Abstract
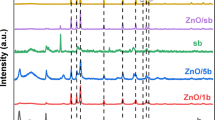
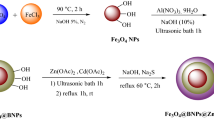
4-Chlorophenol (4-CL) is a toxic and persistent industrial pollutant resistant to conventional treatment, making its removal from wastewater a major environmental challenge. Visible-light photocatalysis provides a clean and efficient route for its complete mineralization. This study introduces a novel ZnO-functionalized sulfonated carbonaceous bentonite (ZnO@SB) nanohybrid, designed to enhance visible-light absorption, charge separation, and surface reactivity. The composite was synthesized via controlled sulfonation of organic-rich bentonite followed by uniform ZnO nanoparticle deposition. Structural and spectroscopic analyses confirmed successful functionalization and high ZnO dispersion across the sulfonated matrix. Under visible light, ZnO@SB (0.5 g/L, pH 8) achieved 100% degradation of 4-CL (5 mg/L) in 30 min and 100% TOC removal in 60 min (complete mineralization), following pseudo-first-order kinetics (k₁ = 0.1657 min⁻¹, R² > 0.98). The quantum yield increased from 7.39 × 10⁻⁸ to 2.96 × 10⁻⁷ with higher catalyst loading. The photocatalyst retained > 90% activity after five cycles, with Zn²⁺ leaching below 0.005 mg/L, indicating excellent chemical stability. Mechanistic studies confirmed the dominant roles of superoxide (O₂•⁻) and hydroxyl (•OH) radicals in driving hydroxylation, dechlorination, and aromatic ring cleavage. The novelty of this work lies in the synergistic integration of sulfonated carbonaceous bentonite with ZnO, which simultaneously enhances adsorption, charge transfer, and visible-light response. This multifunctional hybrid provides a low-cost, stable, and highly efficient photocatalyst for scalable visible-light-driven degradation and mineralization of chlorinated phenolic pollutants.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data will be available up on request to corresponding author.
References
Dehghani, M. H. et al. Sustainable remediation technologies for removal of pesticides as organic micro-pollutants from water environments: A review. Appl. Surf. Sci. Adv. 19, 100558 (2023).
Patel, P. C., Mishra, P. K., Kashyap, J. & Awasthi, S. Cation doped approach for photodegradation of 4-chlorophenol by highly efficient solar-active NiS photocatalyst: the case of Cu²⁺ doping. J. Photochem. Photobiol A: Chem. 437, 114499 (2022).
Dai, M. et al. Rational construction of S-scheme BN/MXene/ZnIn₂S₄ heterojunction with interface engineering for efficient photocatalytic hydrogen production and Chlorophenols degradation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 309, 123004 (2022).
Taheri, E. et al. Mesoporous bimetallic S-doped nanoparticles prepared via hydrothermal method for enhanced photodegradation of 4-chlorophenol. J. Environ. Manage. 349, 119460 (2023).
Hunge, Y. M., Yadav, A. A., Kang, S. W. & Kim, H. Facile synthesis of multitasking composite of silver nanoparticle with zinc oxide for 4-nitrophenol reduction, photocatalytic hydrogen production, and 4-chlorophenol degradation. J. Alloys Compd. 928, 167133 (2022).
Lopes, C., Restivo, J., Orge, C. A., Pereira, M. F. R. & Soares, O. S. G. P. Catalytic hydrodechlorination of 4-chlorophenol: role of metal phase supports and reaction pH. J. Water Process. Eng. 67, 106240 (2024).
Mumtaz, F., Li, B., Al Shehhi, M. R., Feng, X. & Wang, K. Treatment of phenolic wastewater by hybrid technologies: A review. J. Water Process. Eng. 57, 104695 (2024).
Ayach, J. et al. Conventional versus advanced approaches for heavy-metal removal in wastewater: A filter-based perspective. Polymers 16, 1959 (2024).
Zhao, Y., Chang, C., Ji, H. & Li, Z. Challenges of petroleum-wastewater treatment and trends in advanced technologies. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 13, 113767 (2024).
Oyetade, J. A., Machunda, R. L., Hilonga, A. & De Buysser, K. Development of ternary PANI/GO-Fe3O4@ AgNps nanocomposites for photocatalytic remediation of toxic dye effluent under energy-efficient system. Journal of Molecular Structure, 1324, p.140818. (2025).
Satyam, S. & Patra, S. Innovations and challenges in adsorption-based wastewater remediation: A comprehensive review. Heliyon 10 (9), e29573 (2024).
Nthunya, L. N. et al. Fouling, performance and cost analysis of membrane-based water desalination technologies: A critical review. J. Environ. Manage. 301, 113922 (2022).
He, L. et al. Degradation of 4-chlorophenol through in situ generation of reactive chlorine species in a Zn2CoOx electrocatalytic system. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 12(1), p.111911. (2024).
Soomro, M. Y. et al. Fe/Ni bimetallic magnetic nano-alloy as an efficient photo-Fenton-like catalyst for phenol degradation. Environ. Pollut. 360, 124635 (2024).
Patil, D. J. & Grewal, H. S. Comparative study of heterogeneous activation of H2O2 and peroxymonosulfate over nanoporous ZnFe2O4 for dye degradation via batch and continuous-flow channel approach. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 75, p.108007. (2025).
Naik, V. A. & Thakur, V. A. Fe₃O₄@rGO@CdS/Bi₂S₃ magnetic nanocomposite for photo-Fenton dye degradation and Cr(VI) reduction under sunlight. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 160, 111962 (2024).
Oyetade, J. A., Van Hulle, S. W., Machunda, R. L. & Hilonga, A. Development of photocatalytic semiconductors and nanocomposites with excellent optoelectronic and electrochemical properties for dye effluent remediation-A review. Materials Science in Semiconductor Processing, 184, p.108821. (2024).
Zhang, Y. et al. Important role of carbon doping in photocatalytic peroxymonosulfate activation of carbon nitride for efficient 4-Chlorophenol degradation. Chemical Engineering Journal, 493, p.152482. (2024).
Patil, D. J., Kumar, R. & Grewal, H. S. Multifunctional smart engineering nano magnetic materials with ultrahigh synergetic adsorption-photocatalytic performance. Surf. Interfaces. 46, 104106 (2024).
Zeng, W. et al. Recent advances in adsorption and photoreduction of Cr(VI): A review, environ. Pollut Bioavailab. 37, 2493057 (2025).
de Moraes, N. P. et al. ZnO/CeO2/carbon xerogel composites with direct Z-scheme heterojunctions: enhancing photocatalytic remediation of 4-chlorophenol under visible light. J. Rare Earths. 42 (2), 314–322 (2024).
Wang, Y. et al. Fabrication of core-shell shaped heterojunction Bi2MoO6/ln2O3 nanofibers as a highly efficient photocatalyst toward degradation of 4-chlorophenol. J. Water Process. Eng. 69, 106702 (2025).
Ghanbari, S., Fatehizadeh, A., Khiadani, M., Taheri, E. & Iqbal, H. M. N. UV/Cl₂/Br photolysis followed by adsorption for dye-laden textile wastewater. Environ. Sci. Pollut Res. 29, 39400–39409 (2022).
Md. Ahmaruzzaman, S. R. et al. Phenolic compounds in water: Toxicity, sources and sustainable removal solutions. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 12, 112964 (2024).
Yang, X. et al. Adsorption and oxidation activity of ZnO/quartz core-shell for ibuprofen decontamination. Chem. Eng. J. 431, 134312 (2021).
Zamisa, M. K., Seadira, T. W. & Baloyi, S. J. Catalytic wet-air oxidation with pillared clay catalysts for phenol remediation. Environ. Pollut. 361, 124842 (2024).
Zaki, R. M., Jusoh, R., Chanakaewsomboon, I. & Setiabudi, H. D. Recent advances in metal oxide photocatalysts for photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants: A review on photocatalysts modification strategies. Materials Today: Proceedings, 107, pp.59–67. (2024).
Ma, Y. et al. Status and challenges of photocatalysis in environmental applications: photocatalyst deactivation. Nano Res. 18 (9), 94907750 (2025).
Nawaz, A. et al. Fathi-karkan, zinc oxide nanoparticles: pathways to micropollutant adsorption, dye removal, and antibacterial actions—A study of mechanisms, challenges, and future prospects. J. Mol. Struct. 1312, 138545 (2024).
Liu, J. et al. Research progress of zinc oxide-based heterojunction photocatalysts. J. Mater. Chem. A 12, 20838–20867 (2024).
Aremu, O. H., Akintayo, C. O., Naidoo, E. B., Nelana, S. M. & Ayanda, O. S. Synthesis and applications of nano-sized zinc oxide in wastewater treatment: A review. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 18, 3237–3256 (2021).
Zabihi, E. et al. Fabrication of nano-decorated ZnO-fibrillar Chitosan exhibiting a superior performance as a promising replacement for conventional ZnO. Carbohydr. Polym. 274, 118639 (2021).
Dimitropoulos, M. et al. Unveiling the photocorrosion mechanism of zinc oxide photocatalyst: interplay between surface corrosion and regeneration. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 12, 112102 (2024).
Etafo, N. O., Bamidele, M. O., Bamisaye, A. & Alli, Y. A. Revolutionizing photocatalysis: unveiling efficient alternatives to titanium(IV) oxide and zinc oxide for comprehensive environmental remediation. J. Water Process. Eng. 62, 105369 (2024).
Saad, A. M. et al. Photocatalytic degradation of malachite green dye using chitosan-supported ZnO and Ce–ZnO nano-flowers under visible light. J. Environ. Manage. 258, 110043 (2020).
Baig, A., Siddique, M. & Panchal, S. A review of visible-light-active zinc oxide photocatalysts for environmental application. Catalysts 15, 100 (2025).
Abou Zeid, S. & Leprince-Wang, Y. Advancements in ZnO-based photocatalysts for water treatment: A comprehensive review. Crystals 14, 611 (2024).
Ansari, S. A. Development and photocatalytic performance of spherical shape zinc oxide nanoparticles for environmental remediation. J. Nanoelectron Optoelectron. 20, 101–105 (2025).
Rabiei, K. Recent application of clay-based heterogeneous catalyst in organic reactions. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 35, 14263–14284 (2025).
Othman, S. I. et al. Characterization of green ZnO-supported Curcumin intercalated bentonite (ZnO@CU/BEN) as environmental catalysts for effective oxidation of 5-fluorouracil residuals: pathway and toxicity. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 34, 4116–4132 (2024).
Zhang, B. et al. Recent advances of application of bentonite-based composites in environmental remediation. J. Environ. Manage. 362, 121341 (2024).
Arabmofrad, S. et al. Nasiri Sarvi, Preparation and characterization of surface-modified montmorillonite by cationic surfactants for adsorption purposes. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 148, 13803–13814 (2023).
Wasim, M. et al. Synthesis and characterization of curcumin/MMT-clay-treated bacterial cellulose as an antistatic and ultraviolet-resistive bioscaffold. J. Polym. Res. 29, 1–18 (2022).
Tong, L., Liang, T., Tian, Y., Zhang, Q. & Pan, Y. Research progress on treatment of mine wastewater by bentonite composite. Arab. J. Geosci. 15, 99 (2022). (Article ID).
Dardir, F. M., Mohamed, A. S., Abukhadra, M. R., Ahmed, E. A. & Soliman, M. F. Cosmetic and pharmaceutical qualifications of Egyptian bentonite and its suitability as drug carrier for praziquantel drug. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 115, 320–329 (2018).
Hassan, W. A. et al. Sulfonation of natural carbonaceous bentonite as a low-cost acidic catalyst for effective transesterification of used sunflower oil into diesel; statistical modeling and kinetic properties. ACS Omega. 6, 31260–31271 (2021).
Kang, Z., Zhao, Y. & Yang, D. Review of oil shale in-situ conversion technology. Appl. Energy. 269, 115121 (2020).
Sobhy, A., Yehia, A., Hosiny, F. E., Ibrahim, S. S. & Amin, R. Application of statistical analysis for optimizing of column flotation with pine oil for oil shale cleaning. Int. J. Coal Prep Util. 42, 2285–2298 (2022).
Refaai, M. G., Rudayni, H. A., Allam, A. A., Abukhadra, M. R. & Wahed, M. S. A. Photocatalytic Oxidation of Ammonia Using copper-mediated Phosphotungstic Acid Intercalated Sulfonated Bentonite for Sustainable Eutrophication Control: A Case Study from Lake Qarun p.122351 (Environmental Research, 2025).
Ahmed, Z. M. et al. Low-temperature synthesis of a multifunctional NiO/Ni(OH)2 decorated sulfonated bentonite for sustainable and enhanced visible-light-driven degradation and mineralization of bisphenol-A in water. Mater. Today Sustain. 101301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtsust.2026.101301 (2026).
Genel, Y., Genel, İ. & Saka, C. Facile Preparation of sulfonated carbon particles with pomegranate peels as adsorbent for enhanced methylene blue adsorption from aqueous solutions. Biomass Convers. Biorefin. 14, 30693–30705 (2024).
Sripada, S. & Kastner, J. R. Catalytic esterification using solid acid carbon catalysts synthesized by sustainable hydrothermal and plasma sulfonation techniques. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 61, 3928–3940 (2022).
Aniya, V. et al. Translation of lignocellulosic waste to mesoporous solid acid catalyst and its efficacy in esterification of volatile fatty acid. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 264, 198–207 (2018).
Alsebaii, N. M., Sun, X., Salam, M. A. & Abukhadra, M. R. Tailoring the activity of sulfonated coal catalyst during the sonication and infrared-induced transesterification of castor (Ricinus communis) oil: Synergetic, optimization, kinetics, and CI engine assessment. Ind. Crops Prod. 210, 118174 (2024).
Bayram, H., Ustunisik, G., Önal, M. & Sarıkaya, Y. Optimization of bleaching power by sulfuric acid activation of bentonite. Clay Miner. 56 (2), 148–155 (2021).
Dhar, A. K., Himu, H. A., Bhattacharjee, M., Mostufa, M. G. & Parvin, F. Insights on applications of bentonite clays for the removal of dyes and heavy metals from wastewater: a review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 30 (3), 5440–5474 (2023).
Mclaren, A., Valdes-Solis, T., Li, G. & Tsang, S. C. Shape and size effects of ZnO nanocrystals on photocatalytic activity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 131 (35), 12540–12541 (2009).
Huang, M. et al. Spatial separation of electrons and holes among ZnO Polar {0001} and {1010} facets for enhanced photocatalytic performance. ACS Omega. 7 (30), 26844–26852 (2022).
Isaacs, M. A. et al. Unravelling mass transport in hierarchically porous catalysts. J. Mater. Chem. A. 7 (19), 11814–11825 (2019).
Liu, B. et al. Hierarchically porous ZnO/g-C3N4 S-scheme heterojunction photocatalyst for efficient H2O2 production. Langmuir 37 (48), 14114–14124 (2021).
Akinfalabi, S. I., Rashid, U., Yunus, R. & Taufiq-Yap, Y. H. Synthesis of biodiesel from palm fatty acid distillate using sulfonated palm seed cake catalyst. Renew. Energy. 111, 611–619 (2017).
Farabi, M. A., Ibrahim, M. L., Rashid, U. & Taufiq-Yap, Y. H. Esterification of palm fatty acid distillate using sulfonated carbon-based catalyst derived from palm kernel shell and bamboo. Energy Convers. Manage. 181, 562–570 (2019).
Konwar, L. J., Mäkelä-Arvela, P. & Mikkola, J. P. SO₃H-containing functional carbon materials: Synthesis, structure, and acid catalysis. Chem. Rev. 119, 11576–11630 (2019).
Zailan, Z., Tahir, M., Jusoh, M. & Zakaria, Z. Y. A review of sulfonic group-bearing porous carbon catalyst for biodiesel production. Renew. Energy. 175, 430–452 (2021).
Mateo, W. et al. One-step synthesis of biomass-based sulfonated carbon catalyst by direct carbonization-sulfonation for organosolv delignification. Bioresour Technol. 319, 124194 (2021).
Quintana, M. A., Solís, R. R., Blázquez, G., Calero, M. & Munoz-Batista, M. J. Sulfonic grafted graphitic-like carbon nitride for the improved photocatalytic production of benzaldehyde in water. Appl. Surf. Sci. 656, 159717 (2024).
Mustafa, F. H., Attia, H. A. A., Yahya, R., Elshaarawy, R. F. & Hassan, N. Cellulose microfibrils-embedded sulfonated polyethersulfone for efficient Zn²⁺ ion removal from aqueous effluents. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 186, 374–386 (2022).
Singh, K. & Yadav, S. Biosynthesis of a range of ZnO nanoparticles utilising salvia Hispanica L. seed extract and evaluation of their bioactivity. Sci. Rep. 15, 4043 (2025).
Hessien, M. A., Khattab, R. M. & Sadek, H. E. H. Synthesis and characterization of ZnO, Mn3O4, and ZnMn₂O₄ spinel by a new chelation-precipitation method: magnetic and antimicrobial properties. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 35, 1–20 (2024).
Vassileva, P. et al. Biochars as a solution for silver removal and antimicrobial activity in aqueous systems. Appl. Sci. 15, 2796 (2025).
Mekonnen, B. Synthesis and characterization of microporous materials: Towards a versatile adsorbent and a simple model material for the study of adsorption-induced deformation in microporous media, Ph.D. thesis, Université de Pau et des Pays de l’Adour, (2025).
Hijazi, N. et al. Chemical engineering of zeolites: alleviating transport limitations through hierarchical design and shaping. Chem. Soc. Rev. 54, 6335–6384 (2025).
Raha, S. & Ahmaruzzaman, M. ZnO nanostructured materials and their potential applications: progress, challenges and perspectives. Nanoscale Adv. 4 (8), 1868–1925 (2022).
Rahimzadeh, H. et al. Potential of acid-activated bentonite and SO3H-functionalized MWCNTs for biodiesel production from residual olive oil under biorefinery scheme. Frontiers in Energy Research, 6, p.137. (2018).
Sasikala, S. P., Nibila, T. A., Babitha, K. B., Mohamed, A. A. P. & Solaiappan, A. Competitive photo-degradation performance of ZnO modified bentonite clay in water containing both organic and inorganic contaminants. Sustainable Environment Research, 29(1), p.1. (2019).
Alshabanat, M. et al. Preparation and characterization of zno/bentonite nanocomposites for enhanced photocatalytic degradation of pesticides in contaminated water. Scientific Reports, 15(1), p.23816. (2025).
Zyoud, A. H. et al. Kaolin-supported ZnO nanoparticle catalysts in self-sensitized Tetracycline photodegradation: Zero-point charge and pH effects. Appl. Clay Sci. 182, 105294 (2019).
Aadnan, I., Zegaoui, O., Mragui, E. & Esteves da Silva, J. C. G. A. and Physicochemical and photocatalytic properties under visible light of ZnO-Bentonite/Chitosan hybrid-biocompositefor water remediation. Nanomaterials, 12(1), p.102. (2021).
Gebrye, A. B., Mehari, B. & Atlabachew, M. Photocatalytic performance of ZnO immobilized on bentonite for catalytic degradation of malachite green under sunlight irradiation. Hybrid. Adv. 11, 100542 (2025).
Priatna, S. J., Yuliana, A., Melwita, E., Arsyad, F. S. & Mohadi, R. Removal of Methyl orange in aqueous medium using ZnO/bentonite as semiconductor by photocatalytic process. Sci. Technol. Indonesia. 9 (3), 539–545 (2024).
Wang, J. et al. Oxygen vacancy induced band-gap narrowing and enhanced visible light photocatalytic activity of ZnO. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 4 (8), 4024–4030 (2012).
Julita, M., Shiddiq, M. & Khair, M. Determination of band gap energy of ZnO/Au nanoparticles resulting in laser ablation in liquid. Indonesian J. Chem. Res. 10 (2), 83–87 (2022).
de Amadio, M. et al. Bentonites functionalized by impregnation with TiO2, Ag, Pd and Au nanoparticles. Appl. Clay Sci. 146, 1–6 (2017).
Li, X., Simon, U., Bekheet, M. F. & Gurlo, A. Mineral-supported photocatalysts: a review of materials, mechanisms and environmental applications. Energies, 15(15), p.5607. (2022).
Gao, Y. et al. Porous and ultrafine nitrogen-doped carbon nanofibers from bacterial cellulose with superior adsorption capacity for adsorption removal of low-concentration 4-chlorophenol. Chem. Eng. J. 420, 127411 (2020).
Farhan, A. M. et al. Characterization and statistical physics modeling of two coal hybridized nanostructures with two forms of polyaniline (nanofibers hydrogel and nanorods) as adsorbents for toxic 4-chlorophenol. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 35, 6399–6421 (2025).
Hadi, S., Taheri, E., Amin, M. M., Fatehizadeh, A. & Aminabhavi, T. M. Advanced oxidation of 4-chlorophenol via combined pulsed light and sulfate radicals methods: effect of co-existing anions. J. Environ. Manage. 291, 112595 (2021).
Abdullah, R. R., Shabeed, K. M., Alzubaydi, A. B. & Alsalhy, Q. F. Novel photocatalytic polyether Sulphone ultrafiltration membrane reinforced with oxygen-deficient tungsten oxide (WO₂.₈₉) for congo red dye removal. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 177, 526–540 (2022).
Wang, C., Sun, R., Huang, R. & Cao, Y. A novel strategy for enhancing heterogeneous Fenton degradation of dye wastewater using natural pyrite: kinetics and mechanism. Chemosphere 272, 129833 (2021).
Salam, M. A., AbuKhadra, M. R. & Mohamed, A. S. Effective oxidation of Methyl parathion pesticide in water over recycled glass-based MCM-41 decorated by green Co₃O₄ nanoparticles. Environ. Pollut. 259, 113874 (2020).
Martin, M. V., Alfano, O. M. & Satuf, M. L. Cerium-doped TiO₂ thin films: assessment of radiation absorption properties and photocatalytic reaction efficiencies in a microreactor. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 7, 103478 (2019).
Cao, S. & Piao, L. Considerations for a more accurate evaluation method for photocatalytic water splitting. Angew Chem. Int. Ed. 59, 18312–18320 (2020).
Huda, A. et al. Comparative photocatalytic performances towards acid yellow 17 and direct blue 71 degradation using Sn₃O₄ flower-like structure. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1282, 012097 (2019).
Zada, A. et al. Review on the hazardous applications and photodegradation mechanisms of Chlorophenols over different photocatalysts. Environ. Res. 195, 110742 (2021).
Mostafa, D. et al. Insight into the impact of calcination on the catalytic performance of synthetic hematite nano-rods during the photo-Fenton oxidation of 4-chlorophenol toxic residuals. Surf. Interfaces 59, 105970 (2025).
Rangarajan, G., Jayaseelan, A. & Farnood, R. Photocatalytic reactive oxygen species generation and their mechanisms of action in pollutant removal with biochar-supported photocatalysts: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 346, 131155 (2022).
Domínguez, J. R., Durán-Valle, C. J. & Mateos-García, G. Synthesis and characterisation of acid/basic modified adsorbents: application for Chlorophenols removal. Environ. Res. 207, 112187 (2022).
Zhuo, Q. et al. Electrocatalytic oxidation processes for treatment of halogenated organic pollutants in aqueous solution: A critical review. ACS ES&T Eng. 2, 1756–1775 (2022).
Liu, X. et al. Fenton-like system of UV/glucose-oxidase@kaolin coupled with organic green rust: UV-enhanced enzyme activity and the mechanism of UV synergistic degradation of photosensitive pollutants. Environ. Res. 247, 118257 (2024).
Yang, K., Abu-Reesh, I. M. & He, Z. Degradation of 4-chlorophenol through cooperative reductive and oxidative processes in an electrochemical system. J. Hazard. Mater. 442, 130126 (2023).
Mun, H. et al. Complete 2,4,6-trichlorophenol degradation by anaerobic sludge acclimated with 4-chlorophenol: synergetic effect of nZVI@BMPC and sodium lactate as an external nutrient. J. Hazard. Mater. 476, 135063 (2024).
Veerakumar, P. et al. Photocatalytic degradation of phenolic pollutants over palladium-tungsten trioxide nanocomposite. Chem. Eng. J. 489, 151127 (2024).
Lei, M. et al. Catalytic degradation and mineralization mechanism of 4-chlorophenol oxidized by phosphomolybdic acid/H₂O₂. Sep. Purif. Technol. 257, 117933 (2021).
Zarei, M. Ultrasonic-assisted Preparation of ZrO2/g-C3N4 nanocomposites with high visible-light photocatalytic activity for degradation of 4-chlorophenol in water. Water-Energy Nexus. 3, 135–142 (2020).
Dehdar, A., Asgari, G., Leili, M., Madrakian, T. & Seid-Mohammadi, A. Step-scheme BiVO4/WO3 heterojunction photocatalyst under visible LED light irradiation removing 4-chlorophenol in aqueous solutions. J. Environ. Manage. 297, 113338 (2021).
Gao, Q., Wang, Z., Li, J., Liu, B. & Liu, C. Facile synthesis of ternary dual Z – scheme g – C3N4/Bi2MoO6/CeO2 photocatalyst with enhanced 4–chlorophenol removal: degradation pathways and mechanism. Environ. Pollut. 315, 120436 (2022).
Al-Sharji, Z., Al-Sabahi, J., Kyaw, H. H., Myint, M. T. Z. & Al-Abri, M. Plasmon enhanced photocatalytic degradation of 4-chlorophenol using zinc oxide nanorods decorated with gold nanoparticles as supported catalysts under natural sunlight. Chem. Eng. Process. - Process. Intensif. 188, 109369 (2023).
De Sousa, J. G. M. et al. Visible light-driven ZnO/g-C3N4/carbon xerogel ternary photocatalyst with enhanced activity for 4-chlorophenol degradation. Mater. Chem. Phys. 256, 123651 (2020).
Ma, Y. et al. Synthesis of FeTiO3/TiO2 composites by a cross-linking method for enhanced photocatalytic degradation of 4-chlorophenol and dyes. Res. Chem. Intermed. 47, 997–1007. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11164-020-04312-7 (2020).
Zhang, J. et al. Carbon nanodot-modified feocl for photo-assisted Fenton reaction featuring synergistic in-situ H2O2 production and activation. Appl. Catal. B Environ. Energy. 266, 118665 (2020).
Xing, H., An, C., Wu, L. & Xu, Y. Fabrication of ZnO/Polypyrrole/Carbon nanotube nanocomposite and its application for removal of 4-Chlorophenol from wastewater. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 17, 220510 (2022).
Catrinescu, C., Arsene, D., Apopei, P. & Teodosiu, C. Degradation of 4-chlorophenol from wastewater through heterogeneous Fenton and photo-Fenton process, catalyzed by Al–Fe PILC. Appl. Clay Sci. 58, 96–101 (2012).
Funding
This work was supported and funded by the Deanship of Scientific Research at Imam Mohammad Ibn Saud Islamic University (IMSIU) (grant number IMSIU-DDRSP2602).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
1. ***Zeinab M. Ahmed: *** Methodology, Visualization, validation, Data curation, Formal analysis, Writing -original draft, Writing – review & editing,2. **Ahmed A. Allam: ** Methodology, Funding, Data curation, Formal analysis, Writing -original draft3. ***Mohamed I. El-Sayed*** **:** Supervision, Validation, Writing - original draft, Writing – review & editing4. ***Ibrahim Mohamed Abd El-Gaied*** **:** Supervision, Writing – review & editing5. ***Yasser Salama*** **:** Methodology, Data curation, Formal analysis, Writing -original draft6. **Hassan A. Rudayni: ** Formal analysis, methodology, Writing - original draft, Writing – review & editing7. ***Wail Al Zoubi: *** *Validation, Writing - original draft, Writing – review & editing*8. **Mostafa R. Abukhadra: ** Conceptualization, Formal analysis, supervision, Resources, Data curation, Visualization, methodology, validation, Writing - original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Ahmed, Z., Allam, A., El-Sayed, M. et al. Visible-light photocatalytic mineralization of 4-Chlorophenol over ZnO-loaded sulfonated carbonaceous bentonite: kinetic analysis, pathway elucidation, and catalyst reusability. Sci Rep (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-35956-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-35956-x