Abstract
Near-infrared sensitization of monolayer MoS2 is here achieved via the covalent attachment of a novel heteroleptic nickel bis-dithiolene complex into sulfur vacancies in the MoS2 structure. Photocurrent action spectroscopy of the sensitized films reveals a discreet contribution from the sensitizer dye centred around 1300 nm (0.95 eV), well below the bandgap of MoS2 (2.1 eV), corresponding to the excitation of the monoanionic dithiolene complex. A mechanism of conductivity enhancement is proposed based on a photo-induced flattening of the corrugated energy landscape present at sulfur vacancy defect sites within the MoS2 due to a dipole change within the dye molecule upon photoexcitation. This method of sensitization might be readily extended to other functional molecules that can impart a change to the dielectric environment at the MoS2 surface under stimulation, thereby extending the breadth of detector applications for MoS2 and other transition metal dichalcogenides.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Within the class of 2D materials, transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDCs), such as MoS2, have been shown to be excellent candidates for next generation electronic and optoelectronic applications since they show strong absorption for visible light (α > 106 cm−1)1 and high charge carrier mobilities (μ > 100 s cm2 V−1 s−1) have been recorded2,3, even for single monolayer flakes. In contrast to graphene, MoS2 possesses a band-gap, direct in the case of monolayers, and has shown high on-off ratios (>108) in field-effect transistor (FET) devices4,5 thereby holding much promise for switching applications. Under optical stimulation, MoS2-based FETs have shown very high responsivities (Ɍ = 880 AW−1)6 across the visible region and various studies have sought to extend the sensitivity into the near infrared (NIR) region, and beyond, through charge transfer mechanisms between MoS2 and i.a. other 2D materials7, organic dyes8 or quantum dots – both in direct contact with the MoS29 or via a thin interlayer of TiO210. Especially in the latter case, extremely high responsivities of the order 106 AW−1 have been reported, owing to the passivation of the MoS2 surface by the TiO2 interlayer which effectively suppressed the direct interaction between QDs and the MoS2 channel, thereby preserving the intrinsic high on-off ratio of the MoS2, while allowing photocurrent gain via charge transfer across the interlayer.
In TMDC-based FET devices, since the active layer can be reduced to a single monolayer, the channel conductance is sensitive not just to the nature of the gate dielectric surface, for a given field, but also to the medium to which the opposed surface is exposed, i.e. adsorbed atoms, molecules or ions affect directly the channel between the source and drain electrodes without screening from a bulk semiconductor overlayer11. As such, monolayer TMDC-FETs have been shown to be extremely sensitive to the ambient conditions under which they are measured12, which can severely affect the electrical properties of devices but, if controlled10, also makes them an excellent platform for sensing applications.
Recently, a method to tune the conductance in planar 2- and 3-terminal devices of MoS2 (a representative TMDC) has been demonstrated, based on the covalent binding of thiol-based molecules at sulfur vacancies that exist (or can be introduced) as defects in the MoS2 structure13. By varying the end group of the thiol between electron rich and electron poor groups, it is possible to modify the carrier density in the MoS2, and thereby the threshold voltage (VT) of charge accumulation in the channel, in a controlled and permanent manner. To date, such studies have been limited to passive thiol molecules that are insensitive to external stimuli, thus the response of the devices is limited to the properties of the TMDC, such as its range of light absorption (λcutoff ≈ 700 nm for MoS2) and non-specific interaction with adsorbates. The use of functional molecules as covalently-bound addressable surface sensitizers for TMDC-based planar devices would allow for modulation of the channel conductance under external stimuli via a local and oriented change to the dielectric environment close to the TMDC channel, thereby providing a versatile platform for realizing a range of sensor devices that combine the superior (opto)electrical properties of TMDCs with the sensitivity and selectivity of organic/bio functional molecules. Such a concept has previously been demonstrated for application in biosensing to detect specific binding events of charged antigens to antibodies physadsorbed to the MoS2 channel14,15. However, to date, no sensitization via a unimolecular dipole change has yet been demonstrated.
In this study we demonstrate the principle of near-infrared (NIR) sensitization of monolayer MoS2 phototransistors via direct covalent attachment of a heteroleptic nickel bis-dithiolene (NiDT) chromophore to the MoS2 surface. NiDTs are attractive targets as sensitizer dyes as they characteristically show high thermal and photochemical stability, as well as strong optical absorption in the NIR (ε = 104–106 M−1 cm−1, λmax = 700–1500 nm) that is highly tuneable through rational ligand design16. By designing a NiDT dye with a single pendant disulfide unit, capable of binding to sulfur vacancies in the MoS2, dye-sensitization is shown to yield MoS2 phototransistors with an extended range of photodetection up to 1500 nm (0.83 eV), due to the oriented charge rearrangement within the dye molecule upon photoexcitation.
Results and Discussion
In a first step, a dithiolene ligand was designed that could serve as an anchor to chalcogen vacancies in TMDCs. The target ligand, 1-phenyl-[1,2,5]-dithiazepane-hex-1-ene-1,2-dithiolate (C4dtpdt), contained a pendant dithiazapane group that could potentially allow a bi-podal binding to the TMDC surface via ring opening at the disulfide bond17, thereby enhancing the binding stability. The synthetic route to the ligand precursor is described in detail in the Supporting Information online, and was achieved in 5 steps with an overall yield of >30%. In order to achieve an oriented change to the potential landscape at the MoS2 surface from the sensitizer molecule under optical stimulation, the target dye was heteroleptic, thus capable of binding only at one terminus. Heteroleptic NiDTs can generally be achieved through a ligand scrambling reaction between two dissimilar homoleptic complexes in an appropriate oxidation state18. Scrambling with neutral Ni(iPr2timdt)2 (1b) (a complex with an exceptionally high molar extinction coefficient)19 was successful and the heteroleptic Ni(C4dtpdt)(iPr2timdt) (2) could be isolated in ca. 20% yield from its homoleptic precursors, as shown in Fig. 1a.
(a) Molecular structure of heteroleptic Ni(C4dtpdt)(iPr2timdt) (2), synthesized by a ligand scrambling reaction between its two homoleptic precursors Ni(C4dtpdt)2 (1a) and Ni(iPr2timdt)2 (1b); (b) UV/Vis/NIR absorption spectra of 2, compared to (1a and 1b) recorded in dichloromethane, showing intermediate values of both peak absorption (λmax) and extinction coefficient (ε); (inset: red shift in λmax for 2 with decreasing solvent polarity, indicating negative solvatochromism).
The electronic characteristics of 2, as studied by absorption spectroscopy and cyclic voltammetry, were shown to be intermediate between 1a and 1b (Table 1, Fig. S1, ESI), with a peak absorption for 2 at λ = 935 nm in dichloromethane (DCM), as shown in Fig. 1b. The complex showed weak negative solvatochromism (Δλ = 35 nm (392 cm−1) between CS2 and MeCN) that scaled well with the refractive index of the solvent (Table S1, Fig. S2, ESI), suggesting some “push-pull” character to the electronic structure of the molecule18. Absorption spectroscopy in certain high donor number (DN) solvents (DMF, DMSO) showed the presence of a new peak at ca. 1200 nm that increased in intensity with time, at the expense of the main NIR peak. The location and progression of this peak was similar to that of the reduced species, studied under spectroelectrochemistry (c.f. Fig. S3, ESI), suggesting a spontaneous reduction of the complex in high DN solvents20. From X-ray structural analysis of 2 (Tables S2 and S3, Fig. S4, ESI), the bond lengths of the core NiSCCS rings are consistent with a greater dithiolate (“pull”) character for the C4dtpdt ligand and a greater dithione (“push”) character for the iPr2timdt ligand. This assignment is further supported by the slight reduction/extension of the C-C and S-Ni bond lengths in the respective ligands of 2, compared those of the symmetric parents 1a/1b where the electron density is equally shared over the two ligands. Such assignment leads to the conclusion that the C4dtpdt ligand makes a greater contribution to the HOMO of 2, with the LUMO residing more on the iPr2timdt ligand, giving the optical transition some degree of intramolecular charge transfer (ICT) character. However, the intermediate electrochemical and optical properties of 2, compared to its parents 1a and 1b suggest the dominant resonance form is a π-delocalized core with the optical transition principally π-π* in origin18.
In order to demonstrate dye sensitization of MoS2 with 2, commercial large-area CVD-grown monolayer MoS2 films, grown on sapphire, were used (Fig. S5, ESI). Dye-sensitization was achieved in a similar manner to that reported by Sim et al.13, whereby thermal annealing was used to introduce sulfur vacancies in the MoS2, which was then soaked in a solution of 2, followed by copious washing with fresh DCM. In all cases, the sensitized films (MoS2-2) were compared to as-received samples (MoS2), as well as control samples MoS2-C and MoS2-1b, processed in an identical manner to MoS2-2, except that they were soaked in pure DCM or 1b in DCM, respectively.
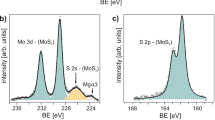
Figure 2 shows the spectroscopic characterization of the various MoS2 films. The binding of 2 to MoS2 is confirmed by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) of MoS2-2, which solely showed the distinct Ni elemental signature by the rising of Ni 2p peaks (Fig. 2a) as well as the Ni 3s peak in the Al 2p region of the sapphire substrate (Fig. 2b). Ni was not observed in either control sample MoS2-C or MoS2-1b. Since the chemical composition and energy levels of 1b and 2 are very similar, it can be concluded that the binding of 2 to MoS2 is achieved via the disulfide moiety of the dithiazepane, rather than by other mechanisms of association, such as serendipitous adsorption, or charge transfer (CT) complex formation. This is confirmed by the increase of the S signal, relative to Mo, in MoS2-2 compared to MoS2-C and MoS2-1b in which the signal ratio stays almost constant (c.f. Fig. S6 and Table S4, ESI).
Spectroscopic characterization of various MoS2 films: (a,b) XPS spectra of Ni 2p region (a) and Ni 3 s region, including Al 2p peak from substrate (b) for MoS2-2, compared to MoS2-C and MoS2-1b (data offset for clarity, colour scheme as for (c)); (c) thin film absorption spectra (absorption coefficient α based on an estimated monolayer thickness of d = 0.85 nm), compared to the thin film spectra of 2 (d = 50 nm), showing no detectable NiDT peak for MoS2-2 (right inset), but a red shift in the MoS2 excitonic transitions (left inset) (note: the slight y-offset and noise at 1150 nm in the MoS2 spectrum was common to as received samples – see ESI for further discussion).
Under UV/Vis/NIR spectroscopy (Fig. 2c), no characteristic NIR absorption could be detected for MoS2-2, and the spectra of MoS2-2, MoS2-C and MoS2-1b were almost identical in the region beyond 1000 nm, as shown in the NIR inset of Fig. 2c,suggesting a low surface coverage of 2 upon binding. Nevertheless, a distinct and reproducible change to the MoS2 absorption could be seen in the position of the A and B excitonic transitions, which were shifted to lower energy, with a broadening of the onset of light absorption, as shown in the visible region inset of Fig. 2c. This was not due to thermal annealing or DCM soaking, as shown by the near identical peak positions for the control samples compared to the as-received sample and thus might represent some electronic change to the MoS2 following sensitization (vide infra).
The functionality of the dye-sensitized MoS2 was assessed in FET devices, studied under photocurrent action spectroscopy. MoS2 was transferred to bottom-gate/bottom-contact (BGBC) Si/SiO2 transistor substrates by surface-energy-assisted transfer using polystyrene as a support, as reported by Gurarslan et al.21 (c.f. Fig. S7, ESI). In an attempt to reduce the strain in the MoS2, induced by a bottom contact geometry, ultra-thin Au source/drain electrodes (d = 9 nm) were initially used, fabricated on a mixed amine/thiol self-assembled monolayer adhesion layer22. The integrity of such electrodes was confirmed by atomic force microscopy and 4-point probe conductivity measurements, yielding a RMS roughness Rq < 1 nm and a sheet resistance Rs < 10 Ω/sq. For unannealed devices using this architecture, transistor analysis of the directly transferred films yielded a relatively low carrier mobility of the order μe ≈ 10−3 cm2 V−1s−1. The mobility values were generally improved following thermal annealing at 250 °C and subsequent soaking in DCM or 2 in DCM (MoS2-C and MoS2-2) to μe ≈ 100 cm2 V−1s−1, in both cases showing a threshold voltage close to −10 V. Due to the relatively broad spread in data, and low sample numbers tested, no statistical relevant difference between the electrical properties of MoS2-C and MoS2-2 was observed.
Figure 3 shows the wavelength-dependent photoconductivity (action spectra) of MoS2 phototransistors with and without sensitization by 2 over a wavelength range 350 nm – 1700 nm. The three excitonic processes of MoS2 are represented in the visible region, with their onset of photoconductivity limited to ca. 700 nm (1.77 eV), consistent with previous reports23. In the case of MoS2-2, the relative heights of these processes are changed, with a marked decrease in the relative contribution of the A excitonic process. Most notably, a new band, centred around 1300 nm, is apparent for MoS2-2, that is not observed in MoS2. This NIR photoresponse is observed in both scanning directions, and its magnitude remains stable over 1 hr of continuous measurement at 1300 nm. While the wavelength of this process does not correspond to that of 2, either in solution (ca. 940 nm, c.f. Fig. 1b), or as a thin film (ca. 1000 nm, c.f. Fig. 2c), it is similar to the peak absorption of the reduced complex [2]− studied under spectroelectrochemistry (c.f. Fig. S3, ESI). Further investigations are necessary to determine whether this redox change is effected in the device under operation, or is symptomatic of the binding mechanism and/or the redox sensitivity of 2 under certain environments (c.f. absorption spectra in DMSO and DMF) – certainly the presence of a charged molecule on the surface of the MoS2 might account for the shift in the A and B absorption peaks observed for MoS2-2 (c.f. Fig. 2c).
Wavelength-dependent photoconductivity of MoS2-2, compared to unsensitized MoS2-C (normalized to the B excitonic process), showing clear photocurrent generation in the NIR for MoS2-2. BGBC transistor substrates were used with ultra-thin Au electrodes as source and drain (L = 30 μm, W = 1 mm), as depicted in the inset, and the action spectra were recorded by lock-in methods at 263 Hz with VDS = 10 V, VGS = 0 V.
In this architecture, measurements under steady-state illumination were complicated by an extremely long-lived persistent photocurrent (PCC) contribution, that did not fully recover for > 10 hrs following visible or NIR illumination. Such an effect is commonly observed for MoS2 devices fabricated on SiO2 substrates6, the origin of which has been traced to carrier trapping both at the MoS2/SiO2 interface24,25, as well as within the MoS225,26. By shortening the channel length (L = 5 μm), using pre-fabricated interdigitated electrode array (IDA) BGBC devices, the recovery time was greatly reduced. It should be noted that the use of this architecture also caused a reduction in carrier mobility to μe ≈ 10−2–10−3 cm2 V−1s−1, even for the annealed films, which was likely due to the increased strain and possible damage caused by the relatively thick bottom contact electrodes over which the MoS2 was spread (Fig. S8, ESI). For such devices, the photocurrent response under illumination at 639 nm and 1310 nm (stimulating MoS2 and 2, respectively) both show a sub-linear increase with increasing light intensity, thus representing a drop in absolute responsivity towards higher light powers, though the relative responsivities at the two wavelengths remain approximately constant, as shown in Fig. S9, ESI. This suggests a constant contribution of 2 to the photocurrent response, rather than a transient effect of charging/discharging under illumination.
Considering the origin of photoresponse in the NIR, we propose a mechanism based on a dipolar change at the MoS2 surface that acts to liberate trapped charges within the MoS2 and/or limit their re-trapping. Coulomb interactions between TMDCs with polar molecules on their surface (as well as surface states on the substrate)27 have been shown to cause a local effective self-energy correction in the TMDC and thereby cause local variations of the bandgap28. Since the dye molecules are directly tethered to sulfur vacancies, which are a known locus of electron trapping and which can further scatter mobile carriers11,29, any change to the dipole moment of the dye affects directly the trap depth and trapping lifetime due to a change in the local dielectric environment of the MoS2. Photoexcitation of 2 is expected to cause a redistribution of electron density away from the anchoring C4dtpdt ligand (vide supra), thus yielding a δ+ close to the MoS2 surface. This local electrostatic change from 2 under NIR illumination effectively reduces the trap depth at the sulfur vacancies, liberating trapped charge carriers, and preventing their re-trapping, thereby leading to an enhanced conductivity in the MoS2 channel under NIR illumination. This mechanism is described pictorially in Fig. 4.
Proposed mechanism of NIR photocurrent generation. Processes occurring in the dark are shown in black, while processes due to NIR stimulation are shown in red. Photoexcitation of the solvatochromic sensitizer dye leads to a dipole change at the surface of the MoS2, thereby liberating trapped charges and preventing their (re-)trapping.
While further studies are needed to fully understand, and thereby optimize, the NIR photocurrent response, certain possibilities can be ruled out at this stage. Unlike for previous studies of MoS2 sensitization by QDs9 and films of organic dye molecules8, it seems unlikely that charge transfer plays a role in the photocurrent response since the LUMO level of 2 is almost the same as that reported for MoS230 (c.f. Table 1) and would be lower in the case of [2]−. Furthermore, in a control experiment conducted by drop casting of a film of 1b on the surface of a MoS2 device, only negligible photocurrent could be detected in the NIR, despite its higher extinction coefficient and significantly higher surface coverage (Fig. S10, ESI). Given the similarity of the frontier orbital energy levels between 1b and 2 (c.f. Table 1), it can be reasoned that charge transfer does not play a role in the photocurrent mechanism. Likewise, if a photothermal mechanism were underlying the photocurrent response in the NIR, it could reasonably be expected that the stronger NIR absorption of a drop cast film of 1b on a MoS2 device would lead to an enhanced NIR photoresponse, compared to that of MoS2-2 (for which the NIR absorption could not be clearly observed, c.f. Fig. 2c). However, this is not the case and thus it is possible to conclude that a photothermal effect does not significantly contribute to the NIR photoresponse of MoS2-2.
Conclusions
In this study, the sensitization of MoS2 films via covalent attachment of a heteroleptic NiDT complex to sulfur vacancies in the MoS2 surface is demonstrated. The sensitizer is shown to extend the range of light detection for MoS2 phototransistors up to 1500 nm, thereby effectively covering the 2nd telecommunications window and, despite a low surface coverage (not directly detectable under absorption spectroscopy), and weak solvatochromism, the NIR sensitization yields a clear, stable and reproducible photocurrent response. Further study will look at optimizing the molecular sensitizer towards stronger dipole change under illumination, as well as optimizing the sensitization method to achieve enhanced sensitizer response without compromising the intrinsic performance of the MoS2. The use of passive dielectrics and top contact architectures are expected to greatly improve the general optoelectronic response of such sensitized devices, allowing a more detailed analysis of especially the relative carrier dynamics following MoS2 and sensitizer stimulation. Furthermore, fabricating devices with an appropriately chosen interlayer (e.g. TiO2) between the MoS2 and the sensitizer molecules10 might help protect the MoS2 channel from serendipitous adsorbates, which can adversely affect the (opto)electronic properties of the devices, as well as to increase dye loading. The resultant devices would also help to clarify the mechanism of photocurrent enhancement - whether the dye molecule is acting on the localized traps or on the electronic bands of the MoS2. It should be noted that the proposed mechanism of conductivity enhancement under sensitizer stimulation is not necessarily limited to photodetection, but would, in principle, also be applicable to technologies, such as optical memories (through the use of photochromic sensitizers) - as long as the sensitizer stimulation results in a local change to dielectric environment close to the MoS2 surface.
Experimental
The synthesis of 1a and 2 is described in detail in the ESI, and follows a typical route for NiDTs31. MoS2 was purchased from 2DSemiconductors as a single batch as continuous monolayer films on 10 × 10 mm2 sapphire wafers. Dye-sensitization was carried out based on the method of Sim et al.13 whereby the (transferred) samples were annealed for 1 hr at 250 °C in a N2 filled glovebox. Following rapid cooling, the samples were soaked in a 0.5 mM solution of 2 in DCM and stored in the dark for >48 hrs. The samples were extensively rinsed with fresh DCM, and were then annealed on a hotplate at 50 °C for 10 mins.
UV/Vis/NIR spectroscopy (Perkin Elmer Lambda950) on solutions and thin films were measured in transmission mode. Cyclic voltammetry (Keithley 2450EC) was performed in a three electrode configuration (reference: Ag/Ag+; working: glassy carbon; counter: platinum wire) on ca. 1 mM analyte solution in DCM using 0.1 M TBABF4 (TBA = tetrabutylammonium) as supporting electrolyte.
For (opto)electronic measurements, BGBC transistor substrates comprising Si/SiO2 (300 nm) with ultra-thin Au source drain electrodes using a mixed self-assembled monolayer (SAM) of (3-Aminopropyl)trimethoxysilane/(3-Mercaptopropyl)trimethoxysilane as an adhesion layer22. Au source drain electrodes (d = 9 nm) were deposited under physical vapour deposition at a rate of 0.3 Ås−1 using a shadow mask to define channel dimensions L = 30 μm/W = 1 mm. The substrates were briefly subjected to oxygen plasma immediately prior to film transfer to remove exposed SAM. MoS2 transfer was achieved by surface-energy-assisted transfer using polystyrene as a support, following the method of Gurarslan et al.21. In short, the as-received MoS2 was spin coated with a solution of polystyrene (PS) (Mw = 280 kg/mol, 90 mg/ml in toluene) at 2000 rpm and baked at 90 °C for 15 mins. The film was divided into 4 by scratching with a razor blade. A droplet of water was then applied to release the divided MoS2/PS films from the substrate. The floating films were aligned over the electrode arrays of different substrates and the excess water was removed with a lint-free tissue. After air-drying for 30 mins, the devices were annealed for 1 hr at 80 °C, and further at 150 °C for 30 mins. Polystyrene was removed by rinsing with toluene and the pixel was isolated using a cotton bud. For transistor devices, dye-sensitization was performed after transfer, exactly as described above. Note: the conductivity of the bare ultra-thin electrodes was observed to diminish with aging, due to aggregation of the Au in the film. This process was accelerated by annealing, but was averted when the film was covered by e.g. MoS2. Therefore, in the used devices, the ultra-thin region only extended to the source/drain contacts, which were fabricated immediately before MoS2 transfer which completely covered this region. The traces and contact pads comprised 70 nm Au, with 5 nm Cr as adhesion layer, which provided robust external contacts. The electrical properties of such electrodes were further assessed relative to conventional BGBC devices (70 nm Au/5 nm Cr) using P3HT as semiconductor and essentially showed no statistical difference between the two electrode architectures32.
Action spectra measurements were performed by a lock-in method at 263 Hz, as reported previously33 over a wavelength range 350–1700 nm, as further described in the ESI. Phototransistor characterization (Keithley 2636B/LabVIEW) was performed in the dark or under illumination from a fibre-coupled LED (λmax = 640 nm or 1310 nm, Pmax = 260 μWcm−2 set for both).
Supporting information
Further experimental details, as well as additional experimental data on synthesis, characterization and device testing are available in the Electronic Supporting Information. This material is available free of charge via the Internet at.
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Bernardi, M., Palummo, M. & Grossman, J. C. Extraordinary sunlight absorption and one nanometer thick photovoltaics using two-dimensional monolayer materials. Nano Letters 13, 3664–3670 (2013).
Schmidt, H., Giustiniano, F. & Eda, G. Electronic transport properties of transition metal dichalcogenide field-effect devices: surface and interface effects. Chemical Society Reviews 44, 7115–7736 (2015).
Cui, X. et al. Multi-terminal transport measurements of MoS2 using a van der Waals heterostructure device platform. Nature Nanotechnology 7, 490–493 (2012).
Radisavljevic, B., Radenovic, A., Brivio, J., Giacometti, V. & Kis, A. Single-layer MoS2 transistors. Nature Nanotechnology 6, 147–50 (2011).
Wu, W. et al. High mobility and high on/off ratio field-effect transistors based on chemical vapor deposited single-crystal MoS2 grains. Applied Physics Letters 102, 142106 (2013).
Lopez-Sanchez, O., Lembke, D., Kayci, M., Radenovic, A. & Kis, A. Ultrasensitive photodetectors based on monolayer MoS2. Nature Nanotechnology 8, 497–501 (2013).
Ye, L., Li, H., Chen, Z. & Xu, J. Near-infrared photodetector based on MoS2/black phosphorus heterojunction. ACS Photonics 3, 692–699 (2016).
Yu, S. H. et al. Dye-sensitized MoS2 photodetector with enhanced spectral photoresponse. ACS Nano 8, 8285–8291 (2014).
Kufer, D. et al. Hybrid 2D–0D MoS2–PbS quantum dot photodetectors. Advanced Materials 27, 176–180 (2015).
Huo, N., Gupta, S. & Konstantatos, G. MoS2-HgTe Quantum Dot Hybrid Photodetectors beyond 2 μm. Advanced Materials 29, 1606576 (2017).
Li, S.-L., Tsukagoshi, K., Orgiu, E. & Samori, P. Charge transport and mobility engineering in two-dimensional transition metal chalcogenide semiconductors. Chemical Society Reviews 45, 118–151 (2016).
Ma, N. & Jena, D. Charge scattering and mobility in atomically thin semiconductors. Physical Review X 4, 011043 (2014).
Sim, D. M. et al. Controlled doping of vacancy-containing few-layer MoS2 via highly stable thiol-based molecular chemisorption. ACS Nano 9, 12115–12123 (2015).
Lee, J. et al. Two-dimiensional layered MoS2 biosensors enabled highly sensitive detection of biomolecules. Scientific Reports 4, 7352 (2014).
Nam, H. et al. Two different device physics principles for operating MoS2 transistor biosensors with femtomolar-level detection limits. Applied Physics Letters 107, 012105 (2015).
Mueller-Westerhoff, U. T. & Vance, B. Dithiolenes and related species in Comprehensive Coordination Chemistry Vol. 2 (eds Wilkinson, G., Gillard, R. D. & McCleverty, J. A.) 595–631 (Pergamon, 1987).
Bertin, P. A. et al. Electroactive self-assembled monolayers on gold via bipodal dithiazepane anchoring groups. Langmuir 24, 9069–9101 (2008).
Deplano, P., Pilia, L., Espa, D., Mercuri, M. L. & Serpe, A. Square-planar d8 metal mixed-ligand dithiolene complexes as second order nonlinear optical chromophores: structure/property relationship. Coordination Chemistry Reviews 254, 1434–1447 (2010).
Bigoli, F. et al. New neutral nickel dithiolene complex derived from 1,3-dialkylimidazolidine-2,4,5-trithione, showing remarkable near-IR absorption. Journal of the Chemical Society, Chemical Communications 371–372 (1995).
Warashira, T. & Hoshino, H. Solvent effects for spectroscopic properties of near-infrared absorbing nickel dithiolene complex [Ni(iPr2timdt)2] (iPr2timdt: monoanion of 1,3-diisopropylimidazolidine-2,4,5-trithione). Bulletin of the Chemical Society of Japan 89, 836–841 (2016).
Gurarslan, A. et al. Surface-energy-assisted perfect transfer of centimeter-scale monolayer and few-layer MoS2 films onto arbitrary substrates. ACS Nano 8, 11522–11528 (2014).
Stec, H. M., Williams, R. J., Jones, T. S. & Hatton, R. A. Ultrathin transparent Au electrodes for organic photovoltaics fabricated using a mixed mono-molecular nucleation layer. Advanced Functional Materials 21, 1709–1716 (2011).
Klots, A. R. et al. Probing excitonic states in suspended two-dimensional semiconductors by photocurrent spectroscopy. Scientific Reports 4, 6608 (2014).
Wu, Y.-C. et al. Extrinsic origin of persistent photoconductivity in monolayer MoS2 field effect transistors. Scientific Reports 5, 11472 (2015).
Bartolomeo, A. D. et al. Electrical transport and persistent photoconductivity in monolayer MoS2 phototransistors. Nanotechnology 28, 214002 (2017).
Furchi, M. M., Polyushkin, D. K., Pospischil, A. & Mueller, T. Mechanisms of photoconductivity in atomically thin MoS2. Nano Letters 14, 6165–6170 (2014).
Guo, Y. et al. Charge trapping at the MoS2-SiO2 interface and its effects on the characteristics of MoS2 metal-oxide-semiconductor field effect transistors. Applied Physics Letters 106, 103109 (2015).
Rösner, M. et al. Two-dimensional heterojunctions from nonlocal manipulations of the interactions. Nano Letters 16, 2322–2327 (2016).
Qui, H. et al. Hopping transport through defect-induced localized states in molybdenum disulphide. Nature Communications 4, 2642 (2013).
Park, S. et al. Direct determination of monolayer MoS2 and WSe2 exciton binding energies on insulating and metallic substrates. 2D Materials 5, 025003 (2018).
Rauchfuss, T. B. Synthesis of transition metal dithiolenes in Dithiolene chemistry: synthesis, properties, and applications Vol. 52 (eds. Stiefel, E. I. & Karlin, K. D.) 1–53 (John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 2004).
Pallasch, S. Towards transistor architectures for large area molybdenum disulfide devices. (Bachelor Thesis, Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, 2019).
Reissig, L., Dalgleish, S. & Awaga, K. Towards high-bandwidth organic photodetection based on pure active layer polarization. Scientific Reports 8, 15415 (2018).
Sworakowski, J., Lipiński, J. & Janus, K. On the reliability of determination of energies of HOMO and LUMO levels in organic semiconductors from electrochemical measurements. A simple picture based on the electrostatic model. Organic Electronics 33, 300–310 (2016).
Acknowledgements
SD and LR are grateful to the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports and Technology (MEXT) of Japan for a Grant-in-Aid for Young Scientists to SD (16K17971) and LR (16K17853). KA and YS thank the financial support of Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research from MEXT (16K13977, 16H06353 and 18H04482), and of the JSPS Bilateral and Core-to-Core Programs. Financial support by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft through the CRC 951 is gratefully acknowledged. This work was carried out in the framework of the Joint Lab GEN_FAB and was supported by the HySPRINT innovation lab at Helmholtz‐Zentrum Berlin.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
S.D. and E.L.K. conceived the idea of sensitized MoS2 devices. S.D. designed and conducted all the mentioned experiments, as well as analysed and interpreted the data, except where indicated: photocurrent action spectra were measured by L.R., single-crystal XRD were resolved by Y.S. and XPS analyses were performed by G.L. All authors contributed to the discussion of the results and the writing of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Dalgleish, S., Reissig, L., Shuku, Y. et al. Potential modulations in flatland: near-infrared sensitization of MoS2 phototransistors by a solvatochromic dye directly tethered to sulfur vacancies. Sci Rep 9, 16682 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-53186-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-53186-2