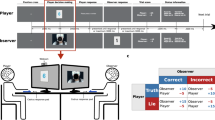
Abstract
This dataset contains behavioral and electroencephalographic (EEG) data collected simultaneously from 59 participants during the execution of the Iowa Gambling Task (IGT). It includes demographic general information (sex, age, and field of study), performance-related data from the IGT (decision, reaction times, wins, losses, and total credits), and the corresponding EEG recordings (21 electrodes in 10-20 system).
Similar content being viewed by others
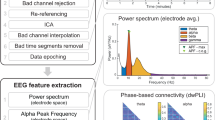
Data availability
The dataset is available via Mendeley Data®20. All files are publicly accessible for download without requiring a Mendeley account or any other login.
Code availability
An additional repository containing all relevant code has been made publicly available. The repository includes scripts for figure reproduction and preprocessing pipeline and procedures can be accessed via GitHub (https://github.com/lasaid-udg/IGT_EEG_dataset_processing_and_validation).
References
Bechara, A., Damasio, A. R., Damasio, H. & Anderson, S. W. Insensitivity to future consequences following damage to human prefrontal cortex. Cognition 50, 7–15 (1994).
Chiu, Y.-C. et al. Recollecting cross-cultural evidences: are decision makers really foresighted in Iowa gambling task? Front. Psychol. 11, 537219 (2020).
Beitz, K. M., Salthouse, T. A. & Davis, H. P. Performance on the Iowa Gambling Task: From 5 to 89 years of age. J. Exp. Psychol. Gen. 143, 1677–1689 (2014).
Van Den Bos, R., Homberg, J. & De Visser, L. A critical review of sex differences in decision-making tasks: Focus on the Iowa Gambling Task. Behav. Brain Res. 238, 95–108 (2013).
Evans, C. E., Kemish, K. & Turnbull, O. H. Paradoxical effects of education on the Iowa Gambling Task. Brain Cogn 54, 240–244 (2004).
Bechara, A., Tranel, D. & Damasio, H. Characterization of the decision-making deficit of patients with ventromedial prefrontal cortex lesions. Brain 123, 2189–2202 (2000).
Wang, T. et al. Exploring the Complex Relationship between Depression and Risky Decision-Making: A Meta-Analysis. J. Affect. Disord. Rep. 17, 100771 (2024).
Shurman, B., Horan, W. P. & Nuechterlein, K. H. Schizophrenia patients demonstrate a distinctive pattern of decision-making impairment on the Iowa Gambling Task. Schizophr. Res. 72, 215–224 (2005).
Ono, Y. et al. Reduced prefrontal activation during performance of the Iowa Gambling Task in patients with bipolar disorder. Psychiatry Res. Neuroimaging 233, 1–8 (2015).
Kornev, D. et al. Gaming behavior and brain activation using functional near‐infrared spectroscopy, Iowa gambling task, and machine learning techniques. Brain Behav 12, 4 (2022).
Aram, S. et al. The Iowa gambling task: A review of the historical evolution, scientific basis, and use in functional neuroimaging. Sage Open 9, 3 (2019).
Bechara, A. & Damasio, A. R. The somatic marker hypothesis: A neural theory of economic decision. Games Econ. Behav. 52, 336–372 (2005).
Mapelli, D., Di Rosa, E., Cavalletti, M., Schiff, S. & Tamburin, S. Decision and dopaminergic system: an ERPs study of Iowa gambling task in Parkinson’s disease. Front. Psychol. 5, 684 (2014).
Bianchin, M. & Angrilli, A. Decision preceding negativity in the iowa gambling task: an ERP study. Brain Cogn 75, 273–280 (2011).
Balconi, M. & Angioletti, L. Neurophysiology of gambling behavior and internet use vulnerability: a comparison between behavioral and EEG measures. Clin. EEG Neurosci. 53, 268–277 (2022).
Steingroever, H. et al. Data from 617 healthy participants performing the Iowa Gambling Task: A “many labs” collaboration. J. Open Psychol. Data 3, e5–e5 (2015).
Bolla, K. I., Eldreth, D. A., Matochik, J. A. & Cadet, J. L. Sex-related differences in a gambling task and its neurological correlates. Cereb. Cortex 14, 1226–1232 (2004).
Nonohay, R. G. D. & Gauer, G. Integrative approach to cognitive parameters in decision making. Rev. Pensam. Contemp. Adm. 12, 109–123 (2018).
Steingroever, H., Pachur, T., Šmíra, M. & Lee, M. D. Bayesian techniques for analyzing group differences in the Iowa Gambling Task: A case study of intuitive and deliberate decision-makers. Psychon. Bull. Rev. 25, 951–970 (2018).
Chávez-Sánchez, M., Torres-Ramos, S., Roman-Godinez, I. & Salido-Ruiz, R. A. An electroencephalographic and behavioral dataset from the Iowa Gambling Task application on non-clinical participants. Mendeley Data, https://doi.org/10.17632/2pw2m39yct.1 (2025)
Solis-Ortiz, S., Ramos, J., Arce, C., Guevara, M. A. & Corsi-Cabrera, M. EEG oscillations during menstrual cycle. Int. J. Neurosci. 76, 279–292 (1994).
Steingroever, H. et al. Performance of healthy participants on the Iowa Gambling Task. Psychol. Assess. 25, 180 (2013).
Stevenson, N. J. et al. A dataset of neonatal EEG recordings with seizure annotations. Sci. Data 6, 1–8 (2019).
Cui, J. F., Chen, Y. H., Wang, Y., Shum, D. H. & Chan, R. C. Neural correlates of uncertain decision making: ERP evidence from the Iowa Gambling Task. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 7, 776 (2013).
Kóbor, A. et al. Different strategies underlying uncertain decision making: Higher executive performance is associated with enhanced feedback‐related negativity. Psychophysiology 52, 367–377 (2015).
Zhong, N. et al. Smaller feedback-related negativity (FRN) reflects the risky decision-making deficits of methamphetamine dependent individuals. Front. Psychiatry 11, 320 (2020).
Latibeaudiere, A., Butler, S. & Owens, M. Decision-making and performance in the Iowa Gambling Task: recent ERP findings and clinical implications. Front. Psychol. 16, 1492471 (2025).
Acknowledgements
M.C.S. acknowledges Science, Humanities, Technology, and Innovation Secretariat (SECIHTI) for the scholarship (CVU: 1184330) awarded to pursue his postgraduate’s studies, which contributed to the development of this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
M.C.S. acquired, organized, and reviewed the data, including drafting the manuscript. S.T.R. provided participant registration and data acquisition support. I.R.G. developed data preprocessing and storage, including the software to apply the IGT. R.A.S.R. contributed to experimental methodology design and EEG signal re-referencing strategy. S.T.R., I.R.G. and R.A.S.R. completed the editing process and formatting of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Chávez-Sánchez, M., Torres-Ramos, S., Román-Godínez, I. et al. Behavioral and electroencephalographic dataset simultaneously acquired during the Iowa gambling task. Sci Data (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41597-026-06662-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41597-026-06662-0