Abstract
In order to alleviate the problem of corner gas accumulation caused by air leakage in goaf of high gas coal seam. The rapid film-forming sealing material for the corner wall and the grouting sealing material for the corner roof were developed and optimized, and the’ plugging-injection’ combined air leakage sealing scheme was proposed. Orthogonal test was used as the research method, and the 12 h and 24 h decay rate, gel viscosity, and setting time of the blocking film were used as the research indexes to screen out the optimal ratio of the materials. The engineering test shows that: (1) 1.5% sodium alginate solution and 7.5% calcium chloride solution can be sprayed in turn to quickly form a plugging film and stick to the corner wall; (2) 2.5% polyvinyl alcohol, 0.6% borax and 0.5% thickener were mixed into water and stirred to obtain polymer plugging slurry. (3) According to the monitoring results, the gas concentration of each monitoring point decreased by more than 62% after using the plugging material, and the gas concentration in the upper corner decreased by 67%. The air leakage decreased by more than 50%, and the upper corner decreased by 57%. The air leakage blocking program composed of these two new materials can effectively reduce the accumulation of gas in the corner, reduce the probability of gas protrusion accidents in the coal face, and ensure the safe mining of the coal face.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Coal is an important fossil energy source, and is listed as one of the three pillars of primary energy in the world along with oil and natural gas1,2. China is the world’s largest coal producer and consumer, and according to the relevant data released by the National Bureau of Statistics of China, China’s coal production has been on a continuous upward trend in general. In 2023, China’s raw coal production was 4.71 billion tons, a year-on-year increase of 2.9%, which is the highest in the history of China’s coal production3,4. China’s coal production and the trend of change in the past fifty years are shown in Fig. 1.
Gas is an associated material in the process of coal formation, and it exists in the coal body and the surrounding rock layers in two states: adsorption and free state, which can be transformed into each other and are in a dynamic equilibrium5,6,7. In the process of coal mining, the stress disturbance of the original rock brought by mining will destroy the dynamic balance of the gas in the coal body, resulting in the release of a large amount of gas, which will lead to gas protrusion, explosion, asphyxiation and other disasters8,9,10,11,12 .
Air leakage in the mining airspace will carry gas emission, which has a huge impact on the safety production of udder and lower corners and the coal face8,13,14,15,16. Michael and Vlasseva17 by establishing a mathematical model to simulate the distribution of pressure and wind speed in the goaf, the airflow transport law in the goaf was obtained. This study has brought great help to the gas migration and prevention work in goaf areas. Experts Michael and Vlasseva18 from the United States simulated the variation of airflow velocity in goaf using a false assumption of turbulence, and obtained the airflow flow pattern in the goaf based on the pressure distribution area. BiS19 et al. used Herschel Bulkey(H-B) flow type grouting material and optimized the gas leakage model based on fluid mechanics, taking into account factors such as grouting material performance parameters, crack roughness characteristic parameters, pressure difference inside and outside the borehole, and radial diffusion length of grouting material. The model was numerically simulated and analyzed using MATLAB software, and improvement suggestions were proposed to solve the problem of gas leakage. Chen et al.20 developed a new type of cementitious material using sulfoaluminate concrete lime and gypsum as the main materials. Its good expansion performance after solidification can reduce cracks caused by shrinkage to a certain extent. Guo Xin et al.21 developed a high fluidity and good expansion sealing material using ultra-fine cement as the substrate, along with water reducing agents, expansion agents, and retarders. The differences in microstructure and pore structure between this material and traditional cement-based materials were analyzed using scanning electron microscopy and mercury intrusion porosimetry. The experimental results showed that this material is easy to inject, has strong permeability, and superior sealing performance. Niu Xingang22 developed a light corner sealing airbag in view of the current situation of using U-shaped ventilation in most coal mines in China. The application of this research reduces the gas overrun accident in the upper corner, and puts forward a new direction for the existing coal mine corner plugging technology. Zhang Junxiang et al.23 studied the characteristics of poor mechanical properties of underground broken coal and rock. They prepared a new type of polymer foam plugging material by using organic resin as the base material, adding crosslinking agent, foaming agent and so on. They carried out plugging simulation test and engineering field test respectively. Their test results show that the material has better plugging effect than traditional materials, and can prolong the extraction period of boreholes.
Based on previous studies, it is found that in the study of air leakage and plugging materials in coal mine goaf, previous scholars mainly focused on single grouting plugging or corner wall plugging. There are relatively few studies on the combination of corner wall sealing and grouting sealing in the corner fracture expansion development area. In view of the above research status, this paper proposes a ' plugging-injection combination ' air leakage plugging technology scheme by combining the film forming property of alginate and the gel forming property of polyvinyl alcohol. In this paper, alginate was selected as the basic material for rapid film-forming plugging material on the upper and lower corner walls. Alginate solution and calcium chloride solution were sprayed on the surface of the wall in turn to form a uniform and dense film. In this paper, polyvinyl alcohol PVA1788 (polymerization degree 1700, alcoholysis degree 88%) was selected as the basic material for gelling of drilling grouting plugging material in the crack expansion area of corner roof. Sodium tetraborate decahydrate was added as crosslinking agent, and sodium carboxymethyl cellulose was added as thickening retarder. The advantages of the two types of plugging materials are dynamically combined to form a set of plugging technology schemes suitable for high gas coal seams. Design single factor and multi-factor orthogonal experiments. In the experiment, the optimum ratio of film thickness, 12 h and 24 h film thickness attenuation ratio, colloidal condensation time, colloidal condensation viscosity and other influencing factors were studied. And the scheme was applied in the West 2109 coal face of Weijiadi Coal Mine.
Engineering background
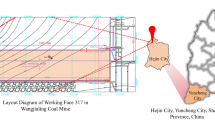
Weijiadi Coal Mine is located in Baiyin City, Gansu Province, China. It is a coal and gas outburst mine. The coal field is a typical ‘high gas and easy desorption ‘coal seam, and the gas content of the coal seam is extremely large. West 2109 coal face is the main mining face of Weijiadi coal mine, located in the upper one coal seam of the east wing of the west second mining area. The coal seam has developed primary fissures, mainly in powder form, and belongs to the coal seam with prominent coal and gas. The west end of the 2109 coal face is a thin coal zone, with a recoverable thickness of less than 0.8m, and the coal seam is gradually thickening along the strike direction from west to east. The thickness of the coal seam is 0.7m–21.62m, the average thickness is 11.21m. The profitable thickness of the coal seam is 1.1m–21.5m, the average profitable thickness is 10.81m. The recoverable thickness of the coal seam is 1.1m–21.5m, the average recoverable thickness is 7.9m. The thickness of the coal seam with gangue is 0–4 layers, the thickness is 0.03m–0.89m. The total thickness of the coal seam is thicker in east and thinner in west, the angle of inclination of the seam is 9°–21°, the average is 9° .The total thickness of the coal seam is generally thick in the east and thin in the west. Figure 2 is the map of Weijiadi Coal Mine and West 2109 coal face.
Test scheme
Test reagent
The reagents required for the test are shown in Table 1 below:
Test instruments
In order to carry out the preferred test of rapid film-forming plugging material on the wall surface of the corner and drilling grouting gel plugging material in the crack expansion area of the top plate of the corner, the selected instruments are: digital thickness measuring instrument, digital viscometer, electric thermostatic incubator, digital desktop acidimeter, glass slides, thermometers, electronic scales, and beakers.
Test content and test methods
Corner fast film-forming plugging material optimization test scheme
-
1.
Testing contents.
-
1.
Film thickness test. The thickness of the film is mainly determined by the amount of alginate solution, but too much alginate solution will cause problems such as uneven film thickness and poor wall hanging effect. Nine 1m2 molds were taken, and sodium alginate and calcium chloride solutions were sprayed into the molds respectively. After the film formation reaction was completed, the plugging film was taken out, and the film thickness was measured and recorded using a digital display thickness measuring instrument.
-
2.
12 h and 24 h thickness attenuation measurement. The film formed by the crosslinking reaction will encapsulate a part of the unreacted solution, and the liquid part will evaporate over time, so the film thickness will have a certain degree of attenuation. Based on the advancing speed of the west 2109 coal face, 12 h of effective plugging can basically meet the demand of the upper and lower corners. The 9 groups of films formed in the previous step were placed in a thermostat for 12 h, and the thickness attenuation ratio was measured and calculated. At the same time, in order to meet the needs of the actual project site, considering the objective situation that there is still a plugging demand after 12 h when the propulsion speed is slow in the field, 9 groups of films were placed in a constant temperature incubator for 24 h, and the thickness attenuation ratio was measured.
The following Figs. 3 and 4 are the thermostat and digital display thickness measuring instrument required for the test.
-
1.
-
2.
Material optimization test design scheme.
In order to select the best film-forming ratio under the factors of film-forming thickness, 12 h and 24 h thickness attenuation ratio, which have a direct impact on the plugging effect, the orthogonal experimental design method was used, and the test was based on 1m2 film-forming. The influencing factors were sodium alginate concentration (%), sodium alginate dosage (L/m2), calcium chloride concentration (%) and calcium chloride dosage (L/m2). Three reference levels were selected for each factor. The orthogonal experimental factor level table is shown in Table 2.
Table 2 Orthogonal test factor level.
Test scheme of drilling grouting gel plugging material in crack expansion development area of corner roof
-
1.
Testing contents.
-
1.
Colloid setting time test. In this study, the factors affecting the coagulation of the colloid were the concentration of the crosslinking agent and the pH value of the crosslinking agent. In this experiment, acid-base titrant and digital desktop acidity meter were used to adjust and measure the pH value.
-
2.
Gel viscosity (Adhesion) test. The higher viscosity represents that the plugging gel has better adhesion to the interior of the fractures and better plugging effect on the fractures. In this study, sodium carboxymethyl cellulose was used as a thickener. Sodium carboxymethyl cellulose can adjust the viscosity of the gel. In this study, the viscosity of each group of gels was tested and recorded, and 1m2 of each group of gels was selected for adhesion test. The test instrument and part of the structure are shown in Figs. 5, 6 and 7.
-
1.
-
2.
Material optimization test design scheme.
The factors that have a direct impact on the plugging effect are gelation time and gelation viscosity. Six groups of different crosslinking agent concentrations (0.2% ~ 1.2%, with a concentration gradient of 0.2%) were designed and measured. Based on the optimal ratio of primary gelation time, the optimal gelation time of 6 groups under different PH (4 ~ 9, with 1 as the PH increasing gradient) was designed and measured. Finally, under the above optimal gelation time ratio, the optimal gelation viscosity and adhesion under 6 different thickener concentrations (0.2% ~ 0.7%, 0.1% as the concentration gradient) were designed and measured.
Result and discussion
Effect of different material rations on film thickness and thickness attenuation ration
The results of orthogonal test of the corner wall rapid film-forming plugging material are shown in Table 3. In this orthogonal test, a total of 4 factors that have a direct impact on the film formation of the material were selected. Each factor selected 3 levels for orthogonal test, considering 3 indicators that have a direct impact on the plugging effect. The experimental results are shown in Fig. 8.
Table 3 is the summary of orthogonal test results, extreme value and variance analysis. Km−n (m = 1 ~ 3, n = 1 ~ 3) is the extreme value of three evaluation indexes, and Rm (m = 1 ~ 3) is the corresponding variance. The larger the film thickness, the better the plugging effect under the same conditions. Therefore, it can be seen from the data in Table 3 that A3B3C3D3 is the best ratio under this influencing factor. Since R1 (b) is much larger than the other three indicators, the amount of alginate (L / m2) has a major effect on the film thickness. For the 12 h and 24 h thickness attenuation ratio (%), the smaller the value, the better the plugging effect under the same conditions. Therefore, from the data of Table 3, it can be seen that A3B3C1D3 is the best ratio under the influence of 12 h thickness attenuation ratio, and A2B2C1D3 is the best ratio under the influence of 24 h thickness attenuation ratio (%). The R2 and 3 (a) are much larger than the other 6 (two groups). Therefore, the alginate concentration (%) has a major impact on the above two indicators.
Figure 8 (a) and (b) are the thickness attenuation statistics of 9 schemes after 12 h and 24 h constant temperature standing. Observing Table 2 and combining Fig. 8 (a) and (b), it can be seen that the film thickness of the 9 groups of test ratio schemes has a certain degree of attenuation over time. The reason for the above phenomenon is that the plugging membrane is a fluid with water as the solvent. After the crosslinking reaction of the two materials, a part of the unreacted complete solution will evaporate, resulting in a decrease in the thickness of the film. It can be seen from Fig. 8 (a) that after 12 h of constant temperature standing, the attenuation ratio of the thickness of the plugging film in each group is more than 19%. Among them, the attenuation ratio of scheme 1 is the largest, which is 28.57%, and the attenuation ratio of scheme 8 is the smallest, which is 19.01%. In Fig. 8 (b), the thickness attenuation ratio after 24 h of constant temperature standing is similar to that after 12 h, and the attenuation ratio of scheme 1 is the largest, which is 47.62%. Scheme 8 has the smallest attenuation ratio, which is 37.8%.
From the above experimental data, it can be seen that the scheme 8, that is, 1.5% sodium alginate solution and 7.5% calcium chloride solution were sprayed at a ratio of 4:3 to form a plugging film in the film thickness, 12 h and 24 h thickness attenuation ratio can achieve the best effect. Sodium alginate has good film-forming properties and high liquid viscosity after being dissolved in water. The 1.5% concentration of sodium alginate solution can reduce the loss caused by solution flow as much as possible under the premise of ensuring good spraying effect and meeting the engineering field application. And the higher concentration of viscous solution volatilizes less water, so the effect of forming film is the best at this ratio (Table 4).
Effect of different material ratios and PH on colloid coagulation time
Take 6 200 ml beakers and add 100 ml water in turn. Six portions of 2.5 g PVA1788 were weighed, and 0.2 g, 0.4 g, 0.6 g, 0.8 g, 1.0 g and 1.2 g of borax were weighed respectively. The PVA powder and borax powder were mixed evenly and slowly added to 6 groups of 100 ml water, respectively, and stirred at a constant speed to form a colloid and record the time. Under the optimal colloid coagulation ratio selected by the above experiments, the pH of the slurry was adjusted to 4 ~ 9 by using the acid-base titration solution, and the above experiments were repeated again and the gel time of the slurry was recorded and summarized in Table 5. The experimental results are shown in Fig. 9.
From Fig. 9; Table 3, it can be seen that with the increase of borax content, the gelation time gradually prolonged. This is because in the process of stirring, the hydrolysis of borax to produce B (OH) 4−accelerates the hydrolysis of polyvinyl alcohol and the complexation reaction to form a polymer gel, which effectively alleviates the problem that polyvinyl alcohol is difficult to dissolve at room temperature. However, as the amount of borax increases, the hydrolysis time of borax will increase, resulting in a lag in the crosslinking reaction and an increase in the gelation time.
From the analysis of Fig. 9; Table 4, with the increase of PH value, the coagulation time of colloid decreases significantly. This is because the main molecular structure of polyvinyl alcohol is 1,3-propanediol, which contains a large amount of -OH. -OH is an important functional group for the crosslinking reaction between polyvinyl alcohol and (OH) 4−. Under acidic conditions, the content of H + in the solution is high, and the priority of hydration reaction between -OH and H + is much higher than that of crosslinking reaction, resulting in a large amount of -OH consumed. Therefore, the crosslinking reaction was forced to delay. Based on the consideration of grouting time and grouting cost in the engineering site, 2.5% polyvinyl alcohol + 0.6% borax is the best ratio of crosslinking reaction. On this basis, the PH is adjusted to 6 ~ 7, and the reaction time is controlled at about 35 min, which can better meet the requirements of grouting in the engineering site.
Effect of different thickener concentrations on viscosity and adhesion properties
Viscosity and adhesion are important indicators to measure the plugging effect of grouting plugging materials. Higher viscosity and adhesion mean that the colloid has a better plugging effect. After the slurry is injected into the coal seam, with the passage of time, the liquid flows while the crosslinking reaction gradually occurs and generates a complex gel. The gel generated by stays in the fracture with its strong cohesiveness and effectively bonds and adheres to the upper and lower walls of the fracture, and finally plays a plugging effect. Therefore, the viscosity of the grouting material after gelation in the pores plays a decisive role in the plugging effect. The effects of different concentrations of thickeners on viscosity and adhesion are shown in Table 6. The data of viscosity and adhesion ability after gelling under different concentrations of thickeners are shown in Fig. 10.
From Fig. 10; Table 6, it can be seen that with the increase of thickener concentration, the gel viscosity increased linearly in the early stage and gradually balanced in the later stage. When the concentration of sodium carboxymethyl cellulose was greater than or equal to 0.5%, the gel viscosity gradually stabilized. The adhesion of the gel is characterized by the sliding distance at the same time when it is placed vertically on the glass plane. It is not difficult to see that with the increase of viscosity, the sliding distance of the colloid at the 4 times gradients of 5 ~ 20 min is significantly reduced, and the adhesion ability is significantly increased. Therefore, 0.5% sodium carboxymethyl cellulose is the best thickener concentration.
Combined with the above measured data, the influence of material ratio on film thickness, 12 h and 24 h thickness attenuation ratio was comprehensively considered. The effect of borax concentration and PH value on the gelation time, the effect of different sodium carboxymethyl cellulose concentration on the viscosity of the gel, and the effect of the gel on the sliding amount of the smooth glass surface at the same time gradient. The optimal ratio of the rapid film-forming plugging material on the corner wall is: 1.5% sodium alginate: 7.5% calcium chloride = 4:3; the best ratio of grouting sealing material in the fracture fissure expansion area of the corner roof is: 2.5% polyvinyl alcohol + 0.8% borax + 0.5% sodium carboxymethyl cellulose, supplemented by 1% inorganic salt to enhance water retention, and PH is 6 ~ 7.
Capping program
The air leakage in the goaf is the important case of gas overrun in the upper and lower corners. Because the air flow turns sharply at the corner, the air flow velocity here is low and it is easy to form an eddy current zone. At the same time, the gas accumulated in the goaf is easy to accumulate here under the influence of air leakage and its own floating in the air.
At present, for the problem of gas accumulation in the upper and lower corners, Weijiadi Coal Mine adopts a simple sandbag-stacked wall to seal the wall surface. The sandbag-stacked wall is placed at the upper and lower corners, and a layer of yellow mud is applied on the surface to strengthen the sealing of the sealing wall. However, its sealing is poor, and the gas in the goaf can still diffuse to the corner through the sealing wall. Therefore, in order to solve the above problems, a fast film-forming plugging material for the corner wall and a drilling grouting plugging material for the crack expansion area of the corner roof were developed. The " plugging-grouting " combined with the upper and lower corner gas overrun comprehensive control scheme formed by the dynamic combination of the advantages of the two materials was applied to the West 2109 working face of Weijiadi Coal Mine. The air leakage, gas concentration and temperature were selected as the evaluation parameters of the plugging scheme and the field measurement was carried out.
Corner wall rapid film-forming plugging
Sodium alginate is a kind of carbohydrate, which is a polymer formed by linear (1 → 4) bonded β-D-mannuronic acid and α-L-guluronic acid24,25. The molecular structure contains hydroxyl ether bond. When it encounters alkaline ions, especially Ca2+, complexation reaction occurs and film-forming behavior occurs. When the sodium alginate solution meets with Ca2+, the chemical bond connecting Na+ in the molecule is broken and cross-linked with Ca2+ to form a new chemical bond. In each sodium alginate molecule, substitution reaction occurs with the hydroxyl group adjacent to the ether bond to form an ether bond connecting the two molecules26,27,28,29. The above two chemical reactions synthesize calcium alginate molecules with high degree of polymerization by bonding dispersed sodium alginate molecules. The above reactions occur repeatedly, and the generated calcium alginate molecules are bonded horizontally and vertically to form a polymer. The polymer is macroscopically a dense polymer plugging film. The mechanism of plugging film formation is shown in Fig. 11.
Based on the above laboratory material optimization and film forming mechanism analysis, combined with the current situation of the upper corner plugging of the west 2109 working face of Weijiadi Coal Mine, the rapid film forming plugging material is sprayed on the surface of the original plugging wall to form a dense film to make up for the effect of plugging the wall ventilation. Figure 12 (a) is the effect before the plugging membrane is not used, and Fig. 12 (b) is the plugging effect after the new plugging membrane is used. The comparison between the two shows that the plugging effect of the project site after the plugging membrane is used is significantly improved and more regular.
Drilling grouting plugging in fracture expansion development area of corner roof
Polyvinyl alcohol is a water-soluble polymer with good gelation property30,31. The large amount of -OH contained in the molecular chain of polyvinyl alcohol can carry out a series of chemical reactions between functional groups, and combine two or more polyvinyl alcohol molecules together by bridging to form a gel with high polymerization and high molecular weight32,33. Polyvinyl alcohol gel has become a popular plugging material because of its strong viscosity and expansibility. Borax is a commonly used crosslinking agent. Borax is a white solid powder at room temperature, and it will quickly dissolve into boric acid solution after encountering water. Boric acid solution in water will accept negatively charged OH−, and then generate borate ions (B(OH)4− ), B (OH)4− and the alcohol group on the polyvinyl alcohol condensation reaction to remove the water molecules at the same time, polyvinyl alcohol molecules cross-linked together, and ultimately to form a hydrogen bond in the form of bonding to form a high polymer, the macro performance of the elastic, viscosity and expansion of the gel34,35,36. The gelation mechanism of polyvinyl alcohol gel is shown in Fig. 13.
Based on the optimization of grouting materials and the analysis of gelling mechanism, combined with the fracture morphology and fracture characteristics of the fracture expansion development zone of the roof fissure in the corner of the west 2109 working face of Weijiadi Coal Mine, the length of the borehole in the plastic zone of the surrounding rock is designed to be 5 m, and the length of the borehole in the fracture caving zone is designed to be 8 m, so that the end of the borehole can penetrate into the fine-grained sandstone. The plugging slurry injected into the rock mass has a complex reaction at the edge of the flow, which makes the slurry become thick and eventually the gelling hysteresis flow, and the formed colloid stays and adheres to the fracture to complete the plugging.
Measurement and analysis of plugging solutions
In this field monitoring, 4 monitoring and 2 eddy current zones were set up in the upper and lower corners and goaf, a total of 6 monitoring points. Monitoring point 1 is used to monitor the air volume of the air intake roadway and the gas content in the air flow. Monitoring point 2 (vortex zone 1) is used to monitor the air volume in the lower corner, the gas concentration in the air flow and the air leakage. Monitoring point 3 and monitoring point 4 : located between the work, mainly used to monitor the change of air flow between the working face of the intake and return air roadway, the gas concentration in the air flow and the air leakage. Monitoring point 5 (vortex zone 2) is used to monitor the air volume in the upper corner, the gas concentration in the air flow and the air leakage. Monitoring point 6 is to monitor the air volume of the return airway, the gas concentration in the air flow and the air leakage.
In order to obtain the changes of gas concentration and air leakage before and after the plugging scheme, six groups of field monitoring were carried out at the six measuring points (as shown in Fig. 14), and the average value and data change ratio were calculated. The change of gas concentration before and after plugging is shown in Fig. 15, and the change of air volume is shown in Figs. 16 and 17.
Conclusion
-
1.
A rapid film-forming sealing material has been developed utilizing alginate and calcium chloride, while a gel-based sealing material has been formulated using polyvinyl alcohol, borax, and a thickening agent. The mechanisms underlying these two reaction processes have been elucidated, and a technical solution for air leakage sealing has been proposed by integrating the advantages of both materials.
-
2.
Through a 4-factor, 3-level orthogonal experimental design, the optimal material formulation was obtained for achieving the best film thickness and the lowest thickness reduction ratio. Single-factor experiments were conducted to investigate the effects of cross-linker concentration, sodium carboxymethyl cellulose concentration, and pH on the colloidal properties. The results demonstrated that the optimal formulation and dosage for the rapid film-forming material were 1.5% alginate (3 L/m²) and 7.5% calcium chloride (4 L/m²). For the grouting sealing material, the optimal formulation was 2.5% polyvinyl alcohol, 0.8% borax, 0.5% sodium carboxymethyl cellulose, with an inorganic salt content set at 15% (by some unspecified measure or weight), and a pH range of 6–7.
-
3.
A field test of sealing materials and techniques was conducted at the West 2109 working face of Weijiadi Coal Mine. The results indicated that, following the application of the sealing materials, the methane concentration at various monitoring points decreased by over 62%, with a specific reduction of 67% at the upper corner, and the air leakage rate was reduced by more than 50%. The data confirmed that the “combined plugging and injection” method for sealing air leakage effectively decreased both the air leakage rate and methane concentration, virtually eliminating the risk of methane outbursts at the coal face, thereby ensuring the safety of personnel and the safe extraction of coal at the coal face.
Data availability
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Zhu, H. T. et al. China’s future energy vision: Multi-scenario simulation based on energy consumption structure under dual carbon targets. Energy 301 (2024).
Stala-Szlugaj, K. & Grudzinski, Z. World steam coal management. Gospodarka Surowcami Mineralnymi-Mineral Resour. Manage. 37(2), 5–26 (2021).
Guo, J. Research report on the economic situation of China’s coal industry from 2023 to 2024. China coal. 50(03), 12–20 (2024).
Wang, Q., Song, X. X. & Liu, Y. China’s coal consumption in a globalizing world: insights from multi-regional input-output and structural decomposition analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 711 (2020).
Chen, L. P. et al. Energy dissipation and crack propagation in gas-containing coal under impact loading: an experimental study. Powder Technol. 441 (2024).
Yang, D. D. et al. Study on the characteristics of coal and gas outburst hazard under the influence of high formation temperature in deep mines. Energy 268 (2023).
Zhang, C. L. et al. Study on the influence law and mechanism of coal seam permeability on coal and gas outbrust. J. China Coal Soc. 1–15 .
Guo, H. J. et al. Kinetic characteristics of desorption and diffusion in raw coal and tectonic coal and their influence on coal and gas outburst. Fuel 343 (2023).
Zhang, H. T. et al. Numerical simulation on stress evolution and deformation of overlying coal seam in lower protective layer mining. Alex Eng. J. 59(5), 3623–3633 (2020).
Qiao, Z. et al. Principles of formulating measures regarding preventing coal and gas outbursts in deep mining: based on stress distribution and failure characteristics. Fuel 356 (2024).
Ji, P. et al. Coal deformation characteristics during methane displacement by pulsed nitrogen injection: new method of using pulsed energy to improve coal permeability. Energy 308, 132779 (2024).
Ji, P. et al. Experimental study on enhanced coal seam gas extraction by uniform pressure/pulse pressure N2 injection. Fuel 351, 128988 (2023).
Miao, D. J. et al. New technology for preventing and controlling air leakage in goaf based on the theory of wind flow boundary layer. Processes 10(5) (2022).
Fu, X. et al. Study on coal pulverization characteristics and gas desorption mechanism based on impact crushing experiment. Heliyon 10(10) (2024).
Zhang, J. G. et al. Study on changes in pore pressure and temperature during coal and gas outburst stimulated by mining-induced stress. J. China Coal Soc. 1377 (2023).
Meng, Y. & Li, Z. P. Experimental study on diffusion property of methane gas in coal and its influencing factors. Fuel 185, 219–228 (2016).
Michael, V. On void aerodynamics in a porous media of a gob area. In Elena Source: Proceedings of the 7th US Mine Ventilation Symposium, 275–280 (1995).
Michaylov, M. & Vlasseva, E. U. O. M. On void aerodynamics in a porous media of a gob area, United States, 1995 (Society for Mining, Metallurgy, and Exploration, Inc., 1995).
Bi, S. et al. Study on the model and law for radial leakage of drilling fluid in fractured formations. ACS Omega. 7(44), 39840–39847. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega (2022).
Chen, X. et al. Research on expansion property of inorganic hole sealing material of coal mine. Mater. Res. Innovations. 19(sup8), S8–142 (2015).
Guo, X. et al. Experimental research on performance of new gas drainage boreholesealing material with high fluidity. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2021 (2021).
Niu, X. The Research on Sealing Technology of the Angle in Full Mechanized Coal Face with High Gas 15–25 (Anhui University of Science & Technology, 2015).
Zhang, J. X. et al. Experimenta1-study and application of new polymer foam plugging material. J. China Coal Soc. 43 (S1), 158–166 (2018).
Kaczmarek, B. Improving sodium alginate films properties by phenolic acid addition. Materials 13(13) (2020).
Song, R. et al. Preparation and properties of α-Co(OH) 2 /SA nanofiltration membranes with a brick and mortar biomimetic structure. Separ Purif. Technol. 345 (2024).
Zhou, H. et al. Fabrication and evaluation of calcium alginate/calcium polyphosphate composite. Mater. Lett. 180, 184–187 (2016).
Xu, Y. & Xiong, F. Development of instantly forming membrane dust suppressant for construction sites. Saf. Environ. Eng. 22(04), 94–98 (2015).
Li, H. K. et al. Ca2+, Fe3+ co-crosslinked tannic acid-bridged sodium alginate gel membrane for organic solvent nanofiltration. Separ Purif. Technol. 350 (2024).
Deng, S. N. et al. Deep removal of COS by carbon aerogel in natural gas: a 3D network structure of nitrogen doped and Cu based adsorbent. Separ Purif. Technol. 342 (2024).
Lambertini, L. et al. Poly (vinyl alcohol) gels cross-linked by boric acid for radiation protection of astronauts. Acta Astronaut. 221, 142–154 (2024).
Bialik-Was, K., Królicka, E. & Malina, D. Impact of the type of crosslinking agents on the properties of modified sodium alginate/poly (vinyl alcohol) hydrogels. Molecules 26(8) (2021).
Chen, J. et al. Preparation and characterization of graphene oxide reinforced PVA film with boric acid as crosslinker. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 132(22) (2015).
Gadhave, R., Mahanwar, P. & Gadekar, P. Study of cross-linking between boric acid and different types of polyvinyl alcohol adhesive. Open. J. Polym. Chem. 9, 16–26 (2019).
Zhang, H., Zhao, H., Ji, D., Jing, S. & Guo, Y. Gas control technology for coal and gas outburst mines based on new sealing materials. Geohazard Mech. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ghm.2024.04.004
Peng, Z., Zhang, C. & Li, F. A laboratory study on a PVA gel plugging agent. Nat. Gas. Ind. 37(06), 72–78 (2017).
Sun, F. Study on the Preparation and Properties of New Polyvinyl Alcohol Gel Sealing Material for Mining 9–13 (China University of Mining and Technology, 2021).
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Deep Earth Probe and Mineral Resources Exploration-National Science and Technology Major Project(2024ZD1004503),the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51474220), the National Natural Science Foundation of Gansu(24JRRD003), S&T Program of Hebei (23567602 H).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Zhao, Li, Zhang were all involved in the writing of the manuscript. Zhao mainly provided research ideas and research innovations. Directed some of the experiments.Li was primarily involved in data processing for the manuscript and in field engineering applications.Zhang performed mainly experimental design and experimental data processing, graphics processing and some engineering field work.All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, H., Li, Z. & Zhang, H. Research and application of high gas coal seam air leakage control technology based on polymer material cross-linking mechanism. Sci Rep 15, 10260 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-83527-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-83527-9