Abstract
The Gamma Factory (GF) project aims to generate high-intensity \(\gamma\)-ray beams of tunable energy and relatively small energy spread. Such beams can be optimized to generate an intense photo-neutron source, capable of driving an advanced nuclear energy system (ANES) for nuclear waste transmutation and supplying electrical power that is necessary for the GF operation mode of the Large Hadron Collider storage ring. In this study, we investigate the feasibility of driving ANES with the GF beam which is optimized to maximize the neutron production rate. The dependence of the ANES thermal power on the distance between the positions of the ANES and the GF \(\gamma\)-ray source is evaluated. For the \(\gamma\)-ray beam reaching the intensity of \(\sim 10^{19}\) photons per second, the ANES thermal power could exceed 500 MWt. Under the assumption that ANES operates over 20 years, the transmutation rate could reach \(30\%\) for five typical long-lived fission products (LLFPs): \(^{79}\)Se, \(^{99}\)Tc, \(^{107}\)Pd, \(^{129}\)I, \(^{137}\)Cs. Our comparative studies show that although the neutron production efficiency of the GF \(\gamma\)-ray beam (per MW of the beam power) is approximately 14 times lower than that of the 500 MeV proton beam, the overall net ANES power production efficiency for the GF beam driver scheme could be comparable to that of the proton beam driver scheme, while providing additional transmutation capacity, not available for the proton beam driven scheme. It is suggested that the GF-driven ANES could provide a viable solution for the efficient transmutation of the loaded LLFPs with no prior isotopic separation, and generate the requisite electrical power for its operation, with reduced production of LLFPs over its operation cycle.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Nuclear power is considered as a strategic choice to solve the future energy supply and to ensure sustainable economic and social development1,2. At present, it supplies around one-quarter of the world’s clean electricity3. Along with the development of nuclear power, the generation of spent nuclear fuel (SNF) also grows accordingly. While less than one third of the SNF inventory is reprocessed each year4, about 10, 000 t remains to be disposed5. How to safely dispose the stored and newly generated SNF is becoming an urgent issue to ensure the sustainable development of nuclear power6.
To solve the SNF problem, the “partitioning-transmutation” concept has been suggested in the 1990s7,8,9,10,11. After recovering U and Pu from SNF by PUREX process, high-level radioactive hazards are mainly constituted of radiotoxic transuranics (TRUs) and long-lived fission products (LLFPs), including \(^{79}\)Se, \(^{93}\)Zr, \(^{99}\)Tc, \(^{107}\)Pd, \(^{129}\)I, \(^{135}\)Cs, \(^{137}\)Cs. Transmutation of LLFPs mainly relies on neutron capture reactions or photo-neutron reactions12,13,14,15. LLFPs can be transmuted into short-lived or stable nuclei by using a high-flux neutron or photon source. To perform an efficient transmutation of LLFPs, isotopic separation becomes a necessity since LLFPs have relatively small isotopic abundances. However, no isotope-separation system for high-level nuclear wastes is so far technologically and economically feasible on an industrial scale16.
Recently, a novel concept of the advanced nuclear energy system (ANES) has been proposed for transmuting LLFPs efficiently without isotopic separation17. Such ANES consists of a photo-neutron source (PNS) and a subcritical reactor. The operation aspects of ANES are similar to those of a canonical Accelerator Driven System (ADS). However, there are significant differences between the photon-beam-driven ANES and the proton-beam-driven ADS—both in the role of the driver beam and in the scheme of neutron production.
Seven LLFPs are loaded in the reactor core for the neutron-driven transmutation. For the ANES operating mode at a thermal power of 500 MWt, its PNS must be driven by a high-intensity photon beam, of \(10^{19}\) photons per second. Such a flux is many orders of magnitudes higher than that of the existing and the future electron-beam-driven laser-Compton scattering sources18,19.
The Gamma Factory (GF) proposal18 is currently being studied within the CERN Physics Beyond Colliders (PBC) framework20,21. PBC was created as a discussion, support, and evaluation forum for studies of complementary options for the future CERN particle-beam-driven research programme.
One of the multiple goals of GF is to generate high-intensity \(\gamma\)-ray beams of tunable energy and relatively small energy spread, with energies up to \(\approx 400\) MeV, and photon fluxes exceeding those of the currently available \(\gamma\) sources by many orders of magnitudes18. The leap in the GF photon flux can be achieved by colliding laser photons with the atomic beams of partially stripped ions circulating in one of the CERN storage rings.
The GF photon beam can be optimized to maximize the production rate of 7–20 MeV photons. Photons in this energy range can be produced by atomic beams stored in the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) rings. They can excite the giant dipole resonance (GDR) in medium-mass and heavy nuclei22. Since the cross section for these processes is in the barn range, a large fraction of the LHC radio-frequency (RF) power can be converted into the power of neutron and radioactive-ion beams by colliding the GF photon beam with stationary targets18,19,23. The GF \(\gamma\)-ray beam can open new avenues: (1) for the development of the photon-beam-driven ANES, and (2) for the highly efficient transmutation of nuclear waste24.
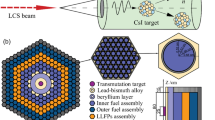
In this paper, we present our exploratory studies of the GF-based ANES, schematically shown in Fig. 1. The GF \(\gamma\)-ray beam produces an intense PNS. Such PNS then delivers neutrons to the subcritical core of the ANES, enabling both the fission energy generation and the nuclear transmutation. Since the operation of GF requires a stable electrical supply of approximately 50 MW, it is assumed in the following that the GF-based ANES produces comparable or higher electric output power to fulfill such a demand. This condition specifies the required minimal power of the GF driver beam.
The paper is organised as follows. An optimized neutron generation scheme is first introduced with the aim of reducing the \(\gamma\)-ray intensity requirement. The dependence of the ANES thermal power on the distance d between the positions of the ANES and GF \(\gamma\)-ray source is then evaluated. Under the assumption that the ANES operates over 20 years, the transmutation rates for seven selected LLFPs are evaluated. After that, the respective advantages of the photon-beam-driven and the proton-beam driven ANES are discussed. Finally, some supplementary information on the used computational methods and the studied materials is provided.
Gamma Factory \(\gamma\)-ray beam
The GF idea18 is to use bunches of partially stripped ion (PSI) beam, circulating in the LHC, and to collide them with laser photon pulses stored in a Fabry–Perot (FP) cavity; cf. Fig. 1a. In the process of a resonant absorption of a laser photon by PSI, followed by a spontaneous atomic-transition emission of a secondary photon, the initial laser-photon frequency is boosted by a factor of up to \(4\gamma ^{2}_{L}\), where \(\gamma _{L}\) is the relativistic Lorenz factor of the partially stripped ion beam. The GF \(\gamma\)-ray beams produced by the atomic-transition emissions can push the intensity limits of the presently operating light sources by at least 7 orders of magnitude in the particularly interesting \(\gamma\)-ray energy domain of \(1\, \textrm{MeV}\lesssim E \lesssim 400\) MeV. The GF \(\gamma\)-ray beam is characterized by a strong correlation between the photon energy E and its emission angle \(\theta\). The energy tunability of the GF \(\gamma\)-ray beam is achieved by simultaneously tuning the Lorenz factor \(\gamma _{L}\) of the PSI beam and by adjusting the wavelength \(\lambda\), or the incident angle \(\theta _{l}\), of the stored laser photons to assure the resonant photon absorption. The \(\gamma\)-ray energy can be expressed as25,26:
where \(E_{\textrm{max}} = (1+\beta )\gamma _L\hbar \omega ^{\prime }\), \(\beta\) is the ion speed normalized by the speed of light in the vacuum, and \(\hbar \omega ' = \hbar \omega \gamma _L (1 + \beta \cos \theta _l)\), where \(\hbar \omega\) is the laser photon energy. For small values of \(\theta\) and \(\theta _{l}\), it can be approximated as:
Up to now, all the high-intensity \(\gamma\)-ray beams have been generated by colliding laser photons with electron beams. The cross section for the inverse Compton-scattering process is by a factor of up to \(10^{9}\) smaller than the resonant atomic photo-excitation cross section of PSIs. This is the main reason why the intensity of the PSI-beam-driven \(\gamma\)-ray beam can be higher than that of the electron-beam-driven ones by many orders of magnitude18.
Several essential GF-project milestones have already been achieved:
-
1.
Demonstration of efficient production, storage and operation of the PSI beams in the SPS and LHC27,28,29,30,31, including the assessment of stability and measurement precision in a beam position and momentum in the SPS area where laser pulses would interact with atomic-beam bunches32.
-
2.
Design33 and experimental demonstration of the stable storage of more than 200 kW of average power in a Fabry–Perot resonator (\(\sim\)700 kW has already been achieved)33,34,35,36.
-
3.
Development of dedicated simulation tools37,38,39 to conduct detailed GF feasibility studies and to evaluate the quality of the proposed GF research tools in several branches of science: particle physics40,41,42, nuclear physics23,43,44, atomic physics44,45,46,47,48, fundamental physics44,49,50,51,52 and accelerator physics36,40,53,54,55,56,57,58,59.
The optimal PSIs for the ANES application are the helium-like calcium ions, \(\hbox {Ca}^{18+}\). A detailed discussion of the production and storage of the Ca beam in the CERN accelerator complex can be found in55. A specific choice of the atomic transition: \(1s^2\, ^1\textrm{S}_0 \rightarrow 1s2p\, ^1\textrm{P}_1\), selected for the studies presented in this paper, maximizes the fraction of the GF photon flux in the relevant GDR energy region of 7–20 MeV.
In all the published to date GF applications studies, the required photon flux has been limited to \(\sim \,10^{17}\,\gamma /\)s. Such intensities can be reached within the current CERN accelerator infrastructure operation constraints. The GF-driven ANES case, as we shall discuss in this paper, requires increasing photon flux by two orders of magnitude. To achieve such a goal, the following two upgrades to the LHC RF system will have to be made:
-
Currently, the LHC RF power is generated by \(300\,\text {kW/400}\) MHz klystrons supplying 4.8 MW power to the LHC beams60,61. In order to continuously produce \(\sim \,10^{19}\,\gamma /\)s by the stored \(\hbox {Ca}^{+18}\) beam, the klystron power will have to be increased by a factor of 4 to fully compensate for the ion energy loss in the process of \(\gamma\)-ray emission. (LEP2, an earlier storage ring installed in the LHC tunnel, was already operating with 44 klystrons, each of 1.3 MW power, delivering the 57 MW RF-power to the electron beam.)
-
The present LHC circumferential voltage of 8 cavities (two cryomodules) is \(C_v = 16\) MV61. For the \(\sim \,10^{19}\, \gamma /\)s beam produced by He-like Ca ion bunches, \(C_v\) will have to be increased to the value of \(\sim \,180\) MV. (LEP2 was operating with \(C_v = 3650\) MV to compensate for the average \(\sim \,3\) GeV per-turn energy loss of each of the electrons/positrons.)
For the current laser-technology accessible case of the 500 ps long, 5 mJ pulse-power and 20 MHz repetition-rate “Erbium laser” photon pulses, stored in the FP cavity and colliding with the \(\hbox {Ca}^{18+}\) ion bunches of \(10^9\) ions/bunch at the zero-degree crossing geometry, the maximal achievable \(\gamma\)-ray production rate could reach the value of \(\sim \,10^{18}\,\gamma /\)s, which is a factor of 10 lower than that required for the ANES application. The proposed solution to reach the requisite \(\gamma\)-beam intensity in collisions of laser pulses with PSIs at a realistic crossing angle of 1 deg requires the implementation of 20 identical FP cavities, similar to those designed for the GF Proof-of-Principle experiment62. In the studies presented in this paper, these cavities are assumed to be implemented, in the 40-meter-long LHC straight section with the constant spacing of 2 m. The assumed large \(\beta ^* = 50\) m collision optics, in the centre of the cavities assembly, allows to minimize the variation of the transverse ion-bunch size in the interaction point (IP) region.
The full set of parameters used in the GF \(\gamma\)-ray beam simulations, including the specification of the \(\hbox {Ca}^{18+}\)-beam parameters, the laser-pulse parameters, and the optics of the IP region is presented in Table 1. A PSI beam-cooling scheme allowing to reduce the PSI-bunch length to 1.5 cm is discussed in55.
As shown in Fig. 2, the power of the GF \(\gamma\)-ray beam produced is expected to be 16.6 MW, provided that the simulation parameters presented in Table 1 remained constant over the \(\gamma\)-ray beam production time. In reality, the beam power may be gradually decreasing over the run-time because of uncompensated losses of ions in collisions with residual-gas particles in the LHC rings. As a consequence, the day-average \(\gamma\)-ray beam power could, in general, be smaller than the peak power, defined canonically as the maximal one, at the beginning of the run, and specified by the parameters in Table 1. For three 5-hour-long He-like Ca ion-beam runs per day, and for the 5-hour-long beam lifetime—as extrapolated from the LHC test runs with the H-like Pb beam31—the day-average number of emitted photons per second is, by a factor of 2.5, lower than its peak value. This reduction can, however, be compensated by the continuous increase, as a function of the running time, of the power of the laser photon pulses stored in the FP cavity. The factor 7 tuning margin here was already established in the dedicated GF studies33,34,35,36. In the following, it is assumed that the average GF-beam power per run can be made equal to its peak value specified by the beginning-of-the-collision-run parameters of Table 1.
It may be worthwhile to note that for the 1.5 cm long ion bunches, the \(\gamma\)-ray beam power will be delivered in the form of short, \(\approx \,50\) ps long, \(\gamma\)-ray pulses of \(\approx \,16.6\) GW separated by 50 ns long gaps. For the ANES studies presented in this paper, the timing structure of the \(\gamma\)-ray pulses is of secondary importance as the neutron moderation time (a microsecond range) is sizeably larger than the 50 ns interval between the beam pulses. For the ANES application where the timing structure of the neutron flux, rather than the photon flux, matters, the \(\gamma\)-ray beam can be considered as the continuous one at the time-scale of microseconds.
The spectrum of the GF \(\gamma\)-ray beam covers the required GDR and photo-fission domain of energies and reaches a sufficiently large beam intensity and a sufficiently small angular divergence to be used as the driver of PNS.
The transverse-plane distributions of the GF \(\gamma\)-ray beam hits at the three studied distances the \(^{238}\)U target which produces the required PNS and has a fixed radius of 9 cm, from the \(\gamma\)-beam production zone of \(d = 300\), 500 and 800 m are shown in Fig. 3. Since the LHC superconducting magnets have to be shielded from the excessive neutron fluxes, the ANES system cannot be placed at distances smaller than 300 m from the GF \(\gamma\)-ray source production zone.
Figure 3 demonstrates the effects reflecting the divergence of the GF \(\gamma\)-ray beam and the correlation of the \(\gamma\)-ray beam energy with its emission angle. As the distance to the ANES system increases, the energies of those \(\gamma\)-rays that hit the PNS target rise.
Photo-neutron production
The neutron production rate of PNS per \(\gamma\)-ray \(P_{\gamma n}\) depends on the \(\gamma\)-ray spectral distribution and the GDR cross section. The neutrons are produced in both the photo-fission64 and photo-neutron processes. In our studies, the neutron production cross sections \(\sigma _{x n}\) is calculated by the TALYS software65. For the \(^{238}\)U target, \(\sigma _{x n}\) reaches its maximal value of \(\approx \,730\) mb at the photon energy of 14 MeV. For the photon energy ranging from 10.46 MeV to 16.39 MeV, \(\sigma _{x n}\) exceeds 1/2 of its maximal value. This energy range is thus optimal for photo-neutron production.
Fine-tuning of the laser wavelength66 and of the corresponding resonant \(\gamma _L\) of the \(\hbox {Ca}^{+18}\) beam allows to maximize the number of photons in the optimal energy range for PNS placed at various distances d from the GF photon source.
The photo-neutron production rate \(P_{\gamma n}\) is shown in Fig. 4 as a function of the distance d for three different laser wavelength settings. It is shown that, for the fixed PNS target radius, \(P_{\gamma n}\) decreases with the increasing d due to the \(\gamma\)-ray beam divergence. For \(\lambda =1395\) nm, \(P_{\gamma n}\) is marginally higher for the other two laser wavelengths.
Our simulations show that approximately 30\(\%\) of the total number of photo-neutrons can be attributed to the photo-fission reactions. \(P_{\gamma n}\) reaches a value of 0.023, which does not include the contribution of the secondary fission reactions induced by the produced neutrons inside the \(^{238}\)U target. Since the contribution of neutrons produced by the secondary reaction is negligible relative to that of the primary reaction. Note that this value is by a factor of 2 higher than that given by Sun et al.17. This is because the \(^{238}\)U target nucleus, considered in our studies, has a higher neutron-production cross-section as compared to the CsI target used in17. Therefore, for the \(^{238}\)U target, the \(\gamma\)-ray intensity that is required to drive ANES operating at the same thermal power could be reduced accordingly.
Performance of ANES
The geometrical layout of ANES, cf. Fig. 1b, is almost the same as the one shown in17. The target material used for PNS is changed to \(^{238}\)U. In addition, the enrichment of \(^{235}\)U loaded in the fuel assembly is changed to the value of \(25.25\%\), which leads to the initial effective neutron multiplication factor \(k_{\textrm{eff}}=0.979\). PNS produces mainly fast neutrons with energies peaked at a MeV-level. Neutrons escaping from the \(^{238}\)U target have to be moderated into thermal or epithermal neutrons which can be readily absorbed by the fuel assemblies, inducing the nuclear fission process. A lead-bismuth eutectic (LBE) layer and a beryllium (Be) layer are used for neutron moderation and multiplication, respectively (see Fig. 1). The former also plays a key role in cooling the \(^{238}\)U target. The optimised thicknesses for these layers are \(T_{\textrm{Be}}=16\) cm and \(T_{\textrm{LBE}}=2\) cm. The spectra of neutrons emitted from the PNS \(^{238}\)U target, the LBE coolant and the Be moderator are presented in Fig. 5.
Spectral distributions of neutrons escaped from different layers of ANES for the GF \(\gamma\)-ray beam with \(\lambda =1550\) nm, together with the cross-section curve of the \(^{235}\)U(n,f) reaction. The thicknesses of the LBE and Be layers used in the Geant4 simulations are \(T_{\textrm{LBE}}=2\) cm and \(T_{\textrm{Be}}=16\) cm, respectively.
The GF \(\gamma\)-ray beam, for \(\lambda =1550\) nm and \(d=300\) m, produces \(\sim \,1.6\times 10^{16}\) neutrons/s per MW of beam power which escape from the PNS target.
The cross-section curve of \(^{235}\)U(n,f) reaction is also shown in Fig. 5. One can see that the neutron spectrum softens significantly in the moderator. The moderated neutrons have more than two orders of magnitudes higher fission, (n,f), reaction cross sections than the PNS-originated fast neutrons. Their supply increases the neutron flux in the reactor core such that the effective subcritical neutron multiplication factor67 reaches the maximal value of \(k_{s}\) = 0.993 for ANES placed at a distance of 300 m from the GF photon source.
The overall efficiency of the GF photon beam in the increasing neutron flux in the reactor core is often quantified in terms of the \(k_{s}\) and \(k_{\textrm{eff}}\) reactor parameters by the neutron worth68 parameter defined as:
For the ANES system discussed in this paper \(\varphi \approx\) 3.07. It is two times higher than that given in17, for the same integrated photon flux.
The neutron spectra in different regions of the subcritical reactor core are shown in Fig. 6. The neutron flux decreases along the radial direction, in particular in the LLFPs assembly, where neutrons are absorbed by the transmutation processes. In the region of LLFPs assembly, the shape of the neutron spectrum is very similar to those in the region of the inner fuel assembly. In the shield region, the neutron flux is three orders of magnitudes lower than that in the inner region of the fuel assembly, indicating effective shielding that reduces significantly the neutron radiation coming from ANES.
The performance of ANES can be quantified in terms of: \(k_{\textrm{eff}}\), \(k_{s}\), the reactivity \(\rho\), the effective multiplication factor for prompt neutrons \(k_{p}\), the effective delayed neutron fraction \(\beta _{\textrm{eff}}\), the neutron generation time \(\Lambda\) and the neutron worth \(\varphi\)69,70. Values of these parameters for the GF-beam-driven ANES are collected in Table 2. The initial value of \(k_{\textrm{eff}}\) is 0.979. During two years of burn-up, \(k_{\textrm{eff}}\) decreases to 0.902. The system reactivity \(\rho =(k_{\textrm{eff}}-1)/k_{\textrm{eff}}\) is then calculated to be less than \(-0.021\). Such a negative \(\rho\) value measures the safety of the proposed ANES setup.
The ANES thermal power \(P_{t \gamma }\) can be evaluated by the following formula17:
where \(I_{\gamma }\) is the \(\gamma\)-ray beam intensity at IP and \(\bar{v}\) is the average number of fission neutrons. The dependence of \(P_{t \gamma }\) on d is shown in Fig. 7a. At \(\lambda =1395\) nm, \(P_{t \gamma }\) reaches the value of 528 MW. It is slightly higher than those obtained for the two other laser wavelengths owing to the highest photo-neutron yield, as shown in Fig. 3a. (Here, the operation-time dependence of \(P_{t \gamma }\) is not taken into account. The reactor thermal power should be considered as the initial one at the starting point of the ANES operation. It will decrease with the speed of burning of nuclear fuel unless the GF photon flux is increased to compensate for the diminishing flux of fission neutrons.)
The thermal power \(P_{t \gamma }\) of the subcritical reactor as a function of the distance d between the GF photon source and ANES for the spectrum-integrated photon intensity \(I_\gamma =10^{19}\,\gamma /\)s at IP (a), and the dependence of the required \(I_\gamma\) on the thermal power \(P_{t \gamma }\) and the distance d (b). In panel (b), the values of the key parameters used in the calculations are: \(P_{\gamma n}=0.023\), \(\varphi =3.07\) and \(k_{\textrm{eff}}=0.979\).
According to Eq. (4), the spectrum-integrated photon-beam intensity \(I_{\gamma }\) which is necessary to reach the required \(P_{t \gamma }\) depends upon the distance d between the ANES and photon-source positions. A contour plot for such dependence is shown in Fig. 7b. It indicates that reaching higher \(P_{t \gamma }\) requires larger \(I_{\gamma }\) or the smallest allowed distance d. If ANES is positioned 320 m away from the GF photon source, its initial thermal power exceeds 500 MWt when \(I_{\gamma }=10^{19}\,\gamma /\)s.
To transmute LLFPs efficiently, the minimal thermal power of the order of 100 MWt is required. For such a power, \(I_{\gamma }\) in the GF-driven ANES should exceed \(10^{18}\,\gamma /\)s, which is \(\sim \,5.5\) times lower than the one estimated in17 for an idealized and unrealistic case of ANES placed right at the position of the electron-beam-driven photon source.
Transmutation of LLFPs
Transmutation of LLFPs over 20 years irradiation for the initial thermal reactor power of 500 MWt. The percentages of transmuted LLFPs after 20 years of the ANES operation are in the following order: \(^{99}\)Tc\(\le ^{129}\)I\(\le ^{107}\)Pd\(\le ^{79}\)Se\(\approx ^{137}\)Cs\(\le ^{135}\)Cs\(\le ^{93}\)Zr.
The time dependence of transmuted LLFPs over 20 years of continuous operation of the GF-beam-driven ANES has been simulated. As shown in Fig. 8, the mass of the transmuted LLFPs in the LLFPs assembly increases approximately linearly with the ANES operation time. During the 20-year-long operation time, the reduction of the number of the \(^{79}\)Se, \(^{99}\)Tc, \(^{107}\)Pd, \(^{129}\)I and \(^{137}\)Cs isotopes is higher than \(35\%\), whereas for \(^{93}\)Zr and \(^{135}\)Cs, the transmutation rates are less than \(20\%\). Similar results have been obtained in the fast neutron transmutation design71. The low transmutation efficiency for \(^{93}\)Zr and \(^{135}\)Cs isotopes is mainly due to their relatively small neutron capture cross sections.
The rate of transmuted LLFPs is used to evaluate the effective half-life \(T_{\textrm{eff}}\)17, the transmutation rate TR and the support ratio SR for these LLFPs. \(T_{\textrm{eff}}\) is defined as the effective half-life of LLFPs considering both the transmutation process and the natural decay in the reactor core. TR is the ratio of the mass of the transmuted LLFPs to that of the initially loaded ones, and SR is the ratio of the mass of the transmuted LLFPs to that of the produced ones. The values of these parameters for the GF-driven ANES are shown in Table 3. \(T_{\textrm{eff}}\) of the transmuted LLFPs in the GF beam-driven ANES is \(\sim \,100\) years. This value is significantly smaller than the one for non-transmuted LLFPs for which \(T_{\textrm{eff}}\) is larger than \(10^6\) years. For the \(^{99}\)Tc, \(^{107}\)Pd, \(^{129}\)I and \(^{137}\)Cs isotopes, TR reaches \(\sim \,2\)–\(3\%\) per year. SR is larger than 1.0 for \(^{79}\)Se, \(^{99}\)Tc, \(^{107}\)Pd, \(^{129}\)I and \(^{137}\)Cs, indicating their decreasing yields as a function of the operation time of ANES. For the \(^{93}\)Zr and \(^{135}\)Cs isotopes, SR is smaller than 1.0 both due to the small neutron capture cross sections and the large production yields. Considering the transmuted mass of the LLFPs is comparable to the LLFPs produced in fuel assemblies, the total amount of LLFPs in ANES will remain almost constant. It should be noted that the averaged TR over the seven LLFPs can reach \(2.02\%\) per year for the GF-beam-driven ANES. This is slightly higher than \(1.94\%\) per year given in17 and \(1.51\%\) per year in a fast reactor system71. As a consequence, the presented ANES system could be a viable solution for the efficient transmutation of the loaded LLFPs with no prior isotopic separation, and meanwhile with reduced production of LLFPs over its operation cycle.
Discussion
In this section, we discuss the relative advantages and disadvantages of the photon-beam-based ANES and the proton-beam-based one. Additional Geant4 simulations have been performed to study the neutron production in metallic \(^{238}\)U irradiated by the 500 MeV proton beam. Note that such a proton beam could be produced by the China initiative Accelerator Driven System6. The simulation results show that each proton produces on average \(\sim \,18\) neutrons. These proton-neutrons have the average energy of 12.32 MeV, which is significantly higher than 5.96 MeV obtained with the GF \(\gamma\)-ray beam. The 1 MW proton beam can then produce \(\sim \,2.25\times 10^{17}\) neutrons escaping from the PNS target. The Be-layer moderated neutron flux generated by the proton beam (per MW of the beam power) is thus approximately 14 times higher than that of the GF \(\gamma\)-ray beam of the same power, as shown in Fig. 9.
The intensity ratio of neutrons escaped from different layers of the proton-based ANES to that of the GF-based ANES (per MW of the beam power). The energy of the proton beam used in the Geant4 simulations is 500 MeV, and the thicknesses of the LBE and Be layers are \(T_{\textrm{LBE}}=2\) cm and \(T_{\textrm{Be}}=16\) cm, respectively.
The ratios of the neutron flux in different regions of ANES for the proton and photon beams of the same beam power are shown in Fig. 10. The proton beam produces over 20 times higher the neutron flux in the reactor core compared to the photon-beam-driven scheme. This is attributed to a higher neutron production efficiency and a larger proton-neutron worth \(\varphi _{p}\) \(\sim \,4.2\), compared to \(\varphi =3.07\) for the photon-beam case. The neutron spectra of the proton-beam-based ANES are similar to those of the photon-beam one. The neutron flux in the proton-driven ANES decreases along the radial direction in a similar way as for the photon-driven one.
The thermal power of the proton-beam-driven ANES can be expressed in a similar way as for the photon-beam-driven one:
where \(I_{p}\) is the proton beam intensity and \(P_{p n}=18.4\) is the neutron production rate. According to Eqs. (4) and (5), the photon and proton beam powers required to drive the thermal power of 500 MWt are evaluated to be \(\sim \,16.4\) and 0.86 MW, respectively.
Compared to the GF \(\gamma\)-ray beam, the operation of a high-energy proton beam of the same MW power requires higher electrical power of an accelerator site. For example, to generate the proton beam of 0.75 MW power, the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (JPARC) requires the electrical power of 60 MW72. To produce the \(\gamma\)-ray beam power of 16.6 MW, GF would need the electrical power of \(\sim \,80\) MW. The main electric power consumers for the GF photon-beam production scheme are: (1) the LHC cryogenic system: \(\sim \,36\) MW; (2) the LHC cooling: \(\sim \,8\) MW; (3) the LHC magnets and power converters: \(\sim \,4\) MW on average; (4) the LHC ventilation: \(\sim \,2\) MW; (5) the LHC RF: 3.5 MW for the current 16 MV RF system, and 30 MW for the \(16\;\)MW GF photon-beam production (as discussed in section 2). Note that the rigidity of the PSI beam at the LHC is sufficiently high to allow for multiple emissions of the \(\gamma\)-rays over the PSI revolution time, with negligible particle-beam losses. In the GF scheme, the power of the RF system can thus be directly converted into the power of the GF photon beam with the unprecedented \(21\%\) overall energy efficiency, which outperforms the energy efficiency of the present ICS and FEL photon sources by 3–4 orders of magnitude.
The above comparison shows that the electrical power required to produce a 1 MW proton beam is 17 times higher than that of GF \(\gamma\)-ray beam. Therefore, even if the \(\gamma\)-ray beam has the lower neutron production efficiency, the overall electrical power efficiency of the GF-driven ANES could be comparable to that of the proton-beam-driven ANES. It remains to be added that while producing the MW-class proton beams represents a serious technological challenge, related to the beam-dynamics effects that are specific to high-density bunches of charged fermions, there is no intensity limit for the high-density “bosonic” photon beams. Its power is determined by the RF power of the PSI storage ring. As a fraction of the ANES power can be used to generate the requisite RF power, the photon-beam-driven scheme may become more attractive for high-power ANES facilities.
There is also another reason to develop the photon-beam-driven ANES. The PNS-driven transmutation scheme which is common to both the proton and photon-driven ANES can be complemented, only in the latter case, by the direct photon transmutation73. The GF photon beam covers the energy domain of 7–9 MeV. Photons in this energy domain can transmute, via resonant photo-fission processes, those of LLFPs which are abundantly produced in the fuel assembly and remain resistant to neutron transmutation17.
The efficiency of the photo-transmutation induced by the GF \(\gamma\)-rays in this energy range is estimated by assuming the following composition of the photon-beam target: selenium, iodine and cesium are loaded in form of compounds, like ZnSe and CsI, to ensure stable chemical forms, while zirconium, technetium and palladium are loaded in metallic forms17. Such a target would have to be placed in front of ANES and should cover the angular range allowing to capture the 7–9 MeV photons. Table 4 shows the isotopic proportions, the photo-neutron reaction thresholds and the annual transmutation masses of these LLFPs. One can see that the annual transmutation masses of \(^{99}\)Tc, \(^{129}\)I and \(^{137}\)Cs are an order of magnitude lower than those in ANES. However, for the \(^{93}\)Zr and \(^{135}\)Cs isotopes for which the neutron-transmutation SR is smaller than 1.0, as shown in Table 3, the photo-fission would be the only way to partially transmute 21 and 32 g/year of these isotopes. Moreover, using the optimized \(\gamma\)-ray beam at energies between 7 and 9 MeV for the photo-transmutation of \(^{93}\)Zr and \(^{135}\)Cs will offer a unique opportunity for the safe disposal of these LLFPs—something that is not reachable for the proton-based ANES.
Conclusions
In this paper, we have presented the exploratory studies of the GF photon-beam-driven ANES, generating up to 500 MW of the thermal power with the efficient transmutation of the loaded and produced LLFPs. Such an ANES is driven by the high-flux PNS which is generated by the optimized GF \(\gamma\)-ray beam. The performance of the GF-based ANES and the resulting transmutation capability have been analyzed. For the GF-driven ANES operating at the thermal power of 500 MW over 20 years, the ratios of the amount of the transmuted LLFPs to that of the produced ones, SRs, are larger than 1.0 for the \(^{79}\)Se, \(^{99}\)Tc, \(^{107}\)Pd, \(^{129}\)I and \(^{137}\)Cs isotopes. The effective half-lives of these LLFPs, \(T_{\textrm{eff}}\), can be reduced from almost \(10^6\) years to about 100 years, which dramatically decreases their cooling times.
Compared to the proton-based ANES, the relative advantages and disadvantages of the GF-based ANES have also been evaluated. Although the neutron production efficiency of the GF \(\gamma\)-ray beam (per MW of the beam power) is about 14 times lower than that of the \(\sim \,1\) GeV proton beam, the GF photon-beam-driven ANES may have a comparable net electrical power supply efficiency and could provide a complementary transmutation method for those of LLFPs that are resistant to the neutron-driven transmutation.
Methods and materials
Computational models and methods
The GF \(\gamma\)-ray source generation was simulated with GF-CAIN63 which is a GF-customized40,46,62 version of the Monte Carlo program CAIN74 developed at KEK–Tsukuba, Japan, for the ILC project75. The beam parameters of the PSI and Erbium laser shown in Table 1 were employed as input for these simulations.
Then, the GF \(\gamma\)-ray source was imported into Geant4 (version 4.10.3)76, which was used to simulate the PNS generation and the following neutron moderating processes. Considering that the photo-neutrons result mainly from the photo-neutron and photo-fission reactions on the \(^{238}\)U target, we then employed the QGSP model in Geant4 to simulate the former reaction and Geant4-GFDPO64 to model the latter.
The production of the proton-neutrons was also simulated with Geant4 by invoking the BERT_HP model77,78. Accordingly, the energy, position and momentum distributions of both PNS and the proton-neutron source were obtained. This source information was further imported into MCNPX (version 2.7)79 which was used to evaluate the performance of ANES. The reaction cross sections required for the MCNPX simulations were taken from the ENDF-VII.1 library80. In the MCNPX simulations, the necessary physical processes, including the neutron-capture, neutron-fission and photo-nuclear reactions were taken into account. In addition, the burn-up calculations of the GF-based ANES were performed using MCNPX. The effective neutron multiplication factor \(k_{\textrm{eff}}\) has a statistical error lower than \(0.1\%\) and the reaction rate for evaluation of the transmutation efficiency is within the \(0.5\%\) statistical precision.
Selection of LLFPs
The selected LLFPs are \(^{79}\)Se (0.096 wt%), \(^{93}\)Zr (8.06 wt%), \(^{99}\)Tc (8.37 wt%), \(^{107}\)Pd (0.82 wt%), \(^{129}\)I (1.87 wt%), \(^{135}\)Cs (13.2 wt%) and \(^{137}\)Cs (13.5 wt%)81,82,83. These radionuclides can cause long-term radioactivity during the geological disposal of SNF14. The compositions of LLFPs were obtained from the burn-up simulation of uranium dioxide pellets by fast breeder reactor core at 50 GWd/t for two years. Without the isotopic separation, such compositions were used as the initial compositions of LLFPs in the pins. The details of these compositions are presented in17.
Selection of \(^{238}\)U target
The metallic \(^{238}\)U was selected for photo-neutron production, since it is widely used in nuclear energy, easy to obtain without enrichment process and has a large neutron production cross section84. Particularly, \(^{238}\)U target possesses an excellent neutron generation property in the case of the target radius smaller than \(\approx 15\) cm85. In our study, the \(^{238}\)U target which produces the required PNS has a fixed radius of 9 cm and a thickness of 2 cm. Majority of photons which do not produce neutrons and fission products are converted over the distance of 1 cm to electron–positron pairs. These pairs are evacuated subsequently from the ANES assembly and absorbed downstream behind ANES—thus reducing significantly the heat load in the PNS target. This is an important aspect to be taken into account while comparing the target heat-load constraints for the proton-beam ADS and the GF-beam ANES systems—the latter can use significantly higher beam power for the same heat load.
The LBE coolant temperature of the lead-based fast reactor ranges from 400 to \({600}^\circ \hbox {C}\)86). The 800 MWt ADS designed by Xi’an Jiaotong University operates with a coolant temperature range of \({300}^\circ \hbox {C}\)–\({530}^\circ \hbox {C}\)87. If we assume that the operation aspects of the ANES system presented in this paper are similar to those of the ADS of similar thermic power, then its coolant temperature is expected to stay below \({600}^\circ \hbox {C}\), which is sizeably lower than the melting point of the \(^{238}\)U target (\(\sim \,{1132}^\circ \hbox {C}\)). The precise thermodynamic studies for the ANES configuration presented in this paper remain to be done. Such studies are beyond the scope of the current (initial study) paper.
It is worthwhile to add that although LBE has great heat dissipation properties and is commonly used as a liquid metal target for spallation neutron production88,89, the \(P_{\gamma n}\) value of LBE is 6.6 times lower than that of the uranium target due to the small photo-neutron production cross section. In our design, in order to achieve sufficiently large \(P_{\gamma n}\) and, simultaneously, reduce the target overheating effect, the \(^{238}\)U target has a dual-layer structure with a channel in the middle for the LBE flow. Moreover, the entire target is immersed in the coolant to ensure effective heat dissipation and prevent the target overheating. The dual-layer structure configuration is shown in Fig. 1b.
Data availability
Data generated during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Wang, C., Engels, A. & Wang, Z. Overview of research on China’s transition to low-carbon development: The role of cities, technologies, industries and the energy system. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 81, 1350–1364 (2018).
Chen, Y. et al. Prospects in China for nuclear development up to 2050. Prog. Nucl. Energy 103, 81–90 (2018).
y León, S. B. World Nuclear Performance Report 2023. Tech. Rep. (World Nuclear Association, 2023). https://world-nuclear.org/our-association/publications/global-trends-reports/world-nuclear-performance-report-2023
Fukuda, K., Danker, W., Lee, J., Bonne, A. & Crijns, M. IAEA Overview of Global Spent Fuel Storage (Storage of spent fuel from Power Reactors, C &S Paper Series, 2003).
Holdsworth, A. F., Eccles, H., Sharrad, C. A. & George, K. Spent nuclear fuel-waste or resource? The potential of strategic materials recovery during recycle for sustainability and advanced waste management. In Waste, vol. 1, 249–263 (MDPI, 2023).
Gu, L. & Su, X. Latest research progress for LBE coolant reactor of China initiative accelerator driven system project. Front. Energy 1–22 (2021).
Andriamonje, S. et al. Experimental determination of the energy generated in nuclear cascades by a high energy beam. Phys. Lett. B 348, 697–709 (1995).
Rubbia, C. et al. Conceptual design of a fast neutron operated high power energy amplifier. CERN-AT-95-44-ET (1995).
Salvatores, M. & Palmiotti, G. Radioactive waste partitioning and transmutation within advanced fuel cycles: Achievements and challenges. Prog. Part. Nucl. Phys. 66, 144–166 (2011).
OECD. Physics and safety of transmutation systems: A status report. OECD Pap. 6, 13. https://doi.org/10.1787/oecd_papers-v6-art13-en (2006).
Zhan, W.-L. et al. Advanced fission energy program-ADS transmutation system. Bull. Chin. Acad. Sci. 27, 375–381 (2012).
Wang, X.-L. et al. Photo-transmutation of long-lived radionuclide \(^{135}\)Cs by laser-plasma driven electron source. Laser Part. Beams 34, 433–439 (2016).
Wang, X. et al. Transmutation prospect of long-lived nuclear waste induced by high-charge electron beam from laser plasma accelerator. Phys. Plasmas 24 (2017).
ur Rehman, H., Lee, J. & Kim, Y. Optimization of the laser-Compton scattering spectrum for the transmutation of high-toxicity and long-living nuclear waste. Ann. Nucl. Energy 105, 150–160 (2017).
Rehman, H. U., Lee, J. & Kim, Y. Comparison of the laser-Compton scattering and the conventional Bremsstrahlung X-rays for photonuclear transmutation. Int. J. Energy Res. 42, 236–244 (2018).
Imasaki, K. et al. Gamma-ray beam transmutation. Energy Convers. Manag. 49, 1922–1927 (2008).
Sun, X. et al. Transmutation of long-lived fission products in an advanced nuclear energy system. Sci. Rep. 12, 2240 (2022).
Krasny, M. W. The Gamma Factory proposal for CERN. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1511.07794. arXiv:1511.07794 [hep-ex] (2015).
Budker, D. et al. Expanding nuclear physics horizons with the Gamma Factory. Ann. Phys. 534, 2100284 (2022).
Jaeckel, J., Lamont, M. & Vallée, C. The quest for new physics with the physics beyond colliders programme. Nat. Phys. 16, 393–401 (2020).
Krasny, M. et al. The CERN Gamma Factory Initiative: An ultra-high intensity gamma source. In 9th International Particle Accelerator Conference, Vancouver, Canada, CERN-ACC-2018-161, CERN-PBC-CONF-2021-017. https://doi.org/10.18429/JACoW-IPAC2018-WEYGBD3 (2018).
Berman, B. L. & Fultz, S. Measurements of the giant dipole resonance with monoenergetic photons. Rev. Mod. Phys. 47, 713 (1975).
Nichita, D., Balabanski, D. L., Constantin, P., Krasny, M. W. & Płaczek, W. Radioactive ion beam production at the gamma factory. Ann. Phys. 534, 2100207. https://doi.org/10.1002/andp.202100207. arXiv:2105.13058 (2022).
Krasny, M. W. Gamma factory. In The Future of the Large Hadron Collider: A Super-Accelerator with Multiple Possible Lives (eds Brünning, O. et al.) 297–303 (World Scientific, 2023). https://doi.org/10.1142/9789811280184_0021.
Wu Chao, A., Tigner, M., Weise, H. & Zimmermann, F. (eds.) Handbook of Accelerator Physics and Engineering, Gamma Factory (World Scientific, 2023).
Luo, W. et al. Estimates for production of radioisotopes of medical interest at extreme light infrastructure—Nuclear physics facility. Appl. Phys. B 122, 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00340-015-6292-9 (2016).
Hirlaender, S. et al. Lifetime and beam losses studies of partially strip ions in the SPS (\(^{129}\)\(\text{Xe}^{39+}\)). In 9th International Particle Accelerator Conference,10.18429/JACoW-IPAC2018-THPMF015. https://doi.org/10.18429/JACoW-IPAC2018-THPMF015 (2018).
Dutheil, Y. et al. Gamma Factory for CERN initiative—progress report. PoS EPS-HEP2019, 020. https://doi.org/10.22323/1.364.0020 (2020).
Kröger, F. M. et al. Charge state tailoring of relativistic heavy ion beams for the Gamma Factory project at CERN. X Ray Spectrom. 49, 25–28. https://doi.org/10.1002/xrs.3039 (2019).
Gorzawski, A. et al. Collimation of partially stripped ions in the CERN Large Hadron Collider. Phys. Rev. Accel. Beams 23, 101002. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevAccelBeams.23.101002 (2020) arxiv:2007.12507..
Schaumann, M. et al. First partially stripped ions in the LHC (\(^{208}\text{ Pb}^{81+}\)). In Journal of Physics: Conference Series (eds Boland, M., Tanaka, H., Button, D. & Dowd, R.). CERN-PBC-Note-2021-019. https://doi.org/10.18429/JACoW-IPAC2019-MOPRB055 (2019).
Ramjiawan, R. L. et al. SPS MD5044: Machine stability characterisation of Gamma Factory SPS Proof-of-Principle Experiment. CERN-ACC-NOTE-2022-0014; CERN-PBC-Notes-2022-006. https://cds.cern.ch/record/2807037?ln=en (2022).
Martens, A. et al. Design of the optical system for the gamma factory proof of principle experiment at the CERN Super Proton Synchrotron. Phys. Rev. Accel. Beams 25, 101601. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevAccelBeams.25.101601 (2022).
Lu, X. Y. et al. Stable 500 kW average power of infrared light in a finesse 35 000 enhancement cavity. Appl. Phys. Lett. 124, 251105. https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0213842 (2024).
Lu, X. Y. et al. 710 kW stable average power in a 45,000 finesse two-mirror optical cavity. Opt. Lett. 49, 6884–6887. https://doi.org/10.1364/OL.543388 (2024).
Granados, E. et al. Prospects for extreme light sources at the CERN accelerator complex. In Compact EUV & X-ray Light Sources 2024. https://doi.org/10.1364/euvxray.2024.etu3a.3 (2024).
Płaczek, W. et al. Gamma Factory at CERN—Novel research tools made of light. Acta Phys. Polon. B 50, 1191–1203. https://doi.org/10.5506/APhysPolB.50.1191 (2019) arxiv:1903.09032.
Curatolo, C., Krasny, M., Placzek, W. & Serafini, L. New simulation programs for partially stripped ions—laser light collisions. In 9th International Particle Accelerator Conference. https://doi.org/10.18429/JACoW-IPAC2018-THPMF076 (2018).
Krasny, M. W., Petrenko, A. & Płaczek, W. BE-ABP Gamma Factory Software Workshop. https://indico.cern.ch/event/1076086/ (2021).
Apyan, A., Krasny, M. W. & Płaczek, W. Gamma Factory high-intensity muon and positron source: Exploratory studies. Phys. Rev. Accel. Beams 26, 083401. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevAccelBeams.26.083401 (2023) arxiv:2212.06311.
Krasny, M. W. Electron beam for LHC. Nucl. Instrum. Meth. A 540, 222–234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nima.2004.11.022 (2005) arxiv:hep-ex/0405028.
Płaczek, W. & Krasny, M. W. Gamma Factory and precision physics at the LHC. Acta Phys. Polon. Suppl. 17, A28. https://doi.org/10.5506/aphyspolbsupp.17.5-a28 (2024).
Budker, D. et al. Expanding nuclear physics horizons with the Gamma Factory. Ann. Phys. 534, 2100284. https://doi.org/10.1002/andp.202100284 (2022) arxiv:2106.06584..
Budker, D., Gorchtein, M., Krasny, M. W., Pálffy, A. & Surzhykov, A. Physics opportunities with the Gamma Factory. Ann. Phys. 534, 2200004. https://doi.org/10.1002/andp.202200004 (2022).
Budker, D. et al. Atomic physics studies at the Gamma Factory at CERN. Ann. Phys. 532, 2000204. https://doi.org/10.1002/andp.202000204 (2020) arxiv:2003.03855..
Bieroń, J., Krasny, M. W., Płaczek, W. & Pustelny, S. Optical excitation of ultra-relativistic partially stripped ions. Ann. Phys. 534, 2100250. https://doi.org/10.1002/andp.202100250 (2022) arxiv:2106.00330.
Serbo, V. G., Surzhykov, A. & Volotka, A. Resonant scattering of plane-wave and twisted photons at the Gamma Factory. Ann. Phys. 534, 2100199. https://doi.org/10.1002/andp.202100199 (2022) arxiv:2108.01859.
Flambaum, V. V., Jin, J. & Budker, D. Resonance photoproduction of pionic atoms at the proposed Gamma Factory. Phys. Rev. C 103, 054603. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevC.103.054603 (2021) arxiv:2010.06912.
Wojtsekhowski, B. & Budker, D. Local Lorentz invariance tests for photons and hadrons at the Gamma Factory. Ann. Phys. 534, 2100141. https://doi.org/10.1002/andp.202100141 (2022) arxiv:2104.03784..
Karbstein, F. Vacuum Birefringence at the Gamma Factory. Ann. Phys. 534, 2100137. https://doi.org/10.1002/andp.202100137 (2022) arxiv:2106.06359.
Balkin, R., Krasny, M. W., Ma, T., Safdi, B. R. & Soreq, Y. Probing axion-like-particles at the CERN Gamma Factory. Ann. Phys. 534, 2100222. https://doi.org/10.1002/andp.202100222 (2022) arxiv:2105.15072.
Chakraborti, S., Feng, J. L., Koga, J. K. & Valli, M. Gamma factory searches for extremely weakly interacting particles. Phys. Rev. D 104, 055023. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevD.104.055023 (2021) arxiv:2105.10289.
Krasny, M. W., Petrenko, A. & Płaczek, W. The Gamma Factory path to high-luminosity LHC with isoscalar beams. PoS ICHEP2020, 690. https://doi.org/10.22323/1.390.0690 (2021).
Zimmermann, F. Accelerator technology and beam physics of future colliders. Front. Phys. 10, 888395. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphy.2022.888395 (2022).
Krasny, M. W., Petrenko, A. & Płaczek, W. High-luminosity Large Hadron Collider with laser-cooled isoscalar ion beams. Prog. Part. Nucl. Phys. 114, 103792. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ppnp.2020.103792 (2020) arxiv:2003.11407.
Cooke, D. A. et al. Measurement and application of electron stripping of ultrarelativistic \(^{208}{\rm Pb} ^{81+}\). Nucl. Instrum. Meth. A 988, 164902. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nima.2020.164902 (2021) arxiv:2006.16160.
Zimmermann, F. et al. Muon collider based on Gamma Factory, FCC-ee and plasma target. JACoW IPAC2022, 1691–1694. https://doi.org/10.18429/JACoW-IPAC2022-WEPOST009 (2022).
Zimmermann, F. et al. Advanced accelerator concepts for dark sector searches and fast muon acceleration. JACoW IPAC2024, MOPR17. https://doi.org/10.18429/JACoW-IPAC2024-MOPR17 (2024).
Zimmermann, F. Beam physics Frontier problems. JACoW eeFACT2022, 42–51. https://doi.org/10.18429/JACoW-eeFACT2022-TUYAT0101 (2023).
Brüning, O. S., Collier, P., Lebrun, P., Myers, S., Ostojic, R., Poole, J. & Proudlock, P. (eds) LHC Design Report Vol. 1: The LHC Main Ring (2004).
Zurbano Fernandez, I. et al. High-Luminosity Large Hadron Collider (HL-LHC): Technical design report. Tech. Rep. (CERN, 2020). https://doi.org/10.23731/CYRM-2020-0010
Krasny, M. W. et al. Gamma Factory Proof-of-Principle experiment. Letter-of-Intent (LoI), CERN-SPSC-2019-031, SPSC-I-253 (2019).
Płaczek, W. Monte Carlo event generator GF-CAIN for photon–PSI collisions with atomic resonant absorption and emission. The program available from the author: wieslaw.placzek@uj.edu.pl (2023).
Shi, X.-M. et al. Geant4 development for actinides photofission simulation. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A Accel. Spectrom. Detect. Assoc. Equip., 169222 (2024).
Koning, A. J. & Rochman, D. Modern nuclear data evaluation with the TALYS code system. Nucl. Data Sheets 113, 2841–2934 (2012).
Liu, Y. et al. A fully hybrid integrated Erbium-based laser. Nat. Photonics, 1–7 (2024).
Xoubi, N. Neutronic design study of accelerator driven system (ADS) for Jordan subcritical reactor as a neutron source for nuclear research. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 131, 71–76 (2018).
Fang, Z.-X. et al. Theoretical analysis of long-lived radioactive waste in pressurized water reactor. Nucl. Sci. Tech. 32, 72 (2021).
Carta, M., Dulla, S., Peluso, V., Ravetto, P. & Bianchini, G. Calculation of the effective delayed neutron fraction by deterministic and Monte Carlo methods. Sci. Technol. Nucl. Install. 2011, 109–124 (2011).
Verboomen, B., Haeck, W. & Baeten, P. Monte Carlo calculation of the effective neutron generation time. Ann. Nucl. Energy 33, 911–916 (2006).
Chiba, S. et al. Method to reduce long-lived fission products by nuclear transmutations with fast spectrum reactors. Sci. Rep. 7, 13961 (2017).
Morita, Y. et al. Capacitor bank of power supply for J-PARC MR main magnets. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A Accel. Spectrom. Detect. Assoc. Equip. 901, 156–163 (2018).
Hayakawa, T. et al. Proposal for selective isotope transmutation of long-lived fission products using quasi-monochromatic \(\gamma\)-ray beams. J. Nucl. Sci. Technol. 53, 2064–2071 (2016).
Yokoya, K. Monte Carlo program CAIN version 2.42 (KEK, 2011).
International Linear Collider (ILC). https://linearcollider.org
Hartling, K., Ciungu, B., Li, G., Bentoumi, G. & Sur, B. The effects of nuclear data library processing on Geant4 and MCNP simulations of the thermal neutron scattering law. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A Accel. Spectrom. Detect. Assoc. Equip. 891, 25–31 (2018).
Guthrie, M. P., Alsmiller, R. G. & Bertini, H. W. Calculation of the capture of negative pions in light elements and comparison with experiments pertaining to cancer radiotherapy. Nucl. Instrum. Methods 66, 29–36 (1968).
Bertini, H. W. & Guthrie, M. P. News item results from medium-energy intranuclear-cascade calculation. Nucl. Phys. A 169, 670–672. https://doi.org/10.1016/0375-9474(71)90710-X (1971).
Pelowitz, D. MCNPX User’s Manual, Version 2.5.0. Los Alamos National Laboratory Report, LA-CP-05-0369 (2005).
Grossi, M. R. The database on nuclear power reactors. https://pris.iaea.org/pris/
Kailas, S., Hemalatha, M. & Saxena, A. Nuclear transmutation strategies for management of long-lived fission products. Pramana 85, 517–523 (2015).
Yang, W., Kim, Y., Hill, R., Taiwo, T. & Khalil, H. Long-lived fission product transmutation studies. Nucl. Sci. Eng. 146, 291–318 (2004).
Wang, H. et al. Spallation reaction study for long-lived fission products in nuclear waste. In EPJ Web of Conferences, vol. 239, 06003 (EDP Sciences, 2020).
Filipescu, D. et al. Photofission and photoneutron cross sections for \(^{238}\)U and \(^{232}\)Th. In EPJ Web of Conferences, vol. 284, 04010 (EDP Sciences, 2023).
Ismailov, K., Saito, M., Sagara, H. & Nishihara, K. Feasibility of uranium spallation target in accelerator-driven system. Prog. Nucl. Energy 53, 925–929 (2011).
Loewen, E. P. & Tokuhiro, A. T. Status of research and development of the lead-alloy-cooled fast reactor. J. Nucl. Sci. Technol. 40, 614–627 (2003).
Lu, T. et al. Preliminary safety analysis on loss of flow accidents and external source transients for LBE cooled ADSR core. Prog. Nucl. Energy 88, 134–146 (2016).
Sasa, T., Saito, S., Obayashi, H. & Ariyoshi, G. 250 kW LBE spallation target for ADS development in J-PARC. In Proceedings of the 3rd J-PARC Symposium (J-PARC2019), 011051 (2021).
Bauer, G. Overview on spallation target design concepts and related materials issues. J. Nucl. Mater. 398, 19–27 (2010).
Acknowledgements
This work has been supported by the National Key R&D Programme of China (Grant No. 2022YFA1603300) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. U2230133). The research of WP has been supported in part by a grant from the Priority Research Area (DigiWorld) under the Strategic Programme Excellence Initiative at the Jagiellonian University in Krakow, Poland.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Baolong Hu: Conceptualization, Methodology, Software, Data curation, Writing-original draft, Supervision, Writing-Reviewing and Editing. Mieczyslaw Witold Krasny: the Gamma Factory (GF) project leader; the initiator and overall coordinator of the GF-beam and ANES aspects of the presented studies; the author of the photon-beam production scheme for the ANES application; co-author of the draft of the paper and its revision; contribution to editing. Wiesław Płaczek: the author of the GF-CAIN Monte Carlo generator and the GF software used in the presented studies; responsible for the optimisation of the laser-photon–ion collision scheme and the numerical simulations of the GF photon-beam production; co-author of the draft of the paper and its revision; contribution to editing. Yun Yuan: Supervision, Reviewing and Editing. Xiaoming Shi: Methodology, Software. Kaijun Luo: Methodology, Software. Wen Luo: Conceptualization, Methodology, Software, Data curation, Writing-original draft, Supervision, Writing—Reviewing and Editing.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, B., Krasny, M.W., Płaczek, W. et al. Efficient transmutation of long-lived fission products in a Gamma Factory beam driven advanced nuclear energy system. Sci Rep 15, 12562 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-025-96505-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-025-96505-6