Abstract
Urban bridges serve not only as transportation infrastructure but also as essential carriers of urban culture. However, existing bridge evaluation systems primarily focus on engineering performance and functional benefits, lacking systematic methods for assessing bridges’ cultural suitability. This study pioneers integrating cultural suitability into a comprehensive bridge evaluation system, establishing a fuzzy comprehensive evaluation method to evaluate bridges’ cultural appropriateness. The method constructs an evaluation index system across six dimensions: spatial accessibility, network convenience, bridge quality, spatial integration, traffic rationality, and interactive participation, evaluating bridges’ cultural suitability through both quantitative and qualitative approaches. Using the Tianjin Liberation Bridge as a case study, the assessment results show an overall cultural suitability score of 4.054, with strong performance in artistic quality (4.323) and spatial integration (4.247), aligning with the bridge’s status as a historical landmark of Tianjin’s port opening and an urban cultural icon. Through cross-validation of expert assessments and public questionnaire surveys, the evaluation system demonstrates strong performance in the comprehensiveness of indicator selection, operability of the assessment process, and accuracy of evaluation results. This evaluation system provides new perspectives and decision-making basis for urban bridge planning, design, and renovation, holding significant theoretical and practical implications for promoting the coordinated development of bridge construction and urban culture.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Urban bridges are critical elements of urban infrastructure that transcend their basic transportation function to become important symbols of cultural identity and urban development1. With the deepening of urbanization, the artistic value of bridges in urban landscapes has become increasingly prominent, evolving into significant elements that shape urban characteristics and enrich citizens’ experiences2. Modern bridge design must consider not only engineering performance and functional efficiency3,4,5, but also emphasize structural aesthetic value and its harmonious integration with urban landscapes and cultural environments6,7,8. Advancements in infrastructure construction have also driven higher public expectations for urban architectural aesthetic quality9, enhancing bridges’ aesthetic value and overall harmony, which is an urgent issue.
Among various types of urban bridges, cross-river bridges hold special significance. They not only overcome natural barriers but also serve as iconic landmarks that shape urban visual characteristics and carry cultural heritage10. In modern metropolitan areas, cross-river bridges often evolve into urban landmarks, significantly shaping the urban visual landscape and becoming important carriers of regional cultural values and historical narratives11. Therefore, studying bridge artistry and exploring how to integrate cross-river bridges into urban cultural environments better while enhancing their harmonious aesthetics in the landscape has become a crucial direction in current bridge artistic research.
Recent years have seen numerous methodologies and frameworks in urban landscape integration research12,13, encompassing various aspects from spatial design to functional layout14,15,16. However, these studies largely approach urban infrastructure from a macro perspective, failing to adequately address the unique challenges faced by bridges as distinctive architectural elements. Particularly regarding the relationship between bridge landscapes and regional culture, there is currently a lack of systematic methods to assess and quantify bridges’ cultural suitability in urban landscapes. Therefore, significant gaps remain in research on the harmonious relationship between bridges and urban landscapes, necessitating further integration of bridges into comprehensive urban landscape design while fully considering their cultural symbolism and historical value.
Cultural suitability, defined as the degree of harmony between architectural structures and their local cultural, historical, and social context, has become a crucial consideration in contemporary urban design. This concept encompasses not only aesthetic integration but also the capacity of buildings to reflect and reinforce local cultural values and historical narratives17. In bridge design, integrating cultural suitability poses unique challenges because bridges serve as both functional infrastructure and cultural landmarks. Introducing the concept of cultural suitability into bridge artistic research effectively addresses the current lack of integration of cultural and landscape considerations.
Cultural suitability refers to how well a structure, such as a bridge, aligns with and respects the local cultural context—including historical significance, aesthetic preferences, and community values. Unlike traditional engineering metrics that focus primarily on a bridge’s structural integrity or material quality, cultural suitability considers how a bridge’s design resonates with the people who interact with it, both functionally and symbolically. For example, in Tianjin’s Liberation Bridge, cultural suitability was considered through its design, which reflects the city’s historical heritage and local architectural style, creating a sense of identity for the community. Similarly, the Sydney Harbour Bridge was not only an engineering achievement but also a symbol of the city’s identity, fostering cultural and emotional connections among residents and tourists alike. By integrating cultural suitability into the evaluation framework, we recognize that a bridge is not merely a functional structure but also a symbolic link between infrastructure and a region’s cultural identity. This approach emphasizes a holistic understanding of bridge planning and maintenance, where the cultural context informs and enhances decision-making.
Bridges are vital infrastructure, and ensuring their safety and longevity requires comprehensive assessment methods. Traditionally, evaluations focus on engineering metrics like structural integrity and load capacity, but modern approaches also incorporate risk and vulnerability assessments. These assess a bridge’s susceptibility to environmental conditions, wear, and potential damage from natural or human factors. Detecting and addressing defects such as cracks and corrosion is crucial to preventing failures and extending the lifespan of bridges. Risk assessment helps identify high-risk structures and prioritize interventions, while defect-detection techniques, ranging from visual inspections to non-destructive testing (NDT), are essential for detecting early damage18,19. By integrating these methodologies with cultural context, our study aims to enhance bridge planning and maintenance decisions, offering a more holistic evaluation beyond traditional engineering considerations.
This study advances the field by developing a comprehensive evaluation system for assessing the cultural suitability of urban cross-river bridges. The research makes several significant contributions: (1) It establishes a systematic framework that incorporates cultural suitability into bridge evaluation, addressing a critical gap in existing assessment methodologies; (2) It employs fuzzy comprehensive evaluation methods to handle the inherent complexity and uncertainty in cultural assessment, providing more nuanced and reliable results; (3) It validates the evaluation system through a detailed case study of the Tianjin Liberation Bridge. As a landmark structure built after Tianjin’s port opening, with significant value in architecture, art, and transportation, it serves as an ideal case for demonstrating the framework’s practical applicability; (4) It emphasizes the importance of cultural considerations in bridge design, potentially influencing future approaches to urban infrastructure development.
This paper is structured as follows: section “Literature review” reviews relevant literature on bridge design evaluation and cultural suitability assessment. Section “Data sources and methods” presents the methodology and evaluation framework. Section “Case study” applies the framework to the case study. Section “Discussion” discusses the findings and their implications, and section “ Conclusions” concludes with recommendations for future research and practice.
Literature review
Problems faced by urban cross-river bridges
The design and construction of urban cross-river bridges are closely related to urban culture and regional characteristics. However, bridge construction still faces several problems. Firstly, bridges and roads are often built by different construction organizations, leading to a lack of coordination between bridges and their surrounding environments, especially in areas with lower road grades10,11. Secondly, most bridges share a similar design style, lacking regional uniqueness and innovation12. Moreover, urban cross-river bridges, which provide passage for vehicles and offer scenic views for pedestrians, face safety hazards and flood risks13,14. Thirdly, most studies focused on the engineering performance of cross-river bridges rather than their regional cultural suitability, resulting in a lack of research on common principles and construction models for bridge design. Therefore, to better address the above problems, it is necessary to conduct in-depth research and discussions on the regional cultural suitability of urban cross-river bridges.
Cultural suitability of urban cross-river bridges
Cross-river bridges are not only key nodes of urban traffic but also significant carriers of urban culture and history. They are endowed with symbolic meanings of connection, communication, and cooperation across various cultural and historical contexts15. Therefore, the design and construction of bridges should consider not only their engineering and technical performance but also their cultural suitability16. The unique nature of bridges imparts specific values, such as cultural suitability17. In recent years, the design of cross-river bridges has shifted from solely engineering evaluations to more comprehensive cultural assessments, including their structures, architecture, and landscapes20,21. A new standard for bridge design is that both safety and harmony with the surroundings are required2. Achieving cultural suitability in urban cross-river bridge design requires careful consideration, including in-depth research, cooperation with local governments, and continuous evaluation, to ensure the bridge serves practical functions and reflects regional culture. However, there is a lack of a comprehensive evaluation system to ensure that cross-river bridges reflect their cultural suitability, not only for assessing the cultural suitability of existing bridges but also for providing design references and inspiration for future bridges22.
Moreover, the evaluation factors play an essential role in the cultural suitability assessment of cross-river bridges. These evaluation factors include not only natural geographical elements such as terrain and climate but also socio-economic factors such as transportation, economy, population, culture, and urbanization23,24,25,26,27,28,29. These evaluation factors are crucial for ensuring the success of bridge design in terms of practicality, safety, and integration with the surrounding cultural and social environment. Analyzing these factors allows for a more comprehensive understanding of bridges’ suitability in specific cultural and social contexts, guiding bridge design not only to meet technical and functional requirements but also to reflect and integrate with local culture and environmental characteristics.
In summary, urban cross-river bridges play a vitally important role in modern urban construction, serving not just as crucial links for transportation but also as carriers of urban culture and history. However, challenges exist in addressing disconnection with urban development, homogenization of design, safety risks, and a lack of systematic summarization. The cultural suitability has gradually gained attention in modern bridge design, emphasizing their harmonious integration with the surrounding environment and reflection of regional culture. To better address these issues and advance bridge construction, in-depth research, cross-sector cooperation, and a complete evaluation system are needed to ensure bridge designs not only meet functional requirements but also reflect local culture and traditions.
Data sources and methods
Establishing a comprehensive and systematic evaluation system for Regional Cultural Suitability of Urban Cross-River Bridges (RCSUCRB) involves three main steps: (1) development of the indicator system, (2) determination of indicator weights, and (3) judgment scoring. To construct the RCSUCRB model, we first conducted a literature review to identify the key factors influencing cultural suitability, as discussed in section “Literature review”. The evaluation of cultural suitability inherently involves the fuzzy characteristics of human attributes and the complex relationships between various influencing factors. The RCSUCRB model is designed with flexibility, allowing its components—such as risk assessment methodologies, defect detection techniques, and the multi-level index for cultural suitability evaluation to be universally transferable. These elements can be adapted to various types of infrastructure and locations, providing a scalable approach to bridge planning and assessment. For instance, the risk assessment process and AHP-based weighting system can be applied to regions with similar climate, geological conditions, or infrastructure concerns, irrespective of local cultural differences. While certain cultural aspects may need to be tailored based on local contexts, the core methodology for assessing structural integrity and environmental risks remains broadly applicable. This adaptability enables the RCSUCRB model to be expanded for diverse global infrastructure assessments, offering a customizable framework while retaining its core principles.
Therefore, this work adopts the fuzzy comprehensive evaluation method based on the Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP)21,24. This method is suitable for evaluations influenced by multiple factors and aims to establish a scientifically reasonable evaluation system, as shown in Fig. 1.
Semantic text analysis method
Semantic text analysis is an advanced text analysis method that delves into the semantic meanings of texts to identify keywords, concepts, and their relationships30. This method first uses web crawling technology to fetch content related to the research topic. Then, word-frequency analysis software is used to segment and analyze the retrieved data, thereby extracting keywords closely associated with the research focus. When dealing with high-frequency words, it is necessary to filter out common words unrelated to the research topic, such as words like “this paper” and “analysis” found in webpage titles, abstracts, and keywords. Through these steps, key indicators can be distilled from existing literature, design methods, and aesthetics studies, including content at the goal, criteria, element, and indicator levels. The specific operational details of this method are well documented in numerous publications, such as31,32,33,34, and thus will not be elaborated upon in this paper.
AHP (analytic hierarchy process)
In the RCSUCRB model, it’s essential to determine the weights to ensure scientific rigor and reliability. Methods of weight determination are generally divided into two categories: subjective weighting35 and objective weighting36. Objective weighting can avoid interference from decision-makers’ subjective judgments, but it requires sufficient statistical data37,38. Given that studies on the suitability of cross-river bridges are still in their early stages and related statistical data are relatively scarce, the knowledge and experience of experts in this field are particularly valuable. To make full use of these resources, this work proposes adopting the expert scoring method, combined with the AHP, for determining weights. AHP, a classical subjective weighting method, allows the setting of preference scales during comparisons, effectively quantifying experts’ opinions and judgments. The internal consistency check in AHP further ensures logical rigor, ensuring that the weights derived from expert questionnaires are scientifically valid. The detailed steps and calculation procedures of the method have been described in the articles of37,39.
-
1.
Construction of the judgment matrix.
Following the development of the comprehensive indicator system for urban cross-river bridge suitability, it is necessary to construct a judgment matrix, which serves as the basis for calculating indicator weights. The elements of the judgment matrix are assigned values using Saaty’s 1–9 scale method (Table 1).
If there are n elements B1, …, Bn, their pairwise comparisons produce a judgment matrix B = (bij) n*n. And for the judgment matrix: bij > 0; bij = 1/bji (i, j = 1, 2…n); bii = 1. After comparing the importance of indicators, 20 experts in related fields are invited to score the importance of pairwise evaluation indicators. The results served as the raw data for calculating the indicators’ weights.
-
2.
Consistency test of the judgment matrix.
In the evaluation system for regional cultural suitability of urban cross-river bridges, comparisons across multiple factors may lead to deviations. Hence, it is necessary to control the degree of deviation within an acceptable range by conducting a consistency test on the judgment matrix. The steps are as follows:
-
1.
According to \({\text{A}}\cdot{\text{W}}={{\text{\varvec{\uplambda}}}_{{\text{max}}}}\cdot{\text{W}}\) (A is the Matrix vector), then the eigenvalue \({{\text{\varvec{\uplambda}}}_{{\text{max}}}}\)is obtained.
-
2.
To get the consistency index, \({\text{~CI}}=\frac{{{{\text{\varvec{\uplambda}}}_{{\text{max}}}} - {\text{n}}}}{{{\text{n}} - 1}}\), where CI is the consistency index, and n is the order of the Matrix.
-
3.
Calculation of the consistency factor (CR), \({\text{CR}} = \frac{{{\text{CI}}}}{{{\text{RI}}}} = \frac{{{{\lambda }}_{{{\text{max}}}} - {\text{n}}/\left( {{\text{n}} - 1} \right)}}{{{\text{RI}}}}\) (CI = consistency index and RI = random index). In the CI, when pairwise comparisons are completely random, in the AHP, the pairwise comparisons in a judgment matrix are considered adequately consistent if the corresponding CR is less than 10%. The RI coefficient is presented in Table 2.
Fuzzy comprehensive evaluation
The evaluation of regional cultural suitability for urban cross-river bridges involves many factors, whose relationships are relatively fuzzy. Additionally, evaluators’ subjective perception may negatively affect the evaluation results. Therefore, based on field research, data characteristics, and the literature, and on indicator weight calculations using the Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP), this work proposes employing the fuzzy comprehensive evaluation method. This method allows for a multidimensional, comprehensive judgment of the evaluation event’s levels, thereby providing a scientific quantitative evaluation of the fuzzy factors41,42. Finally, the fuzzy comprehensive evaluation results are determined for the regional cultural suitability of urban cross-river bridges.
The steps for the fuzzy comprehensive evaluation are as follows:
-
1.
The Factor Set is a set of all factors that affect the evaluation object, expressed as:
-
2.
The Comment Set is a set of evaluation grades made by the evaluator, expressed as:
-
3.
To clarify the importance of each factor, a corresponding weight \({W_i}\) is assigned to each factor \({u_i}\left( {i=1,2,3, \ldots ,m} \right)\). The weight set is represented as:
This must satisfy the normalization and non-negativity conditions, i.e. \(\mathop \sum \limits_{{{\text{i}} = 1}}^{{\text{n}}} {\text{W}}_{{\text{i}}} = 1{\text{~}}\left( {{\text{W}}_{{\text{i}}} \ge 0,\;{\text{i}} = 1,2, \ldots ,{\text{n}}} \right)\).
-
4.
Fuzzy relationship matrix.
Starting from one factor, the degree of affiliation for each element in the factor set is determined. Let \({{\text{u}}_{\text{i}}}\) represent the \({\text{i}}\)-th factor in the factor set, and\({\text{~}}{{\text{r}}_{{\text{ij}}}}\) represent the degree of affiliation between the \({\text{i}}\)-th factor and the \({\text{j}}\)-th comment \({{\text{v}}_{\text{j}}}\). The evaluation result for \({{\text{u}}_{\text{i}}}\) is represented as a fuzzy set:
The single-factor evaluation set is expressed as:
Construct the fuzzy relation matrix:
-
5.
Fuzzy comprehensive evaluation.
The basic model of fuzzy comprehensive evaluation can be expressed as :
Where \(^\circ\) represents fuzzy operations. Finally, the grade of the evaluation object is determined by the maximum membership degree principle:
Construction of the RCSUCRB system
Index system
Data collection
Firstly, search Chinese databases for keywords such as “cross-river bridges,” “urban cross-river bridges,” and “large cross-river bridges,” and obtain a total of 1,672 data entries. Secondly, extract high-frequency keywords for analysis of the Chinese research focus. Finally, filter the extracted high-frequency words and remove unrelated words such as “this paper,” “analysis,” “proposal,” “discussion,” “problem,” etc. Finally, a list of keyword frequencies can be obtained, as shown in Table 3.
Cognitive analysis of word frequency
Analysis of high-frequency keywords usually reveals the hotspots. On this basis, the work synthesizes high-frequency keywords to construct an index system for assessing the regional cultural suitability of urban cross-river bridges.
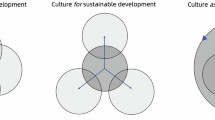
Several core features of urban cross-river bridges are summarized: Firstly, traffic demand is the primary focus, with significant attention paid to solving traffic issues. Secondly, terms related to the artistic aspect of urban cross-river bridges show a close connection with the regional culture. Thirdly, safety is also an essential premise of bridge construction research. Therefore, urban cross-river bridges display their core elements in terms of connectivity, artistic, and safety, as shown in the following figure (Fig. 2).
In the design and evaluation of urban cross-river bridges, connectivity, aesthetics, and safety constitute three core dimensions that interact dynamically. Connectivity primarily measures the bridge’s capacity in traffic networks, which underlies the flow of urban traffic. Artistic quality reflects the bridge’s uniqueness and its integration with regional culture, history, and environment. Safety focuses on the bridge’s ability to withstand disturbances at both spatial and public levels, a critical indicator of its safety, stability, and durability. Connectivity is the foundation of safety; safety is a principle of artistic features, including personal, cultural, historical, and biological aspects; artistic quality is the baseline for connectivity. The interrelationship among these three dimensions provides essential guiding principles for the multidimensional optimization of urban cross-river bridge design, highlighting the multiple requirements of modern urban cross-river bridges.
Establishment of the indicator system
To evaluate the regional cultural suitability of urban cross-river bridges, we developed a four-level assessment framework consisting of Goal level (A), Criteria level (B), Element level (C), and Indicator level (D). At Criteria Level B, we define the broad categories that capture the essential dimensions of cultural suitability, including connectivity, artistic quality, and safety. These criteria serve as the core aspects to be evaluated. Each criterion at Level B is further decomposed into Element Level C, where specific, measurable elements are identified. These elements address the finer details and sub-factors that contribute to the overall cultural suitability of the bridge. In other words, the elements at Level C act as the practical components that guide a more granular evaluation of each criterion. The relationship between Criteria Level B and Element Level C is hierarchical, with the elements serving as building blocks that directly support and enhance the evaluation of the broader criteria. This structure ensures that each element is aligned with its corresponding criterion, creating a clear and logical progression from general categories to specific details. Through a comprehensive process involving literature review, field inspections, and expert consultations, we identified and refined these elements. This approach ensures that the evaluation framework is both grounded in current research and responsive to practical needs (Table 4).
Weight system
Following the calculation method described in section “AHP (analytic hierarchy process)”, this work calculates the weight values and the consistency ratio (CR) for the original statistical data using SPSSAU. The judgment matrices, weight values, and consistency check results for each level of the urban cross-river bridge regional cultural suitability evaluation system are as follows(Fig. 3).
Grading system
Establishment of the indicator system
The evaluation set V = {5, 4, 3, 2, 1}, representing “excellent, good, average, below average, poor,” was established to assess the regional cultural suitability of urban cross-river bridges. Data collection was carried out through three methods: field research, questionnaire surveys, and literature review, with data sources detailed in Table 5. Qualitative evaluation indicators were assessed using questionnaire surveys targeting tourists, nearby residents, and passersby, while quantitative evaluation indicators were collected through field research and literature review. In formulating the evaluation standards for the indicators, values were assigned based on highly recognized existing research standards. They were organized and compiled into the urban cross-river bridge regional cultural suitability evaluation standard table after consultation with relevant experts, as detailed in Table 5.
Division of evaluation levels
Based on the urban cross-river bridge regional cultural suitability evaluation standard table and relevant literature on grading standards43,44, the final division of evaluation levels and corresponding scores for the regional cultural suitability of urban cross-river bridges was established. The grading table is detailed in Table 6.
Following these steps, this study established an evaluation system for assessing the suitability of urban cross-river bridges and refined the reference values and level divisions for the corresponding indicators.
Case study
Introduction to Tianjin liberation bridge
The Tianjin Liberation Bridge is located on the Haihe River between the east station of Tianjin Railway Station and Jiefang North Road. It is currently the only bridge across the Haihe River that can open in both directions. It is a landmark building in Tianjin after the city’s opening to the outside world, holding significant value in architecture, art, and transportation31. Several attractions are located around the Liberation Bridge, including Jinwan Plaza, Italian Style Street, and the Haihe River scenic line. Residential areas nearby include Chaohui Li, Rongyu Rongjing, Yonghe Li, Longtai Li, etc., while office areas include Maoye Building, Longmen Building, and Peace Financial Innovation Service Building, among others.
Data collection
The research area is centered on Tianjin’s Liberation Bridge and covers a 500-meter radius (Fig. 4). Based on the scoring standards for the indicators of urban cross-river bridges’ regional cultural suitability (Table 3), quantitative indicators were scored through literature review and field research. The research data were collected via a combination of online and in-person surveys. A total of 298 questionnaires were distributed, of which 286 were valid, resulting in a 96% validity rate. The questionnaire consisted of three main sections: demographic information, perception of the bridge and surrounding area, and satisfaction with the bridge’s regional cultural suitability. A 5-point Likert scale was used for most questions, ranging from 1 (Strongly Disagree/Very Poor) to 5 (Strongly Agree/Excellent). Representative questions included: “How would you rate the aesthetic appeal of the Liberation Bridge?” and “To what extent do you think the bridge contributes to the cultural identity of Tianjin?” The questionnaire was administered both online and in-person, ensuring a broad demographic reach. Socio-demographic data from respondents indicated a balanced distribution across age groups, with 60% male and 40% female respondents, 70% of whom were familiar with the area. This approach aimed to gather diverse insights into the perceptions of both local residents and tourists.
Location information of Tianjin’s liberation bridge: http://bzdt.ch.mnr.gov.cn/.
Evaluation result analysis
Based on the evaluation results of the indicators for regional cultural suitability of Tianjin’s Liberation Bridge at the indicator layer (D), a first-level fuzzy comprehensive evaluation matrix for the element layer (C) can be constructed. Before calculation, it is necessary to confirm the membership degrees for qualitative and quantitative indicators, which are determined according to actual conditions. Qualitative indicators cannot be quantified with definite values and thus require social statistics methods for scoring. This paper assesses qualitative indicators via survey questionnaires, e.g., the membership matrix for “Popularity D9” is {0.7, 0.27, 0.03, 0, 0}. Quantitative indicators are analyzed according to the evaluation grade standards, with the corresponding value or range membership degree set to 1; otherwise, it is set to 0. This paper employs field research and a literature review to score quantitative indicators; e.g., the membership matrix for “Land Use Mix D1” is {0, 1, 0, 0, 0}.
First-level fuzzy comprehensive evaluation
According to the element layer (C) of the evaluation system for urban cross-river bridges’ regional cultural suitability, the object of study can be divided into six subsystems. Based on the collected data for the final membership degrees of the indicator layer (D) evaluation factors, fuzzy relationship matrices are obtained for spatial accessibility (RC1), network convenience (RC2), bridge quality (RC3), spatial integration (RC4), traffic rationality (RC5), and interactive participation (RC6).
The weight vectors for each evaluation factor in the element layer (C) derived from the evaluation system are as follows: AC1 = {0.0255, 0.0255, 0.0509}; AC2 = {0.0191, 0.0295, 0.025, 0.0545}; AC3 = {0.0311, 0.0733, 0.0483, 0.0348, 0.0521, 0.0397, 0.0794}; AC4 = {0.0362, 0.0561, 0.1031, 0.0941}; AC5 = {0.0098, 0.0137, 0.0057, 0.0115}; AC6 = {0.0299, 0.0254, 0.0161}.
After performing calculations with the determined fuzzy relationship matrices RC and weight vectors AC, and following normalization, the first-level fuzzy evaluation results are obtained as follows:
After normalization, the membership degree evaluation for C1 is obtained as follows:
Spatial Accessibility — BC1 = {0 0.75 0.25 0 0};
Similarly, the results for other aspects are obtained:
Network convenience – BC2 = {0.425, 0.425, 0.149, 0, 0};
Bridge quality – BC3 = {0.313, 0.321, 0.197, 0.124, 0.046};
Spatial integration – BC4 = {0.496, 0.315, 0.144, 0.03, 0.015};
Traffic rationality – BC5 = {0.14, 0.86, 0, 0, 0};
Interactive participation – BC6 = {0.49, 0.312, 0, 0.198, 0};
Based on the principle of maximum membership degree, the results indicate that the elements of Tianjin’s Liberation Bridge rated “good” include network convenience, spatial integration, and interactive participation. Those evaluated as “quite good” include bridge quality, spatial accessibility, and traffic rationality.
Second-level fuzzy comprehensive evaluation
Based on the first-level fuzzy comprehensive evaluation results, a fuzzy relationship matrix for the criteria layer (B) can be constructed.
The weight vectors for each evaluation factor in the criteria layer (B) are: AB1 = {0.1, 0.13}; AB2 = {0.36, 0.29}; AB3 = {0.04, 0.08}.
After calculating with the fuzzy relationship matrix RB and weight vector AB, and normalizing, the second-level fuzzy Matrix is obtained:
Connectivity evaluation – BB1 = {0.283, 0.399, 0.388, 0, 0};
Artistic quality evaluation – BB2 = {0.548, 0.304, 0.086, 0.046, 0.017};
Resilience evaluation – BB3 = {0.366, 0.425, 0, 0.208, 0};
Based on the principle of maximum membership degree, the criteria layer (B) evaluation results for Tianjin’s Liberation Bridge indicate that the artistic quality evaluation is “good.” In contrast, the resilience and connectivity evaluations are “quite good.
Third-level fuzzy comprehensive evaluation
Based on the second-level fuzzy comprehensive evaluation results, a fuzzy relationship matrix for the goal layer (A) can be constructed.
According to the formula, the final evaluation result for the regional cultural suitability of Tianjin’s Liberation Bridge is BA = {0.429, 0.314, 0.155, 0.087, 0.014}. Based on the principle of maximum membership degree and the calculation of BA, the overall comprehensive evaluation result for the regional cultural suitability of Tianjin’s Liberation Bridge is “good.”
Evaluation result analysis
The final score for the overall evaluation of Tianjin’s Liberation Bridge’s regional cultural suitability is 4.054. According to the scoring and grading criteria for the regional cultural suitability evaluation of urban cross-river bridges, the regional cultural suitability level of Tianjin’s Liberation Bridge is “excellent,” as illustrated in the following figure (Fig. 5).
Third-level fuzzy comprehensive evaluation
The connectivity evaluation score (B1) is 3.995, rated “Good.” Specifically, the score for spatial accessibility (C1) is 3.95, also rated “Good,” mainly because the Liberation Bridge is located in the core area of Tianjin and is surrounded by comprehensive infrastructure. Its prime geographic location has led to a high mix of land uses in the vicinity, including commercial and office space. However, the score is slightly reduced due to the prevalence of older residential areas. The score for network convenience (C2) is 4.272, rated “Excellent,” mainly due to the bridge’s traffic convenience and the extensive layout of public transportation routes, making it a critical traffic hub connecting various districts of Tianjin and featuring a dense public transport network with a distinct regional layout.
Third-level fuzzy comprehensive evaluation
The evaluation score for artistic quality (B2) is 4.323, rated as “Excellent.” The score for bridge quality (C3) is 3.734, rated as “Good,” primarily because of the bridge’s long history, high fame, and unique design style. The Liberation Bridge’s distinctive design, nighttime illumination, and its significance in modern history mark it as a landmark of Tianjin. The score for spatial integration (C4) is 4.247, rated as “Excellent,” with the bridge offering expansive views and integrating its design elements with the surrounding environment, showcasing significant historical and cultural value.
Resilience (B3) analysis
The resilience evaluation score (B3) is 3.946, rated “Good.” The score for traffic resistance to environmental disturbance (C5) is 4.14, indicating “Good,” mainly due to the low rate of traffic accidents, short congestion durations, and low flood risk at the Liberation Bridge. The pedestrian safety score (C6) is 4.094, rated “Excellent,” as the bridge features pedestrian paths on both sides, facilitating public tours and sightseeing. The slower traffic speed helps ensure public safety and enhances the enjoyment of the bridge’s landscape, despite the surrounding area’s scarcity of biological resources.
Development strategies
For the development of the Liberation Bridge, recommendations are made in three areas:
Connectivity (B1): Increase investment in surrounding infrastructure, such as adding public transport stops, improving road quality, and expanding bicycle lanes to enhance regional traffic connectivity. Additionally, adopt intelligent transportation system technologies, such as bright traffic lights and real-time traffic monitoring, to optimize traffic flow and reduce congestion.
Artistic Quality (B2): Enhance the protection and promotion of the historical and cultural significance of the Liberation Bridge, for example, by installing historical and cultural display boards and organizing cultural activities to highlight the bridge’s historical value and cultural connotations. At the same time, incorporate local cultural elements into the design and maintenance of the bridge, such as using regionally distinctive art and design styles in its lighting, decorations, and surrounding environment. Additionally, the unique features of the Liberation Bridge itself can be extracted and applied to decorate the surrounding urban environment, such as through the use of colors, shapes, and other design elements, further enhancing the expression and visual coherence of regional culture.
Resilience (B3): Regarding vehicle management, it is recommended to encourage residents to detour during peak hours, reserving more road space for tourists to alleviate traffic congestion and reduce the risk of accidents effectively. In terms of security management, it is essential to strengthen the regulation of street vendors around the bridge, prohibiting the placement of stalls in areas prone to congestion or where pedestrians frequently stop. Additionally, by organizing public events and providing more rest areas, the public can be encouraged to more actively engage with and enjoy the bridge and its surroundings, enhancing the overall efficiency and experience of the space.
Discussion
Applicability of the RCSUCRB
An in-depth analysis of the RCSUCRB’s application to Tianjin’s Liberation Bridge leads to the following conclusions: The successful application of the model not only verifies its theoretical soundness and practical applicability but also highlights the value of the RCSUCRB system in real-world operations. The evaluation results for the Liberation Bridge closely align with its actual engineering status, demonstrating the model’s logical consistency and precision. The model excels in comprehensiveness, featuring a complete and precise indicator system that covers all the essential dimensions of urban cross-river bridges. In terms of operability, the model’s ease of interpretation and detailed scoring rules provide professionals with a convenient method for accurate assessments, ultimately yielding evaluation results through rigorous mathematical derivations, such as comprehensive fuzzy analysis. However, the case study also revealed some issues that need to be addressed. Despite excluding certain random factors that do not affect the overall validity of the assessment, caution should still be exercised when interpreting these results.
For instance, the division of evaluation sets (V) should be analyzed more thoroughly in future research. Taking the Liberation Bridge as an example, some indicators scored high (such as D9), while others scored low (such as D25). To distinguish the characteristics of different bridges, it is necessary to refine the evaluation indicators further and adjust the corresponding membership functions. Additionally, the scoring rules themselves require improvement. For example, the existing scoring rules for connectivity and artistic quality are not stringent enough, leading to the Liberation Bridge scoring disproportionately high on some indicators (e.g., D10, D12). Therefore, this evaluation model should be applied to additional urban cross-river bridges to optimize them further.
Expandability of the RCSUCRB
When discussing the generalizability and scope of the RCSUCRB model, it’s clear that it cannot be directly applied across countries and regions because each area has unique social, economic, and cultural characteristics. As mentioned in section “ Construction of the RCSUCRB system”, although the RCSUCRB model has some generalizability, careful consideration is required when applying it across regions. The model’s indicator system was established based on an extensive literature review and combined with the Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) and expert scoring to build a weighting system. Additionally, the evaluation model is constructed using comprehensive fuzzy evaluation methods. When the RCSUCRB model is used to evaluate the cultural suitability of bridges across different countries and regions, more region-specific evaluation indicators should be proposed to address specific needs and characteristics. This suggests that while the model’s foundational framework has a certain universality, its particular application requires regional adjustments and the customization of indicators and weights. Furthermore, the model’s weighting system and scoring rules for single factors should be flexibly adjusted in line with the methods proposed in this study, taking into account specific regional characteristics and the influence of cultural, historical, and socio-economic backgrounds. Therefore, applying the RCSUCRB model requires detailed localization adjustments that respect regional characteristics to ensure the accuracy and practicality of its evaluation results.
Weight evaluation of the RCSUCRB
In modern infrastructure construction, bridges are not only transportation infrastructure but also essential embodiments of urban culture. However, previous bridge evaluation models often failed to account for bridges’ cultural suitability adequately. Nowadays, the harmonious integration of bridges with their surroundings is critical. This integration not only reflects bridges’ functionality but also their cultural and aesthetic values. Through in-depth case studies, the cultural attributes of cross-river bridges can be effectively promoted. For example, the weighting system in Fig. 2 and the detailed data analysis indicate that, in terms of cultural suitability, the artistic quality (B2) of bridges is the priority factor. Additionally, bridge quality (C3) and spatial integration (C4) are also considered important factors. This indicates that, when evaluating the cultural suitability of cross-river bridges, the quality of the bridge and the degree of scenic integration with the surrounding environment are the main criteria for assessing its distinctiveness. Therefore, future bridge design and assessment should place greater emphasis on the harmonious integration of bridges with the environment and cultural and aesthetic values.
Conclusions
This work systematically analyzes the challenges faced by cross-river bridges and emphasizes the importance of cultural suitability. Additionally, the Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP), combined with fuzzy comprehensive evaluation methods, is proposed to construct a framework, named RCSUCRB, for evaluating the cultural suitability of cross-river bridges. The evaluation framework encompasses assessment indicators, a weighting method, and an evaluation model. To validate the model’s effectiveness and practicality, Tianjin’s Liberation Bridge was selected for a case study. The results demonstrate that RCSUCRB can provide valuable insights for professionals in constructing high-quality, culturally suitable urban bridges.
The methodology of this work integrates a literature review, survey questionnaires, AHP, and fuzzy comprehensive evaluation methods, establishing a general process not only for evaluating the cultural suitability of cross-river bridges but also for assessing the cultural suitability of other urban infrastructure.
Looking ahead, several promising avenues for future research could further enhance the framework for evaluating regional cultural suitability in urban cross-river bridges. One potential direction is the integration of advanced technologies, such as artificial intelligence and machine learning, to automate and refine the assessment process, thereby improving both the precision and scalability of evaluations. Additionally, expanding the framework to encompass a broader range of bridge types and geographic regions could offer a more comprehensive understanding of how cultural suitability varies across different urban contexts. It would also be valuable to incorporate the perspectives of local communities and stakeholders, integrating their views into the evaluation process to ensure that the framework better reflects local cultural identities. Finally, conducting longitudinal studies and empirical research would help validate the proposed model, providing deeper insights into its long-term effectiveness and adaptability.
Data availability
The data in this paper are available from the authors.
References
Liu, F., Zhang, T., Alghazzawi, D. M. & Soltan, M. A. A. Optimisation of modelling of finite element differential equations with modern Art design theory. Appl. Math. Nonlinear Sci. 7, 277–284. https://doi.org/10.2478/amns.2021.2.00089 (2022).
Zhou, H., Currà, E., Leng, J., Xu, Y. & Hu, W. Contradiction and consistency: deconstruction of landscape bridges based on multiple temporal-spatial scales. Front. Architect. Res. 11, 53–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foar.2021.08.002 (2022).
Ji, G. & Sun, H. Assessing urban river landscape visual quality with extreme learning machines: a case study of the yellow river in Ningxia Hui autonomous Region, China. Ecol. Ind. 165, 112173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2024.112173 (2024).
Wang, J., Ye, Z., Lin, Y., Wang, Z. & Guo, J. Traffic conflict analysis in continuous confluence area of cross-river Bridge driven by vehicle trajectory data. Traffic Inj. Prev. 2024, 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1080/15389588.2024.2385585 (2024).
Dong, Z., Sun, Z., Wu, S., Tong, F. & Wang, D. Influence of soil liquefaction effect on seismic failure mechanism of river-crossing simply-supported girder bridges subjected to near-fault ground motions. Eng. Fail. Anal. 154, 107664. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfailanal.2023.107664 (2023).
Xue, S. & Shen, R. Research on fatigue failure and structural measures of suspenders in the Jinsha river railway suspension Bridge. Eng. Fail. Anal. 162, 108359. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfailanal.2024.108359 (2024).
Sánchez-Haro, J., Fernández, B., Capellán, G. & Merino, E. Simplified method to detect resonance effects in railway bridges. Viaduct over Aragón river and Almonte Bridge application. Eng. Struct. 305, 117668. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engstruct.2024.117668 (2024).
Chen, J., Qu, Y. & Sun, Z. Protection mechanisms, countermeasures, assessments and prospects of local scour for cross-sea Bridge foundation: a review. Ocean Eng. 288, 116145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oceaneng.2023.116145 (2023).
Yang, W., Zhang, D. & Wang, A. Field measurement analysis of the influence of simultaneous construction of river channel and Bridge on existing double shield tunnels. Undergr. Space. 7, 812–832. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.undsp.2021.12.008 (2022).
Li, X. et al. Prediction of riverside greenway landscape aesthetic quality of urban canalized rivers using environmental modeling. J. Clean. Prod. 367, 133066. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.133066 (2022).
Arriaza, M., Cañas-Ortega, J. F., Cañas-Madueño, J. A. & Ruiz-Aviles, P. Assessing the visual quality of rural landscapes. Landsc. Urban Plann. 69, 115–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landurbplan.2003.10.029 (2004).
Daniel, T. C. Whither scenic beauty? Visual landscape quality assessment in the 21st century. Landsc. Urban Plann. 54, 267–281. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0169-2046(01)00141-4 (2001).
Makino, K. An empirical research framework for the aesthetic appreciation of the urban environment. City Cult. Soc. 13, 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccs.2017.06.001 (2018).
Czepiel, A., Fink, L. K., Seibert, C., Scharinger, M. & Kotz, S. A. Aesthetic and physiological effects of naturalistic multimodal music listening. Cognition 239, 105537. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cognition.2023.105537 (2023).
Pipinato, A. The History, Aesthetic, and design of bridges. In Innovative Bridge Design Handbook 3–18 (Elsevier, 2022).
Tang, M. C. Forms and aesthetics of bridges. Engineering 4, 267–276. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eng.2017.12.013 (2018).
Dai, Y. Application of regional culture in landscape architecture design under the background of data fusion. Sci. Program. 2022, 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/6240313 (2022).
Andrić, J. M. & Lu, D. G. Risk assessment of bridges under multiple hazards in operation period. Saf. Sci. 83, 80–92 (2016).
Decò, A. & Frangopol, D. M. Risk assessment of highway bridges under multiple hazards. J. Risk Res. 14 (9), 1057–1089 (2011).
Lian, Q. & Yuan, W. The concept of harmony in aesthetics of urban landscape bridge. In Proceedings of the 2018 10th International Conference on Measuring Technology and Mechatronics Automation (ICMTMA) 81–85 (IEEE, 2018).
Ma, J., Chen A. & He, J. General framework of Bridge wide life design. J. Tongji Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2007, 1003–1007. (2007).
Monaco, A. L. et al. Structural defects for condition assessment of existing bridges: some results of a territorial case study. Procedia Struct. Integr. 62, 153–160 (2024).
Xue, Q. R. & Yang, X. H. Evaluation of the suitability of human settlement environment in Shanghai City based on fuzzy cluster analysis. Therm. sci. 24, 2543–2551. https://doi.org/10.2298/TSCI2004543X (2020).
Chen, J. F., Hsieh, H. N. & Do, Q. H. Evaluating teaching performance based on fuzzy AHP and comprehensive evaluation approach. Appl. Soft Comput. 28, 100–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2014.11.050 (2015).
Feng, B. & Ma, Y. Network construction for overall protection and utilization of cultural heritage space in Dunhuang City, China. Sustainability 15, 4579. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15054579 (2023).
Huang, S., Xu, J. & Wang, J. Cross-cultural validation of the chinese cultural value scale in tourism. Heliyon 9, e22474. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e22474 (2023).
Lin, F., Zhang, X., Ma, Z. & Zhang, Y. Spatial structure and corridor construction of intangible cultural heritage: a case study of the Ming great wall. Land 11, 1478. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11091478 (2022).
Strong, A. E. & White, T. L. Using paired cultural modelling and cultural consensus analysis to maximize programme suitability in local contexts. Health Policy Plann. 35, 115–121. https://doi.org/10.1093/heapol/czz096 (2020).
Wu, F. et al. Evaluation of the human settlements environment of public housing community: a case study of Guangzhou. Sustainability 12, 7361. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12187361 (2020).
Amur, Z. H., Kwang Hooi, Y., Bhanbhro, H., Dahri, K. & Soomro, G. M. Short-text semantic similarity (STSS): techniques, challenges and future perspectives. Appl. Sci. 13, 3911. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13063911 (2023).
Lei, Z. & Qing, Y. Cultural and creative design of Tianjin bridges based on AHP. Packaging Eng. 44, 347–353. https://doi.org/10.19554/j.cnki.1001-3563.2023.10.039 (2023).
Cheok, S. M., Hoi, L. M., Tang, S. K. & Tse, R. Crawling parallel data for bilingual corpus using hybrid crawling architecture. Procedia Comput. Sci. 198, 122–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2021.12.218 (2022).
Kumar, M. & Vig, R. Learnable focused meta crawling through web. Procedia Technol. 6, 606–611. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.protcy.2012.10.073 (2012).
Muehlethaler, C. & Albert, R. Collecting data on textiles from the internet using web crawling and web scraping tools. Forensic Sci. Int. 322, 110753. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.forsciint.2021.110753 (2021).
Habib, H. R. et al. Application of AHP and Geospatial technologies to assess ecotourism suitability: a case study of saint martin’s Island in Bangladesh. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2023, 103357. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rsma.2023.103357 (2023).
Chen, C. H. A novel multi-criteria decision-making model for Building material supplier selection based on entropy-AHP weighted TOPSIS. Entropy 22, 259. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22020259 (2020).
Liu, Y., Eckert, C. M. & Earl, C. A review of fuzzy AHP methods for decision-making with subjective judgements. Expert Syst. Appl. 161, 113738. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2020.113738 (2020).
Awasthi, A., Govindan, K. & Gold, S. Multi-tier sustainable global supplier selection using a fuzzy AHP-VIKOR based approach. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 195, 106–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2017.10.013 (2018).
Mosadeghi, R., Warnken, J., Tomlinson, R. & Mirfenderesk, H. Comparison of fuzzy-AHP and AHP in a Spatial multi-criteria decision making model for urban land-use planning. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 49, 54–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compenvurbsys.2014.10.001 (2015).
Nguyen, M. T., Vu, Q. H., Truong, V. H. & Nguyen, H. H. A comprehensive evaluation of private sector investment decisions for sustainable water supply systems using a fuzzy-analytic hierarchy process: a case study of Ha Nam Province in Vietnam. Heliyon 9, e19727. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e19727 (2023).
Lin, S. S., Shen, S. L., Zhou, A. & Xu, Y. S. Risk assessment and management of excavation system based on fuzzy set theory and machine learning methods. Autom. Constr. 122, 103490. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autcon.2020.103490 (2021).
Wang, L., Zhang, H., Wang, J. & Li, L. Picture fuzzy normalized projection-based VIKOR method for the risk evaluation of construction project. Appl. Soft Comput. 64, 216–226. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2017.12.014 (2018).
Zhou, J. et al. Landslide susceptibility assessment using the analytic hierarchy process (AHP): a case study of a construction site for photovoltaic power generation in Yunxian County, Southwest China. Sustainability 15, 5281. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15065281 (2023).
Yucesan, M. & Kahraman, G. Risk evaluation and prevention in hydropower plant operations: a model based on pythagorean fuzzy AHP. Energy Policy. 126, 343–351. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2018.11.039 (2019).
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge that we used ChatGPT only for language correction and copy-editing purposes. No generative Al was used for content creation.
Funding
Tianjin Research Innovation Project for Postgraduate Students of China, grant number 2022BKY089.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Shunping He and Zihang Liu are co-first authors who contributed equally to this work. Shunping He: Conceptualization, methodology, data analysis, and manuscript writing. Zihang Liu: Literature review, data collection, and analysis. Xuefeng Shang: Methodology development and revision of the manuscript. Yuxue Zhang: Data curation and interpretation of the results. Chao Ma (Corresponding Author): Supervision, project administration, and manuscript finalization.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
He, S., Liu, Z., Shang, X. et al. An evaluation system for regional cultural suitability of urban cross-river bridges: insights into the liberation bridge in Tianjin. Sci Rep 16, 5516 (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-35225-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-35225-x