Abstract
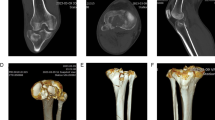
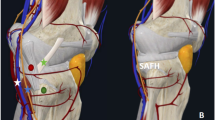
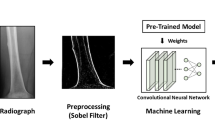
Tibial plateau fractures account for approximately 1% of skeletal fractures, with treatment strategies varying based on fracture type, displacement, and articular involvement. Diagnosis is labor-intensive, time-consuming, repetitive, and subject to considerable inter-observer variability. Automated and precise approaches could improve accuracy and efficiency in fracture severity classification. With advances in artificial intelligence (AI), especially deep learning, such techniques are increasingly applied in medicine, yet their performance depends on high-quality training data. Here, we present a first-of-its-kind open-access dataset for AI-based analysis of tibial plateau fractures. The dataset comprises 421 heterogeneous anterior-posterior radiographs from 186 patients (mean age 45.88 ± 17.54 years; 37 females, 149 males), including normal and fractured knees. Fractures were classified by expert orthopedic surgeons and radiologists using the Schatzker system: type I (14.51%), II (18.27%), III (6.45%), IV (5.91%), V (6.45%), VI (17.20%), and normal (31.18%). All images were segmented to generate tibial bone masks, supporting morphological analysis, AI training, and automated fracture assessment. This dataset facilitates AI-driven fracture detection, classification, preoperative planning, and orthopedic assistant education.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The dataset utilized in this study is publicly available in the cloud and can be accessed on Zenodo (https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.18007397)18 under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) license. All data were anonymized and prepared following ethical standards. Researchers are encouraged to use the dataset for academic and non-commercial research purposes.
Code availability
The dataset provides patient-specific data in MATLAB .mat files, each containing structured information for tibial plateau fracture images and segmentation masks. The MATLAB and Python scripts for reading, processing, and visualizing the data are available at the following repository: https://github.com/ali-kazemi8/PlaTiF-Tibial-Plateau-Fracture-Dataset.git.
References
Perlepe, V. et al. Can we assess healing of surgically treated long bone fractures on radiograph? Diagnostic and Interventional Imaging 99, 381–386, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diii.2018.02.004 (2018).
Petinaux, B., Bhat, R., Boniface, K. & Aristizabal, J. Accuracy of radiographic readings in the emergency department. The American Journal of Emergency Medicine 29, 18–25, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajem.2009.07.011 (2011).
Jacofsky, D., Haidukerwych, G. & Scott, W. Tibia plateau fractures. Scott WN. Insall & Scott Surgery of the knee. Philadelphia: Churchill Livingstone, 1133-1146 (2006).
Rudran, B., Little, C., Wiik, A. & Logishetty, K. Tibial Plateau Fracture: Anatomy, Diagnosis and Management. Br J Hosp Med (Lond) 81, 1–9, https://doi.org/10.12968/hmed.2020.0339 (2020).
Schatzker, J. & Kfuri, M. Revisiting the management of tibial plateau fractures. Injury 53, 2207–2218, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.injury.2022.04.006 (2022).
Mthethwa, J. & Chikate, A. A review of the management of tibial plateau fractures. Musculoskelet Surg 102, 119–127, https://doi.org/10.1007/s12306-017-0514-8 (2018).
Kfuri, M. & Schatzker, J. Revisiting the Schatzker classification of tibial plateau fractures. Injury 49, 2252–2263, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.injury.2018.11.010 (2018).
Ramponi, D. R. & McSwigan, T. Tibial Plateau Fractures. Adv Emerg Nurs J 40, 155–161, https://doi.org/10.1097/TME.0000000000000194 (2018).
Avci, M. & Kozaci, N. Comparison of X-Ray Imaging and Computed Tomography Scan in the Evaluation of Knee Trauma. Medicina (Kaunas) 55, https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina55100623 (2019).
Muhammad, N. A., Sabarudin, A., Ismail, N. & Karim, M. K. A. A systematic review and meta-analysis of radiation dose exposure from computed tomography examination of thorax-abdomen-pelvic regions among paediatric population. Radiation Physics and Chemistry 179, 109148, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radphyschem.2020.109148 (2021).
Lawson, M. et al. A review of current imaging techniques used for the detection of occult bony fractures in young children suspected of sustaining non-accidental injury. J Med Imaging Radiat Oncol 66, 68–78, https://doi.org/10.1111/1754-9485.13270 (2022).
Liu, P.-r. et al. Artificial Intelligence to Diagnose Tibial Plateau Fractures: An Intelligent Assistant for Orthopedic Physicians. Current Medical Science 41, 1158–1164, https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-021-2501-4 (2021).
Bandyopadhyay, O., Biswas, A. & Bhattacharya, B. B. Long-bone fracture detection in digital X-ray images based on digital-geometric techniques. Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine 123, 2–14, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmpb.2015.09.013 (2016).
Shen, W. et al. Automatic segmentation of the femur and tibia bones from X-ray images based on pure dilated residual U-Net. Inverse Problems and Imaging 15, 1333–1346, https://doi.org/10.3934/ipi.2020057 (2021).
Huitema, J. M. et al. Are 3D-printed Models of Tibial Plateau Fractures a Useful Addition to Understanding Fractures for Junior Surgeons? Clin Orthop Relat Res 480, 1170–1177, https://doi.org/10.1097/CORR.0000000000002137 (2022).
Markhardt, B. K., Gross, J. M. & Monu, J. Schatzker Classification of Tibial Plateau Fractures: Use of CT and MR Imaging Improves Assessment. RadioGraphics 29, 585–597, https://doi.org/10.1148/rg.292085078 (2009).
Zeltser, D. W. & Leopold, S. S. Classifications in Brief: Schatzker Classification of Tibial Plateau Fractures. Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research® 471, 371–374, https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-012-2451-z (2013).
Kazemi, A. et al. PlaTiF: Tibial Plateau Fracture Dataset. Zenodo https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.18007397 (2025).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
A.K.: Conceptualization, Project Administration, Investigation, Data Curation, Methodology, Writing – Original Draft & Editing. K.S.: Writing – Original Draft, Formal Analysis. A.Z.: Image segmentation, Investigation, Writing – Original Draft. S.E.: Clinical Expertise for Validation, Data Annotation. E.N.: Clinical Expertise for Validation, Writing – Review & Editing. A.A.: Supervision, Writing – Review & Editing. P.F.: Supervision, Conceptualization, Writing – Review & Editing. M.H.N.: Supervision, Clinical Expertise for Validation, Writing – Review & Editing. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Kazemi, A., Same, K., Zamanirad, A. et al. PlaTiF: A pioneering dataset for orthopedic insights in AI-powered diagnosis of tibial plateau fractures. Sci Data (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41597-026-06560-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41597-026-06560-5