and mentalizers: capturing individual variation in metaphor interpretation via intersubject representational dissimilarity. Lingue e linguaggio 34, 61–81 (2025).
Bambini, V. et al. The costs of multimodal metaphors: comparing ERPs to figurative expressions in verbal and verbo-pictorial formats. Discourse Process 61, 44–68 (2024).
Taverniers, M. Metaphor. in Handbook of Pragmatics 1–36, https://doi.org/10.1075/hop.8.met3 (John Benjamins Publishing Company, Amsterdam, 2003).
Cameron, L. Metaphor in Educational Discourse. (Continuum, 2003).
Berber Sardinha, T. Metaphor probabilities in corpora. in Confronting Metaphor in Use: An applied linguistic approach (eds. Zanotto, M. S., Cameron, L. & Cavalcanti, M. C.) 127–147, https://doi.org/10.1075/pbns.173.09ber (John Benjamins Publishing Company, 2008).
Kövecses, Z. Metaphor and Emotion. Language, Culture, and Body in Human Feeling. (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 2000).
Ljubešić, N., Fišer, D. & Peti-Stantić, A. Predicting Concreteness and Imageability of Words Within and Across Languages via Word Embeddings. in Proceedings of The Third Workshop on Representation Learning for NLP (eds. I. Augenstein, K. Cao, H. He, F. Hill, S. Gella, J. Kiros, H. Mei & D. Misra) 217–222, https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/W18-3028 (Association for Computational Linguistics, Melbourne, Australia, 2018).
Grave, E., Bojanowski, P., Gupta, P., Joulin, A. & Mikolov, T. Learning Word Vectors for 157 Languages. in Proceedings of the Eleventh International Conference on Language Resources and Evaluation (LREC 2018) (eds. Calzolari et al.) (European Language Resources Association (ELRA), Miyazaki, Japan, 2018).
Janschewitz, K. Taboo, emotionally valenced, and emotionally neutral word norms. Behav Res Methods 40, 1065–1074 (2008).
Sulpizio, S. et al. Taboo language across the globe: A multi-lab study. Behav Res Methods 56, 3794–3813 (2024).
Culpeper, J. & Haugh, M. The metalinguistics of offence in (British) English. Journal of Language Aggression and Conflict 9, 185–214 (2021).
Cepollaro, B., Sulpizio, S., Bianchi, C. & Stojanovic, I. Slurs in quarantine. Mind Lang 39, 381–396 (2024).
Domaneschi, F., Cepollaro, B. & Stojanovic, I. Literally ‘a jerk’: an experimental investigation of expressives in predicative position. Lang Cogn 17, e13 (2025).
Czopp, A. M., Kay, A. C. & Cheryan, S. Positive Stereotypes Are Pervasive and Powerful. Perspectives on Psychological Science 10, 451–463 (2015).
Lucisano, P. & Piemontese, M. E. Gulpease: una formula per la predizione della leggibilità di testi in lingua italiana. SCUOLA E CITTÀ 3, 110–124 (1998).
Honnibal, M., Montani, I., Van Landeghem, S. & Boyd, A. spaCy: industrial-strength natural language processing in Python. Zenodo https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.1212303 (2020).
Le Mens, G., Kovács, B., Hannan, M. T. & Pros, G. Uncovering the semantics of concepts using GPT-4. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 120, e2309350120 (2023).
Wang, H. et al. Prompting Large Language Models for Topic Modeling. in 2023 IEEE International Conference on Big Data (BigData) 1236–1241, https://doi.org/10.1109/BigData59044.2023.10386113 (IEEE, 2023).
Gilardi, F., Alizadeh, M. & Kubli, M. ChatGPT outperforms crowd workers for text-annotation tasks. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 120, e2305016120 (2023).
Bulatov, V., Alekseev, V. & Vorontsov, K. Determination of the Number of Topics Intrinsically: Is It Possible? in Recent Trends in Analysis of Images, Social Networks and Texts (eds. Ignatov, D. I. et al.) 3–17, https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-67008-4_1 (Springer, 2024).
Jacobs, A. M. The Gutenberg English Poetry Corpus: Exemplary Quantitative Narrative Analyses. Frontiers in Digital Humanities 5, 5 (2018).
Xu, X. Interpreting metaphorical statements. J Pragmat 42, 1622–1636 (2010).
McGregor, S., Agres, K., Rataj, K., Purver, M. & Wiggins, G. Re-Representing Metaphor: Modeling Metaphor Perception Using Dynamically Contextual Distributional Semantics. Front Psychol 10, 765 (2019).
Winter, B. & Strik-Lievers, F. Semantic distance predicts metaphoricity and creativity judgments in synesthetic metaphors. Metaphor and the Social World 13, 59–80 (2023).
Stamenković, D., Milenković, K., Ichien, N. & Holyoak, K. J. An Individual-Differences Approach to Poetic Metaphor: Impact of Aptness and Familiarity. Metaphor Symb 38, 149–161 (2023).
Garello, S. The visibility of speech. Pragmatics & Cognition 30, 353–376 (2023).
Carston, R. Figurative Language, Mental Imagery, and Pragmatics. Metaphor Symb 33, 198–217 (2018).
Carston, R. Metaphor: Ad hoc concepts, literal meaning and mental images. Proceedings of the Aristotelian Society 110, 295–321 (2010).
Katz, A. N., Paivio, A. & Marschark, M. Poetic comparisons: Psychological dimensions of metaphoric processing. J Psycholinguist Res 14, 365–383 (1985).
Pompei, C. et al. ‘Broccoli is candy’: the role of metaphors in children’s persuasive communication. Language Development Research 5, 204-236 (2025).
Sopory, P. & Dillard, J. P. The Persuasive Effects of Metaphor: A Meta-Analysis. Hum Commun Res 28, 382–419 (2002).
Mitić, A. J., Mitić, I. & Stamenković, D. Can reading habits affect metaphor evaluation? Exploring key relations. Open Linguist 11, 20250053 (2025).
Schäffner, C. & Shuttleworth, M. Metaphor in translation. Target. International Journal of Translation Studies 25, 93–106 (2013).
Kövecses, Z. Language, Figurative Thought, and Cross-Cultural Comparison. Metaphor Symb 18, 311–320 (2003).
Ifantidou, E. & Hatzidaki, A. Metaphor comprehension in L2: Meaning, images and emotions. J Pragmat 149, 78–90 (2019).
Kövecses, Z. Metaphor, language, and culture. DELTA: Documentação de Estudos em Lingüística Teórica e Aplicada 26, 739–757 (2010).
R Core Team. R: A language and environment for statistical computing. (2021).
Chang, W. et al. shiny: Web Application Framework for R. https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=shiny (2022).
Chang, W. & Borges Ribeiro, B. shinydashboard: Create Dashboards with ‘Shiny’. https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=shinydashboard (2021).
Acknowledgements
This work received support from the European Research Council under the EU’s Horizon Europe programme, ERC Consolidator Grant “PROcessing MEtaphors: Neurochronometry, Acquisition and Decay, PROMENADE” [101045733]. The content of this article is the sole responsibility of the authors. The European Commission or its services cannot be held responsible for any use that may be made of the information it contains. We thank Prof. Filippo Domaneschi for his valuable input in refining the definition and conceptual scope of the inclusiveness measure. We are also grateful to Prof. Gloria Cappelli and Cordelia Katrina Bacci for their assistance in refining the English adaptation of metaphorical items based on verbs.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Maddalena Bressler: Methodology, Validation, Investigation, Formal analysis, Data Curation, Visualization, Writing - Original Draft. Veronica Mangiaterra: Methodology, Software, Validation, Investigation, Formal analysis, Data Curation, Visualization, Writing - Original Draft. Paolo Canal: Investigation, Data Curation, Writing - Review & Editing. Federico Frau: Investigation, Data Curation, Writing - Review & Editing. Fabrizio Luciani: Investigation, Writing - Review & Editing. Biagio Scalingi: Investigation, Writing - Review & Editing. Chiara Barattieri di San Pietro: Investigation, Writing - Review & Editing. Chiara Battaglini: Investigation, Writing - Review & Editing. Chiara Pompei: Investigation, Writing - Review & Editing. Fortunata Romeo: Investigation, Writing - Review & Editing. Luca Bischetti: Conceptualization, Methodology, Validation, Formal analysis, Visualization, Supervision, Writing - Original Draft. Valentina Bambini: Conceptualization, Methodology, Data Curation, Supervision, Writing - Original Draft, Resources, Funding acquisition.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Bressler, M., Mangiaterra, V., Canal, P. et al. Figurative Archive: an open dataset and web-based application for the study of metaphor. Sci Data (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41597-025-06459-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41597-025-06459-7