Abstract
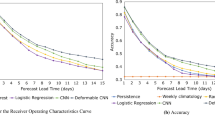
Conventional deep learning models struggle with balancing feature extraction and long-term temporal representation in Short-Term Load Forecasting (STLF). This study proposes a Convolutional Neural Network–Embedded Deep Residual Network (CNN-Embedded DRN) designed to enhance early-stage feature extraction and generalization capability across diverse climatic conditions. The objectives of this study are to integrate Convolutional Neural Network (CNN)-based local feature extraction into the DRN framework for capturing fine-grained temporal and spatial load patterns, to employ residual learning for mitigating gradient degradation and improving network stability, to evaluate the model’s predictive performance against baseline and ablation models across two datasets representing temperate (ISO-NE) and tropical (Malaysia) climates, and to validate its statistical significance and seasonal robustness through bootstrap analysis and multi-seasonal evaluation. The results demonstrate that the proposed CNN-Embedded DRN consistently outperforms all comparative models, achieving the lowest Mean Absolute Percentage Error (MAPE) values of 1.5303% and 5.0566% on the ISO-NE and Malaysia datasets, respectively. The inclusion of residual network (ResNet) and CNN-Embedded ResNet as ablation experiments confirms that CNN-based local feature extraction effectively complements residual learning, while bootstrap analysis verifies that the observed improvements are statistically significant. The proposed model provides a reliable and generalizable framework for STLF, offering improved accuracy, robustness, and adaptability under varying climatic and demand conditions. Future research will focus on extending this framework toward multi-regional and multi-scale forecasting, incorporating attention mechanisms for enhanced long-term dependency modeling, and exploring adaptive hybrid residual architectures for real-time energy management applications.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated and/or analysed during the current study are not publicly available due to licensing and institutional restrictions, but are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- 1D CNN:
-
One-dimensional convolutional neural network
- Adam:
-
Adaptive moment estimation
- ANN:
-
Artificial neural network
- BiGRU:
-
Bidirectional gated recurrent unit
- BiLSTM:
-
Bidirectional long short-term memory
- CNN:
-
Convolutional neural network
- Conv1D:
-
One-dimensional convolutional layer
- CRN:
-
Convolutional residual network
- DNN:
-
Deep neural network
- DRN:
-
Deep residual network
- ELM:
-
Extreme learning machines
- FC:
-
Fully connected
- GAP:
-
Global average pooling
- GAP1D:
-
One-dimensional global average pooling
- GRU:
-
Gated recurrent unit
- ISO-NE:
-
New England independent system operator
- LF:
-
Load forecasting
- LSTM:
-
Long short-term memory
- MAE:
-
Mean absolute error
- MAPE:
-
Mean absolute percentage error
- MSE:
-
Mean square error
- MW:
-
Megawatt
- MTLF:
-
Medium-term load forecasting
- NMSE:
-
Normalized mean square error
- N-HiTS:
-
Neural Hierarchical interpolation for time series forecasting
- Pooling1D:
-
One-dimensional pooling layer
- R:
-
Correlation coefficient
- R2 :
-
Coefficient of determination
- RBF:
-
Radial basis function
- ReLU:
-
Rectified linear unit
- ResNet:
-
Residual network
- ResNetPlus:
-
Modified ResNet structure
- RNN:
-
Recurrent neural network
- SELU:
-
Scaled exponential linear unit
- STLF:
-
Short-term load forecasting
- SVR:
-
Support vector regression
- VSTLF:
-
Very short-term load forecasting
References
Ahmad F A, Liu J, Hashim F & Samsudin K. Short-term load forecasting utilizing a combination model: a brief review. Int. J. Technol. 15, 121–129 (2024). https://doi.org/10.14716/ijtech.v15i1.5543
Liu, J., Ahmad, F. A., Samsudin, K., Hashim, F. & Ab Kadir, M. Z. A. Performance evaluation of activation functions in deep residual networks for short-term load forecasting. IEEE Access 13, 78618–78633. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2025.3565798 (2025).
Koponen, P., Ikäheimo, J., Koskela, J., Brester, C. & Niska, H. Assessing and comparing short term load forecasting performance. Energies 13, 2054. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13082054 (2020).
Ceperic, E., Ceperic, V. & Baric, A. A strategy for short-term load forecasting by support vector regression machines. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 28, 4356–4364. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPWRS.2013.2269803 (2013).
Hippert, H. S., Pedreira, C. E. & Souza, R. C. Neural networks for short-term load forecasting: A review and evaluation. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 16, 44–55. https://doi.org/10.1109/59.910780 (2001).
Kuster, C., Rezgui, Y. & Mourshed, M. Electrical load forecasting models: A critical systematic review. Sustain. Cities Soc. 35, 257–270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2017.08.009 (2017).
Cecati, C., Kolbusz, J., Różycki, P., Siano, P. & Wilamowski, B. M. A novel RBF training algorithm for short-term electric load forecasting and comparative studies. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 62, 6519–6529. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2015.2424399 (2015).
Chen, Y. et al. Short-term load forecasting: similar day-based wavelet neural networks. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 25, 322–330. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPWRS.2009.2030426 (2009).
Zhao Y, Luh P B, Bomgardner C & Beerel G H. Short-term load forecasting: multi-level wavelet neural networks with holiday corrections. Proc. IEEE Power Energy Soc. Gen. Meet. 1–7 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1109/PES.2009.5275304
Eren, Y. & Küçükdemiral, İ. A comprehensive review on deep learning approaches for short-term load forecasting. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 189, 114031. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2023.114031 (2024).
Li L, Ota K & Dong M. Everything is image: CNN-based short-term electrical load forecasting for smart grid. Proc. 14th Int. Symp. Pervasive Syst. Algorithms Netw. 344–351 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/ISPAN-FCST-ISCC.2017.78
Jurado, M., Samper, M. & Rosés, R. An improved encoder-decoder-based CNN model for probabilistic short-term load and PV forecasting. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 217, 109153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsr.2023.109153 (2023).
Narayan A & Hipel K W. Long short term memory networks for short-term electric load forecasting. Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. Syst. Man Cybern. 2573–2578 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/SMC.2017.8123012
Bento, P., Pombo, J., Mariano, S. & Calado, M. R. Short-term load forecasting using optimized LSTM networks via improved bat algorithm. Proc. Int. Conf. Intell. Syst. https://doi.org/10.1109/IS.2018.8710498 (2018).
Kwon, B. S., Park, R. J. & Song, K. B. Short-term load forecasting based on deep neural networks using LSTM layer. J. Electr. Eng. Technol. 15, 1501–1509. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42835-020-00424-7 (2020).
Tang, X., Dai, Y., Liu, Q., Dang, X. & Xu, J. Application of bidirectional recurrent neural network combined with deep belief network in short-term load forecasting. IEEE Access 7, 160660–160670. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2950957 (2019).
Ran, P., Dong, K., Liu, X. & Wang, J. Short-term load forecasting based on CEEMDAN and transformer. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 214, 108885. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsr.2022.108885 (2023).
Jiang B, Liu Y, Geng H, Zeng H & Ding J. A transformer based method with wide attention range for enhanced short-term load forecasting. Proc. 4th Int. Conf. Smart Power Internet Energy Syst. 1684–1690 (2022).
Li, S., Zhang, W. & Wang, P. TS2ARCformer: A multi-dimensional time series forecasting framework for short-term load prediction. Energies 16, 5825. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16155825 (2023).
Chen, K. et al. Short-term load forecasting with deep residual networks. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 10, 3943–3952. https://doi.org/10.1109/TSG.2018.2844307 (2018).
Tian, Y., Yu, S., Wen, M., Zhang, K. & Chen, Y. Short-term load forecasting scheme based on improved deep residual network and LSTM. Proc. CIRED Berlin Workshop CIRED 2020, 117–120. https://doi.org/10.1049/oap-cired.2021.0257 (2020).
Li, H., Zhang, P. & Li, C. Short-term load forecasting for distribution substations based on residual neutral networks and long short-term memory neutral networks with attention mechanism. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2030, 012087. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/2030/1/012087 (2021).
Sheng, Z., Wang, H., Chen, G., Zhou, B. & Sun, J. Convolutional residual network to short-term load forecasting. Appl. Intell. 51, 2485–2499. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-020-01932-9 (2021).
Sheng, Z., An, Z., Wang, H., Chen, G. & Tian, K. Residual LSTM based short-term load forecasting. Appl. Soft Comput. 144, 110461. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2023.110461 (2023).
Ding, A., Liu, T. & Zou, X. Integration of ensemble GoogLeNet and modified deep residual networks for short-term load forecasting. Electronics 10, 2455. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10202455 (2021).
Ullah, K. et al. Short-term load forecasting: A comprehensive review and simulation study with CNN-LSTM hybrids approach. IEEE Access https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2024.3440631 (2024).
Hua, Q. et al. A short-term power load forecasting method using CNN-GRU with an attention mechanism. Energies 18, 106. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18010106 (2024).
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S. & Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. Proc. IEEE Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1512.03385 (2016).
Challu, C. et al. N-HiTS: Neural hierarchical interpolation for time series forecasting. Proc. AAAI Conf. Artif. Intell. 37, 6989–6997. https://doi.org/10.1609/aaai.v37i6.25854 (2023).
Zhang, Q., Li, C., Su, F. & Li, Y. Spatiotemporal residual graph attention network for traffic flow forecasting. IEEE Internet Things J. 10, 11518–11532. https://doi.org/10.1109/JIOT.2023.3243122 (2023).
Bao, Y. X., Cao, Y., Shen, Q. Q. & Shi, Q. Global–local spatial–temporal residual correlation network for urban traffic status prediction. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2022, 7344522. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/7344522 (2022).
Ashebir, S. & Kim, S. Energy demand forecasting using temporal variational residual network. Forecasting 7(3), 42. https://doi.org/10.3390/forecast7030042 (2025).
Zhang, J., Chen, F., Cui, Z., Guo, Y. & Zhu, Y. Deep learning architecture for short-term passenger flow forecasting in urban rail transit. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 22(11), 7004–7014. https://doi.org/10.1109/TITS.2020.3000761 (2020).
Yamashita, R., Nishio, M., Do, R. K. G. & Togashi, K. Convolutional neural networks: An overview and application in radiology. Insights Imaging 9, 611–629. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13244-018-0639-9 (2018).
Kiranyaz, S. et al. 1D convolutional neural networks and applications: A survey. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 151, 107398. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymssp.2020.107398 (2021).
Shi, H., Xu, M. & Li, R. Deep learning for household load forecasting—a novel pooling deep RNN. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 9, 5271–5280. https://doi.org/10.1109/TSG.2017.2686012 (2017).
Huang G et al. Snapshot ensembles: train 1, get m for free. Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/1704.00109 (2017). https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1704.00109
Khoshkangini, R., Tajgardan, M., Lundström, J., Rabbani, M. & Tegnered, D. A snapshot-stacked ensemble and optimization approach for vehicle breakdown prediction. Sensors 23, 5621. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23125621 (2023).
Kingma D P & Ba J. Adam: a method for stochastic optimization. Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/1412.6980 (2014). https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1412.6980
Johnston, M. G. & Faulkner, C. A bootstrap approach is a superior statistical method for the comparison of non-normal data with differing variances. New Phytol. 230, 23–26. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.17159 (2021).
Funding
The authors declare that no external funding was received for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
J.L. and F.A.A. contributed to the conceptualization of the study. J.L. developed the methodology and conducted the investigation with F.A.A. J.L. prepared the original draft. J.L., F.A.A., K.S., F.H., and M.Z.A.A.K. contributed to the review and editing of the manuscript. F.A.A., K.S., F.H., and M.Z.A.A.K. provided supervision. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix
Appendix
1. ISO-NE dataset:
https://www.iso-ne.com/isoexpress/web/reports/load-and-demand
2 Malaysia dataset:
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, J., Ahmad, F.A., Samsudin, K. et al. Deep residual networks with convolutional feature extraction for short-term load forecasting. Sci Rep (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-35410-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-35410-y