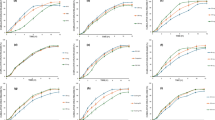
Abstract
This study presents an innovative approach that combines quality by design (QbD) principles with artificial neural networks (ANNs) to predict and optimize the formulation of carbopol-based emulsions. By integrating these two strategies, we enhance our understanding of formulations by linking critical material attributes and process parameters to critical quality attributes, such as viscosity. The predictive model was refined by selecting key variables: mixing time, mixing speed, and viscosity. These variables were used to estimate carbopol concentration and to capture the nonlinear relationships that influence emulsion behavior. Experimental data were employed to train, validate, and test the ANN model, which was then compared with four commercial formulations to evaluate its predictive accuracy and practical relevance. Notably, the model demonstrated excellent predictive performance for systems with viscosities exceeding 50,000 mPas, underscoring its applicability to high-viscosity pharmaceutical products. This integrated QbD-ANN framework offers a systematic and effective method for formulation optimization, reducing experimental workloads while improving process understanding. The findings indicate a strong correlation between predicted and experimental values, confirming the robustness and reliability of the QbD-ANN approach. Integrating the three key variables enables a more in-depth examination of the interactions between process and formulation, providing a comprehensive tool for understanding and controlling emulsion viscosity. In conclusion, this study establishes a data-driven methodology that facilitates rational pharmaceutical development, ensuring product quality, reproducibility, and innovation in alignment with modern pharmaceutical quality management principles.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data is provided within the manuscript or supplementary information files.
References
Yu, L. X. et al. Understanding pharmaceutical quality by design. AAPS J. 16, 771–783 (2014).
Gholap, A. D., Choudhary, S., More, M. P. & Patil, P. O. Advances in artificial intelligence in drug delivery and development: A comprehensive review. Comput. Biol. Med. 165, 108702 (2024).
Srinivas Murthy, B. R., Gupta, V., Sharma, A. & Patel, R. Advances in artificial intelligence for drug delivery and development. Front. Health Inf. 13, 1–15 (2024).
Serrano, D. R., García-García, A., O’Connor, A. & Lalatsa, A. Artificial intelligence (AI) applications in drug discovery and delivery: revolutionizing personalized medicine. Pharmaceutics 16, 1328 (2024).
Tran, T. T. V., Tayara, H. & Chong, K. T. Recent studies of artificial intelligence on in Silico drug distribution prediction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24, 1815 (2023).
Negut, I. & Bita, B. Exploring the potential of artificial intelligence for hydrogel development—A short review. Gels 9, 845 (2023).
Taskinen, J. & Yliruusi, J. Prediction of physicochemical properties based on neural network modelling. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 55, 1163–1183 (2003).
Lu, M., Wang, X., Li, Q., Zhang, Y. & Chen, H. Artificial intelligence in pharmaceutical sciences. Engineering 27, 37–69 (2023).
Paruthi, S., Raghav, Y. Y., Kumari, P., Kumar Tipu, R. & Sharma, N. AI based predictive modelling for compressive strength of metakaolin-based geopolymer concrete incorporated with nano titanium. J. Struct. Integr. Maintenance 10 (3). (2025).
Ali, K. A., El-Sherbiny, I. M., Salem, H. M. & El-Gizawy, S. A. Influence of artificial intelligence in modern pharmaceutical formulation and drug development. Future J. Pharm. Sci. 10, 53 (2024).
Momeni, M., Afkanpour, M., Rakhshani, S., Mehrabian, A. & Tabesh, H. A prediction model based on artificial intelligence techniques for disintegration time and hardness of fast disintegrating tablets in pre-formulation tests. BMC Med. Inf. Decis. Mak. 24 (1), 88 (2024).
Obaidullah, A. J. & Mahdi, W. A. Machine learning-based analysis on pharmaceutical compounds interaction with polymer to estimate drug solubility in formulations. Sci. Rep. 15 (1), 23683 (2025).
Hajibolouri, E. et al. Using data-driven models to simulate the performance of surfactants in reducing heavy oil viscosity. Sci. Rep. 14, 27670 (2024).
Álvarez-Gómez, C., Fonseca-Benítez, A. V. & Guevara-Pulido, J. Design, synthesis, and in vitro evaluation of a carbamazepine derivative with antitumor potential in a model of acute lymphoblastic leukemia. PLoS ONE. 20, e0319415 (2025).
Huertas, T. et al. Structure-based design of an antibacterial peptide from the myotoxin II sequence, evaluating its effectiveness against Gram-negative bacteria and its safety. Sci. Rep. 15, 24350 (2025).
Tummala, S. R. & Gorrepati, N. AI-driven predictive analytics for drug stability studies. J. Pharm. Insights Res. 2, 188–198 (2024).
Johnson, K. B. et al. Precision medicine, AI, and the future of personalized health care. Clin. Transl. Sci. 14, 86–93 (2021).
Vanpariya, F., Shiroya, M., Malaviya, M. & Emulgel A review. Int. J. Sci. Res. 10, 847 (2021).
Huan, S. et al. Two-phase emulgels for direct ink writing of skin-bearing architectures. Adv. Funct. Mater. 29, 1902990 (2019).
Begum, S. G., Reddy, P. N., Rajesh, K. & Kumar, P. A. A review on emulgels—A novel approach for topical drug delivery. Asian J. Pharm. Res. Dev. 7, 70–77 (2019).
Richa, A. & Roy, C. Self-assembled pH-stable gellan/κ-carrageenan bigel: rheological studies and viscosity prediction by neural network. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. (2023).
Mohammad, S., Akand, R., Cook, K. M., Nilufar, S. & Chowdhury, F. Leveraging deep learning and generative AI for predicting rheological properties and material compositions of 3D printed polyacrylamide hydrogels. Gels 10 (10) (2024).
Yahoum, M. M. et al. Experimental analysis and neural network modeling of the rheological behavior of Xanthan gum and its derivatives. Materials 16 (7), 2565 (2023).
Guevara-Pulido, J., Jimenez, R. A., Morantes, S. J., Jaramillo, D. N. & Acosta‐Guzmán, P. Design, synthesis, and development of 4‐[(7‐Chloroquinoline‐4‐yl) amino] phenol as a potential SARS‐CoV‐2. Mpro Inhibitor ChemistrySelect 7 (15), e202200125. (2022).
Rana, S. & Belokar, R. M. Quality improvement using FMEA: A short review. Int. Res. J. Eng. Technol. 4, 263–267 (2017).
Schober, P., Boer, C. & Schwarte, L. A. Correlation coefficients: appropriate use and interpretation. Anesth. Analgesia. 126, 1763–1768 (2018).
Alexander, D. L., Tropsha, A. & Winkler, D. A. Beware of R2: Simple, unambiguous assessment of the prediction accuracy of QSAR and QSPR models. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 55, 1316–1322 (2015).
Deng, B. et al. Predicting rheological properties of HAMA/GelMA hybrid hydrogels via machine learning. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 168, 107005 (2025).
Li, W., Zhang, R., Chen, Y., Zhao, S. & Liu, H. Developing a machine learning model for accurate nucleoside hydrogels prediction based on descriptors. Nat. Commun. 15, 2603 (2024).
Mohammad, S., Alavi, M., Martinez, P. A. & Karim, A. Leveraging deep learning and generative AI for predicting rheological properties and material compositions of 3D printed polyacrylamide hydrogels. Gels 10, 660 (2024).
Aru, P. B., Singh, R., Kumar, V. & Sharma, N. Quality by design (QbD) in pharmaceutical development: A comprehensive review. GSC Biol. Pharm. Sci. 26, 328–340 (2024).
Suriyaamporn, P., Opanasopit, P., Ngawhirunpat, T. & Rojanarata, T. The artificial Intelligence-Powered new era in pharmaceutical research and development: A review. AAPS PharmSciTech. 25, 188 (2024).
Kapoor, D. U. et al. AI-driven design and optimization of nanoparticle-based drug delivery systems. Sci. Eng. Health Stud. (2024).
Food, U. S. & Administration, D. Artificial intelligence and machine learning (AI/ML) in drug development: Discussion paper and request for feedback. Silver Spring, MD. https://www.fda.gov/science-research/science-and-research-special-topics/artificial-intelligence-and-machine-learning-aiml-drug-development (2025).
Selvaraj, C., Chandra, I. & Singh, S. K. Artificial intelligence and machine learning approaches for drug design: challenges and opportunities for the pharmaceutical industries. Mol. Diversity. 26 (3), 1893–1913 (2022).
Acknowledgements
I want to thank the INQA group and the pharmaceutical chemistry program for their assistance at VRI Universidad El Bosque in Bogotá, Colombia.
Funding
INQA Research Group, Universidad El Bosque.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, R.J, J.G-P; methodology, L.D, L.M, R.J, J.G-P software LD, LM, J.G-P validation, L.D, L.M, R.J, J.G-P, formal analysis, L.D, L.M, R.J, J.G-P investigation, L.D, L.M, R.J, J.G-P resources, R.J, J.G-P data curation, L.D, L.M, R.J, J.G-P writing—original draft, L.D, L.M, R.J, J.G-P preparation, L.D, L.M, R.J, J.G-P.; writing—review and editing, R.J, J.G-P., visualization, R.J, J.G-P.; supervision, R.J J.G-P.; project administration, R.J, J.G-P.; funding acquisition, R.J, J.G-P., All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Duarte, L.S., Molano, L., Jiménez, R.A. et al. Artificial neural network as a strategy to predict rheological properties in emulgel formulations. Sci Rep (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-35795-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-35795-w