Abstract
Fishes from the genus Carasobarbus, widely distributed throughout the river systems of North Africa and West Asia, are commonly referred to as Himris. In the Persian Gulf basin, they are widespread and are also found in fast-flowing rivers or the deeper regions of lakes. In this region, representation of these fishes in scientific collections is scarce, and except for C. luteus, the other species are very poorly documented and frequently misidentified due to their similarities. In this study we analysed the relationships among Carasobarbus species using mitochondrial genes (Cyt b, COI) and present morphological characters based on examinations. Our results revealed three new species which we describe here. Carasobarbus doadrioi, new species, is distinguished by 40–44 scales on the lateral line and a prominent black blotch on end of caudal peduncle in specimens < 85 mm SL. Carasobarbus hajhosseini, new species is distinguished by 32–34 scales on the lateral line and long head length (20–24% SL). Carasobarbus saadatii, new species, is distinguished by 38–40 scales on the lateral line and short head length (19–20% HL). In the Persian Gulf basin, Carasobarbus species exhibit uncorrected genetic distances of 1.6 to 5.5% in the COI barcode region and 2.6% to 9.9% in the Cyt b gene. This study highlights the importance of investigating the unexplored diversity that exists within poorly sampled and understudied freshwater fish group. Such investigations are essential for developing a comprehensive understanding of the true extent of biodiversity, which is critical for informing effective conservation and protection strategies.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Carasobarbus Karaman, 1971 is a small genus of Cyprinidae comprising 10 valid species distributed across Southwest Asia and Northwest Africa1,2,3. These fishes known as Himris and characterized by large scales and special forms of the lips4,5. Three species of Himris are currently known from the Persian Gulf basin: Carasobarbus luteus (Heckel, 1843), C. kosswigi (Ladiges, 1960), and C. sublimus (Coad & Najafpour, 1997), with the latter considered to be endemic to Iran. Initially, C. kosswigi was described as Cyclocheilichthys Bleeker, 1859, C. sublimus as Barbus Daudin 1805, and C. luteus as Systomus McClelland 1838. Bianco and Bănărescu6 considered luteus as Carasobarbus validating the genus. Karaman7 erected Kosswigobarbus and placed kosswigi in it. However, Borkenhagen et al.8 synonymized this genus with Carasobarbus. In the following, Borkenhagen and Krupp2 conducted a comprehensive taxonomic revision of the genus Carasobarbus, revealing three valid species inhabiting Iran: C. luteus, C. kosswigi, and C. sublimus. They mentioned that C. sublimus is present in Zohre and Karkheh drainages, and C. kosswigi is found in Karun and Tigris drainages.
The elusive nature of Carasobarbus species and the challenges associated with sampling them have rendered the study of these fishes extremely difficult. This is especially accentuated because some species are rare and easily misidentified with other species inhabiting the same habitats. After approximately 15 years of field expeditions across Iran, Iraq, and Türkiye, during which Carasobarbus specimens were collected from the type localities of C. kosswigi and C. sublimus, as well as other populations from the Tigris to Zohreh drainages, a comprehensive examination revealed significant morphological and genetic differences among them. Our findings provide evidence supporting the existence of three undescribed species in Iran, which we describe based on a combination of morphological and molecular genetic characters.
Materials and methods
Fish sampling and preservation
All fish specimens used in this study were sampled following local guidelines and rules. All experimental protocols are approved routine procedures by ethics committee in Lund University. All methods were carried out in accordance with relevant guidelines and regulations, and all methods are reported in accordance with ARRIVE guidelines. The sampling permits were issued by the local environment department. Fish were euthanized with an overdose of clove oil, fixed in 10% formalin for 24 h, and preserved in ethanol 70%. The samples used in molecular analyses were fixed in 99% EtOH (whole body or a fin clip).
Morphological examination
Measurements were made point-to-point with a digital calliper and recorded to 0.1 mm. Counts and measurements were made on the left side of specimens whenever possible, following Kottelat & Freyhof9. Head length and measurements of body parts are given as proportions of standard length (SL). Subunits of the head are presented as proportions of head length (HL). Standard length (SL) was measured from the tip of the snout to the posterior extremity of the hypural complex. The skin fold at the posterior part of the gill cover was included in the measurement of HL. The length of the caudal peduncle was measured from behind the base of the posterior anal-fin ray to the posterior extremity of the hypural complex, at mid-height of the caudal-fin base. The last two branched rays articulating on a single pterygiophore in the dorsal and anal-fins are noted as "11/2". The distribution map (Fig. 1) was created with QGIS v.3.18 software (http://qgis.org). In addition to examined specimens of C. sublimus, morphometric data were obtained from Coad and Najafpour1.
DNA extraction, PCR amplification and sequencing
Genomic DNA was extracted using Macherey & Nagel NucleoSpin® Tissue kits following the provided protocol. The barcode region of the COI (cytochrome c oxidase subunit 1) gene was amplified using FishF1-5′TCAACCAACCACAAAGACATTGGCAC3′ and FishR1-5′TAGACTTCTGGGTGGCCAAAGAATCA3′10, and the Cyt b genetic marker using GluF-5’AACCACCGTTGTATTCAACTACAA3’ and ThrR5’ ACCTCCGATCTTCGGATTACAAGACCG3’11. The T7Promoter (5’TAATACGACTCACTATAGGG3’) and T3 (5’ATTAACCCTCACTAAAGGG3’) standard sequences were added to the sequence of forward and reverse primers respectively, to simplify the sequencing of different PCR products on the same plate. Sequencing of the PCR products was performed at an external sequencing service provider.
Molecular data analysis
The obtained sequences and the ones downloaded from GenBank (Tables 1, 2), were aligned using MAFFT12,13 as implemented in Geneious v. 10.0.2 (Biomatters, http://www.geneious.com/). The obtained datasets were concatenated in Geneious to create three different datasets: COI dataset, Cyt b dataset, and the concatenated dataset. In the case of the concatenated dataset, in the ingroup, we only kept the samples with both genetic markers amplified from the same specimen. This was not possible for the outgroups as none of the sequences in Genbank, used for outgroups, came from the same specimen for both genes. In these cases, sequences from unrelated specimens were concatenated together. This does not affect the phylogenetic results of the ingroup. To determine intraspecific species uncorrected pairwise genetic distances (p-distances) (Tables 3, 4), we employed Mega 614.
Both maximum likelihood (ML) and Bayesian (BI) methods have been used to construct phylogenetic relationships of the group. In the case of ML approach, IQ-TREE 1.6.1215,16 were used. In this case, the optimal substitution model and the best partitioning scheme based on the codon information, was investigated using ModelFinder17 with the Bayesian information criterion (BIC). In the case of single marker datasets, the codon position information was provided, and in the concatenated dataset both codon position and gene separation were provided to the program. The bootstrap (− b 500) approximations was used to calculate support values18. FigTree 1.4.4 (http://tree.bio.ed.ac.uk/software/figtree/) was used to visualize the resulting trees. In the case of the BI approach, MrBayes 3.2.719 were used with two parallel simultaneous analyses for 2 × 107 generations, each with four MCMC chains, and sampling every 2000 generations. The initial 25% of generations were discarded as the burn-in. An rjMCMC20 approach was implemented using the nst = mixed command. The proper convergence of the runs was verified using Tracer 1.721.
Three distance-based molecular species delimitation methods were used: automatic barcode gap discovery (ABGD)22, assemble species by automatic partitioning (ASAP)23, and Bayesian Poisson Tree Processes model (bPTP)24. The ABGD analysis were performed on its online webserver (https://bioinfo.mnhn.fr/abi/public/abgd/abgdweb.html), exploring a range of ABGD settings with a parameter range of Pmin = 0.001, Pmax = 0.1, and a gap width of 1.5 over ten steps. The ASAP analysis was also made, using Simple Distance (p-distances), via its web interface (https://bioinfo.mnhn.fr/abi/public/asap/asapweb.html). The bPTP analysis was run only on the in-group on the online implementation of it (https://species.h-its.org/) using default settings.
ZooBank
This published work and the Nomenclatural Acts it contains have been registered in ZooBank with the LSID urn:lsid:zoobank.org:pub:891DC1CD-C71C-4783-B009-F3141E542A9D, urn:lsid:zoobank.org:act:9296233A-FA76-41E7-9814-7D22FCF37CDC, urn:lsid:zoobank.org:act:B056DC31-E811-4B1C-850B-0DE8767A07F5, and urn:lsid:zoobank.org:act:B4B0C801-0C84-4247-B488-767EC4307CF9.
Results
We were able to generate 38 new sequences (22 COI + 16 Cyt b) for six species of Carasobarbus from Iran, Iraq and Türkiye, in addition to 173 sequences from NCBI GenBank (Tables 1 and 2). The final alignment for COI consisted of 770 base pairs, with 676 positions being constant, 88 being parsimony informative and 6 being singletons (calculated just between in-group species), and for Cyt b the alignment was 1143 base pairs, with 872 positions being constant, 240 being parsimony informative and 29 being singletons (calculated just between in-group species for both genes).
The COI gene of Carasobarbus displayed an interspecific uncorrected-p genetic distance of 1.6% between C. luteus and C. chantrei as well as C. doadrioi sp. n., C. saadatii sp. n. and C. chantrei to 5.5% between C. sublimus. Average intraspecific distance for Carasobarbus species was 0.20%, ranging from 0.0 in C. canis, C. hajhosseini, and C. kosswigi to 0.72% in clade 1 of C. fritschii/harterti species group (Table 3).
For the Cyt b gene, the genetic distances between species ranged from 2.6% between C. luteus/apoensis, C. chantrei and C. exulatus to 9.9% between C. harterti and C. chantrei as well as between C. hajhosseini, C. fritschi and C. harterti. Also, the average intraspecific distance was 0.30%, ranging from 0.04% in C. canis and C. harterti to 0.66% in C. fritschii. Table 4 shows the genetic distances between and within the Carasobarbus species for Cyt b gene.
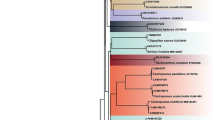
The general topology of Cyt b, COI and concatenated dataset trees (Figs. 2, 3 and 4) were in agreement with previously published phylogenies that focused on the genus Carasobarbus8,25. The COI and Cyt b dataset both resulted in acceptable trees with some nodes which were harder to resolve (not well supported). The increased sampling size, in the case of individual gene datasets, appears to improve the result compared to the prior phylogenetic works. The concatenation of the two genetic markers resulted in the best resolved tree even though the number of represented species was reduced. In general, all species analysed in any of the datasets was recovered as monophyletic apart from C. harterti and C. fritschii in the COI dataset. In this case, the resolution of the COI dataset for this part seems to not be adequate, and some samples identified as C. harterti are placed with C. fritschii and vice versa.
Phylogenetic tree of Carasobarbus based on the maximum likelihood and Bayesian analyses of the mitochondrial COI barcode region. Numbers present at each node are bootstrap/posterior probability support values. The result of the three different species delimitation methods is shown using the vertical bars.
Key to species of Carasobarbus in Persian Gulf basin
1a - Lower lip without median lobe; one pair of barbels (two pair in the Makran population).
………………C. luteus
1b - Lower lip with median lobe; two pair barbels.
………………2
2a - 24 − 29 total lateral-line scales; lower lip lobe well-developed (Coad and Najafpour, (1) data included).
………………C. sublimus
2b – 32–44 total lateral-line scales; lower lip lobe slightly to relatively developed.
.………………3
3a - 32–37 total lateral-line scales.
………………4
3b - 38–44 total lateral-line scales.
………………5
4a – Lower lip lobe well-developed; 32–77 [mode 36] total lateral-line scales; head length 25–27% SL; posterior barbel 13–20% HL; snout length 36–44% HL.
………………C. kosswigi
4b - Lower lip lobe slightly developed; 32–34 [mode 33–34] total lateral-line scales; head length 20–24% SL; posterior barbel 21–38% HL; snout length 25–31% HL.
………………C. hajhosseini sp. n.
5a – A prominent black blotch on end of caudal peduncle in specimens < 85 mm SL; head length 22–25% SL; dorsal fin height 19–26% SL; distance between base of pelvic and anal fins 24–25% SL.
………………C. doadrioi sp. n.
5b – No black blotch on end of caudal peduncle in specimens < 85 mm SL; Head length 19–20% SL; dorsal fin height 26–30% SL; distance between base of pelvic and anal fins 26–28% SL.
………………C. saadatii sp. n.
Carasobarbus doadrioi, new species
Holotype. BIAUBM 6-H, 75.3 mm SL; Iran: Chaharmahal and Bakhtiari prov., Khersan River at Atishgah, Karun River drainage, Persian Gulf Basin, 31.24358, 50.99075.
Paratypes. AJRPC 17-P, 7, 69.3–45.2 mm SL; data same as holotype.
New material used in molecular genetic analysis. AJRPC-DNA 198A (COI: PP515175, Cyt b: PP548209), 198B (COI: PP515176, Cyt b: PP548210), 198C (COI: PP515177, Cyt b: PP548211), same data as holotype; AJRPC-DNA 1715 (COI: PP515188, Cyt b: not sequenced), Iran: Lorestan prov., Sezar River at Absardeh, Karun River drainage, Persian Gulf Basin, 33.20562, 48.88326.
Diagnosis
Carasobarbus doadrioi is distinguished from C. sublimus, C. hajhosseini sp. n. and C. kosswigi by having more scales on lateral line (40–44 vs. 27–37). Carasobarbus doadrioi sp. n. is similar to C. saadatii sp. n. and is distinguished by having a prominent black blotch on end of caudal peduncle in specimens < 85 mm SL (vs. no black blotch), longer head length (22–25 vs. 19–20% SL), shorter dorsal fin height (19–26 vs. 26–30% SL) and shorter distance between base of pelvic and anal fins (24–25 v. 26–28% SL). It is distinguished from C. luteus by having two pair of barbels (vs. one pair), well-developed median lobe on the lower lip (vs. without median lobe) and more scales on the lateral line (40–44 vs. 25–30) (Table 5).
Description
See Figs. 5, 6, 7 and 8 for general appearance, Table 6 for morphometric data. Body moderately high, laterally compressed, without nuchal hump. The greatest body depth in front or at dorsal-fin origin. Ventral head profile straight, dorsal head profile with a slight to pronounced hump near nostrils. Head short and narrow. Maximum body depth larger than head length. Triangular axillary scale at pelvic-fin base present. Pelvic-fin origin below vertical of last unbranched or first branched dorsal-fin ray. Caudal fin forked. Pectoral fin reaching approximately 70–90% of distance between pectoral- to pelvic-fin origin. Pelvic fin not reaching anus. Eye large, markedly smaller than snout. Mouth inferior, lips thick and fleshy with a well-developed median lob. Two pairs of barbels, rostral barbel reaches to anterior part of eye and maxillary barbel reaching to posterior part of eye.
Dorsal fin with 4 (n = 8) unbranched rays and 11½ (n = 8) branched rays, outer margin deeply concave. Anal fin with 3 (n = 8) unbranched and 6½ (n = 8) branched rays, outer margin straight. Pectoral fin with 14 (n = 5), 15 (n = 3) rays. Pelvic fin with 7 (n = 1)–8 (n = 7) rays. Lateral line with 40 (n = 3), 41 (n = 2), 42 (n = 1), 43 (n = 1), 44 (n = 1) scales. Scale rows between dorsal-fin origin and lateral line 7 (n = 8). Scale rows between anal-fin origin and lateral line 6 (n = 11).
Coloration
In life: Body silverish or cream-white. Back darker than belly. Series of scales over the lateral line outlined by dark pigmentation, evident in anterior and fade in posterior. Fins with scattered dark melanophores on rays and membranes. In formalin: Cream-brown, back darker than belly. Series of scales over the lateral line with dark anterior pigmentation, fading posteriorly. Fins with scattered dark melanophores on rays and membranes.
Distribution
Known from the lower Dez and Karun drainages.
Etymology
This species name derives from the name of the Spanish ichthyologist Ignacio Doadrio Villarejo, in honour of his invaluable contribution to the study of the fishes of the world.
Habitat
Carasobarbus doadrioi sp. n. is found in the deep, slow current of large rivers (Fig. 9). It typically favours areas with abundant vegetation with rocky substrates during the summer. Generally, the species is most abundant in the middle and lower Karun drainage. Luciobarbus esocinus Heckel, 1843, Garra rufa (Heckel, 1843), Acanthobrama marmid Heckel, 1843, Alburnus sellal Heckel, 1843, Chondrostoma regium (Heckel, 1843), Squalius berak Heckel, 1843, Oxynoemacheilus euphraticus, Glyptothorax cous (Linnaeus 1766) and G. alidaei Mousavi-Sabet, Eagderi, Vatandoust & Freyhof, 2021 were found coexisting with the new species.
Carasobarbus hajhosseini, new species
Holotype. BIAUBM 7-H, 190.6 mm SL; Iran: Ilam prov. Seymareh River at Talkhab, Karkheh drainage, Persian Gulf basin, 33.27771, 47.21252.
Paratypes. AJRPC 18-P, 4, 85.8–184.3 mm SL; same data as holotype. AJRPC 19-P, 2, 95.0–108.9 mm SL; Iran: Lorestan prov. Kahman River at Doab, Karkheh drainage, Persian Gulf basin, 33.78557, 48.20640. AJRPC 20-P, 1, 117.5 mm SL; Iran: Lorestan prov. Karkheh River at Pa Alam, Karkheh drainage, Persian Gulf basin, 32.83141, 48.03337. AJRPC 21-P, 1, 136.9 mm SL; Iran: Lorestan prov. Karkheh River at Mamulan, Karkheh drainage, Persian Gulf basin, 33.37823, 47.95654. AJRPC 22-P, 1, 113.2 mm SL; Iran: Lorestan prov. Karkheh River at Kal Sefid, Karkheh drainage, Persian Gulf basin, 33.08346, 47.53871. AJRPC 23-P, 1, 93.7 mm SL; Iran: Ilam prov. Karkheh River at Pol Zaal, Karkheh drainage, Persian Gulf basin, 32.98729, 47.76504.
New material used in molecular genetic analysis. AJRPC-DNA 225 (COI: PP515178, Cyt b: PP548212), Iran: Lorestan prov. Kahman River at Doab, Karkheh drainage, Persian Gulf basin, 33.78557, 48.20640; AJRPC-DNA 571A (COI: PP515182, Cyt b: PP548215), 571B (COI: PP515183, Cyt b: PP548216) same data as holotype.
Diagnosis
Carasobarbus hajhosseini sp. n. is distinguished from C. sublimus, C. saadatii sp. n. and C. doadrioi sp. n. by having more scales on lateral line (32–34 vs. 24–29 in C. sublimus; 40–44 in C. doadrioi sp. n.; 38–40 in C. saadatii sp. n.).
Carasobarbus hajhosseini sp. n. is similar to C. kosswigi but can be distinguished by slightly developed lower lip lobe (vs. well-developed), shorter head (20–24 vs. 24–27% SL), shorter posterior barbel (13–20 vs. 21–38% HL) and shorter snout (25–31 vs. 36–44% HL).
Also, the new species can be distinguished from C. luteus by having two pair of barbels (vs. one pair), well-developed median lobe on the lower lip (vs. without median lobe) and more scales on the lateral line (32–34 vs. 25–30).
Description
See Figs. 10, 11, 12 and 13 for general appearance, Table 6 for morphometric data. Body moderately high, laterally compressed, without nuchal hump. The greatest body depth at a level in front of or point of dorsal fin origin. Ventral head profile straight, dorsal profile has a slight to pronounced hump near nostrils. Head short and narrow. Maximum body depth larger than head length. Triangular axillary scale at pelvic-fin base. Pelvic-fin origin below vertical of last unbranched dorsal fin ray. Caudal fin forked. Tip of anal fin, when pressed to body, reaching to hypural complex. Pectoral fin reaching approximately 70–90% distance from pectoral-fin origin to pelvic-fin origin. Pelvic fin not reaching anus. Eye large, but smaller than snout. Mouth inferior, lips thick and fleshy with a small median lob. Two pairs of barbels, rostral not/or reaches to anterior part of eye and maxillary reaching to the posterior part of eye.
Dorsal fin with 4 unbranched rays and 10½ (n = 6)–11½ (n = 5) branched rays, outer margin deeply concave. Anal fin with 3 (n = 11) unbranched and 6½ (n = 11) branched rays, outer margin straight. Pectoral fin with 13 (n = 4), 14 (n = 6), 15 (n = 1) rays. Pelvic fin with 8 (n = 7)–9 (n = 4) rays. Lateral line with 32 (n = 3), 33 (n = 4), 34 (n = 4) scales. Scale rows between dorsal-fin origin and lateral line 6 (n = 11). Scale rows between anal-fin origin and lateral line 5 (n = 11).
Coloration
In fresh: Body silverish or cream-white. The back darker than the belly. Upper lateral line scales outlined by dark pigmentation, evident in anterior and fade in posterior. Fins with scattered dark melanophores on rays and membranes. In formalin: Body cream-brown, back darker than belly. Upper lateral line scales outlined by dark pigmentation, prominent in anterior section, fades towards posterior.
Distribution
The new species is known from the Gamasiab, Kahman, Kashkan and Seymareh in Karkheh drainage.
Etymology
The species is named in honour of Haj Hossein Javadi Pour (HHJP), who is the father of the first author of this study (AJR).
Habitat
Carasobarbus hajhosseini is commonly found in the deep, swiftly flowing sections of rivers and dam reservoirs (Fig. 14). It typically favours areas with abundant vegetation, and during the summer, it can also be observed in shallower waters. Generally, the species is most abundant in the middle and lower Karkheh drainage. Luciobarbus esocinus, Capoeta shajariani Jouladeh-Roudbar, Eagderi, Murillo-Ramos, Ghanavi & Doadrio, 2017, Garra gymnothorax Berg, 1949, Chondrostoma regium, Alburnus sellal, Squalius lepidus Heckel, 1843, Squalius berak, Turcinoemacheilus saadii Esmaeili, Sayyadzadeh, Özuluğ, Geiger & Freyhof, 2014, Glyptothorax cous and G. alidaei were found coexisting with the new species.
Carasobarbus saadatii, new species
Holotype. BIAUBM 8-H, 187.6 mm SL; Iran: Khuzestan prov., Karun River at Gotvand, Persian Gulf Basin, 32.27319, 48.83521.
Paratypes. AJRPC 24-P, 4, 122.9–179.4 mm SL; data same as holotype.
New material used in molecular genetic analysis. AJRPC-DNA 1860 (COI: PP515189, Cyt b: PP548217), 1861 (COI: PP515190, Cyt b: PP548218), 1862 (COI: PP515191, Cyt b: PP548219), 1863 (COI: PP515192, Cyt b: PP548220) same data as holotype.
Diagnosis. Carasobarbus saadatii sp. n. is distinguished from C. sublimus (Fig. 18), C. hajhosseini sp. n. and C. kosswigi (Figs. 19, 20 and 21) by having more scales on lateral line (38–40 vs. 27–37).
The new species can be distinguished from C. luteus (Fig. 22) by having two pair of barbels (vs. one pair), well-developed median lobe on the lower lip (vs. without median lobe) (Fig. 23) and more scales on the lateral line (38–40 vs. 25–30).
Description
See Figs. 15, 16 and 17 for general appearance, Table 7 for morphometric data. Body moderately high, laterally compressed, without nuchal hump. The greatest body depth at point of origin of dorsal fin. Ventral head profile straight, dorsal profile has a slight to pronounced hump near the nostrils. A rounded keel on back in front of dorsal fin. Head short and narrow. Maximum body depth larger than head length. Triangular axillary scale at pelvic-fin base. Pelvic-fin origin below vertical of last unbranched dorsal fin ray. Caudal fin forked. Tip of anal fin, when pressed to body, reaching to hypural complex. Pectoral fin reaching approximately 70–80% distance from pectoral-fin origin to pelvic-fin origin. Pelvic fin not reaching anus. Eye large, but smaller than snout. Mouth inferior, lips thick and fleshy with a well-developed median lob. Two pairs of barbels, rostral reaches to eye and maxillary reaching to the posterior part of eye.
Dorsal fin with 4 (n = 5) unbranched rays and 10½ (n = 5) branched rays, outer margin deeply concave. Anal fin with 3 (n = 5) unbranched and 6½ (n = 5) branched rays, outer margin straight. Pectoral fin with 14 (n = 2)–15 (n = 3) rays. Pelvic fin with 8 (5) rays. Lateral line with 38 (n = 1), 39 (n = 2), 40 (n = 2) scales. Scale rows between dorsal-fin origin and lateral line 6 (n = 4)–7 (n = 1). Scale rows between anal-fin origin and lateral line 5 (n = 6).
Coloration
In fresh: Body silverish or cream-white. The back darker than the belly. Upper lateral line scales outlined by dark pigmentation, evident in anterior and fade in posterior. Fins with scattered dark melanophores on rays and membranes. In formalin: Body cream-brown, back darker than belly. No dark pigmentation on anterior and posterior section of scales.
Distribution
The new species distributed in the lower Karun drainage as well as the Great Zab in the Tigris drainage.
Etymology
The species is named in honour of Mohamadali Saadati (Mashhad), acknowledging his significant contributions to the taxonomy of freshwater fishes in Iran. He holds the distinction of being the first Iranian Ichthyologist, conducting a systematic study on the taxonomy and distribution of freshwater fishes in Iran in 1977. To this day, his findings continue to be utilized by several Ichthyologists in Iran.
Habitat
The new species is usually found in the deeper parts of rivers and dam reservoirs, where water flows are slower and there is ample vegetation and cover (Fig. 24). During the summer months, it disperses into faster-flowing waters as well, likely due to warming water temperatures in their typical habitat. It prefers areas along the banks and around islands where tree roots and aquatic plants are accessible. This allows it to forage while remaining hidden among the vegetation to avoid predators. The species appears to be most abundant in the middle and lower Karun. Luciobarbus barbulus (Heckel, 1847), Capoeta aculeate (Valenciennes, 1844), Garra rufa, Chondrostoma regium, Alburnus sellal, Squalius lepidus, Squalius berak and Glyptothorax cous, were found coexisting with the new species.
Discussion
In general, fishes of the genus Carasobarbus are bottom feeders, with morphological characters specialised for such behaviour. This is especially visible in the differences in the development of their mouth structure and lips. Similar developments have been observed in other species of barbs26,27. The lips development in Carasobarbus fishes, seems to be a suitable character to separate species28. In the newly described species, the C. hajhosseini species present the smaller lips (less developed). On the other hand, C. doadrioi species, appear to show the most developed lips among them. Check the ventral head view figure (Fig. 23) to compare these differences and observe that both latter mentioned species show both ends of the spectrum. Carasobarbus saadatii species also present intermediate lips development similar to C. sublimus for example, but we do not have an acceptable picture to show in this work.
Borkenhagen and Krupp2 questioned the locality data of the C. sublimus specimen (CMNFI 1979-0277), as the morphometric and meristic characters (scales in the lateral line, above the lateral line, and around the least circumference of the caudal peduncle; length of the dorsal, pectoral, ventral, and anal fins) of this specimen are within the range of C. sublimus and outside the range of C. kosswigi. This discrepancy is unsurprising because the Karkheh population belongs to C. hajhosseini, and the range of these characters matches the locality mentioned for this voucher specimen. However, they considered C. hajhosseini populations as C. sublimus, and C. doadrioi and C. saadati as C. kosswigi, which caused the range of morphometric characters to expand and positioned C. kosswigi and C. sublimus as paraphyletic in the phylogenetic trees.
In general, nearly all the internal nodes are well resolved in all three datasets (COI, Cyt b and concatenated datasets) used in molecular phylogenetic analyses. But as expected, the concatenated dataset resulted in the best resolved tree. Both genetic markers used in the concatenated dataset are mitochondrial markers, i.e. they sare the same evolutionary history. This point out that the improvement in the phylogenetic resolution is most probably due to the increment in the phylogenetic signal coded in a longer sequence fragment. This point underlines the importance of including multiple markers to be able to resolve remaining obscure relationships within the genus. On the other hand, being hexaploid, complicates the inclusion of any nuclear marker in any genetic study in near future29. This point is important as some species of the genus (for example C. luteus) is widespread in a variety of habitats and therefore will not be surprising to find that different populations does not share the same evolutionary history. This will not be visible without analysing both mitochondrial and nuclear genomic markers.
In the obtained mitochondrial phylogenetic results in the actual study, the only unresolved relationship, is the one between C. doadrioi, C. hajhosseini and C. saadatii. The very short internal branch at this level, when present, shows a potential rapid speciation event, resulting in small number of conserved changes to resolve this relationship. In our results, based on the partial COI gene, two clearly separate clades are formed with both containing sequences identified as C. harterti and C. fritschii. This is most probably the result of misidentification, or also it can be due to introgression events. As we do not have access ourselves to the material used in this case (genetic material was retrieved from GenBank), we cannot further develop on this and corroborate the identity of each of the clades. On the other hand, using other individuals identified as these two species, they do separate well in the results of the cyt b gene dataset, with no further issues. Another possible issue which will need further investigation is the inclusion of samples identified as C. apoensis within the C. luteus clade, with practically no genetic difference with them. This point was also mentioned in Borkenhagen28. Based on this observation we recommend a systematic revision of both C. apoensis and C. luteus in further studies.
Comparative materials examined
Carasobarbus kosswigi. Iran: – VPFC NeypahnSeyfolah 1400.7., 1, 85 mm SL; Iran: Kermanshah prov.: Alvand River at Neypahn Seyfolah, Karkheh, 34.408611, 45.586944. – VPFC Hajij 1394.4., 1, 114 mm SL; Iran: Kermanshah prov.: Sirvan River at Hajij, Tigris drainage, 35.15678, 46.32132 (now under dam).
Türkiye: – FFR 416, 17, 124–176 mm SL; FFR 417, 1, 170 mm SL; FFR 421, 4, 129–168 mm SL; Siirt prov.: Botan River at 8 km southwest of Siirt, Tigris drainage, 37.85268, 41.88749.
Carasobarbus sublimus. Iran: – VPFC Zard 1400.9., 2, 72–132 mm SL; Iran: Fars prov., Zard River at Zard Mashin, Marun drainage, 31.37633, 49.72072. – VPFC Fahlian 1400.10., 2, 111–92 mm SL; Iran: Fars prov., Fahlian River at Fahlian bridge, Zohre drainage, 30.18520, 51.52443.
Carasobarbus luteus. Iran: – VPFC Siyahgav 1400.9., 7, 65–95 mm SL; Iran: Ilam prov., Siyah Gav Lake, near Abdanan, Tigris drainage, 32.86564, 47.70155. – VPFC Golabi 1400.10., 1, 130 mm SL; Iran: Fars prov., Golabi spring, near Darab, Kol drainage, 28.78766, 54.37183.
New material used in molecular genetic analysis
Carasobarbus kosswigi. Türkiye: AJRPC-DNA 1882 (COI: PP515193, Cyt b: PP548221), 1883 (COI: PP515194, Cyt b: PP548222), Şırnak prov.: Tigris River at 4 km north of Cizre, 37.375610 42.147106; 1884 (COI: PP515195, Cyt b: PP548223), Şırnak prov.: Tigris River at Damlarca, 37.404131 42.070865. Iran: AJRPC-DNA 45 (COI: PP515174, Cyt b: PP548208), Kermanshah prov.: Alvand River at Neypahn Seyfolah, Karkheh, 34.408611, 45.586944.
Carasobarbus sublimus. Iran: AJRPC-DNA 400A (COI: PP515179, Cyt b: PP548213), 400B (COI: PP515180, Cyt b: PP548214), Iran: Fars prov., Zard River at Zard Mashin, Marun drainage, 31.37633, 49.72072.
Carasobarbus luteus. Iran: AJRPC-DNA 554B (COI: PP515181) Kermanshah prov.: Alvand River at Neypahn Seyfolah, Karkheh, 34.408611, 45.586944; 707 (COI: PP515184) Khuzestan prov., Karun River at Gotvand, Persian Gulf Basin, 32.27319, 48.83521; Iraq: AJRPC-DNA 1465 (COI: PP515187), Al Najaf prov.: Euphrates River at Kafal, Persian Gulf Basin, 32.22339, 44.36113; 1376 (COI: PP515185), 1377 (COI: PP515186), Maysan prov.: Tigris River at Amareh, Persian Gulf Basin, 31.85783, 47.13605.
Data availability
All the specimens obtained in this study are deposited in local publicly accessible (upon request) zoological collections. The genetic data obtained in this study is deposited in NCBI’s GenBank, the accession numbers for each gene marker is mentioned after each specimen’s voucher code.
Change history
18 October 2024
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-75851-x
Abbreviations
- SL:
-
Standard length
- HL:
-
Lateral head length
- BIAUBM:
-
Babol Islamic Azad University Biological Museum, Babol, Iran
- AJRPC:
-
A. Jouladeh-Roudbar personal fish collection, Tehran, Iran
- VPFC:
-
S. Vatandoust Personal Fish collection, Qaem Shahr, Iran
- FFR:
-
Faculty of Fisheries, Recep Tayyip Erdogan University, Rize, Turkey
References
Coad, B. W. & Najafpour, N. Barbus sublimus, a new species of cyprinid fish from Khuzestan province, Iran. Ichthyol. Explor. Freshw. 7, 273–278 (1997).
Borkenhagen, K. & Krupp, F. Taxonomic revision of the genus Carasobarbus Karaman, 1971 (Actinopterygii, Cyprinidae). ZooKeys 339, 1–53. https://doi.org/10.3897/zookeys.339.4903 (2013).
Coad, B. W. Carps and Minnows of Iran (Families Cyprinidae and Leuciscidae) Volume I: General Introduction and Carps (Family Cyprinidae) (Canadian Museum of Nature, 2021).
Kaya, C., Turan, D. & Unlu, E. The latest status and distribution of fishes in upper Tigris River and two new records for Turkish freshwaters. Turk. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 16(3), 545–562. https://doi.org/10.4194/1303-2712-v16_3_07 (2016).
Jouladeh-Roudbar, A., Ghanavi, H. R. & Doadrio, I. Ichthyofauna from Iranian freshwater: Annotated checklist, diagnosis, taxonomy, distribution and conservation assessment. Zool. Stud. 59, e21. https://doi.org/10.6620/ZS.2020.59-21 (2020).
Bianco, P. G. & Bănărescu, P. M. A contribution to the knowledge of the Cyprinidae of Iran (Pisces, Cypriniformes). Bull. Soc. Fr. Ichthyol. 6(2), 75–96 (1982).
Karaman, M. S. Süßwasserfische der Türkei. 8. Teil: Revision der Barben Europas, Vorderasiens und Nordafrikas. Mitt. Hambg. Zool. Mus. Inst. 67, 175–254 (1971).
Borkenhagen, K., Esmaeili, H. R., Mohsenzadeh, S., Shahryari, F. & Gholamifard, A. The molecular systematics of the Carasobarbus species from Iran and adjacent areas, with comments on Carasobarbus albus (Heckel, 1843). Environ. Biol. Fish. 91, 327–335. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10641-011-9787-1 (2011).
Kottelat, M. & Freyhof, J. Handbook of European Freshwater Fishes (Kottelat, Cornol & Freyhof, 2007).
Ward, R. D. et al. DNA barcoding Australia’s fish species. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 360(1462), 1847–1857. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2005.1716 (2005).
Machordom, A. & Doadrio, I. Evidence of a Cenozoic Betic-Kabilian connection based on freshwater fish phylogeography (Luciobarbus, Cyprinidae). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 18(2), 252–263. https://doi.org/10.1006/mpev.2000.0876 (2001).
Katoh, K., Misawa, K., Kuma, K. I. & Miyata, T. MAFFT: A novel method for rapid multiple sequence alignment based on fast Fourier transform. Nucleic Acids Res. 30(14), 3059–3066. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkf436 (2002).
Katoh, K. & Standley, D. M. MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: Improvements in performance and usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 30(4), 772–780. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/mst010 (2013).
Tamura, K., Stecher, G., Peterson, D., Filipski, A. & Kumar, S. MEGA 6: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 30, 2725–2729. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/mst197 (2013).
Nguyen, L. T., Schmidt, H. A., Von Haeseler, A. & Minh, B. Q. IQ-TREE: A fast and effective stochastic algorithm for estimating maximum-likelihood phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 32(1), 268–274. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msu300 (2015).
Trifinopoulos, J., Nguyen, L. T., von Haeseler, A. & Minh, B. Q. W-IQ-TREE: A fast online phylogenetic tool for maximum likelihood analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 44(W1), W232–W235. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw256 (2016).
Kalyaanamoorthy, S., Minh, B. Q., Wong, T. K., Von Haeseler, A. & Jermiin, L. S. ModelFinder: Fast model selection for accurate phylogenetic estimates. Nat. Methods 14(6), 587–589. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.4285 (2017).
Guindon, S. et al. New algorithms and methods to estimate maximum-likelihood phylogenies: Assessing the performance of PhyML 3.0. Syst. Biol. 59(3), 307–321. https://doi.org/10.1093/sysbio/syq010 (2010).
Ronquist, F. et al. MrBayes 3.2: Efficient Bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space. Syst. Biol. 61(3), 539–542. https://doi.org/10.1093/sysbio/sys029 (2012).
Huelsenbeck, J. P., Larget, B. & Alfaro, M. E. Bayesian phylogenetic model selection using reversible jump Markov chain Monte Carlo. Mol. Biol. Evol. 21(6), 1123–1133. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msh123 (2004).
Rambaut, A., Drummond, A. J., Xie, D., Baele, G. & Suchard, M. A. Posterior summarisation in Bayesian phylogenetics using Tracer 1.7. Syst. Biol. 67(5), 901–904. https://doi.org/10.1093/sysbio/syy032 (2018).
Puillandre, N., Lambert, A., Brouillet, S. & Achaz, G. ABGD, automatic barcode gap discovery for primary species delimitation. Mol. Ecol. 21(8), 1864–1877. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-294X.2011.05239.x (2012).
Puillandre, N., Brouillet, S. & Achaz, G. ASAP: Assemble species by automatic partitioning. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 21(2), 609–620. https://doi.org/10.1111/1755-0998.13324 (2021).
Zhang, J., Kapli, P., Pavlidis, P. & Stamatakis, A. A general species delimitation method with applications to phylogenetic placements. Bioinformatics 29(22), 2869–2876. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btt499 (2013).
Borkenhagen, K. A new genus and species of cyprinid fish (Actinopterygii, Cyprinidae) from the Arabian Peninsula, and its phylogenetic and zoogeographic affinities. Environ. Biol. Fish. 97, 1179–1195. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10641-014-0315-y (2014).
Nagelkerke, L.A.J. The barbs of Lake Tana, Ethiopia. Morphological diversity and its implications for taxonomy, trophic resource partitioning, and fisheries. Dissertation, Univ., Diss., 296 (1997).
Levin, B. A. et al. Adaptive radiation of barbs of the genus Labeobarbus (Cyprinidae) in an East African river. Freshw. Biol. 64, 1721–1736 (2019).
Borkenhagen, K. Taxonomy, phylogeny and zoogeography of the hexaploid Torini of the Middle East and North Africa. Dissertation, Frankfurt am Main, XIII, 148 (2017).
Yang, L. et al. Phylogeny and polyploidy: Resolving the classification of cyprinine fishes (Teleostei: Cypriniformes). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 85, 97–116 (2015).
Funding
Open access funding provided by Lund University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
A.J.R. and H.R.G. designed the experiment. A.J.R., S.V. and C.K. sampled the individuals. A.J.R. performed the wet laboratory experiments and morphological analyses. A.J.R. and H.R.G. performed the molecular analyses, and wrote the manuscript with inputs from all authors. S.V. and C.K. helped obtain permits for sampling. H.R.G. secured the funding and supervised the work.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The original online version of this Article was revised: The Nomenclatural Acts and the ZooBank registration LSID numbers for this publication [urn:lsid:zoobank.org:pub:891DC1CD-C71C-4783-B009-F3141E542A9D], [urn:lsid:zoobank.org:act:9296233A-FA76-41E7-9814-7D22FCF37CDC], [urn:lsid:zoobank.org:act:B056DC31-E811-4B1C-850B-0DE8767A07F5] and [urn:lsid:zoobank.org:act:B4B0C801-0C84-4247-B488-767EC4307CF9] were omitted.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Jouladeh-Roudbar, A., Kaya, C., Vatandoust, S. et al. New insights into the phylogeny of Carasobarbus Karaman, 1971 (Actinopterygii, Cyprinidae) with the description of three new species. Sci Rep 14, 21801 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-71463-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-71463-7