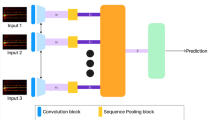
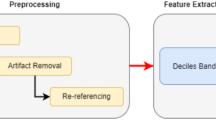
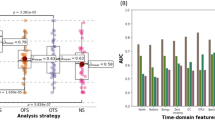
Abstract
It has become pertinent to develop early and accurate diagnosis tools for these neurological diseases, such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s. The diagnosis may be high frequency electroencephalogram (EEG) signal based. These techniques promise good results but fail to obtain the desired clinically relevant features because of the intrinsically non-stationary and noisy nature of high frequency EEG components. Limitations of existing methods include suboptimal signal processing, ineffective strategies for feature selection, lack of robustness in feature fusion mechanisms, and limited explainability for clinical adoptions. This work, therefore, proposes a holistic framework in the context of clinical detection of neurological disorders using high frequency EEG signals which are enhanced as a pipeline of multi-blocks. The combination of Hilbert-Huang transform (HHT) with a modified empirical mode decomposition ensures that the decomposition is adaptive in nature and effective noise reduction leads to preprocessing of the data. Wavelet Packets transform (WPT) in conjunction with shannon entropy-based feature selection reduces the dimensions of the data without information loss, which aids in meaningful extraction of temporal and frequency domain features. Canonical correlation analysis with multi-view representation learning allows integration of EEG features along with clinical metadata as auxiliary information to create a common feature space for increased sensitivity in diagnosis. A new multi-scale convolutional recurrent neural network (MS-CRNN) uses an attention mechanism to process the combined features and find spatiotemporal dependencies while focusing on patterns that are important for diagnosis. The method is demonstrated through grad-cam and integrated gradient techniques that help in visualizing and quantitatively attributing feature extraction. This method was 94% accurate; 92% sensitive; and 93% specific when identifying issues early on. The high accuracy in making clinical interpretation and diagnosis has set a new bar for clinicians and has encouraged public policy to support early intervention.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
This paper has used two datasets for experiments: Temple University Hospital (TUH) EEG Corpus [31] and the CHB-MIT Scalp EEG Database [32].
References
Shi, W. et al. Removal of ocular and muscular artifacts from Multi-Channel EEG using improved Spatial frequency filtering. IEEE J. Biomedical Health Inf. 28 (6), 3466–3477. https://doi.org/10.1109/JBHI.2024.3378980 (2024).
Zheng, W. L. et al. Predicting neurological outcome from electroencephalogram dynamics in comatose patients after cardiac arrest with deep learning. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 69 (5), 1813–1825. https://doi.org/10.1109/TBME.2021.3139007 (2022).
Klymenko, M. et al. Byte-Pair encoding for classifying routine clinical electroencephalograms in adults over the lifespan. IEEE J. Biomedical Health Inf. 27 (4), 1881–1890. https://doi.org/10.1109/JBHI.2023.3236264 (2023).
Yu, Y. et al. Explainable wavelet neural network for EEG artifacts detection and classification. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 32, 3358–3368. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNSRE.2024.3452315 (2024).
Lee, B. et al. Synergy through integration of wearable EEG and virtual reality for mild cognitive impairment and mild dementia screening. IEEE J. Biomedical Health Inf. 26 (7), 2909–2919. https://doi.org/10.1109/JBHI.2022.3147847 (2022).
Ansari, A. H. et al. A deep shared Multi-Scale inception network enables accurate neonatal quiet sleep detection with limited EEG channels. IEEE J. Biomedical Health Inf. 26 (3), 1023–1033. https://doi.org/10.1109/JBHI.2021.3101117 (2022).
Chu, C. et al. An enhanced EEG microstate recognition framework based on deep neural networks: an application to parkinson’s disease. IEEE J. Biomedical Health Inf. 27 (3), 1307–1318. https://doi.org/10.1109/JBHI.2022.3232811 (2023).
Wen, D. et al. Feature extraction method of EEG signals evaluating Spatial cognition of community elderly with permutation conditional mutual information common space model. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 31, 2370–2380. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNSRE.2023.3273119 (2023).
Siddiqa, H. A. et al. Single-Channel EEG Data Analysis Using a Multi-Branch CNN for Neonatal Sleep Staging, IEEE Access., 12, 29910–29925, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2024.3365570. (2024).
Caro, V., Ho, J. H., Witting, S. & Tobar, F. Modeling neonatal EEG using Multi-Output Gaussian processes. IEEE Access. 10, 32912–32927. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3159653 (2022).
Aymen, A. et al. Catalyzing EEG signal analysis: unveiling the potential of machine learning-enabled smart K nearest neighbor outlier detection. Int. j. inf. Tecnol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41870-024-02123-2 (2024).
Tu, Z. et al. Accurate machine Learning-based monitoring of anesthesia depth with EEG recording. Neurosci. Bull. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12264-024-01297-w (2024).
Castiblanco Jimenez, I. A. et al. Effective affective EEG-based indicators in emotion-evoking VR environments: an evidence from machine learning. Neural Comput&Applic. 36, 22245–22263. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-024-10240-z (2024).
Hasnaoui, L. H. & Djebbari, A. Robust dimensionality-reduced epilepsy detection system using EEG wavelet packets and machine learning. Res. Biomed. Eng. 40, 463–484. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42600-024-00355-6 (2024).
Pontes, E. D. et al. Concept-drifts adaptation for machine learning EEG epilepsy seizure prediction. Sci. Rep. 14, 8204. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-57744-1 (2024).
Hsiao, F. J. et al. Altered brainstem–cortex activation and interaction in migraine patients: somatosensory evoked EEG responses with machine learning. J. Headache Pain. 25, 185. https://doi.org/10.1186/s10194-024-01892-2 (2024).
Handa, P., Mathur, M. & &Goel, N. E. E. G. Datasets in machine learning applications of epilepsy diagnosis and seizure detection. SN COMPUT. SCI. 4, 437. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42979-023-01958-z (2023).
Chen, B. et al. Abnormal brain function network analysis based on EEG and machine learning. Mob. NetwAppl. 28, 1421–1442. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11036-023-02112-y (2023).
Gupta, V. & Ather, D. B. U. S. A. Deep learning model for EEG signal analysis. Wirel. PersCommun. 136, 2521–2543. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-024-11409-4 (2024).
Lim, Z. Y. et al. MLTCN-EEG: metric learning-based Temporal convolutional network for seizure EEG classification. Neural Comput&Applic. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-024-10783-1 (2024).
Tripathi, A. K., Ahmed, R. & &Tiwari, A. K. Review of deep learning techniques for neurological disorders detection. Wirel. PersCommun. 137, 1277–1311. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-024-11464-x (2024).
Panda, S., Mishra, S. & &Mohanty, M. N. Hybrid WCA–PSO optimized ensemble extreme learning machine and wavelet transform for detection and classification of epileptic seizure from EEG signals. Augment Hum. Res. 8, 4. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41133-023-00059-z (2023).
Falach, R. et al. Annotated interictal discharges in intracranial EEG sleep data and related machine learning detection scheme. Sci. Data. 11, 1354. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41597-024-04187-y (2024).
Göker, H. Multi-channel EEG-based classification of consumer preferences using multitaper spectral analysis and deep learning model. Multimed Tools Appl. 83, 40753–40771. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-023-17114-x (2024).
Zhang, H. et al. The applied principles of EEG analysis methods in neuroscience and clinical neurology. Military Med. Res. 10, 67. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40779-023-00502-7 (2023).
Latifoğlu, F. et al. A novel approach for parkinson’s disease detection using Vold-Kalman order filtering and machine learning algorithms. Neural Comput&Applic. 36, 9297–9311. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-024-09569-2 (2024).
Garcia-Aguilar, G. The strange and promising relationship between EEG and AI methods of analysis. CognComput 16, 2411–2419. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12559-023-10142-7 (2024).
Kayabekir, M. & Yağanoğlu, M. SPINDILOMETER: a model describing sleep spindles on EEG signals for polysomnography. PhysEngSci Med. 47, 1073–1085. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13246-024-01428-7 (2024).
Singh, J. & Sharma, D. Automated detection of mental disorders using physiological signals and machine learning: A systematic review and scientometric analysis. Multimed Tools Appl. 83, 73329–73361. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-023-17504-1 (2024).
Li, J. et al. Three-stage transfer learning for motor imagery EEG recognition. Med. BiolEngComput. 62, 1689–1701. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-024-03036-9 (2024).
Obeid, I. & Picone, J. The temple university hospital eeg data corpus, Frontiers in neuroscience 10 196. Guttag, J.(2010). CHB-MIT Scalp EEG Database (version 1.0.0). PhysioNet. (2016). https://doi.org/10.13026/C2K01R
Singh, S., Jadli, H. & Priya, P. KDTL: knowledge-distilled transfer learning framework for diagnosing mental disorders using EEG spectrograms. Neural Comput&Applic. 36, 18919–18934. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-024-10207-0 (2024).
TaheriGorji, H. et al. Using machine learning methods and EEG to discriminate aircraft pilot cognitive workload during flight. Sci. Rep. 13, 2507. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-29647-0 (2023).
Poikonen, H. et al. Nonlinear and machine learning analyses on high-density EEG data of math experts and novices. Sci. Rep. 13, 8012. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-35032-8 (2023).
Georgis-Yap, Z., Popovic, M. R. & Khan, S. S. Supervised and unsupervised deep learning approaches for EEG seizure prediction. J. Healthc. Inf. Res. 8, 286–312. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41666-024-00160-x (2024).
Pattnaik, S. et al. Transfer learning based epileptic seizure classification using scalogram images of EEG signals. Multimed Tools Appl. 83, 84179–84193. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-024-19129-4 (2024).
Tveter, M. et al. Advancing EEG prediction with deep learning and uncertainty Estimation. Brain Inf. 11, 27. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40708-024-00239-6 (2024).
Mari, T. et al. Machine learning and EEG can classify passive viewing of discrete categories of visual stimuli but not the observation of pain. BMC Neurosci. 24, 50. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12868-023-00819-y (2023).
Göker, H. Automatic detection of parkinson’s disease from power spectral density of electroencephalography (EEG) signals using deep learning model. PhysEngSci Med. 46, 1163–1174. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13246-023-01284-x (2023).
Khosravi, M. et al. Fusing convolutional learning and attention-based Bi-LSTM networks for early alzheimer’s diagnosis from EEG signals towards IoMT. Sci. Rep. 14, 26002. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-77876-8 (2024).
Li, H., Li, L. & Zhao, D. An improved EMD method with modified envelope algorithm based on C2 piecewise rational cubic spline interpolation for EMI signal decomposition. Appl. Math. Comput. 335, 112–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amc.2018.04.008 (2018).
Karthiga, M. et al. Eeg based smart emotion recognition using meta heuristic optimization and hybrid deep learning techniques. Sci. Rep. 14, 30251. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-80448-5 (2024).
Senthil Kumar, S. et al. ResDense fusion: enhancing schizophrenia disorder detection in EEG data through ensemble fusion of deep learning models. Neural Comput&Applic. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-024-10701-5 (2024).
Wang, Y. et al. Improved empirical wavelet transform combined with particle swarm optimization-support vector machine for EEG-based depression recognition. EURASIP J. Adv. Signal. Process. 2024 (101). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13634-024-01199-z (2024).
Singh, V. K. et al. EEG signal based human emotion recognition Brain-computer interface using deep learning and High-Performance computing. Wirel. PersCommun. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-024-11656-5 (2024).
Bashir, N. et al. A machine learning framework for major depressive disorder (MDD) detection using Non-invasive EEG signals. Wirel. Pers. Commun. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-023-10445-w (2023).
Rogala, J. et al. Enhancing autism spectrum disorder classification in children through the integration of traditional statistics and classical machine learning techniques in EEG analysis. Sci. Rep. 13, 21748. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-49048-7 (2023).
Xu, Z. & Liu, S. Decoding consumer purchase decisions: exploring the predictive power of EEG features in online shopping environments using machine learning. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Commun. 11, 1202. https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-024-03691-1 (2024).
A, A. Resting state EEG microstate profiling and a machine-learning based classifier model in epilepsy. Cogn. Neurodyn. 18, 2419–2432. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11571-024-10095-z (2024).
Rehab, N., Siwar, Y. & Mourad, Z. Machine learning for epilepsy: A comprehensive exploration of novel EEG and MRI techniques for seizure diagnosis. J. Med. Biol. Eng. 44, 317–336. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40846-024-00874-8 (2024).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Princess Nourah bint Abdulrahman University Researchers Supporting Project number (PNURSP2026R393), Princess Nourah bint Abdulrahman University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
Funding
This work was supported by Princess Nourah bint Abdulrahman University Researchers Supporting Project number (PNURSP2026R393), Princess Nourah bint Abdulrahman University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Data analysis and code writing: RA with the help of CD, GS, SS. Data acquisition and preprocessing: SS, UA and SA. Writing, original draft preparation, RA and CD. Writing, review and editing: MO, LB. Funding acquisition: MO. Project administration: SA. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Human ethics and consent to participate declarations
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Agrawal, R., Dhule, C., Shukla, G. et al. Iterative multiblock framework for high frequency EEG based neurological disorder detection. Sci Rep (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-37126-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-37126-5