Abstract
The Internet of Medical Things represents an interconnected medical technology that comprises mobile applications, medical services, as well as networks. These medical equipment and software are connected to medical systems across an internet connection. Security and confidentiality of healthcare information, flexibility, and data availability are the most complicated IoT problems to tackle. The utilization of multimedia in medical systems permits the collection, processing, and delivery of clinical data in many different types of styles, comprising texts, images, and speech, throughout the web via different effective components. Yet, processing huge quantities of information, such as every individual’s findings and images, demands additional human labour and represents safety risks. The fundamental architecture characteristics of blockchain systems including robust data encryption and strong peer-to-peer systems are beneficial and affordable options for addressing a few of these demands. Similarly, Blockchain-aided devices are effective in the field of medical science, due to their resource distribution and verification processes that enable access to information. Current investigations struggle to understand the rising need for enhanced data integration over distinct clinical services and platforms, which results in the evolution of application-centric approaches to patient-centric applications. Therefore, this work presented the efficient multimedia data processing in Internet of Healthcare Things (IoHT) based on Blockchain technology. For the improvement of healthcare resource distribution and to avoid the risk in IoHT, efficient blockchain technology is initiated to manage the security control in a real-time system. Further, the access control is managed by developing the advanced model called Dual Attention-based Deep Bayesian Network (DA-DBN). The developed system provides the secured framework for the multimedia content in IoHT using blockchain technology and DA-DBN by generating a hash of each data. This process helps in determining the changes or alterations in the blockchain. Finally, the performance of the proposed scheme concerning the blockchain is validated against the conventional approach. The result demonstrates the potential of the proposed system in securing the IoHT-based health management. The outcomes reveal that the proposed DA-DBN achieved 23.88% faster access control than SVM leading to improved efficiency and enhanced security. Therefore, the proposed model is well suited for multimedia data processing and secure access to the IoHT applications.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Healthcare organizations present numerous healthcare supports including critical care centers and specialized outpatient facilities1. Moreover, they offer extra services to ensure the privacy of the victim. Currently, healthcare organization utilizes information management networks for tracking and guaranteeing data access to the healthcare organization in an organized pattern2. Managing the clinical information assists the medical professionals in utilizing and understanding the victim’s medical records, which ensures proper care to the victim as well as creates appropriate decisions to boost the clinical quality, preserving the integrity and security of the healthcare information3. The utilization of the multimedia approach in clinical applications helps to preserve and process medical records in diverse forms including text, image, or audio information4. At present, medical organizations transformed themselves into robust and effectual models. IoMT comprises a set of clinical applications and numerous wireless devices to transmit medical records5. However, the wide utilization of the latest innovations has resulted in high computational expenses6. This approach integrates various smart applications that enable the victim to transmit their medical records to the professionals, which enhances the recognition and tracking of the development of the particular disease7.
IoMT enables accurate information processing, and faster implementation and minimizes the possibility of error rate effectively8. The usage of multimedia processing in medical applications permits data preservation, processing, and exchange of medical information in a wide range including images, audio, or text files through utilizing internet services9. Therefore, blockchain technologies are employed to overcome these issues10. The utilization of blockchain approaches is increasing rapidly, due to its efficiency in preserving private information as well as ensuring the privacy of the stored data11. In addition, due to widespread blockchain technology, they are employed to present transparency to the victim12. Moreover, they have the ability to guarantee privacy measures and access, when a huge volume of intruders utilizes IoT artifacts or applications13.
Moreover, preserving the information collected from numerous applications and permitting the development of organizations during the absence of the government fog, blockchain techniques have the ability to monitor, organize, and perform transactions14. Additionally, the blockchain technique encodes every transmission and monitors the information attained from the IoT applications, which relocate from a particular position to another position15. In order to promote the enhancements of IoMT in a safe and protected pattern, deep learning approaches along with training datasets are employed on the consumer’s private systems16. Recent investigations have concentrated on the application of deep learning approaches to medical applications and IoMT information. Moreover, deep learning systems have ensured the security and privacy of the private or personal information of the victim17.In18, the Variational AutoEncoder (VAE) is developed to ensure the privacy of the IoMT.The deep learning model in19 provides lightweight authentication to the IoMT devices. Additionally, this model employs an effective training framework to train the information collected from the IoMT application or to update the collected data to the system owner.
Challenges in the IoHT and how the proposed model addresses the issues
Data privacy and confidentiality are the greatest issues associated with the data available on the IoHT and the data are often subjected to unauthorized access, which causes potential privacy issues and data breaches. The IoHTsystem has heterogeneous devices and the features of the system are dynamic and distributed in nature, this characteristic of the IoHT system is not handled by the traditional centralized access control mechanisms19. The flexibility of the models is very poor also it is often susceptible to attacks. The dynamic environment of the IoHT may change the trust level of the user so differentiating the untrusted entities from the authorized user is a challenging task. In the IoHT system, processing the multimedia health data necessitates advanced privacy preservation approaches. The adaptability of the conventional access control approaches is very low and they are susceptible to attack so cannot improve the security of the data. The prior models may have increased the chance of data leakages and they could notprovide strong security to the sensitive information within the network18. To solve the inefficiency of the current solutions, this research proposed a dual attention-based model for access control within the network, which greatly prevents the occurrence of severe attacks on the data of the IoHT. This access control approach reduces the false access grants that may be used to prevent data leakage within the network. The proposed approach is the privacy-aware access control approach, which helps to provide strong security to the sensitive data of the IoHT network.
The primary contribution of the paper
The major contributions offered by the designed multimedia data processing and access control model are presented here.
-
To develop a novel framework to execute multimedia data processing and secure access to the IoHT applications by integrating the concept of blockchain. The prime function of the model is to process and preserve the multimedia information associated with healthcare and to ensure the privacy of the stored information by permitting the authenticated user to process the stored information. The proposed model effectively handles the hurdles such as inter operability, and regulatory compliance for enhancing the access management in the blockchain network.
-
To design an authentication model DA-DBN to determine the authenticated user by processing the user attributes and access control to the authenticated user. This model is designed by embedding the functions of dual attention with the Deep Bayesian Network(DBN) model. This integration assists the authentication to make accurate decisions in access control. Moreover, the dual attention protocol can learn the most significant characteristics from the given input information, permitting the DBN mode to create more accurate decisions based on access control. The suggested DA-DBNleverages the advantages of the DA and DBN so it prevents evolving cyberthreats for enhancing the productivity of the user’s experience.
-
To implement a blockchain technology to preserve the multimedia data related to healthcare. The blockchain captures the transaction on a public ledger, which can be accessed by every user. This transparent nature of blockchain assists in creating trust between the consumers. Moreover, the blockchain enables only the authenticated user to utilize or modify the data stored within it, which helps to avoid the risk of third-party access and data misuse. The preservation of data using the blockchain system enhances the immutability of the data and ensures the secure access of data within the IoMT network.
The layout of the introduced multimedia data processing and secure access control model is explained here. Initially, the recent study based on access control is presented in Section II. The overview of the designed authentication model is given in Section III. Section IV describes the execution procedure of the designed model. Section V describes the security challenges and the impact of blockchain techniques in multimedia data processing. Finally, the result and conclusion of the designed model are discussed in SectionVI and Section VII.
Literature survey
Related works
In 2023, Talobaet al.20 have suggested an adaptive system to overcome the issues faced by the traditional approaches by employing IoT applications in the medical sector that helped to enhance the effectiveness of victim care. Additionally, blockchain technology was employed to address the challenges associated with the security threats that were caused due to unauthorized access. The key intent of this designed model was to ensure the privacy of the medical reports by employing the concept of blockchain.
In 2023, Ranjanet al.21 have designed unique blockchain-aided geospatial service architecture BCGeo for smart medical applications. The key function of this model was to guarantee the geospatial medical service in remote regions. Moreover, an analytical queuing approach was employed to determine the victim with high-risk factors. Further, the effectiveness of this designed model was evaluated by considering a few evaluation measures and the resultant graphs revealed the effectiveness of the designed approach over classical approaches.
In 2022, Goharet al.22 have offered a safe and effective model Patient-Centric Healthcare Framework (PCH) by utilizing IoT, cloud, and blockchain. This model employed electronic records to reveal how the medical information was processed by fulfilling the requirements of security policies. Additionally, a set of evaluations was implemented to showcase the effectiveness of the introduced model across traditional approaches. Hence, the simulation results revealed that the designed model was more advanced than traditional approaches by offering greater transactions.
In 2022, Luonget al.23 have implemented a unique healthcare application by employing zero-knowledge succinct non-interactive argument of knowledge (zk-SNARK) and blockchain. The key intent of the introduced model was to avoid the risk of unauthorized access. This model examined the effectiveness of the designed model has the capacity to address numerous attacks including collusion and man-in-the-middle (MitM). At last, the performance of the designed model was investigated with respect to the computational expenses.
In 2020, Rahmanet al.24 have designed an effective lightweight model, where the blockchain was employed to handle the edge training policy and authentication of the employed federated nodes. This model was more applicable for encryption datasets and inferencing procedures. Every federated edge node executed additional encryption procedures, while the blockchain employ numerous encryption procedures for aggregating and upgrading the system parameters. Moreover, this model was evaluated by diverse deep learning approaches to demonstrate the efficacy of the designed model.
In 2020, Ratheeet al.25 have presented a security model to process multimedia information related to the medical sector by creating the hash of every piece of information, which assists the user in monitoring the modifications within the data. Evaluations were monitored over traditional approaches and the resultant values revealed that the designed model has attained a greater success rate than other approaches.
In 2023, Mahajanet al.26 have implemented a blockchain-aided secure biomedical image processing system. This model comprises a blockchain layer, edge layer, cloud storage, and fog computing layer. Here, the edge layer was responsible to accumulate and transmit the clinical reports to the higher levels. Further, the transmitted data were preserved on the blockchain-based cloud platform via fog nodes by employing a cryptographic technique. The designed model employed the CT and chest X-ray images to perform simulation performance. The simulation results revealed that the suggested model has offered greater performance with respect to PSNR, and MSE.
In 2024, Abbaset al.27 have designed a Blockchain-aided Secure Data Management Framework (BSDMF) to process medical information based onIoMT to transmit the victim’s personal information safely as well as to boost the accessibility and scalability of the medical information. The designed BSDMF has offered safe data transmission among the servers and clinical applications and among the cloud and personal servers. Moreover, the designed IoMT-aided security model utilized blockchain technology to ensure secure data transmission among the connected nodes of the system. The evaluation outcome demonstrated that the designed BSDMF model has attained greater performance in terms of response time, accuracy, and precision.
In 2023, Ali et al.28 have proposed Homomorphic encryption to enhance the privacy of the IoT system. This model preserved the privacy of the medical data throughout the computation process. Here, the access control was incorporated to enable fine-grained permission control within the IoT network, which helps to prevent the viewing of data from unauthorized parties.
In 2023, Ali et al.29 have suggested a pre-trained model with blockchain devices for training the model. Here, the global model is updated by aggregating all local models. The high efficiency and low latency services are offered by the proposed model and it also provides a high level of security to the data.
In 2024, Dhasarathaet al.30 have presented Blockchain-enabled reinforcement FL for the IoMT application. The secure communication within the network is ensured by this model. In the IoMT application, the security and scalability of the data is enhanced by this model.
Differentiation of the proposed model from existing blockchain-based IoHT frameworks
The traditional blockchain-based IoHT models still encounter difficulties regarding scalability, confidentiality, and access management. The hybrid blockchain model20 improves the trust among nodes however it still struggles from dependence on centralized control, producing possible trust issues. Moreover, the BCGeo framework confirms health geo informatics in remote regions but suffer with scaling challenges and data security vulnerabilities. Furthermore, the existing PCH22 requires additional authentication layers, leading to increased latency and complexity. Additionally, the zk-SNARK-based approach23 efficiently averts not permitted access and oppose collusion attacks however demands significant computational resources, constraining its utility in practical IoHTs ettings. However, the developed DA-DBN model combined with the blockchain mechanism addresses these limitations by reducing reliance on a central point, thus guaranteeing tamper-proof and transparent trust management. Also, it improves the scalability and competence via efficient dual attention mechanisms which seamlessly adjust to the user needs, mitigating the problem of delays and significant processing demands. Moreover, the suggested DA-DBN improves the access management by precisely differentiating genuine users from possible attackers using probabilistic inference, thereby minimizing the data security risks and insider threats. Therefore, the developed system guarantees protected multimedia healthcare data processing and gains superior precision, quicker access control, and enhanced resilience against cyber attacks than traditional blockchain-based IoHT solutions.
Problem statement
The transmission of biomedical information plays a crucial role in the smart healthcare industry, whet it utilizes the IoT to offer medical services. Privacy preservation of this sensitive medical information is more important and it is encountered by blockchain technology, which provides a secure system for the real-time condition. Various studies have utilized multi-media healthcare information to secure them in blockchain-based systems, However, managing huge medical data faces many challenges like.
-
The security administration in IoMT is more important because it deals with sensitive information, which tends to be health threats. Various techniques in the earlier literature failed to manage the huge medical data. Therefore, this work initiated the blockchain-based secure platform for enhancing the security of medical information.
-
The deployment of the IoT solution for the medical field still requires more cost because of the centralized clouds and the server farms. Hence this work utilized the blockchain technology-based advanced optimization mode for cost-effective multimedia data storage.
-
In IoT devices, there is the chance for several threats, initiated by different intruders. It tends to be complexto process multimedia data with high security. To tackle this issue, this work developed blockchain technology along with an advanced model to protect healthcare multimedia data.
-
Managing the huge multimedia data from the medical field leads to maximizing the security risk and the human effort. The presented technology plays an important role in enhancing the quality of data management. However, it faces complexity because of the high-cost technology. This work initiated the advanced adaptive model to secure medical information by efficiently allocating healthcare information.
-
The existing techniques are constantly scrutinized by various users and tend to malevolent alteration prone from third parties. To improve trust and security among different entities, the new transparent model is proposed using the heuristic algorithm and blockchain technology.
The features and the complexities in the earlier data processing model in IoHT are defined in Table. 1.
Blockchain framework with multimedia data processing and secure access control in IoHT using deep learning network
Dataset details
The dataset needed for this work has been synthetically generated and those details are given in Table 2.
Security challenges in IoHT multimedia data processing
IoHT multimedia data processing plays a major role in the field of medical science. They employ the linked medical devices to transmit healthcare information with other applications. The IoHT presents various advantages in improving patient monitoring and managing medical records more effectively31. However, they face certain challenges particularly, while processing multimedia information. Generally, multimedia healthcare data comprises the private information of the victim, clinical images, videos, audio, and treatment reports. Safeguarding the privacy of this sensitive information from third-party access is challenging32. Moreover, IoHT networks are sensitive to the assaults caused by wireless applications that include MitM and eavesdropping attacks. Additionally, the threats associated with the system traffic will influence the privacy of the private data preserved on the IoT applications33. In the medical sector, multimedia information is frequently transferred via numerous devices, which leads to unauthorized to the transmitted data. Multimedia processing employs the information accumulated from the different sources that results in security gaps34. Various IoHT applications possess minimal computational resources and struggle to implement the latest privacy policies that make them more sensitive to attack. In these cases, guaranteeing the privacy of the multimedia data is challenging and demands additional resources for processing35. In addition, it is significant to guarantee that the transmitted multimedia information remains the same throughout the transmission process, this procedure is essential to ensure the integrity of the multimedia data employed for processing.
Blockchain technology in IoHT data processing
IoMT is a variant of IoT that is particularly designed to concentrate on medical applications. In the field of medical science, managing the security of the victim’s healthcare reports is essential to guarantee that the private information of the victims is safe and not accessed by a third party without authorization. However, in certain cases, maintaining the privacy of healthcare information is challenging. In order to address these issues, blockchain technology is employed in the IoMT because of its advantages in guaranteeing the security of the data during transactions. Moreover, the confidentiality and decentralized nature of the blockchain have offered superior performance in healthcare. The utilization of blockchain improves the privacy and security of the information stored on IoT medical applications. It ensures the privacy of the medical records by permitting only the authorized user to utilize the preserved information. Moreover, embedding the blockchain technique with the medical application is essential to increase the data allocation and privacy of the victim. Moreover, the victim’s personal information related to healthcare is preserved on the blockchain, thus only the authenticated user can access or utilize the stored information. This improves the confidentiality of the victim as well as boosts data privacy. In addition, embedding blockchain technology with IoHT data processing offers a safer and more transparent path to preserve and handle the information created by the linked medical application. Furthermore, they guarantee the integrity of the preserved information by generating an absolute record within the ledger, which represents that the data preserved on the blockchain cannot be modified or accessed without proper authentication. The blockchain improves the accessibility of information by minimizing the problems associated with third-party access and data breaches. The blockchain framework ensures that only authorized users can access healthcare information since this framework records and encrypts the multimedia data using cryptographic keys. In addition, the attributes of the user are used by the access control approach for safeguarding sensitive information from unauthorized parties. The transaction of the data is once recorded in the blockchain; it cannot be altered because of the cryptographic hashes of the blockchain network. In the blockchain network, all transactions are recorded on the shared ledger.
Multimedia data processing and secure access control in IoHT: methodology
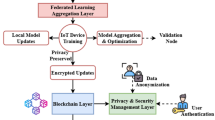
Multimedia data processing is the process of evaluating diverse forms of input like text, image, audio, and video concurrently. Multimedia data processing offers improved interaction via different sensor inputs as well as offers wide resources to access the diverse information attained from numerous resources by categorizing the data into text, audio, image video etc. Moreover, they are frequently employed in the field of medical science to process the healthcare information of the patients within the hospital. In the case of healthcare, multimedia data processing is challenging due to the heterogeneity of the information accumulated from diverse resources. Moreover, privacy and security concerns are the prime challenges faced in multimedia data processing. However, the clinical images are highly sensitive and demand robust measures to address security issues. In this framework, a novel multimedia data processing and access control framework is constructed to address the challenges faced by traditional models while ensuring the privacy of medical records preserved on IoT devices by employing blockchain technology. Multimedia data processing is executed to preserve the clinical information in multilevel storage of huge text information that has the ability to substitute the memory data types. Additionally, this model employs blockchain techniques to maintain the privacy of the healthcare information of the victim in a real-world application. Moreover, access control is performed on the designed DA-DBN model, which is constructed by integrating the dual attention mechanism with the DBN model. This designed framework offers a safe and effective model for preserving the multimedia healthcare information within the IoHT by employing the blockchain technique and the designed DA-DBN model to guarantee access to the authorized user. Access control protocol guarantees that only the authenticated user has the right to process or access the stored multimedia information on the blockchain. At last, a set of experiments is executed to reveal the effectiveness of the introduced approach over classical techniques. The architectural view of the designed multimedia data processing and access control model is shown in Fig. 1.
In this work, the blockchain system adopts the private or the public blockchain ledger that is more responsible for securing and storing multimedia healthcare data and transactional records in the IoHT network. Here, the cryptography associated with each multimedia text data is effectively stored in the blockchain system. The transaction request is initiated once the multimedia data is assessed by the user. Here, the immutable audit trait is ensured since the data is recorded in the blockchain network.
Here, the consensus algorithm is used by the blockchain network to verify each transaction before incorporating it into the blockchain network. This process may be used to ensure that only verified data modifications are done on the IoHT framework. Here, the malicious modification of the data is prevented and the data integrity is maintained by blockchain consensus because it carefully analyzes each request for processing the data. In addition to that, the access control policies are automated by the utilization of the smart contract approach. The authentication attributes are verified by the smart contract when the healthcare data is accessed by the user. The access is granted by the user once they meet the authorization criteria which can result in the release of tokens or encryption keys. In order to enhance the access control/authentication, the DA-DBN is used in this work and these models process some of the attributes of the user. The blockchain transaction provides the secure token once they are authenticated. Only, the authorized user can access the data because of the tokens. Furthermore, the integrity of the data is maintained by the hash of each data since it helps to detect the unauthorized tampering of the data.
Novelty of the proposed model
The novelty of this research lies in the incorporation of blockchain with a DA-DBN to attain safe and intelligent access control in IoHT. Not like existing encryption techniques, which merely guard information at static or dynamic levels, our proposed method combines blockchain-reliable data with probabilistic insights to guarantee both protected storage and effective access control. This approach mitigates the susceptibility of centralized systems and ensures an unchangeable record of data access. Also, the proposed system clearly targets access control in theIoHT context, where multimedia healthcare data from several origins are managed and examined. Moreover, the work employs dual attention with a Bayesian network, allowing the system to extract both global dependencies and local contextual features in multimedia healthcare data when assessing uncertainty. Also, it aids in enhancing the accuracy and dependability of access control in IoHT systems. The combination of a dual attention mechanism and DBN is a major advancement over conventional authentication techniques, especially for confidential healthcare information. Additionally, the model specifically handles the regulatory compliance (HIPAA, GDPR), which makes it more robust and also prioritize legal conformity, which is frequently unnoticed in past studies. The integration of DA-DBNs authentication ability and the blockchain immutably helps the model to provide a multi-layered security model intended to guard clinical information from illicit access, falsification, and cyber attacks, which is a primary problem in clinical settings.
Dual attention-based deep Bayesian network for secure access control in IoHT
Dual attention mechanism
Advantages of using dual attention mechanism over single attention or traditional encryption
Traditional Encryption protects the information at stored or in motion but fails to assist in determining information access policies. If access credentials are mishandled or exposed, encryption can’t distinguish genuine and malevolent users alone. In which the classical encryption does not has the ability to adjust to the varied, and complex IoHT system, where user faith might vary over and over again. Moreover, Single attention concentrates on single feature set. Where, the channel attention improves the significant aspects but overlook related spatial structure. Though, spatial attention pays more focus on positions, it neglects the global dependencies. In multimedia IoHT data, depending on single attention might source the system to ignore slight thread indicators or susceptible behaviors which assist to differentiate attackers from valid users. However, Dual attention combines both channel and spatial mechanism that supports the system in extracting specific and wide range dependencies concurrently, which is essential in clinical IoHT data that engages multimodal signals. Furthermore, by leveraging the user attributes and context-dependent device behavior, the proposed DA-DBN gained enhanced robustness against unauthorized entry.
How dual attention mechanism enhances the access control
The dual attention mechanism is a major factor in improving the permission management, especially in its capability to adjust policies vigorously. It performs by permitting the model to particularly concentrate on significant data while managing access, allowing context-aware and fine-grained control. Also, the DBN component quantifies unreliability’s and evaluates the honesty of the users, systems, and information assets. The attention mechanism is able to highlights the appropriate risk factors to amend the access policy on the basis of supposed threat linked with a specific access request. For example, handling confidential patient information from a strange unconfirmed device may trigger superior verification needs. Moreover, by capturing minute information from both the information and the background, the dual attention mechanism offers the capability to define specific and versatile access policies, which enable the model to provide access regarding particular attributes of the user instead of depending on fixed roles alone. Furthermore, the model has the ability to dynamically select and utilize suitable security protocols in terms of data’s confidentiality and the current security threats. Dynamic access control facilitates adherence to stringent regulations like HIPAA and GDPR by guaranteeing that entry to user data is firmly forbidden and auditable. The dual attention mechanism enables the model to make informed access decisions on the basis of the context of the circumstances and the confidentiality of the information, offering a more vigorous to protecting confidential healthcare information.
The DA36 is a combination of Squeeze-Excitation (SE) and Convolutional Block Attention Module (CBAM). This combination enables the framework to process diverse aspects of the input attributes concurrently which permits the model to learn both spatial and channel characteristics at diverse levels.
While considering the input data \(G\), the DA layer processes the input to offer a feature map \(G{\prime}\), in which \(G \in T^{J \times E \times V}\) and \(G{\prime} \in T^{J \times E \times V}\). The entire procedure executed on the DA layer is expressed in Eq. (1).system is described
Here, the resultant feature maps attained from the SE and CBAM layers are indicated as \(G_{SE}\) and \(G_{CBAM}\). The SE procedures are numerically defined in the below equations.
In the above equations, the terms \(Z_{d}\) and \(Z_{r}\) represent the feature maps obtained from the squeeze and excitation layers. The terms \(Mlp\) indicate the multi-perceptron and global average pooling layers. Additionally, the functions implemented \(G_{CBAM}\), which evaluate the spatial and channel feature maps are defined in the below equations.
In this equation, the average and max pooling layers are indicated as \(Ag_{pool}\) and \(Mx_{pool}\), the resultant feature maps attained from the spatial and channel attention units are expressed as \(Z_{sp}\) and \(Z_{c} \left( G \right)\).
The underlying issues in the DBN are solved by the incorporation of DA. By employing the DA mechanism, the DBN model can effectively concentrate on the numerous aspects of the input information including applications, and user attributes, which assist in making an exact decision based on access control. Moreover, this mechanism concentrates on the characteristics of the devices and the present situation of the user to decide whether the access should be denied or gained. Additionally, dual attention protocol can assist in determining the significant characteristics for differentiating the legitimate users and security threats within the model, which is effective in determining the impact of third-party access to the information preserved on the blockchain.
Deep Bayesian network
DBN37 is an adaptive model that employs the Bayesian systems and deep learning models including DNN to process high dimensional information, they are widely employed to evaluate the probability for prediction. This model utilizes probability distribution including Gaussian prior, located across the weight \(E\) of the system \(Q\left( E \right)\). Then, the possibility of the system is described in Eq. (8).
In Eq. (8), the outcome of the system that is attained with respect to the weight \(E\) is denoted as \(g_{E} \left( c \right)\), Moreover, the inference within the DBN demands posterior \(Q\left( {E|F} \right)\) that is hard to infer. To overcome this challenge, the posterior is approximated by employing the Monte Carlo dropout that is performed by executing an arbitrary dropout function on each weight level throughout the training and testing phases. Additionally, the Monte Carlo dropout has the ability to execute estimated variation interferences that assist in reducing the kullback–Leibler divergence towards the true posterior and it is described in Eq. (9).
In Eq. (9), where, the value of \(\hat{E}_{y}\) is similar to \(w_{\theta } \left( E \right)\), which describes the dropout distribution. Additionally, during the testing phase, the possibility of the classification for the input \(c\) is evaluated by dividing the input \(Y\) times by employing the Monte Carlo dropout and by averaging the outcome of the Softmax layer. By employing the Bayesian inference, the DBN model can manage the problems due to data uncertainty; this function makes the DBN model more effective in access control, where the user behaviour is irregular. Moreover, the DBNcan attain the most significant feature from the given data that permits them to determine the relevant patterns within the user’s access behaviour. In addition, the DBN model assistsin reducing the problems related to overfitting. The pictorial illustration of the DBN model is given in Fig. 2.
Multimedia data processing in Ioht through Blockchain technology with high security
Authentication attributes
The authentication procedure is implemented by employing the details accumulated by the user and includes:
-
Username
-
The private ID of the user
-
Transaction performed by the user
-
Public and private keys of the user
-
Password created by the user
Dual attention-based DBN for access control
The unauthorized access of the data in the IoMT is prevented by this model. The user authentication and the access control operation are enhanced by the DA-DBN with the integration of the DA with the DBN. The significant features of the data are amplified by the channel attention module within the DA. In addition, the most relevant spatial region of the data is focused by the spatial attention module. The application and the user attribute data are effectively captured by the spatial attention module. The accuracy of the access control process is enhanced by capturing both spatial and temporal features in the data. Here, the relevant information in the input data is captured by the dual attention that is connected with the hidden layer of the network. Authentication is the primary phase to ensure the privacy of the data preserved on the system. Implementing the authentication procedures guarantees that only the authenticated user to utilize the preserved data. In this developed system, user authentication is executed to offer access control to the authenticated user. Generally, access control is referred to as the security procedure that enables the authenticated user to access digital resources including preserved information, devices, and other models. Access control employs authentication and authorization procedures to validate the user by employing the user attributes. In this framework, user authentication for access control is executed by utilizing the designed DA-DBN model. This framework is designed by integrating a dual attention mechanism within the DBN framework.
Furthermore, dual attention permits the network to concentrate on diverse aspects of input information concurrently; this adaptive nature makes them effective in learning both global and local information within the given input. Particularly, in the case of complicated databases, the dual attention protocol assists in identifying inappropriate data by permitting the framework to obtain the significant feature that assists in enhancing the decision-making ability of the model. Moreover, the dual attention protocol has the ability to learn the most significant characteristics from the given input information, permitting the DBN mode to create more accurate decisions based on access control, which is essential to figuring out legitimate users. Additionally, by employing the function of dual attention, the DA-DBN model can process both temporal and spatial features. This ability allows the model to process diverse information simultaneously, which allows the model to determine access control more effectively and accurately. The diagrammatic illustration of the designed DA-DBN-aided access control model is given in Fig. 3.
Blockchain criteria for multimedia data processing
The multimedia healthcare data are managed more securely by the decentralized ledger called as blockchain. In the blockchain system, each modification is considered as transaction, which is used to attain intelligent traceability to the system. The access control adopted here prevents the entry of the unauthenticated person reducing the probability of the data modification. Here, the integrity of the data is ensured by storing the multimedia data within the blockchain system. The blockchain system protects the data against the security attacks to ensure the integrity. The collection of the transaction is preserved in the blocks of the network. The consensus mechanisms in the blockchain verify the validity of the new blocks. All transaction in the distributed ledger is constantly updated on the distributed ledger of the blockchain system. Utilizing multimedia data processing in the medical sector creates an effective environment to process, preserve, and transmit the victim’s medical records in diverse patterns including text, image, or audio files. However, they face certain challenges associated with security issues that may influence the performance of medical applications. Integrating blockchain techniques with multimedia data processing offers more significant measures to overcome the struggles related to security. The blockchain technique has the ability to process huge quality medical data by maintaining the integrity of the preserved information. The metadata related to the healthcare, access logs and authorization details is securely stored by the blockchain system since it acts as the decentralized ledger in the IoHT system.
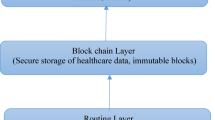
Blockchain limits the functions of IoT devices by tracking the required data from the nearest IoT to offer effective performance while transmitting a set of information from one position to another. Additionally, the blockchain collects the intermediate function, accessibility information from the victim, and their medical reports. They ensure the privacy of the stored information by encrypting the medical records into a private key and only the authorized user knows the private key to access the preserved data. Implementing multimedia processing on the healthcare application offers a secure healthcare management system by monitoring the functions and medical records of the victim. In addition, the utilization of blockchain techniques in medical applications has presented various advantages in the medical sector by guaranteeing the privacy and transparency of victim reports by permitting only the victims to access the data as well as permitting the victim to decide whom to utilize the stored data. In this developed model, blockchain technology is employed to store the victim’s multimedia data as well as to guarantee the privacy of the stored information by permitting the authorized user to process or modify the preserved data. The pictorial illustration to describe the blockchain criteria for multimedia data processing is presented in Fig. 4.
Consensus mechanism and its suitability for IoHT:PBFT is used in the proposed system, particularly within a Blockchain-aided IoHT, a probable situation for clinical applications where collaborating organizations like hospitals are identified and have creates trust relationships. PBFT is intended to bear Byzantine faults, as it can attain consensus still if few nodes are malevolent. This is vital for medical data where data security and confidentiality are supreme. PBFT could gain superior expedited data handling and low-delay, which is vital for managing huge volumes of multimedia data created by IoHT devices and for practical access management. Moreover, PoA can be an important factor, mainly in scenarios requiring superior performance within secured settings, where a group ofauthorized healthcare entities validates information. PoA is usually utilized in Blockchain-aided IoHT. Furthermore, the PoA offers high transaction throughput because ofless participating nodes and depends on the Trustworthiness of the validators. The models integration of a DA-DBN can possibly manipulate the choice and observation of PoA validators by evaluating their honesty and performance.
Results and discussions
Simulation setup
The implementation of the designed multimedia data processing and access control model was executed in Python version 3.0 whichwas run on the Intel i3 platform with 8 GB and 500 GB ROM here implementation process uses the Windows PC version11. Further, the performance of the designed model was investigated to reveal the competence of the designed framework. Performance estimation was implemented by employing a few evaluation metrics and the attained outcomes were compared over traditional approaches including Support Vector Machine (SVM)38, Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM)39, Deep Neural Networks (DNN)40, and DBN37.Here, 1500 data are assumed randomly for the initialized attributes here 75% of the data (1125) has been used for the training process and the remaining 25% of the data (375) of the data has been used for the testing process.Details of multimedia data processing/storing (on-chain vs off-chain) are provided in Table 3. This table shows that, huge files such as image sand videos are gathered off chain in effective and reliable system and the hash and meta data policies were stored on-chain. Moreover, while handling multimedia data with a blockchain-based system, the hybrid on-chain/off-chain storage system is more realistic. Here, the on-chain component offers immutable and tamper-proof storage for confidential data, where the off-chain component manages the superior volume of multimedia data effectively. However, on-chain components are expensive and have very limited storage, while the off-chain components necessitate a blockchain link for security.
Evaluation metrics
The metrics employed to showcase the competence of the designed system are listed here.
-
(a)
Accuracy is described in Eq. (10).
$$Acc = \frac{{A_{p} + A_{n} }}{{A_{p} + A_{n} + Z_{p} + Z_{n} }}$$(10) -
(b)
CSI is defined using Eq. (11).
$$CSI = \frac{{A_{p} }}{{A_{p} + Z_{n} + Z_{p} }}$$(11) -
(c)
F1-Score is attained via Eq. (12).
$$F1\,\,Score = \frac{{2*\,A_{p} }}{{2*\left( {A_{p} + A{}_{n} + Z_{n} } \right)}}$$(12) -
(d)
FOR is derived using Eq. (13).
$$FOR = \frac{{Z_{n} }}{{\left( {Z_{n} + A_{n} } \right)}}$$(13) -
(e)
MCC is obtained via Eq. (14).
$$MCC = \frac{{A_{p} \times A_{n} - Z_{p} \times Z_{n} }}{{\sqrt {\left( {A_{p} + Z_{p} } \right)\left( {A_{p} + Z_{n} } \right)} \left( {A_{n} + Z_{p} } \right)\left( {A_{n} + Z_{n} } \right)}}$$(14) -
(f)
Precision is expressed in Eq. (15).
$$\Pr ecision = \frac{{A_{p} }}{{\left( {A_{p} + Z_{p} } \right)}}$$(15) -
(g)
Sensitivity is numerically represented in Eq. (16).
$$Sensitivity = \frac{{A_{p} }}{{\left( {A_{p} + Z_{n} } \right)}}$$(16) -
(h)
Specificity is derived using Eq. (17).
$$Spectivity = \frac{{A_{n} }}{{\left( {A_{n} + Z_{p} } \right)}}$$(17) -
(i)
FPR is expressed using Eq. (18).
$$FPR = \frac{{Z_{p} }}{{Z_{p} + A_{n} }}$$(18)In the above equations, the true positive and negative values are denoted as \(A_{p}\) and \(A_{n}\). The false negative and positive values are indicted as \(Z_{n}\) and \(Z_{p}\).
-
(j)
Cost per transaction is defined as the expenses required for complementing a single transaction procedure within the blockchain.
-
(k)
Transaction Latency is the total time consumed by the transaction to begin in the system and finally established within the block.
-
(l)
Transaction per second is utilized to evaluate the total transactions performed on the network within a particular second.
Epoch count-based performance estimation
The evaluation results obtained by the introduced DA-DBN across different traditional modes are presented in Fig. 5. Here, the efficiency of the developed framework is evaluated by altering the epoch count from 20–100. Adjusting the epoch count improves the learning procedures of the system by enabling deep evaluation of the input information. Additionally, it improves the efficiency of the model by resolving the problems related to overfitting issues by analyzing the competence of the system over diverse epoch counts, which offers highly generalized results during user authentication and access control. Varying the epoch count enables the model to monitor the loss and attain greater accuracy in determining the authenticated user. In addition, increasing the epoch count permits the authentication system to gather the information employed during the training procedure more effectively which leads to high authentication accuracy. While considering Fig. 5. (a), the accuracy of the designed authentication system outperformed classical approaches like SVM, LSTM, DNN, and DBN by22.83%, 17.05%, 32.66%, and 17.05%, when the number of epochs is 20. Moreover, Fig. 5b shows that the proposed DA-DBN model attains highest CSI percentage when compared to other traditional models. Also the developed model reached 99% of F1 score value when considering the epoch as 20, as depicted in Fig. 5c. From the Fig. 5d, e it is proven that the developed model attains better performance with lower FOR value and higher MCC value. Additionally, considering the Fig. 5f the traditional model DNN model attains lower precision, leading to poor generalization and ineffective performance. However, the developed model achieves greater precision value, when taking the epoch as 20. Therefore, the developed DA-DBN is more effective in determining the authenticated user and granting access to the information stored on the blockchain.
Batch size-based performance estimation
The overall performance of the introduced DA-DBN model for user authentication and access control is estimated by adjusting the batch size from 4–64. The results obtained by the developed model over conventional models are given inTable4. Generally, batch size is referred to as the total volume of input information processed during a specific iteration. Higher batch size permits the suggested model to obtain the outcomes with better generalization. On the other hand, smaller batch size presents faster convergence, as well as prevents the risk of overfitting. In this evaluation, the efficiency of the developed system is estimated by considering the accuracy measure presented in Table 4. According to the evaluation outcome, the developed model has outperformed other classical approaches like SVM, LSTM, DNN, and DBN by 14.41%, 13.88%, 19.41%, and 14.95%, when the batch size is 32. Thus, it is clear that the suggested model offers superior performance than the standard model in identifying the authenticated user.
Confusion matrix-based performance evaluation
The suggested authentication model’s confusion matrix is given in Fig. 6. This analysis is executed to determine the effectiveness of the designed authentication model in a tabular format. In the confusion matrix, the effectiveness of the system is high when the true values are greater than the false values. Moreover, the confusion matrix offered a detailed description of how the developed system executes in every class. From Fig. 6, the developed authentication system has offered greater performance than other classical techniques.
ROC-based performance evaluation
The ROC curve attained by the introduced authentication and access control model evaluates the performance with traditional approaches presented in Fig. 7. This analysis defines the performance of the designed model concerning the threshold value. Area under the Curve (AUC) is an effective measure employed to determine the efficacy of the model, it offers the numerical value that describes the competence of the suggested model, permitting rapid evaluation with other traditional models. Moreover, the network with a high AUC value is taken as the effective framework to execute the authentication procedures. Based on the attained graph, the suggested DA-DBN-based user authentication and access control system has attained greater efficiency than other conventional models.
Overall performance evaluation of the developed model
The overall performance of the introduced authentication model is evaluated by considering a few performance measures including precision, accuracy, F1-score, FOR, CSI, and MCC. This evaluation is a model to evaluate the effectiveness of the suggested authentication model with and without a dual attention mechanism and the achieved graph is represented in Fig. 8. According to the simulation outcome, the authentication model has attained greater efficiency in detecting the unauthorized access to the data while deploying the dual attention mechanism. Since, the embedding the dual attention helps to offer more accurate decisions in access control.
Statistical measures-based access control performance estimation
The performance of the developed access control model is estimated by varying the statistical measures concerning the security metrics. The outcomes attained by the designed DA-DBN model over conventional approaches are presented in Fig. 9. Evaluating the performance based on statistical measures helps to determine the best performance of the developed framework in offering access to the authenticated user. Moreover, this analysis is significant for monitoring the performance of the framework throughout the implementation procedure and helps to make accurate decisions. Figure 9a demonstrates that the proposed model attains lower cost per transaction rate when taking the best measure. From Fig. 9b, the security of the designed DA-DBN system is 61%, 59.37%, 71.32% and 44.28% more effective than classical authentication models including SVM, LSTM, DNN and DBN, while considering the best value of the developed model. Additionally, the Fig. 9c, d establishes greater performance while comparing with other traditional models. Thus, it is clear that this designed access control model for the IoHT application permits only the authenticated user to access the healthcare information stored on the blockchain.
Investigationbased on quantitative and qualitative factors in ioht security, multimedia data processing, or access control
Table 5 indicates the comparison of the proposed DA-DBN-based IoHT security approach in terms of various quantitative and qualitative metrics. Here, the comparison is done by considering various metrics such as latency, throughput, error rates, user experience, and security metrics for confirming the efficacy of the presented DA-DBN in providing security to the IoHT network. It is found in Table 5 that the proposed DA-DBN model has a very low latency of 38.99 in the worst metrics. This result indicates that the suggested model can effectively process multimedia data in the IoHT network. In addition, the DA-DBN model provided the highest level of security of 95.97% in the IoHT network which indicates the higher security of data within the IoHT.
Scalability and reliability analysis
Figure 10 illustrates the scalability and reliability assessment of the designed DA-DBN. In Fig. 10a, when considering the data size as 5 Mb, the proposed model attains 98% of reliability, which leads to superior execution than classical models. From Fig. 10b, the accuracy range of the proposed DA-DBN lies between 90 to 95% when the data size is 150. Likewise, at the data size 50, the proposed DA-DBN model attained an accuracy between 89 to 92%. In addition, the reliability of theDA-DBN is very high in all sizes of data. Thus, the results showed that the proposed DA-DBN model is scalableandmorereliable for large data sizes.
Data processing speed
Table 6 indicates the data processing speed of the suggested DA-DBN-based access control approach over the prior models. As per the validated outcome, the suggested DA-DBN attained a lower data processing speed of 23.88 s. The results indicate that the designed DA-DBN model requiresa very minimum amount of time for processing the entire data within the network.
Comparision of the proposed model on multimedia data types
The accuracy of the proposed DA-DBN in handling the multimedia data types is indicated in Table 7. Here, the proposed DA-DBN model attained the largest accuracy value in handling multimedia data (92.3%). In addition, the proposed DA-DBN also attained a higher value of accuracy while handling the images and video data as compared to the baseline model named as DBN.
Case study for confirming the effectiveness of secure access control system
The IoHT system41 is implemented in the hospital intensive care unit for monitoring the condition of the patient. Here, the edge devices are connected to various sensors that are responsible for monitoring the blood pressure, heart rate and oxygen saturation in humans. Here, the blockchain smart contract is integrated with the role-based access control approach for enhancing the security of the patient’s data in the hospital intensive care unit. Across the time series and image data, the critical patients are prioritized by the multimodal attention-based models. This model can ensure that only authorized persons access the medical data. The deterioration of the data within the hospital intensive care unit is prevented by an attention model that provides efficient access control to the network.
Energy consumption required for the proposed scheme
Table 8 is used for analyzing the energy consumption of the proposed DA-DBN model in terms of time. As per the Table results, the suggested DA-DBN consumes minimum energy for the implementation process. The proposed model consumes 0.246602 Kw/h for the access control process which proves the efficiency of the proposed model against prior models.
Comparison of the proposed model over prior works
Comparative analysis of the proposed model over traditional works is provided in Table 9. This analysis helps to evaluate improved security, enhance transparency and guarantee the reliability. Here, the traditional Health lock model attains an accuracy of 0.8%, leading to lack of confidence and lost trust. However, the designed model gained higher accuracy of 0.9%, leads to more reliable and enhanced security. Therefore, the designed DA-DBN gains better performance compared to other traditional models.
Resilience assessment of the proposed model in terms of MITM and Sybil attacks
Resilience assessment of the proposed model in terms of MITM and Sybil attacks is offered in Fig. 11. This analysis is done to evaluate its safety and reliability in real, practical situations. Figure 11a shows that while the transport bypass probability increases, the tamper success probability also improves. Here, the superior level of on-chain evasion = 1e-09 attains lower tamper success probabilities, leading to superior data integrity, enhanced trust and robust protection. Moreover, Fig. 11b shows the Sybil takeover probability vs attacker fraction, and the gained results indicate improved performance with better security. Therefore, the designed model outperforms other traditional models by attaining higher security of data within the IoHT.
Latency and throughput analysis of the proposed model under attack scenarios
Figure 12 depicts the latency and throughput analysis of the suggested model under attack scenarios. This analysis is significant for evaluating the resilience and security effectiveness of the proposed model in practical IoHT. Figure 12a demonstrates that no attacks attain 100 ms of latency, which is comparatively lower, representing consistent and low latency, which leads to quick and practical threat identification. In Fig. 12b, Cybil attempts to attain lower throughput, leading to a weekend security system and loss of trust among users. As a result, the suggested model gained improved security over other conventional approaches.
Comparison of the proposed model with other baselines regarding access control, blockchain effeciency and real world feasability
Figure 13 demonstrates the access control (precision vs Recall) comparison over other baselines. Here, while considering the recall metric, the traditional SVM model attains 85% to 95%, however, the designed DA-DBN model gains 97% to 99% leading to enhanced scalability and improved security. Moreover, from Fig. 14a, the traditional health lock model 87.8% latency, which indicates minimized blockchain effectiveness and system bottlenecks. However, the proposed DA-DBN model achieves lower latency of 40.1%, leading to quicker blockchain operations and better resource usage. Also, the Fig. 14b demonstrates that the designed DA-DBN model outperforms other baselines by gaining superior throughput. Additionally, in Fig. 15a, the latency gradually increases when the node count increases. And the Fig. 15b indicates that as the node count increases the transaction per seconds’ decreases. Additionally, the energy consumption in Fig. 15c shows that the proposed model gains lower energy consumption, representing enhanced efficiency and minimized computational cost. Hence, the proposed model achieved better performance as compared to other baselines.
Discussion
Potential implications of the proposed system for healthcare policy and practice
In the healthcare application and practice, several applications are offered by the proposed DA-DBN. Here, the data of the patients are robustly protected by the proposed DA-DBN model and it performs the secure access control for ensuring the security of the private information. The regulation around medical data security is strengthened by the policymakers with the help of the proposed model. Telemedicine and remote healthcare services are offered by the suggested paradigm. Among the healthcare providers and patients, secure data sharing is facilitated by the suggested model. In addition, the resource utilization is optimized by the healthcare institution by the automated access control mechanism. In this work, the access control approach is used to preserve the privacy of the data and this approach is used for ensuring the security of the patient information by preventing unauthorized access. This framework is adopted by the policymakers to strengthen the security of digital healthcare data. This model uses the DA-DBN, which guides the decision support system in the IOHT. Early detection and personalized treatment are offered in the healthcare practices by the proposed DA-DBN. The comprehensive policies for the healthcare environment are offered by the proposed access control approach. With the help of the proposed model, the future healthcare system will be more personalized and protective also it maintains the integrity of the data in the healthcare system.
In addition, the DA-DBN-based access control approach is more suitable for remote monitoring and consultation (telemedicine) since it can securely collect and transmit healthcare data without any access from third parties. The vital signs are biometric data of the patients that are continuously gathered on the sensor that is worn by the patients. So, the up-to-date data of the patient are remotely monitored by the healthcare professionals for taking the intervention during the emergency condition. Likewise, personalized medicine is also provided by the proposed model by aggregating the specific data of the individual for the tailored treatment plan. The personalized treatment intervention is offered by the suggested model because it can easily identify the unique health patterns from the data. The recovery progress of the patient undergoing the therapy is continuously monitored by the suggested model. The rehabilitation protocols are adjusted by the clinicians based on the data, which helps to enhance the efficiency of the recovery.
Discussion on regulatory compliance
Beyond enhancing the performance and the security, the developed blockchain-aided DA-DBN model also ensures adherence to regulations with medical compliance standard such as HIPAA and GDPR. HIPAA needs privacy, honesty, and traceability of Protected Health Information that our model gains byrobust access management, tamper evident and verifiable logging. Moreover, GDPR highlights authorized processing, patient authorization, and the ability to deny access. These concerns are managed by utilizing smart contracts for privacy rights management, and providing key revocation for cancellation of access. On the whole, the suggested model improves theIoHT system resiliations and also confirms that protective measures stay allied with global healthcare regulations, ensuring its usability for real-world deployment.
Ethical consideration
The designed model safeguards patient privacy by using anonymization of multimedia data previous to processing and implementing access control through blockchain-based authentication. This approach secures confidential dates from being tied to personally identifiable information, a sensuring data honesty and privacy. Also, the unchangeable audit trail of blockchain improves data visibility, thus strengthening patient confidence. Moreover, the model complies with medical regulations like HIPAA and GDPR, guaranteeing that regulatory and legal requirements are upheldamid the multimedia data processing in IoHT.
Tradeoff between dual attentionoverhead vs. security gains
Though the integration of the dual attention mechanism improves the precision and strong access control in IoHT, it also in corporates extra computational expense than single-attention or classical models. This overhead arises from the simultaneous extraction of channel and spatial dependencies that some what maximize the computational complexity. However, the trade-off is acceptable because of the security gains are so considerable. The dual attention allows detailed user authentication, minimizes false access permissions, and improves resistance against illegal access. Furthermore, the extra expense is minimal in relation to the total performance of the model. The developed system has the ability to gain minimized processing time than existing techniques. Hence, the computational expense of the dual attention is balanced by the significant enhancement in confidentiality and dependability for multimedia IoHT applications.
Limitation of the proposed system and its future scope
However, when the complexity of the data is increased, privacy leakage may occurin the proposed model especially when handling heterogeneous types of data. The proposed model cannot be implemented on low-power devices. One of the ongoing challenges is the real-time processing of the suggested model without compromising the security of the data. In addition, the performance of the proposed model may be affected by the unseen healthcare condition of the patient. Thus, future work will focus on considering these issues to develop a lightweight and efficient model, which is more applicable to the healthcare solution. In addition, a future enhancement can be executed to design an effective model to detect security threats on the IoHT applications by employing techniques based on artificial intelligence. The lightweight and secure model will be developed in the upcoming work for the real time implementation of the proposed model without compromising the security of the data. The present experiments and evaluations are on the basis of simulated data that might not take out the practical problems. The IoHT utilization could limit the generalizability of results. Moreover, the difficulty of managing varied data types in the IoHT settings might cause privacy leakage, especially as data volumes enhances. In future, we obtain and analyze real-world IoHT datasets, as well as multimodal data from a variety of sources. Also, we plan to expand the model to real-time patient monitoring by utilizing wearable devices like cameras and biosensors. This will permit constant collection of multimedia health data from patients, allowing more tailored and practical healthcare services within the IoHT settings.
Conclusion
Here, a unique multimedia data processing and access control model was designed for the IoHT application by employing blockchain. The basic function of this model was to ensure the privacy of the medical record preserved on the blockchain. Initially, this model processes the multimedia data that holds the clinical data of the victim, which comprises text, images video, or audio associated with the victim. Moreover, an effective authentication model DA-DBN was designed to execute user authentication by processing the user attributes and access control to the authenticated user. The DA-DBN was designed by integrating a dual attention mechanism with the DBN model. This integration assists the authentication to make accurate decisions related to access control. Furthermore, various simulations were executed to demonstrate the competence of the designed authentication model. The attained results proved that the developed DA-DBN was 15.34%, 10.22%, 24%, and 14.81% more advanced than standard models like SVM, LSTM, DNN, and DBN. According to the evaluation outcome, the developed model was more effective in ensuring secure access control by allowing the authenticated user to process the information stored on the blockchain.
Funding statement
This research is funded by Princess Nourah bint Abdulrahman University Researchers Supporting Project number (PNURSP2025R79), Princess Nourah bint Abdulrahman University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
Data availability
The datasets generated and/or analysed during the current study are not publicly available due to the privacy but are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Abdellatif, A. A. et al. ssHealth: Toward secure, blockchain-enabled healthcare systems. IEEE Netw. 34(4), 312–319 (2020).
Bataineh, M. R., Mardini, W., Khamayseh, Y. M. & Yassein, M. M. B. Novel and secure blockchain framework for health applications in IoT. IEEE Access 10, 14914–14926 (2022).
Kumar, R. et al. Permissioned blockchain and deep learning for secure and efficient data sharing in industrial healthcare systems. IEEE Trans. Industr. Inf. 18(11), 8065–8073 (2022).
Liu, Y., Lu, Q., Zhu, C. & Yu, Q. A blockchain-based platform architecture for multimedia data management. Multimed. Tools Appl. 80(20), 30707–30723 (2021).
Banotra, A., Sharma, J.S., Gupta, S., Gupta, S.K. and Rashid, M., “Use of blockchain and internet of things for securing data in healthcare systems” Multimed. Secur. Algorithm Dev. Anal. Appl., pp.255–267, 2021.
Ghazal, T.M., Hasan, M.K., Abdallah, S.N.H. and Abubakkar, K.A., “Secure IoMT pattern recognition and exploitation for multimedia information processing using private blockchain and fuzzy logic”, Transac. Asian Low Resour. Lang. Info. Process., 2022.
Dhar, S., Khare, A. & Singh, R. Advanced security model for multimedia data sharing in Internet of Things. Transac. Emerg. Telecommun. Technol. 34(11), e4621 (2023).
Kasetti, S. & Korra, S. Multimedia data transmission with secure routing in M-IOT-based data transmission using deep learning architecture. J. Comput. Allied Intell. 1, 2584–2676 (2023).
Jeong, Y. S. Blockchain processing technique based on multiple hash chains for minimizing integrity errors of IoT data in cloud environments. Sensors 21(14), 4679 (2021).
Karthik, G. M., Kalyana Kumar, A. S., Karri, A. B. & Jagini, N. P. Deep intelligent blockchain technology for securing IoT-based healthcare multimedia data. Wireless Netw. 29(6), 2481–2493 (2023).
Arslan, S. S. & Goker, T. Compress-store on blockchain: A decentralized data processing and immutable storage for multimedia streaming. Clust. Comput. 25(3), 1957–1968 (2022).
Mishra, R.K., Yadav, R.K. and Nath, P., “Integration of Blockchain and IPFS: healthcare data management & sharing for IoT environment”, Multimed. Tools Appl., pp.1–22, 2024.
Lakhan, A. et al. Secure blockchain assisted internet of medical things architecture for data fusion enabled cancer workflow. Internet Things 24, 100928 (2023).
Khallaf, F., El-Shafai, W., El-Rabaie, E.S.M. and El-Samie, F.E.A., “Blockchain-based color medical image cryptosystem for industrial Internet of Healthcare Things (IoHT)”, Multimed. Tools Appl., pp.1–55, 2024.
Khan, A. A., Bourouis, S., Kamruzzaman, M. M., Hadjouni, M. & Shaikh, Z. A. Data security in healthcare industrial internet of things with blockchain. IEEE Sens. J. 23(20), 25144–25151 (2023).
Srinivasan, K. et al. Secure multimedia data processing scheme in medical applications. Multimed. Tools Appl. 81(7), 9079–9090 (2022).
Sharma, P., Moparthi, N. R., Namasudra, S., Shanmuganathan, V. & Hsu, C. H. Blockchain-based IoT architecture to secure healthcare system using identity-based encryption. Expert. Syst. 39(10), 12915 (2022).
Almaiah, M. A., Ali, A., Hajjej, F., Pasha, M. F. & Alohali, M. A. A lightweight hybrid deep learning privacy preserving model for FC-based industrial internet of medical things. Sensors 22(6), 2112 (2022).
Almaiah, M. A., Hajjej, F., Ali, A., Pasha, M. F. & Almomani, O. A novel hybrid trustworthy decentralized authentication and data preservation model for digital healthcare IoT based CPS. Sensors 22(4), 1448 (2022).
Taloba, A. I. et al. A blockchain-based hybrid platform for multimedia data processing in IoT-Healthcare. Alex. Eng. J. 65, 263–274 (2023).
Mallick, S. R. et al. BCGeo: Blockchain-assisted geospatial web service for smart healthcare system. IEEE Access Appl. Blockchain Internet Things 11, 58610–58623 (2023).
Gohar, A. N., Abdelmawgoud, S. A. & Farhan, M. S. A patient-centric healthcare framework reference architecture for better semantic interoperability based on blockchain, cloud, and IoT. IEEE Access 10, 92137–92157 (2022).
Luong, D. A. & Park, J. H. Privacy-preserving blockchain-based healthcare system for IoT devices using zk-SNARK. IEEE Access 10, 55739–55752 (2022).
Rahman, M. A., Hossain, M. S., Islam, M. S., Alrajeh, N. A. & Muhammad, G. Secure and provenance enhanced internet of health things framework: A Blockchain Managed federated learning approach. IEEE Access 8, 205071–205087 (2020).
Rathee, G., Sharma, A., Saini, H., Kumar, R. & Iqbal, R. A hybrid framework for multimedia data processing in IoT-healthcare using blockchain technology. Multimed. Tools Appl. 79(15), 9711–9733 (2020).
Mahajan, H. B. & Junnarkar, A. A. Smart healthcare system using integrated and lightweight ECC with private blockchain for multimedia medical data processing. Multimed. Tools Appl. 82(28), 44335–44358 (2023).
Abbas, A. et al. Blockchain-assisted secured data management framework for health information analysis based on internet of medical things. Pers. Ubiquit. Comput. 28(1), 59–72 (2024).
Ali, A., Al-Rimy, B. A. S., Alsubaei, F. S., Almazroi, A. A. & Almazroi, A. A. Healthlock: Blockchain-based privacy preservation using homomorphic encryption in internet of things healthcare applications. Sensors 23(15), 6762 (2023).
Ali, A. et al. A novel homomorphic encryption and consortium blockchain-based hybrid deep learning model for industrial internet of medical things. IEEE Transac. Netw. Sci. Eng. 10(5), 2402–2418 (2023).
Dhasaratha, Chandramohan, Mohammad Kamrul Hasan, Shayla Islam, Shailesh Khapre, Salwani Abdullah, Taher M. Ghazal, Ahmed Ibrahim Alzahrani, Nasser Alalwan, Nguyen Vo, and Md Akhtaruzzaman, “Data privacy model using blockchain reinforcement federated learning approach for scalable internet of medical things,” CAAI Transac. Intell. Technol., 2024.
Ahmad, Wasim, Mohammed Amin Almaiah, Aitizaz Ali, and Mohmood A. Al-Shareeda. “Deep learning based network intrusion detection for unmanned aerial vehicle (uav).” In: 2024 7th World Conference on Computing and Communication Technologies (WCCCT), pp. 31–36. IEEE, 2024.
Alkhdour TA, Almaiah MA, Ali AI, Lutfi AB, Alrawad MA, Tin TT. Revolutionizing Healthcare: Unleashing Blockchain Brilliance Through Fuzzy Logic Authentication. J. Theor. Appl. Info. Technol., 102(4) (2024).
Almaiah MA, Ali AI, Shishakly RI, Alkhdour TA, Lutfi AB, ALRAWAD M.A novel federated-learning based adversarial framework for audio-visual speech enhancement. J. Theor. Appl. Info. Technol., 102(4) (2024).
Davarasan, A., Samual, J., Palansundram, K. & Ali, A. A Comprehensive review of machine learning approaches for android malware detection. J. Cyber Secur. Risk Audit. 2024(1), 38–60 (2024).
Ayub, N. et al. Forecasting multi-level deep learning autoencoder architecture (MDLAA) for parametric prediction based on convolutional neural networks. Eng. Technol. Appl. Sci. Res. 15(2), 21279–21283 (2025).
Hariyani, Y. S., Eom, H. & Park, C. DA-Capnet: Dual attention deep learning based on U-Net for nailfold capillary segmentation. IEEE Access 8, 10543–10553 (2020).
Bodenstedt, S. et al. Active learning using deep Bayesian networks for surgical workflow analysis. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 14, 1079–1087 (2019).
Abdrabou, M. & Aaron Gulliver, T. adaptive physical-layer authentication for IoT in MIMO communication systems using support vector machine. IEEE Internet Things J. 10(22), 19861–19873 (2023).
Zhao, Ge., Li, X. & Li, H. A trusted authentication scheme using semantic LSTM and blockchain in IoT access control system. Int. J. Semant. Web Info. Syst. (IJSWIS) 20(1), 1–27 (2024).
Thilagam, K. et al. “Secure IoT healthcare architecture with deep learning-based access control system”. J. Nanomater. 2022(1), 2638613 (2022).
Khan, H. U. & Ali, Y. Modeling security evaluation framework for IoHT-driven systems using integrated decision-making methodology. Sci. Rep. 14(1), 12233 (2024).
Acknowledgements
Princess Nourah bint Abdulrahman University Researchers Supporting Project number (PNURSP2025R79), Princess Nourah bint Abdulrahman University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
G Karthik Reddy, and Nageswara Rao Lavuri: Conceptualization, Methodology, Software Data curation, Writing- Original draft preparation, Revsiewing and Editing, Software Validation. Krishna Dharavath and Yogapriya J: Conceptualization, Data Curation, visualization, Formal Analysis. Shabana Urooj and Nidal Nasser: Funding Acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project Administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Reddy, G., Lavuri, N.R., Urooj, S. et al. Dual attention-based deep learning with blockchain for multimedia data processing and secure access control in IoHT. Sci Rep 15, 40589 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-025-24384-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-025-24384-y