Abstract
Virtualization is the process of sharing physical machine resources into multiple Virtual Machines (VMs) for the effective utilization of resources. The major issues are in handling physical resources such as high demand of resources, infrastructure issues and operational issues. Also violating Service Level Agreement (SLA) is another problem to lead the violations. In this case, VM consolidation method is used to migrate the VMs and optimize the efficient way to use the resources. So we get minimized energy consumptions. Existing methods has increased energy consumption and overhead issues. In this paper we propose adaptive backtracking methods to provide VM consolidation based on less energy consumptions. We use Adaptive Hill Climbing and Pursuit algorithms to consolidate the VMs and use the VMs with efficient energy consumption. We implement this simulations using Matlab in Hybrid Cloud Environment. The performance factors are obtained with less energy consumption and compare the results with existing methods. Overall our proposed system is achieving 95% of accuracy index with lower energy consumption such as 28%, 30% and 32% with multiple VMs consolidations.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Nowadays Cloud Computing is used in all the business environments such as multinational companies, industries, banking sectors and other commodity environments. Day by day usage of resources and applications are also increased1. The high demand of availability and resource request is evolving in services. Current scenario cloud provides anything as a Service such as infrastructure, platform and application as a services2.
The cloud services are internet based service offerings and many countries are using large volume of resources and resource computations. In this case allocation of VMs and optimizing resources are major issues3. According to the recent cloud survey, virtualization is used in all the cloud services. Which share the resources to multiple users based availability and resource request. Major concern is handling resource with less energy consumption. In this case VMs are mapped with cloud data center so we can access the physical machine are easily.
The cloud services are used in all kind of online services during and after pandemic the usage of resources are day by day increased4. The volumes of resources are stored in cloud space based on SLAs and VMs resources are utilized. The Cloud resources are classified based on their storage level, access controls and turnaround time of each request. In this case each request is classified based on cloud space and cloud service provider resources. Each service is demonstrated based on their consolidated data center features and each physical storage. When we are using Hybrid cloud environment the volume of physical data are recorded and problems are addressed5.
Hybrid Cloud Environment has huge volume of physical machines which composed as logical machines such as VM consolidations6. There are several user can access the resource so we need to provide less energy consumed resource with VM consolidation and better accuracy results. In this paper, “Related works” section deals various related works about VM consolidation and energy utilization, “Hybrid cloud optimization—VM consolidation” section gives problem statement with proposed methods, “VM consolidation—experiments” section explains proposed algorithms with simulations, “Experimental setup” section gives experiments and conclusion.
Related works
The result 2023 cloud magazine the two platforms such as Azure and Google provided less CPU utilization as less than 25%7 and IBM has average result in between 25 and 30%8. Same way Amazon Web Services has more utilization factor and more resources can be accessed by variety of users9. The CPU utilization and energy consumption is major consideration to give effective resource access services. The below Table 1 shows that various cloud services utilization factors.
The Consolidation of VMs are tedious process in cloud environment because we need to considered utilization of resources10, execution11 and turnaround time of CPU12, service level agreements13 and service offerings14. While implementing this we need to take care over and underutilization of resources such migration, placement and optimization. According various related studies need to take care constraint stratification problem, genetic methods, heuristics solutions and NP-hard completeness solutions. Virtualizing data centres is done by using linear programming model based on heuristics solutions. Our proposed idea is to generate decision tree model and trace the parameter from reference or backtracked results15.
Many researchers are suggested that VM allocation in Cloud is different scenarios. Lion optimizer is used to allocate VM on Cloud data center with physical features. From this related research studies we need an efficient VM consolidation method with reduced power consumption, reduced resource wastages and optimal allocations.
Hybrid cloud optimization—VM consolidation
Cloud Optimization is the strategies approach and constructed based on linearity, evolutionary and constraint approaches. In this paper we propose adaptive backtracking VM consolidation approach to optimize the resource with lesser energy consumption. Here we use Adaptive Hill Climbing method to generate hybrid cloud with backtracking resource features using deep learning and Pursuit algorithm is used to calculated utilization factors. The below factors are considered to implement our system,
-
a.
Generate VM consolidation using adaptive backtracking with consideration of SLA violations, VMs, energy factors and migration.
-
b.
Design a VM migration tool and to select under and over utilized machine based on real time movement and threshold values.
-
c.
Place VM based on the request and availability which has generation strategy, crossover issues and development issues.
-
d.
Simulate the experiments using CloudSim for generating cloud platforms and Matlab is used to measure the accuracy and results.
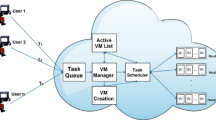
Figure 1 show that assigning resources to VM based on migration result. The live VM migration is applied to move underutilized physical resources to sleep mode and utilized or running machines in active node. So we can consolidate the VMs based on this factor. In this case SLA violation is occurred to negative impact will be created and delay the response time of the user application. Live Migration is addressed by using migrate VMs to overloaded physical machines based on capacities. This process is called VM placement consolidation and it is decision making category of each resources.
Virtual Machine (VM) is presented as
where Machine has two options such as physical and virtual based on host and i is represented as number of resource availability.
Resource Optimization and Utilization are the major challenges to be selected based on cloud service provider availability. From the above Table 2 (Algorithm 1) we migrate the VMs from underutilized status to over utilized status. It is classification process and it is done by using VM migration polices as live status. So the negative system performance is reduced. Finally we get balanced migrated resource sharing system.
VM consolidation—experiments
The physical machine resources are utilization can be done by using dynamic load balancing systems. In the scenario we can set the threshold values based manual operations. The below algorithms is shows that VM consolidation, migration and resource utilization index measurements in Table 3.
The threshold challenges is addressed based on moving ranged resource and it is automatically calculated the resource utilization index. The physical machine resources obtained based on cloud provider results and threshold results. Moving range is measured by using continuous data analytics features from underutilized factors. So we can dynamically allocate the resources regarding CPU utilization, VM migrated results, lower bound values and VM consolidation features.
Figure 2 shows that VM consolidation based on encoding schemes with PM and VM features. It is allocated based on resource availability and utilization factors.
The VM placement solution is encoded in the form of chromosomes. Each chromosome is represented as a gene order, with each gene representing a PM where the VM will be placed. Table 4 shows an example of Virtual machines placed to physical machines and their equivalent chromosome when the number of visual machines is 10 and the number of physical machines is 4. The V1, V2, V3 are placed in M1, while V4, V5 are placed in PM2, and V6, V7, V8, V9 are placed in PM3 finally V10 is placed in PM4.
The pursuit algorithm is implemented based on specific VM placement setting up lower threshold values. The higher threshold values are classified as over utilized factor VM consolidated index is recorded based on following Fig. 2 flowchart. This case we first select the parent node with lowest threshold values and identify the location. Second place the VM based on second node representations in Table 5.
From the Fig. 2, VM consolidation can be done based on threshold values and multiple resource utilization. The fitness function is calculated based number over and under utilized threshold values and physical machine representations. The following is fitness function of utilized resource with x population.
From the above algorithm VM consolidation can be done by using hill climbed results and then pursuit algorithm used to simulate the VM placement and migrations. Above algorithms are tested by using experimental setup in Table 6.
Experimental setup
The Adaptive Backtracking method is simulated by using Matlab environment. Hybrid Cloud Environment created by using CloudSim and Computing system has Intel Core i7 GPU Computer, 16 GB RAM, 1 TB HDD and Window 1O OPS. The performance factors are calculated as follows.
Energy consumption factor
The energy efficiency is calculated based on Physical machine resource utilized factor values and number of VM placed,
VM Migration is calculated from using number over and underutilized resource and availability factor. The fitness function gives the results for VM values status. CPU utilization is calculated based on migrated VM results which pull down the performance and execution time. The accuracy factor is measured by using turnaround time of each executed results.
From the above experiments below Table 7 shows that the result of accuracy and power consumption results based on number of VMs.
The result from above Table 7 the average accuracy in 96% and Energy efficiency is achieved as 0.22. This is very less energy consumed while increased VMs and physical resources in Fig. 3. The above results are compared with existing methods and shown in Table 8.
This case our proposed method results are compared with existing methods such as Decision tree, K-means, Support vector and TensorFlow graph. The results are compared average cpu utilization, turnaround time and energy efficiency index in Fig. 4. The results show that our proposed methods achieved better results.
In this paper we compared the execusion results with some existing VM Scheduling and consolidation methods. The below Table 9 shows that the comparison representation of our proposed method CPU utilization and energy efficiency factors.
From the above Table 9 results, the current research methodologies in cloud computing such as Dynamic Virtual Machine Scheduling Using Residual Optimum Power-Efficiency In The Cloud Data Center, SR-PSO: server residual efficiency-aware particle swarm optimization for dynamic virtual machine scheduling, VMS-MCSA: virtual machine scheduling using a modified clonal selection algorithm results are compared with our proposed method Adaptive Backtracking. Based on the results our proposed method gives 96% accuracy factor (CPU Utilizations) and lesser energy efficiency index.
Conclusion
Cloud computing is the major source to provide various services based on user request. Virtualization is another important factor to convert physical resources in logical services like VMs. We proposed adaptive backtracking VM consolidation method to provide lesser energy consumption and better accuracy results. Hill climbing algorithm is applied to classify the VMs from physical machine resource and availability. Pursuit algorithm is applied to measure threshold values to found over and underutilized resources. From the results Matlab simulator is used to simulate the systems and calculated accuracy as 96%. Also we achieved efficient energy consumption and compared the results with existing methods. In future same consolidation factor can be proposed for live VMs.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Booba, B., Joshphin Jasaline Anitha, X., Mohan, C. & Jeyalaksshmi, S. Hybrid approach for virtual machine allocation in cloud computing. Sustain. Comput. Inform. Syst. 41, 100922 (2023).
Radi, M., Alwan, A. A. & Gulzar, Y. Genetic-based virtual machines consolidation strategy with efficient energy consumption in cloud environment. IEEE Access 11, 48022–48032 (2023).
Manikandan, S. & Chinnadurai, M. Virtualized load balancer for hybrid cloud using genetic algorithm. Intell. Autom. Soft Comput. 32(3), 1459–1466 (2022).
Dogani, J., Khunjush, F. & Seydali, M. Host load prediction in cloud computing with discrete wavelet transformation (DWT) and bidirectional gated recurrent unit (BiGRU) network. Comput. Commun. 198, 157–174 (2023).
Radi, M., Alwan, A., Abualkishik, A., Marks, A. & Gulzar, Y. Efficient and cost-effective service broker policy based on user priority in VIKOR for cloud computing. Basic Appl. Sci. Sci. J. King Faisal Univ. 22(2), 1–8 (2021).
Borne, P. Metaheuristics for the optimization in planning and scheduling. FAC Proc. Vol. 40(18), 1–7 (2007).
Arshad, U., Aleem, M., Srivastava, G. & Lin, J.C.-W. Utilizing power consumption and SLA violations using dynamic VM consolidation in cloud data centers. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 167, 112782 (2022).
Ye, X., Yin, Y. & Lan, L. Energy-efficient many-objective virtual machine placement optimization in a cloud computing environment. IEEE Access 5, 16006–16020 (2017).
Avula, R. N. & Zou, C. Performance evaluation of TPC-C benchmark on various cloud providers. In Proc. 11th IEEE Annu. Ubiquitous Comput., Electron. Mobile Commun. Conf. (UEMCON) 226–233 (2020).
Manikandan, S. & Chinnadurai, M. Effective energy adaptive and consumption in wireless sensor network using distributed source coding and sampling techniques. Wirel. Person. Commun. 2021(118), 1393–1404 (2021).
Manikandan, S., Chinnadurai, M., Maria Manuel Vianny, D. & Sivabalaselvamani, D. Real time traffic flow prediction and intelligent traffic control from remote location for large-scale heterogeneous networking using TensorFlow. Int. J. Future Gener. Commun. Netw. 13, 1006–1012 (2020).
Patel, K. D. & Bhalodia, T. M. An efficient dynamic load balancing algorithm for virtual machine in cloud computing. In Proc. Int. Conf. on Intelligent Computing and Control Systems (ICICCS 2019) India, Vol. 11, 215–224 (2019).
Priyanka, C. & Sankari, S. Comparative analysis on virtual machine assignment algorithm. In 2017 IEEE Int. Conf. on Computing and Communication Technology, Tokyo, Vol. 17, 526–533 (2017).
Sheetal, K. & Anshika, G. Performance evaluation of check pointing and threshold algorithm for load balancing in cloud computing. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Eng. 6(5), 2347–2693 (2021).
Calheiros, N. et al. Cloudsim: A toolkit for modeling and simulation of cloud computing environments and evaluation of resource provisioning algorithms. Softw. Pract. Exp. 41, 23–50 (2015).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
S. Manikandan: Problem Selection, Algorithm, Implementation, Results. E. Elakiya: Implementation, Coding and Testing. K.C. Rajheshwari: Formal Analysis, Design and Results. K. Sivakumar: Experimental Results, Algorithm part and Editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Manikandan, S., Elakiya, E., Rajheshwari, K.C. et al. Efficient energy consumption in hybrid cloud environment using adaptive backtracking virtual machine consolidation. Sci Rep 14, 22869 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-72459-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-72459-z
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Multi-modal emotional analysis in customer relation management and enhancing communication through integrated affective computing
Scientific Reports (2025)
-
AI powered multi feature fusion framework for retrieving images using color, texture and shape descriptors
Scientific Reports (2025)
-
Machine learning based multi-stage intrusion detection system and feature selection ensemble security in cloud assisted vehicular ad hoc networks
Scientific Reports (2025)
-
Enhancing anomaly detection and prevention in Internet of Things (IoT) using deep neural networks and blockchain based cyber security
Scientific Reports (2025)
-
EMLSCF-FCH: A Secure and Efficient Machine Learning-Based Framework for Fog Computing in Healthcare
International Journal of Computational Intelligence Systems (2025)