Abstract
Papillary thyroid cancer (PTC) typically has a favorable prognosis. However, in some cases, the presence of angioinvasion can result in local invasion, recurrence, and distant metastasis, leading to poorer outcomes. Identifying disrupted pathways associated with angioinvasion could lead to the discovery of novel angioinvasive markers in PTC, which, in turn, may suggest more aggressive clinical management strategies, as radioiodine therapy (RAI). This study aims to identify potential markers associated with angioinvasive PTC, with a particular focus on nitrosative stress and endothelial damage. For the purpose of this study, 45 patients with angioinvasive PTC (study group) and 45 patients without angioinvasion and characterized by a very low risk of cancer progression (reference group) were enrolled. We assessed the levels of total antioxidant capacity (TAC), 3-nitrotyrosine (3-NT), placental growth factor (PLGF), integrin subunit alpha V (ITGAV), and integrin subunit alpha V beta 3 (ITGαVβ3) as potential markers for angioinvasion. Our results revealed significant alterations in the concentration patterns of these markers, suggesting their potential utility as screening tools for angioinvasion and as prognostic indicators in PTC patients. Specifically, elevated levels of 3-NT, PLGF, ITGAV, and ITGαVβ3 were observed, while TAC levels were decreased in the study group compared to the reference group (all, p < 0.05). Logistic regression analysis confirmed a significant association of TAC, 3-NT, and PLGF with the occurrence of angioinvasion. PLGF demonstrated an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.82, indicating its clinical significance. However, to enhance screening utility for clinical management, a panel consisting of 3-NT, TAC, and PLGF assessments was created, demonstrating the highest potential utility as an angioinvasion screening tool (3-NT + TAC + PLGF AUC = 0.95).
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Thyroid cancer ranks as the fifth most prevalent type of malignancy worldwide, with an estimated annual incidence of over 62,000 new cases. Among thyroid tumors, differentiated thyroid cancers (DTC) predominate in nearly 90% of cases, with papillary thyroid cancer (PTC) comprising the largest subgroup1. PTC incidence has been steadily rising over the past few decades, making it one of the fastest-growing cancers worldwide2. PTC originates from the follicular epithelium and typically exhibits a favorable prognosis with a high survival rate. However, a subset of patients presents with more aggressive disease progression, often associated with angioinvasion and the occurrence of metastasis Angioinvasion, the infiltration of tumor cells into blood vessels, serves as a crucial step in tumor progression and metastasis. It correlates with increased tumor aggressiveness, recurrence rates, and diminished overall survival3,4,5,6. Thus, recognizing biomarkers associated with angioinvasion carries significant clinical implications as can guide the implementation of more aggressive therapeutic strategies which could improve patient outcomes3,7,8,9. Nitric oxide (NO) is a reactive signaling molecule involved in the regulation of vascular tone, produced by different isoforms of nitric oxide synthase (NOS), including the inducible (iNOS), endothelial (eNOS), and neuronal (nNOS) forms10. Thus, reactive nitrogen species (RNS) generated during carcinogenesis can also instigate DNA damage, promote tumor cell proliferation, and stimulate angiogenesis especially under decreased total antioxidant capacity (TAC) conditions8. RNS, such as peroxynitrite, attack both free and protein-bound tyrosines, resulting in the formation of 3-nitrotyrosine (3-NT). Consequently, 3-NT is a useful biomarker for assessing nitrosative stress11. Based on prior studies in PTC and other cancer types, we hypothesize that nitrosative stress, may contribute to endothelial dysfunction, integrin activation, and angiogenic signaling. This cascade could promote vascular invasion of PTC cells, facilitating metastasis9. Markers of endothelial damage, such as placental growth factor (PLGF), integrin subunit alpha V (ITGAV), and integrin subunit alpha V beta 3 (ITGαVβ3), may be elevated due to the increased oxidative stress observed in more invasive cases of PTC12,13. This complex system may contribute to the process of cancer development and represents a promising target for anticancer therapies and novel screening biomarkers development14,15. While direct studies in angioinvasive PTC are limited, research by Donckier et al., Patel et al., and Nakamura et al. provides a basis for exploring these relationships in PTC-specific settings9,10,14,15,16. Donckier et al. demonstrated overexpression of NOS isoforms and angiogenic factors such as VEGF in PTC tissues, supporting the involvement of nitric oxide pathways in PTC progression14. Similarly, Nakamura et al. reported that nitrotyrosine, a marker of nitrosative stress, correlates with VEGF-D expression and lymph node metastasis in PTC15. PLGF has been shown to promote metastasis in thyroid carcinoma tissues, as evidenced by He et al., while integrins such as ITGAV and ITGαVβ3 have been linked to PTC aggressiveness and metastatic potential in the study of Mautone et al.17,18. These findings provide a literature-based foundation for exploring the role of these markers in angioinvasion risk assessment in PTC16,17. Thus, this study focuses on 3-NT, TAC, PLGF, ITGAV, and ITGαVβ3 due to their involvement in potential PTC angiogenesis. By analyzing the expression levels of these proteins in PTC patients with and without angioinvasion, we aim to elucidate the mechanisms associated with PTC aggressiveness and identify potential biomarkers for clinical screening and management. This study has the potential to refine PTC risk stratification, optimize treatment selection, and enhance prognosis assessment, ultimately improving clinical outcomes and quality of life for PTC patients.
Material and methods
This study was carried out at the Department of Endocrinology, Diabetology, and Internal Diseases, Medical University of Bialystok, Poland. The procedures were approved by the Local Ethics Committee of the Medical University of Bialystok, Poland, and written informed consent was obtained from each participant (APK.002.7.2024).
Studied population
Patients were enrolled between January 2018 and December 2023 at the Department of Endocrinology, Diabetology and Internal Medicine Medical University of Bialystok. In this extensive investigation, a total of 300 patients diagnosed with PTC were enrolled. For the specific objectives of this study, we opted to exclusively include individuals with clear indications of angioinvasion. Inclusion criteria were: age 18–75 years, histologically confirmed PTC, no evidence of distant metastasis. Exclusion criteria included: concurrent Hashimoto’s thyroiditis or other thyroid pathologies, prior or concurrent malignancies, history of chronic treatments, significant comorbidities such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes, autoimmune disorders, or chronic inflammatory diseases, as well as conditions that could alter oxidative or nitrosative stress markers, such as recent infections or surgeries. Our selection criteria were designed to maintain homogeneity within the study cohort. None of the patients were undergoing medication regimens or had any other underlying conditions that could potentially affect peripheral oxidative stress or similar factors. Prior to study enrollment, patients provided confirmation that they had not adhered to restrictive diets, used tobacco products, consumed alcohol, or engaged in excessive physical activity. The presence of comorbidities was also excluded in qualified patients. Consequently, 45 patients diagnosed with angioinvasive PTC were included in the study group, while another 45 patients with PTC assessed as very low risk were chosen as the reference group. Tumor staging was performed according to the cancer tumor-node-metastasis (TNM) classification, and relevant clinicopathological details, including tumor size, multifocality, and lymph node involvement are provided in Table 1. All patients were included in the study post-thyroidectomy, and angioinvasion was confirmed via histopathological examination. Venous blood samples (5.5 mL) were collected post-thyroidectomy and centrifuged to separate serum, which was then frozen at − 80 °C for further analysis. After blood collection, through the interdisciplinary team evaluation, all patients in the study group were qualified for radioiodine therapy (RAI), while patients in the reference group were placed under active surveillance in accordance with the American Thyroid Association (ATA) and local guidelines19,20.
Biochemical measurement
The enzymatic colorimetric method on a Roche C111 device (Roche Diagnostics, Basel, Switzerland) was utilized to assay serum concentrations of triglycerides (TG), low-density lipoprotein (LDL), high-density lipoprotein (HDL), cholesterol (CHOL), and C-reactive protein (CRP). Meanwhile, serum concentrations of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), free triiodothyronine (fT3), free thyroxine (fT4), thyroglobulin (TGB) and antithyroglobulin antibody (TGBAb) were measured using the electrochemiluminescence (ECLIA) method on a Roche E411 device (Roche Diagnostics, Sussex, UK).
The total antioxidant capacity (TAC) status was determined by photometric assay (ImAnOx (TAS/TAC) Kit, KC5200, 64,625 Bensheim, Germany). Human ITGαVβ3 ELISA Kit (FineTest, EH3080, Wuhan, 430,074, Hubei, China) was employed to determine the levels of ITGαVβ3 in serum samples. Following, the Human ITGAV ELISA Kit (FineTest, EH0815, Wuhan, 430,074, Hubei, China) was used to assess the levels of ITGAV. Additionally, the concentration of PLGF was evaluated using the PLGF ELISA Kit (Human) (AVIVA SYSTEMS BIOLOGY, OKBB00242, San Diego, CA 92,121 USA). Finally, the concentration of 3-NT as a marker of nitrosative stress was examined using the 3-NT ELISA Kit (FineTest, EU2560, Wuhan, 430,074, Hubei, China). All of these markers concentrations were determined using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA).
Statistical analysis
Statistical analyses were conducted using version 9.0 of the GraphPad Prism software, developed by GraphPad Software Inc. (San Diego, CA, USA)21. Initially, the Shapiro–Wilk test was conducted to assess the normality of the investigated parameters. It was observed that the studied parameters did not exhibit a normal distribution. As a result, nonparametric tests were employed to compare the statistical differences between the groups. The data were presented as the range and median values. The Mann–Whitney test for independent groups was utilized to evaluate the significant differences in clinical parameters among the studied patients, with a significance level set at p < 0.05.
Moreover, in order to discern whether the markers of nitrosative stress and endothelial damage stem from the tumor or represent a systemic phenomenon triggered by peripheral processes, simple logistic regression analysis was conducted. Additionally, to assess the screening usefulness, receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves were constructed, and the area under the ROC curves (AUC) was scrutinized for examined parameters. The combined screening model’s utility was assessed via multiple logistic regression analysis with calculating AUC through ROC curve designation. Additionally, odds ratios (ORs) were calculated to further evaluate the clinical relevance of the analyzed markers.
Results
To investigate our hypothesis, we categorized the PTC patient cohort into two distinct subgroups. The first subgroup comprised individuals displaying angioinvasion (referred to as the study group), while the second subgroup consisted of PTC patients without this characteristic (referred to as the reference group). In accordance with the 2015 American Thyroid Association guidelines, the reference group was identified as representing the very low-risk PTC.
Biochemical characteristics of the PTC patients
Significant elevations in TGB, TGBAb, CHOL, and LDL concentrations were noted in the study group in comparison to the reference group (p < 0.05; p < 0.05; p < 0.05; p < 0.001; respectively). Conversely, no significant differences were observed among the groups for other parameters, as outlined in Table 2 (p > 0.05).
Nitrosative stress profiling among PTC patients
3-NT
The analysis results revealed that the study group exhibited higher serum levels of 3-NT observed compared to the reference group (p = 0.003) (Table 3; Fig. 1).
TAC evaluation
Upon evaluating parameters related to oxidative stress capacity, notable disparities were detected in the measurements of TAC (p = 0.004) between the study group, defined by the presence of angioinvasion, and the reference group (Table 3; Fig. 1).
Markers of endothelial damage
In the examination of endothelial damage markers, significant variations were observed in the levels of PLGF (p < 0.001) and ITGAV with ITGαVβ3 (p = 0.016; p < 0.001, respectively) between the study group, characterized by angioinvasion occurrence, and the reference group (Table 3; Fig. 1).
Logistic regression profiling of the examined parameters
Additionally, in order to ascertain whether the oxidative stress markers stem from the cancer itself or result from systemic processes triggered by the disease, logistic regression analysis was conducted. Our findings revealed a significant association between angioinvasion and the concentrations of TAC, 3-NT and PLGF. Based on simple logistic regression findings, we developed a logistic regression model using the simultaneous assessment of TAC, 3-NT, and PLGF creating multiple logistic regression model associated with angioinvasion occurrence (Table 4).
The clinical utility
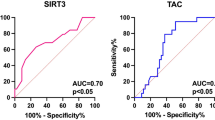
To assess the significance of TAC, PLGF, ITGAV with ITGαVβ3 in angioinvasion screening in PTC patients, the ROC curve analysis was performed. The highest screening utility was presented for PLGF (AUC = 0.82), 3-NT (AUC = 0.70), ITGαVβ3 (AUC = 0.71), TAC (AUC = 0.69), ITGAV (AUC = 0.66) respectively (all p < 0.05) (Fig. 2). Furthermore, a logistic regression model incorporating assessments of 3-NT, TAC, and PLGF was constructed, demonstrating the highest screening utility (AUC = 0.95 for 3-NT + PLGF + TAC) (Fig. 3).
Correlations
Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient was employed to analyze all correlations within the entire patient cohort, aiming to discern relationships with thyroid cancer occurrences. The analysis uncovered significant positive correlations between TAC levels and concentrations of 25-OH vit D (r = 0.34, p < 0.02). Conversely, significant negative correlations were observed between TAC levels and concentrations of LDL, 3-NT, and TGBAb (r = − 0.22, r = − 0.74, r = − 0.3; all p < 0.05, respectively). Furthermore, significant positive correlations were found between 3-NT levels and concentrations of TGB (r = 0.41, p = 0.03) and TGBAb (r = 0.39, p = 0.02). Conversely, a significant negative correlation was noted between 3-NT levels and 25-OH vit D (r = − 0.43, p = 0.01). Additionally, significant positive correlations were identified between PLGF levels and concentrations of TGBAb (r = 0.32, p = 0.04) and TGB (r = 0.41, p = 0.03). Moreover, the analysis revealed a significant negative correlation between ITGAV levels and the concentration of 25-OH vit D (r = − 0.56, p = 0.01), along with a positive correlation between ITGAV levels and ITGαVβ3 (r = 0.78, p < 0.001). Lastly, significant positive correlations between ITGαVβ3 levels and concentrations of TGBAb (r = 0.43, p = 0.02), FT3 (r = 0.33, p = 0.04), and 3-NT (r = 0.49, p = 0.01) were observed.
Discussion
Despite considerable advancements in diagnostic tools and therapeutic interventions for PTC, identifying more aggressive forms of the disease—characterized by angioinvasion and requiring more intensive treatment approaches—remains a persistent clinical challenge7,22. Angioinvasion, defined as the invasion of blood vessels by cancer cells, along with increased levels of oxidative stress, has been identified as significant independent prognostic factors in various types of cancer, including PTC6,7. Thus, thyroid gland utilizing hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) for thyroid hormone production, becomes particularly susceptible to oxidative imbalance23. Even minor disruptions in the balance between ROS synthesis and antioxidant mechanisms in thyroid cells can negatively impact hormone production in PTC patients, while concurrently favoring the progression of angioinvasion24. Studies have shown that increased ROS synthesis promotes PTC angiogenesis, both directly and through the generation of active oxidation products, including peroxidized lipids6. In angioinvasive PTC clinical management, key therapeutic modalities include thyroidectomy and RAI. In our previously performed study, the concentration of malondialdehyde (MDA) in patients with PTC undergoing RAI therapy were assessed. MDA, as a major lipid peroxidation product and oxidative stress marker, was found to be elevated in these patients, along with an observable increase in MDA levels following RAI therapy6. Therefore, in the following study, various oxidative stress markers and proteins associated with the process of angioinvasion in PTC, such as total oxidative capacity (TOC), MDA, 8-hydroxy-2'-deoxyguanosine (8-OHdG) and sortilin were evaluated. Our results suggest that oxidative stress-related markers may be useful in identifying patients with angioinvasive PTC7,8. Our study revealed that oxidative stress-related markers may serve as additional criteria for determining the suitability of RAI treatment in PTC patients. Furthermore, our previously conducted studies strengthen the understanding of the role of oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of angioinvasion in PTC, consistent with the findings reported by Muzza et al., where increased oxidative stress was correlated with more aggressive features of thyroid cancer.13. Monitoring oxidative stress-related processes could support the implementation of personalized medicine approaches, tailoring treatment strategies to individual patient profiles6. Therefore, prompt initiation of treatment, especially among patients with angioinvasive PTC, results in reduced risk of cancer progression. Building on these findings and drawing from existing literature data, identifying patients with angioinvasive PTC remains a crucial aspect of clinical management25,26. In accordance with the 2015 American Thyroid Association guidelines, patients presenting with angioinvasive PTC should be advised to undergo more aggressive therapeutic interventions, with treatment extended intraoperatively until the desired outcomes are achieved27. However, the lack of definitive screening markers presents an additional challenge in clinical practice, as the diagnosis of angioinvasion is made postoperatively, thereby prolonging and complicating therapeutic decision-making19.
While previous studies have focused primarily on genetic alterations such as BRAF V600E and TERT promoter mutations as markers of aggressiveness in PTC28, our study provides a complementary perspective by exploring systemic biochemical markers of nitrosative stress endothelial damage markers. The connection between nitrosative stress and angioinvasion in PTC remains an emerging area of investigation. Our study bridges this gap by exploring how markers such as 3-NT, PLGF, and integrins may reflect or contribute to angioinvasive potential. While the rationale is partly extrapolated from other cancers, these findings lay the groundwork for further mechanistic research in PTC. The results demonstrated that angioinvasion in PTC is associated with elevated levels of 3-NT, decreased TAC, and increased levels of endothelial damage markers, such as PLGF, ITGAV with ITGαVβ3. Consistently, our finding of elevated levels of 3-NT in PTC patients with angioinvasion aligns with the conclusions drawn by Lopes et al., who investigated the roles of nitrosative stress and inflammatory markers in patients with PTC and Hashimoto’s thyroiditis (HT), exploring the potential correlation between these two conditions. The study concluded that PTC is associated with pronounced nitrosative stress potentially contributing to elevated activity of cell proliferation and increased levels of angiogenesis markers, especially in the absence of concurrent HT. These findings suggest that nitrosative stress and inflammation significantly contribute to the PTC formation. Nevertheless, the presence of HT seemed to further modulate these factors, potentially influencing the aggressiveness and progression of PTC, hypothetically having an even greater impact on the increase in nitrosative stress29. The subsequent study, Donckier et al. explored the role of nitric oxide (NO) and endothelin-1 (ET-1) in PTC, focusing on their relationship with angiogenic factors. NOS2 and NOS3 were significantly overexpressed in PTC cells compared to normal tissue, with mRNA levels elevated by 2.6-fold and 4.2-fold, respectively (p < 0.02). Angiogenic markers, including VEGF, VEGFR-1, VEGFR-2, angiopoietin-2, and Tie2, were also upregulated (p < 0.05), and ET-1 expression correlated with NOS2, angiopoietin-1, and angiopoietin-2. These findings suggest that the NO pathway, in coordination with ET-1 and angiogenesis, plays a key role in PTC progression and could serve as a therapeutic target30. Therefore, Patel et al. also investigated the role of NO in thyroid tumors from children and adolescents, focusing on its production and relationship with tumor growth and vascularization. In that study nitrotyrosine (N-TYR), inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), and endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) levels in 41 PTC, 9 follicular thyroid carcinomas (FTC), and 15 benign thyroid lesions were analyzed. Results showed significantly increased staining for N-TYR, iNOS, and eNOS in benign adenomas, PTC, FTC, and autoimmune thyroid lesions compared to surrounding normal thyroid tissue (p < 0.01). N-TYR levels also correlated with vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) expression (r = 0.36, p = 0.007) and lymphocyte density (r = 0.39, p = 0.004). Recurrent disease occurred only in cases with moderate-to-intense N-TYR staining, suggesting a potential link to tumor aggressiveness, although statistical significance was not reached. The findings suggest that NO plays a role in the vascularization of thyroid tumors and autoimmune thyroid diseases, potentially contributing to tumor growth and progression31. In the following study, by Nakamura et al. examined the role of NO in PTC, focusing on its regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor-D (VEGF-D) and its link to lymph node metastasis. In K1 PTC cells, NO donors significantly increased VEGF-D production, while NO synthesis inhibition blocked this effect, demonstrating a direct connection between NO and VEGF-D. In human PTC samples, high nitrotyrosine levels, a marker of NO activity, were observed in 51.8% of cases and correlated with VEGF-D expression and lymph node metastasis. These findings highlight NO’s role in promoting metastasis via VEGF-D, suggesting potential therapeutic targets in NO-related pathways. Moreover, the formation of NO biomarker, nitrotyrosine, was also correlated with VEGF-D expression in human PTC, therefore suggesting potential screening utility15.
To the best of our knowledge, there is still limited literature data focusing on the evaluation of nitrosative stress in thyroid cancer pathogenesis. However, nitrosative stress has been evaluated in various other cancer conditions, indicating the role of nitration stress in the development of angioinvasion. The study conducted by Galiniak et al. aimed to investigate the status of oxidative/nitrosative stress and its role in the development and progression of clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC), demonstrated that in patients with angioinvasion, nitrate/nitrite and MDA levels were significantly elevated compared to results obtained among patients without angioinvasion. Additionally, nitrosative and oxidative stress increased with the progression of the disease, as assessed by TNM classification and histological grade. This study highlights the significant role of oxidative/nitrosative stress in the development and progression of ccRCC, underlining the need for further research into nitrosative stress-related marker evaluation, which could designate the high risk patients with angioinvasion32. In the study conducted by Dorf et al., aimed at evaluating nitrosative stress and protein glycoxidation in patients diagnosed with gastric cancer compared to healthy controls, elevated levels of parameters related to nitrosative stress and protein glycoxidation were observed in patients with gastric cancer compared to healthy controls. Specifically, there were significant increases in markers such as NO, S-nitrosothiols, 3-NT, kynurenine, N-formylkynurenine, dityrosine, advanced glycation end products (AGE). The study also aimed to assess the diagnostic efficacy of these markers in distinguishing between gastric cancer patients based on various histopathological classifications and parameters. The results suggest that nitrosative stress and protein glycoxidation markers may be useful in diagnosing gastric cancer, demonstrating high sensitivity and specificity with received high AUC values in differentiating patients with cancer from healthy individuals33.
The simple logistic regression analysis has also demonstrated a significant association between angioinvasion and the concentrations of TAC, 3-NT, and PLGF. Moreover, the ROC curve analysis has highlighted the clinical utility of PLGF, 3-NT, ITGαVβ3, TAC, and ITGAV as screening tools for high risk of angioinvasion assessment. Particularly, PLGF has emerged as the most promising marker with the highest screening utility, followed by 3-NT, ITGαVβ3, TAC, and ITGAV, respectively. In the study performed by He et al., PLGF has also been shown to play crucial role in the pathological angiogenesis through regulating matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), contributing to the metastasis of thyroid carcinoma development34. In that study, a strong correlation was observed between PLGF and matrix metalloproteinase 9 (MMP9) levels in thyroid carcinoma specimens, with higher levels detected in cases exhibiting metastasis. Moreover, antagonizing PLGF in thyroid carcinoma cells may hold promise as a therapeutic strategy to suppress cancer metastasis, confirming the specificity of PLGF elevation in angioinvasive thyroid cancer34.
Integrins, such as ITGAV and ITGαVβ3, are cell-extracellular matrix adhesion molecules considered functionally related to the development of cancer metastasis. In the study conducted by Mautone et al., the presence of a PTC-specific integrin expression signature was evaluated in correlation with histopathology, specific driver gene mutations, and the aggressiveness of the disease. The study revealed that the PTC variants known as “classical” and “tall cell” exhibit a similar integrin expression pattern, contrasting with the “follicular” variant. Notably, the presence of the BRAFV600E mutation correlated with elevated integrin expression compared to RAS mutations. Additionally, the integrin subunit ITGA3 showed links to advanced disease stage, lymph node metastasis, extrathyroidal extension, high-risk, and poorer prognosis18. During in vitro experiments with PTC cell lines, Mautone et al., underscored the involvement of α3β1 integrin in cell motility and invasion, reinforcing its significance in tumor advancement18. During tumorigenesis and metastasis, integrins regulate localization and activity of proteolytic enzymes that remodel the extracellular matrix. Previous studies have demonstrated blocking of αVβ3 to effectively inhibit proliferation, angiogenesis, and the survival of various cancer cell types35. Assessing concentrations of different integrins may serve as useful predictors of treatment response and outcomes in PTC patients, as demonstrated in the results obtained in this study.
For enhanced screening efficacy in this study, a logistic regression model integrating assessments of 3-NT, TAC, and PLGF was developed, demonstrating the highest screening performance (AUC = 0.95 for 3-NT + PLGF + TAC). This model shows comparable high AUC values to those reported in a previous study, where TAC, 8-OHdG and sortilin were combined into a similar screening panel (TAC + 8-OHdG + sortilin AUC = 0.96)8. Therefore, concentrations of 3-NT, TAC, and PLGF appear to be robust predictors in this study’s context, potentially serving as valuable biomarkers for screening and prognostic purposes related to angioinvasive patients management.
Accordingly, correlation analysis regarding the onset of thyroid cancer angiogenesis holds crucial significance in comprehending the pathophysiological mechanisms associated with tumor development and its capability to invade blood vessels. Positive correlations observed in this study between 3-NT levels and the concentrations of TGBAb and TGB suggest a potential association between nitration stress and the angioinvasive thyroid cancer. This finding is significant as it indicates the possible role of nitration stress in the disease’s pathogenesis and its correlation with commonly use PTC post-operative predictive markers36. This connection underscores the relevance of nitration stress as a potential key pathomechanistic contributor to disease progression and highlights its utility in enhancing the accuracy of prognostic assessments. The significance of positive correlations between PLGF levels and the concentrations of TGBAb and TGB also implies a potential role of this growth factor in the immunological processes related to thyroid cancer and further recurrence of PTC and may enhance screening utility37. This finding also suggests that PLGF may play a role in the mechanisms driving PTC recurrence, further underscoring its importance as a biomarker and potential therapeutic target in disease management. This observation aligns with the results obtained by He et al., who demonstrated that thyroid carcinoma cells produce PLGF to promote metastasis34.Additionally, the identification of negative correlations between vitamin D levels, TAC, and ITGAV highlights the potential impact of vitamin D deficiency on promoting angioinvasion, potentially as a result of decreasing antioxidant capacity. Vitamin D supplementation could potentially lead to an increase in TAC, enhancing the body’s antioxidant capacity and potentially mitigating angioinvasion by reducing integrin concentrations and decreasing 3-NT levels38. This area warrants further investigation due to its potential significant clinical implications for disease prevention and therapy. However, clear recommendations regarding the use of vitamin D supplementation for the prevention of thyroid cancer and angioinvasion have not yet been established39. Moreover, consistent with our previous findings3,6,40, in this study we observed significant alterations in the biochemical profiles of PTC patients with angioinvasion compared to those without. The elevated levels of TGB, TGBAb, CHOL, and LDL in the study group corroborate the association between lipid metabolism dysregulation and angioinvasion in PTC, as previously reported6,7,8. This association underscores the potential utility of lipid metabolism markers in identifying high-risk PTC patients and highlights the growing field of lipidomics, which is currently being explored to discover additional biomarkers for cancer progression and angioinvasion41 and targeted therapeutic interventions29. The assessment of oxidative stress parameters revealed significantly lower TAC levels in the study group compared to the reference group, reinforcing the clinical relevance of reduced TAC as a potential contributor to angioinvasion in PTC. This finding aligns with our prior studies, which similarly identified diminished antioxidant defense as a factor associated with more aggressive disease behavior and endothelial damage, further implicating oxidative stress in the progression of angioinvasive PTC3,7,8,9,40.
It is important to acknowledge that the present study is exploratory and based on a relatively small sample size (n = 45 per group). Although the statistical analyses, including logistic regression and ROC curve assessments, revealed significant associations between 3-NT, TAC, PLGF, and angioinvasion, these results should be interpreted with caution. The findings provide initial insights into potential markers for angioinvasion risk in PTC, but external validation in independent, larger cohorts is necessary to confirm these observations. Furthermore, future studies should incorporate multivariate models that adjust for confounding variables such as age, sex, tumor stage, lipid profile, and comorbidities to strengthen the robustness of the conclusions. It is important to note that this study does not include data on RAI response, disease-free survival (DFS), or recurrence rates41,42. Therefore, the potential use of the proposed biomarker panel to guide RAI qualification or therapeutic decision-making should be considered as a suggestion based on the observed associations between the markers and angioinvasion—a recognized histopathological risk factor for poor prognosis in PTC. The current findings are preliminary and hypothesis-generating, and they highlight the need for future prospective studies incorporating long-term follow-up, clinical outcomes, and survival analysis to validate the prognostic and predictive utility of the panel43,44. A following limitation of this study is the lack of tissue-level validation (e.g., IHC, RT-PCR) to confirm the expression and localization of the proposed markers in PTC tissues. We also acknowledge the limited PTC-specific mechanistic data directly linking nitrosative stress and angioinvasion. Our findings should be interpreted as exploratory, providing a basis for future studies employing experimental models to test causality. Nevertheless, by integrating our results with previously conducted research, we contribute to a more profound understanding of the PTC aggressiveness. This study provides additional evidence for the role of nitrosative stress, endothelial damage, and their interplay in the pathogenesis of angioinvasion in PTC.
Conclusions
The recognition of angioinvasion markers as prognostic factors in individuals diagnosed with PTC has significant implications for improving treatment outcomes through personalized clinical management. Our study highlights the role of specific biomarkers associated with nitrosative stress and endothelial damage in angioinvasive PTC. Markers of nitrosative stress, such as 3-NT, and endothelial damage markers, including PLGF, ITGAV, and ITGαVβ3, exhibited significant alterations in their levels among PTC patients with angioinvasion compared to those without. Additionally, concentrations of 3-NT, TAC, and PLGF emerged as robust predictors in this study, potentially serving as a valuable panel for screening and prognostic purposes related to angioinvasion management. The combination of these biomarkers demonstrated high predictive power (AUC = 0.95) for identifying angioinvasion, which could aid in the detection and management of PTC during RAI qualification. This panel assessment may prove instrumental in treatment planning by identifying patients at higher risk for disease progression and poorer outcomes. Moreover, integrating these biomarkers into clinical practice could facilitate more personalized treatment strategies for PTC patients, ultimately enhancing patient management and outcomes. Future studies should include larger cohorts, external validation, and integration with clinical outcomes such as RAI response and survival rates.
Data availability
The datasets analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Limaiem, F., Rehman, A., Mazzoni, T., Anastasopoulou, C. & Mazzoni, T. Papillary thyroid carcinoma. StatPearls.
Albores-Saavedra, J., Henson, D. E., Glazer, E. & Schwartz, A. M. Changing patterns in the incidence and survival of thyroid cancer with follicular phenotype—papillary, follicular, and anaplastic: A morphological and epidemiological study. Endocrine Pathol. 18(1), 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12022-007-0002-z (2007).
Buczyńska, A. et al. Clinical significance of oxidative stress markers as angioinvasion and metastasis indicators in papillary thyroid cancer. Sci. Rep. 13, 13711. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-40898-9 (2023).
Furlan, J. C., Bedard, Y. C. & Rosen, I. B. Clinicopathologic significance of histologic vascular invasion in papillary and follicular thyroid carcinomas. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 198, 341–348. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2003.11.012 (2004).
Metere, A. et al. A possible role for selenoprotein glutathione peroxidase (GPx1) and thioredoxin reductases (TrxR1) in thyroid cancer: Our experience in thyroid surgery. Cancer Cell Int. 18, 7. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12935-018-0504-4 (2018).
Buczyńska, A. et al. Oxidative stress and radioiodine treatment of differentiated thyroid cancer. Sci. Rep. 11, 17126 (2021).
Buczyńska, A., Kościuszko, M., Krętowski, A. J. & Popławska-Kita, A. Exploring the clinical utility of angioinvasion markers in papillary thyroid cancer: A literature review. Front. Endocrinol. 14, 1261860. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2023.1261860 (2023).
Buczyńska, A. et al. Enhancing angioinvasion assessment in papillary thyroid cancer via a biomarker panel involving TAC, 8-OHdG and Sortilin. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metabol. 109(7), 1866–1872. https://doi.org/10.1210/CLINEM/DGAE007 (2024).
Kościuszko, M., Buczyńska, A., Krętowski, A. J. & Popławska-Kita, A. Could oxidative stress play a role in the development and clinical management of differentiated thyroid cancer?. Cancers 15, 3182. https://doi.org/10.3390/CANCERS15123182 (2023).
Patel, A. et al. Nitrotyrosine, inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), and endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) are increased in thyroid tumors from children and adolescents. J. Endocrinol. Invest. 25, 675–683. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03345100/METRICS (2002).
Ahsan, H. 3-Nitrotyrosine: A biomarker of nitrogen free radical species modified proteins in systemic autoimmunogenic conditions. Hum. Immunol. 74, 1392–1399. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.HUMIMM.2013.06.009 (2013).
Tronci, L. et al. Crosstalk between metabolic alterations and altered redox balance in PTC-derived cell lines. Metabolites 9, 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/METABO9020023 (2019).
Muzza, M. et al. Oxidative stress correlates with more aggressive features in thyroid cancer. Cancers 14, 5857. https://doi.org/10.3390/CANCERS14235857 (2022).
Donckier, J. E., Michel, L., Delos, M., Havaux, X. & Van, B. R. Interrelated overexpression of endothelial and inducible nitric oxide synthases, endothelin-1 and angiogenic factors in human papillary thyroid carcinoma. Clin. Endocrinol. 64, 703–710. https://doi.org/10.1111/J.1365-2265.2006.02535.X;PAGE:STRING:ARTICLE/CHAPTER (2006).
Nakamura, Y. et al. Nitric oxide in papillary thyroid carcinoma: induction of vascular endothelial growth factor d and correlation with lymph node metastasis. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 91, 1582–1585. https://doi.org/10.1210/JC.2005-1790 (2006).
Dorf, J. et al. Could circulating biomarkers of nitrosative stress and protein glycoxidation be useful in patients with gastric cancer?. Front. Oncol. 13, 1213802. https://doi.org/10.3389/FONC.2023.1213802/BIBTEX (2023).
He, J., Shen, N. & Huang, X. Thyroid carcinoma cells produce PLGF to enhance metastasis. Tumor Biol. 36, 8601–8607. https://doi.org/10.1007/S13277-015-3548-2/METRICS (2015).
Mautone, L. et al. Higher integrin alpha 3 beta1 expression in papillary thyroid cancer is associated with worst outcome. Cancers 13, 2937. https://doi.org/10.3390/CANCERS13122937/S1 (2021).
Jarząb, B. et al. Diagnosis and treatment of thyroid cancer in adult patients - Recommendations of Polish Scientific Societies and the National Oncological Strategy. 2022 Update. Endokrynol. Pol. 2022(73), 173–300. https://doi.org/10.5603/EP.a2022.0028 (2022).
Nguyen, Q. T. et al. Diagnosis and treatment of patients with thyroid cancer. Am. Health Drug Benefits 8(1), 30 (2015).
Mitteer, D. R. & Greer, B. D. Using GraphPad Prism’s heat maps for efficient, fine-grained analyses of single-case data. Behav. Anal. Pract. 15, 505–514. https://doi.org/10.1007/S40617-021-00664-7 (2022).
Papp, S. & Asa, S. L. When thyroid carcinoma goes bad: A morphological and molecular analysis. Head Neck Pathol. 9, 16–23. https://doi.org/10.1007/S12105-015-0619-Z (2015).
Szanto, I., Pusztaszeri, M. & Mavromati, M. H2O2 metabolism in normal thyroid cells and in thyroid tumorigenesis: Focus on NADPH oxidases. Antioxidants 8(5), 126. https://doi.org/10.3390/ANTIOX8050126 (2019).
Villanueva, I., Alva-Sánchez, C. & Pacheco-Rosado, J. The role of thyroid hormones as inductors of oxidative stress and neurodegeneration. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longevity 2013, 218145. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/218145 (2013).
Ragazzi, M. et al. Accuracy of world health organisation-grade parameters (necrosis and mitotic activity) and foci of vascular invasion in predicting prognosis of papillary thyroid carcinoma. A case-control validation study. Histopathology 85(1), 62–74. https://doi.org/10.1111/HIS.15173 (2024).
Vural, Ç. et al. Solid variant of papillary thyroid carcinoma: An analysis of 28 cases with current literature. Ann. Diagn. Pathol. 52, 151737. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ANNDIAGPATH.2021.151737 (2021).
Haugen, B. R. et al. American thyroid association management guidelines for adult patients with thyroid nodules and differentiated thyroid cancer: The American thyroid association guidelines task force on thyroid nodules and differentiated thyroid cancer. Thyroid 2016, 26 (2015).
Huang, J. et al. Genetic alterations and allele frequency of BRAF V600E and TERT mutation in papillary thyroid carcinoma with intermediate-to-high recurrence risk: A retrospective study. Clin. Exp. Med. 24, 76. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10238-024-01320-4 (2024).
Lopes, N. M. D. et al. Role of papillary thyroid carcinoma patients with Hashimoto thyroiditis: Evaluation of oxidative stress and inflammatory markers. Clin. Transl. Oncol.: Off. Public. Federation Span. Oncol. Soc. Natl. Cancer Instit. Mexico 24, 2366–2378. https://doi.org/10.1007/S12094-022-02891-Y (2022).
Donckier, J. E., Michel, L., Delos, M., Havaux, X. & Van, B. R. Interrelated overexpression of endothelial and inducible nitric oxide synthases, endothelin-1 and angiogenic factors in human papillary thyroid carcinoma. Clin. Endocrinol. 64, 703–710. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2265.2006.02535.x (2006).
Patel, A. et al. Nitrotyrosine, inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), and endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) are increased in thyroid tumors from children and adolescents. J. Endocrinol. Invest. 25, 675–683. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03345100 (2002).
Galiniak, S., Biesiadecki, M., Mołoń, M., Olech, P. & Balawender, K. Serum oxidative and nitrosative stress markers in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Cancers 15, 3995. https://doi.org/10.3390/CANCERS15153995 (2023).
Dorf, J. et al. Could circulating biomarkers of nitrosative stress and protein glycoxidation be useful in patients with gastric cancer?. Front. Oncol. 13, 1213802. https://doi.org/10.3389/FONC.2023.1213802 (2023).
He, J., Shen, N. & Huang, X. Thyroid carcinoma cells produce PLGF to enhance metastasis. Tumour Biol. J. Int. Soc. Oncodev. Biol. Med. 36, 8601–8607. https://doi.org/10.1007/S13277-015-3548-2 (2015).
Cheuk, I. W. Y. et al. ITGAV targeting as a therapeutic approach for treatment of metastatic breast cancer. Am. J. Cancer Res. 10, 211 (2020).
Xu, S. et al. Predictive value of serum thyroglobulin for structural recurrence following lobectomy for papillary thyroid carcinoma. Thyroid Off. J. Am. Thyroid Associat. 31, 1391–1399. https://doi.org/10.1089/THY.2021.0209 (2021).
Durante, C. et al. Clinical aggressiveness and long-term outcome in patients with papillary thyroid cancer and circulating anti-thyroglobulin autoantibodies. Thyroid 24, 1139. https://doi.org/10.1089/THY.2013.0698 (2014).
Ganguly, K. K., Pal, S., Moulik, S. & Chatterjee, A. Integrins and metastasis. Cell Adhesion Migrat. 7, 251. https://doi.org/10.4161/CAM.23840 (2013).
Palanca, A., Ampudia-Blasco, F. J. & Real, J. T. The controversial role of vitamin D in thyroid cancer prevention. Nutrients 14, 2593. https://doi.org/10.3390/NU14132593 (2022).
Buczyńska, A. et al. The relationship between oxidative status and radioiodine treatment qualification among papillary thyroid cancer patients. Cancers 15, 2436. https://doi.org/10.3390/CANCERS15092436 (2023).
Jiang, N. et al. Plasma lipidomics profiling reveals biomarkers for papillary thyroid cancer diagnosis. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 9, 682269. https://doi.org/10.3389/FCELL.2021.682269/BIBTEX (2021).
Wang, H. et al. Global, regional, and national under-5 mortality, adult mortality, age-specific mortality, and life expectancy, 1970–2016: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. The Lancet 390, 1084–1150. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(17)31833-0 (2017).
Haigh, P. I., Urbach, D. R. & Rotstein, L. E. Extent of thyroidectomy is not a major determinant of survival in low- or high-risk papillary thyroid cancer. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 12, 81–89. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10434-004-1165-1 (2005).
Bergdorf, K. et al. Papillary thyroid carcinoma behavior: Clues in the tumor microenvironment. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 26, 601–614. https://doi.org/10.1530/ERC-19-0074 (2019).
Funding
This research was funded by internal financing of Medical University of Bialystok.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, A.B. and A.PK; Methodology, A.B. and M. Sz; Software, M.K. and A. A; Validation, A.B. and J.DZ.; Formal Analysis, A.B.; Investigation, A.B., A.PK, A.A., and K.S.; Resources, A.PK.; Data Curation, A.B. and M.K.; Writing—Original Draft Preparation, A.B.; Writing—Review and Editing, A.J.K. and A.PK; Visualization, A.B.; Supervision, A.PK.; Project Administration, A.PK.; Funding Acquisition, A.PK. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Ethics Committee of the Medical University of Bialystok, Poland (APK.002.7.2024).
Informed consent
Written informed consent has been obtained from the patients to publish this paper.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Buczyńska, A., Kościuszko, M., Adamska, A. et al. Impact of nitrosative stress and endothelial damage on angioinvasive papillary thyroid cancer. Sci Rep 15, 26245 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-025-10982-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-025-10982-3