Abstract
The aromatic compounds having structural configurations with two or more fused benzene rings are the polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs). Topological indices are valuable tools for studying the structure property relationships of PAHs and also helps in predicting various properties and activities. They find applications widely in computational chemistry, drug design and QSPR studies. This article focuses on analysing the potential predictive index for Sombor index (SO), elliptic Sombor index (ESO), Euler Sombor index (EU), reverse Sombor index (RSO), reverse elliptic Sombor index (RESO) and reverse Euler Sombor index (REU) using regression models for top priority 38 PAHs. From the study it is evident that, SO and RSO have proved to be potential predictive indices among the considered degree-based and reverse degree-based indices. The variation of best predictive index with minimal RMSE are plotted for linear, quadratic and cubic regression models for better understanding.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
A branch of mathematics, that applies the concept of graph theory to study molecular structures is chemical graph theory(CGT). Using CGT, PAHs are modelled into graphs where atoms are represented as vertices and the bond between the atoms are represented as edges. The connectivity of the atoms are analysed with respect to properties of these graphs where researchers gather information about the structure of PAHs molecules1,2,3,4,5.
In general, CGT equips a dynamic framework for understanding the structure property relationships in PAHs molecule which is necessary for applications in the fields of design of new materials, monitoring environment and pharmaceuticals. A powerful tool to encode the structural information of PAH molecules in numerical representation is obtained by molecular descriptors. These molecular descriptors may be distance-based, graph spectral-based, and degree-based are used in QSPR/QSAR (quantitative structure property/activity relationship) studies to predict the physicochemical properties of PAH compounds6,7,8,9,10.
A topological index (TI) is the numerical value associated with the molecular structure of a chemical compound. These indices provide an understanding into various physicochemical properties and biological activities of a molecule11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons(PAHs) are composed of multiple aromatic ring having significant applications in the field of pharmacology, materials science and environmental science19,20,21. In the literature, various TIs are studied to characterize the structural properties of PAHs. They include Wiener index (W) which was the oldest and first TI based on distances between pairs of vertices in a graph. This index contributes information about the molecular size and branching for PAHs.
Hyper-Wiener index (WW) is an extension of the Wiener index which is used in the study of large PAH molecules. The molecular connectivity and symmetry in PAHs are provided using Harary Index (H), since this index is based on average distance between pairs of vertices. The Balaban index (J) gives insights into the degree of molecular branching and symmetry of PAHs as this index is based on topological distance matrix. The information about branching and symmetry of PAHs is obtained by using Randic index (R)22,23,24,25.
The main axioms of core chemistry postulates that there is an intricate link between the molecular structure with that of its physical properties. Topological indices are worthy in extracting appropriate details of the construction of molecules, thereby proving its applications across diverse fields such as medicinal chemistry, pharmacy, materials science and etc.,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33.
In 2021, Gutman introduced Sombor index using Euclidean geometry which has become very popular within a short span of time for its contribution in chemistry and pharmacology. The general form of a vertex degree-based index is a function which is chosen such that, it satisfies symmetry property. The edge uv representation in 2-dimensional coordinate system is called the degree-point of the edge uv. The Euclidean distance between the degree-point \((d_u,d_v)\) and the origin O is \(\sqrt{d_u^2+d_v^2}\) which is the definition of Sombor index34.
In 2023, Gutman et al., introduced another version of Sombor index called elliptic Sombor index referring to the orbits of planets in the solar system which takes elliptic orbits with the Sun as focus point. In astronomy, the perimeter of an ellipse is of great importance from which elliptic Sombor index was derived35.
In 2024, Gutman et al., showed that, in ellipse, the lengths of semi major and the semi minor axes are equal. The area of the ellipse was found to be \(\pi \sqrt{\sqrt{(d_u^2+d_v^2)}(d_u+d_v)}\). Leonard Euler found the approximate perimeter of the ellipse as \(\pi \sqrt{2(d_u^2+d_v^2)(d_u+d_v)^2}\). Using these relations, Euler Sombor index was proposed as \(\sqrt{d_u^2+d_v^2+d_u.d_v}\). Algebraically, there is a geometric analogy of Sombor and Euler Sombor indices36.
Numerous research work have been carried out on the above indices world wide. The information about graph degree could be relied on the new topological index introduced by Gutman in the year 2021, known as Sombor index. It has been proved that, it holds promise for decoding the thermodynamic behaviour of compounds. Hayat et al.,37 proposed the minimum Sombor index of graphs while Sakandar et al.38 employed valency-based indices in QSPR studies for monocarboxylic acids for physicochemical properties.
In a very short time of its existence, the Sombor index has attracted appreciable attention from both chemists as well as mathematicians. Redžepovi’c39 studied about the alkane’s entropy and enthalpy of vaporization by statistical techniques. The mathematical aspects of Sombor index is studied by Gutman et al.40 giving more insights into the topic. The researchers are continuously studying about the Sombor index in which numerous articles are being published for which the extremal values of the index within graphs are considered as the foundation41.
Using domination numbers for trees, Sun and Du42,43 studied for the maximal Sombor index. Zhou et al.44 used unicyclic graphs and classified the Sombor index with matching number. Li et al.45 derived the extreme value of Sombor index for trees with fixed diameter. Réti et al.,46 studied about the maximizing graphs for Sombor index using K-cyclic graphs where K takes the values from 1 to 5.
Narahari et al.47 introduced a new vertex degree-based index known as reverse Sombor index for which mathematical properties are defined recently. Kulli48 established some mathematical properties of reverse elliptic Sombor index for two families of dendrimer nanostars.
Carlos et al.49 recently solved the extremal value problem of elliptic Sombor index with equal number of vertices over the set of chemical graphs and chemical trees. Shanmukha et al.50 focussed on the chemical applicability of elliptic Sombor index using various benzenoid hydrocarbons through curvilinear regression models.
There has been a momentous progress in the study of the correlation capabilities of several families of graph theoretic descriptors. Gutman and Tosovi’c51 initiated this study to assess the quality of degree-based indices which was measured by correlation with the physicochemical properties of octane isomers. It was followed by Malik et al.52 to continue this study for benzenoid hydrocarbons for the characteristics that included total \(\pi\)-electronic energy.
Motivated by the above studies on Sombor index and its various versions, an attempt is made to study degree-based indices: Sombor index, elliptic Sombor index, Euler Sombor index and its reverse degree-based indices. To establish the potential index with respect to various physicochemical properties of top priority 38 PAHs using regression models is carried out.
This article mainly concentrates on
-
Identifying the potential vertex degree-based topological index in the considered indices with respect to physicochemical properties of top priority 38 PAH’s: Sombor index, elliptic Sombor index, Euler Sombor index and its Reverse degree-based indices.
-
To check the potential index, statistical analysis is carried out using regression models.
-
We employ RMSE measure to find the minimal error between the set of actual values and the predicted values.
-
Based on the obtained RMSE values in this work, we opt for minimal RMSE value which signifies minimal error between the actual and predicted values.
-
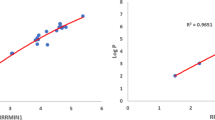
For better understanding of statistical analysis, a scatter diagram is depicted for linear regression model and is extended for quadratic and cubic regression models with minimal RMSE to notice the variation.
Methodology
G=(V, E) is a simple graph with V as vertex set and E as edge set. For a vertex u belonging to V, \(d_u\) indicates the degree of the vertex u53,54. In this work, the top priority 38 PAHs (Fig. 1) are modeled as molecular graphs for which 6 vertex degree-based topological indices are computed.
The considered degree-based indices such as Sombor index, elliptic Sombor index and Euler Sombor index34,35,36 are defined as follows
Reverse degree-based indices such as reverse Sombor index, reverse elliptic Sombor index47,48 are defined as follows
An attempt is made to define reverse Euler Sombor index and is defined as
where \(c_u=\Delta -d_u+1\) for any vertex \(u \in E(G)\) and \(\Delta\) is the maximum vertex degree of the graph G.
Results and discussions
The evaluation of regression models is conducted as follows,
Here, y is the dependent variable. a being the regression constant and \(b_{i}\) where\((i=1,2,3)\) are the regression coefficients and \(x_{i}(i=1,2,3)\) are the independent variables. Samples are used for regression equation, r being the correlation coefficient, SE is the standard error of the estimates and F is the Fisher’s statistic.
RMSE plays a vital role to understand the behaviour of statistical models to evaluate the accuracy of regression models and is used to measure the difference between the actual values and the predicted values. It is defined as
Here, n denotes the number of data points. \(y_{i}\) is the actual value for the \(i^{th}\) data point, \(\hat{y_{i}}\) is the predicted value for the \(i^{th}\) data point.
Regression models
In this study, 8 physicochemical properties (Table 1) of PAHs are considered such as molecular weight\((MW \,\ g/mol)\), melting point\((MP\,\ ^{\circ }C)\), boiling point\((BP\,\ ^{\circ } C)\), molar refractivity\((MR \,\ cm^3)\), polarizability \((PO \,\ {10^{-24}}cm^3)\), molar volume\((MV \,\ cm^3)\), flash point\((FP \,\ ^{\circ } C)\), complexity (C) for which coefficient of correlation are calculated using the computed values of TIs (Table 2).
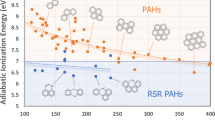
From Table 3, it is obvious that of all the 3 degree-based indices considered in the study SO has high correlation with 7 \((MW,\,\ BP,\,\ MR,\,\ PO,\,\ MV,\,\ FP,\,\ C)\) properties out of 8 properties considered while ESO has high correlation with the property MP. From Table 4, it is obvious that of all the 3 reverse degree-based indices considered in the study RSO has high correlation with 7 \((MW, \,\ MP,\,\ BP,\,\ MR,\,\ PO,\,\ FP,\,\ C)\) properties out of 8 properties considered while RESO has high correlation with the property MV.
Linear regression model: Degree-based TIs are studied using linear regression models for Eq. (1), are as follows
Linear regression model
Reverse degree-based TIs are studied using linear regression models for equation (1), are as follows
Conclusion
This work concentrates on analysing the potential predictive index for SO, ESO, EU, RSO, RESO and REU using regression models for top priority 38 PAHs. From the results, it is evident that Sombor index shows high correlation with considered physical properties compared to that of newly introduced elliptic Sombor and Euler Sombor indices. For best predictive index the minimal RMSE value is considered. From the analysis, it is clear that SO is the best predictive index with minimal RMSE from the considered degree-based indices (Tables 5, 6). RSO is the best predictive index with minimal RMSE from the considered reverse degree-based indices (Tables 7, 8). The variation of best predictive indices with minimal RMSE are plotted for linear, quadratic and cubic regression models for better understanding (Figs. 2, 3). This study may be useful for the researchers who wish to study further about PAHs and also about the applications of the considered indices.
Data availability
The data used to support the working are cited within the text as references.
References
Trinajstic, N. Chemical Graph Theory (CRC Press, 1992).
Farahani, M. R. Some connectivity indices of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs). Adv. Mater. Corros. 1, 65–69 (2013).
Ahmed, W., Zaman, S. & Khalid, F. Analyzing polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons using topological indices and QSPR analysis to reveal molecular complexity. J. Micromech. Mol. Phys. 9, 25 (2024).
Öztürk Sözen, E., Eryaşar, E. & Çakmak, Ş. Szeged-like topological descriptors and COM-polynomials for graphs of some Alzheimer’s agents. Mol. Phys. 122, e2305853 (2024).
Rasheed, M. W., Mahboob, A. & Hanif, I. An estimation of physicochemical properties of heart attack treatment medicines by using molecular descriptor’s. S. Afr. J. Chem. Eng. 45, 20–29 (2023).
Hayat, S., Khan, A., Ali, K. & Liu, J. B. Structure-property modeling for thermodynamic properties of benzenoid hydrocarbons by temperature-based topological indices. Ain Shams Eng. J. 15(3), 102586 (2024).
Hayat, S., Alanazi, S. J. & Liu, J. B. Two novel temperature-based topological indices with strong potential to predict physicochemical properties of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons with applications to silicon carbide nanotubes. Phys. Scr. 99, 055027 (2024).
Prabhu, S., Murugan, G., Arockiaraj, M., Arulperumjothi, M. & Manimozhi, V. Molecular topological characterization of three classes of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. J. Mol. Struct. 1229, 129501 (2021).
Zhao, D. et al. On molecular descriptors of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon. Polycyclic Aromat. Compd. 42(6), 3422–3433 (2022).
Lokesha, V., Deepika, T. & Cangul, I. N. Symmetric division Deg and inverse Sum Indeg indices of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and polyhex nanotubes. Southeast Asian Bull. Math. 41(5), 707 (2017).
Zhou, H. et al. On QSPR analysis of molecular descriptor and thermodynamic features of narcotic drugs. Polycycl. Aromat. Compd. 44, 1–21 (2023).
Öztürk Sözen, E. & Eryaşar, E. An algebraic approach to calculate some topological coindices and QSPR analysis of some novel drugs used in the treatment of breast cancer. Polycycl. Aromat. Compd. 44(4), 2226–2243 (2024).
Furtula, B. & Gutman, I. A forgotten topological index. J. Math. Chem. 53(4), 1184–1190 (2015).
Estrada, E. & Uriarte, E. Recent advances on the role of topological indices in drug discovery research. Curr. Med. Chem. 8(13), 1573–1588 (2001).
Hosoya, H. Topological index. A newly proposed quantity characterizing the topological nature of structural isomers of saturated hydrocarbons. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 44(9), 2332–2339 (1971).
Mondal, S., De, N. & Pal, A. Topological properties of Graphene using some novel neighborhood degree-based topological indices. Int. J. Math. Ind. 11(01), 1950006 (2019).
Mahboob, A., Rasheed, M. W., Amin, L. & Hanif, I. A study of novel molecular descriptors and quantitative structure-property relationship analysis of blood cancer drugs. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 138(9), 856 (2023).
Öztürk Sözen, E. & Eryaşar, E. Graph theoretic approach for calculation of new Banhatti indices VIA recent algebraic polynomials with a chemical application. Mol. Phys. 121(24), e2245072 (2023).
Sahoo, B. M., Ravi Kumar, B. V., Banik, B. K. & Borah, P. Polyaromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs): structures, synthesis and their biological profile. Curr. Org. Synth. 17(8), 625–640 (2020).
Huang, M. & Penning, T. M. Processing contaminants: Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs). Encycl. Food Saf. 2, 416–423 (2014).
Adeniji, A. O., Okoh, O. O. & Okoh, A. I. Analytical methods for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and their global trend of distribution in water and sediment: A review. In Recent Insights in Petroleum Science and Engineering (ed. Zoveidavianpoor, M.) (Intech, 2018).
Li, X. et al. Computing a closed formula of the Wiener index of the Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons PAHk by using the cut method. J. Comput. Theor. Nanosci. 14(7), 3636–3640 (2017).
Rezaei, M., Jamil, M. K. & Foruzanfar, Z. On the terminal wiener indices of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons PAHs. Int. J. Pure Appl. Math. 113(1), 49–57 (2017).
Farahani, M. R. Hosoya, Schultz, modified Schultz polynomials and their topological indices of benzene molecules: First members of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs). Int. J. Theor. Chem. 1(2), 09–16 (2013).
Randić, M. Aromaticity of polycyclic conjugated hydrocarbons. Chem. Rev. 103(9), 3449–3606 (2003).
Huang, R., Mahboob, A., Rasheed, M. W., Alam, S. M. & Siddiqui, M. K. On molecular modeling and QSPR analysis of lyme disease medicines via topological indices. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 138(3), 243 (2023).
Öztürk Sözen, E. & Eryaşar, E. QSPR analysis of some drug candidates investigated for COVID-19 via new topological coindices. Polycyc. Aromat. Compd. 44(2), 1291–1308 (2024).
Roy, Kunal. Topological descriptors in drug design and modeling studies. Mol. Divers. 8, 321–323 (2004).
Gao, W., Wang, W. & Farahani, M. R. Topological indices study of molecular structure in anticancer drugs. J. Chem. 2016, 3216327 (2016).
Gao, W., Siddiqui, M. K., Imran, M., Jamil, M. K. & Farahani, M. R. Forgotten topological index of chemical structure in drugs. Saudi Pharm. J. 24(3), 258–264 (2016).
Aslam, A., Bashir, Y., Ahmad, S. & Gao, W. On topological indices of certain dendrimer structures. Zeitschrift für Naturforschung A 72(6), 559–566 (2017).
Zaman, S., Jalani, M., Ullah, A., Ahmad, W. & Saeedi, G. Mathematical analysis and molecular descriptors of two novel metal-organic models with chemical applications. Sci. Rep. 13(1), 5314 (2023).
Nadeem, M. F., Azeem, M. & Siddiqui, H. M. A. Comparative study of zagreb indices for capped, semi-capped, and uncapped carbon nanotubes. Polycycl. Aromat. Compd. 42(6), 3545–3562 (2022).
Gutman, I., Furtula, B., & Elphick, C. (2014). Three new/old vertex-degree-based topological indices. MATCH communications in mathematical and in computer chemistry.
Gutman, I., Furtula, B. & Oz, M. S. Geometric approach to vertex-degree-based topological indices-Elliptic Sombor index, theory and application. Int. J. Quantum Chem. 124(2), e27346 (2024).
Ivan, G. Relating Sombor and Euler indices. Vojnotehnički glasnik 72(1), 1–12 (2024).
Hayat, S., Arshad, M., & Das, K. C. (2022). On the Sombor index of graphs with given connectivity and number of bridges. arXiv preprint arXiv:2208.09993.
Hayat, S., Arshad, M. & Khan, A. Graphs with given connectivity and their minimum Sombor index having applications to QSPR studies of monocarboxylic acids. Heliyon 10(1), e23392 (2024).
Redžepović, I. & Redžepović, I. Chemical applicability of Sombor indices: Survey. J. Serb. Chem. Soc. 86(5), 445–457 (2021).
Gutman, I. Geometric approach to degree-based topological indices: Sombor indices. MATCH Commun. Math. Comput. Chem 86(1), 11–16 (2021).
Deng, H., Tang, Z. & Wu, R. Molecular trees with extremal values of Sombor indices. Int. J. Quantum Chem. 121(11), e26622 (2021).
Das, K. C. & Shang, Y. Some extremal graphs with respect to Sombor index. Mathematics 9(11), 1202 (2021).
Sun, X. & Du, J. On Sombor index of trees with fixed domination number. Appl. Math. Comput. 421, 126946 (2022).
Zhou, T., Lin, Z., & Miao, L. (2021). The Sombor index of trees and unicyclic graphs with given maximum degree. arXiv preprint arXiv:2103.07947.
Li, S., Wang, Z. & Zhang, M. On the extremal Sombor index of trees with a given diameter. Appl. Math. Comput. 416, 126731 (2022).
Réti, T., Došlic, T. & Ali, A. On the Sombor index of graphs. Contrib. Math 3, 11–18 (2021).
Swamy, N. N., Manohar, T., Sooryanarayana, B. & Gutman, I. Reverse sombor index. Bull. Int. Math. Virt. Inst. 12(2), 267–272 (2022).
Kulli, V. R. Reverse elliptic Sombor and modified reverse elliptic Sombor indices. Int. J. Math. Arch. 15(1), 1–7 (2024).
Espinal, C., Gutman, I., & Rada, J. (2024). Elliptic Sombor index of chemical graphs. Communications in Combinatorics and Optimization.
Shanmukha, M. C., Usha, A., Kulli, V. R. & Shilpa, K. C. Chemical applicability and curvilinear regression models of vertex-degree-based topological index: Elliptic Sombor index. Int. J. Quantum Chem. 124(9), e27376 (2024).
Gutman, I. & Tošović, J. Testing the quality of molecular structure descriptors. Vertex-degree-based topological indices. J. Serb. Chem. Soc. 78(6), 805–810 (2013).
Malik, M. Y. H., Binyamin, M. A. & Hayat, S. Correlation ability of degree-based topological indices for physicochemical properties of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons with applications. Polycycl. Aromat. Compd. 42(9), 6267–6281 (2022).
Harary, F. Graph Theory (Addison-Wesely, 1969).
Kulli, V. R. College Graph Theory (Vishwa International Publication, 2012).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
B.K.—Conceptualization, Article writing. M.C.S.—Conceptualization, Methodology, Article writing, Formal analysis, Resources, Data curation, Investigation. A.U.—Review of the manuscript, Formal analysis,, Suggestions given for correction of manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Kirana, B., Shanmukha, M.C. & Usha, A. Comparative study of Sombor index and its various versions using regression models for top priority polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Sci Rep 14, 19841 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-69442-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-69442-z
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Mathematical study of silicate and oxide networks through Revan topological descriptors for exploring molecular complexity and connectivity
Scientific Reports (2025)
-
Topological modeling and QSPR based prediction of physicochemical properties of bioactive polyphenols
Scientific Reports (2025)
-
Chemical applicability and predictive potential of certain graphical indices for determining structure-property relationships in polycrystalline acid magenta (C20H17N3Na2O9S3)
Scientific Reports (2025)
-
Applications of Sombor topological indices and entropy measures for QSPR modeling of anticancer drugs: a Python-based methodology
Scientific Reports (2025)
-
QSPR modeling of hydroxypropyl beta-cyclodextrin using reverse-degree-based molecular topological indices
Journal of Inclusion Phenomena and Macrocyclic Chemistry (2025)