Abstract
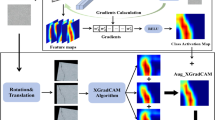
Class activation mapping (CAM) is key to understanding how convolutional neural networks (CNNs) make decisions, but current approaches face considerable challenges. First-order gradient-based methods are often affected by noise and are prone to gradient saturation, leading to less accurate localization. These methods also tend to rely on manual selection and merging of feature maps, limiting their ability to leverage complementary information across network layers and resulting in weaker visual explanations. To address these issues, we propose a smooth second-order gradient class activation mapping (SSG–CAM) method. By incorporating second-order gradients, SSG–CAM captures changes in feature importance to alleviate gradient saturation and integrates a smoothing technique to reduce noise. Additionally, SSG–CAM is integrated with the differential evolution (DE) algorithm to create a collaborative DE–SSG–CAM optimization framework, which automatically screens and fuses the optimal combination of multi-level feature maps. Extensive experiments on multiple benchmark tasks, including weakly supervised object localization and semantic segmentation, demonstrate that our method outperforms existing baselines across various metrics. Notably, the DE–SSG–CAM framework demonstrated a mean Intersection over Union (mIoU) of 62.38% in the complex task of localizing malarial parasite lesions in red blood cells, highlighting its exceptional performance in biomedical image analysis. In this study, we present an accurate and robust visual explanation tool, offering an innovative approach for automatically distilling optimal visual interpretations from deep neural networks.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated and/or analysed during the current study are publicly available. The ImageNet (ILSVRC) dataset is available from the official ImageNet website, [https://image-net.org/](https:/image-net.org) . The PASCAL VOC 2012 dataset is available in the Kaggle repository, [https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/gopalbhattrai/pascal-voc-2012-dataset](https:/www.kaggle.com/datasets/gopalbhattrai/pascal-voc-2012-dataset) . The red blood cell image dataset for malaria detection is also available in the Kaggle repository, [https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/iarunava/cell-images-for-detecting-malaria](https:/www.kaggle.com/datasets/iarunava/cell-images-for-detecting-malaria) .
References
Mo, H. & Zhao, G. J. P. R. RIC-CNN: rotation-invariant coordinate convolutional neural network. Pattern Recogn. 146, 109994 (2024).
Liu, Z. et al. A convnet for the 2020s. in Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. (2022).
Zhang, H. et al. Dino: Detr with improved denoising anchor boxes for end-to-end object detection. arXiv preprint arXiv:.03605, 2022.
Cheng, B., Misra, I., Schwing, A. G., Kirillov, A. & Girdhar, R. Masked-attention mask transformer for universal image segmentation. in Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. (2022).
Peng, C., Li, L. & Peng, D. A Method-Oriented review of explainable artificial intelligence for neurological medical imaging. Expert Syst. 42 (9), e70111 (2025).
Tjoa, E. & Guan, C. A survey on explainable artificial intelligence (xai): toward medical Xai. IEEE Trans. Neural Networks Learn. Syst. 32 (11), 4793–4813 (2020).
Mersha, M., Lam, K., Wood, J., AlShami, A. & Kalita, J. J. N. Explainable artificial intelligence: A survey of needs, techniques, applications, and future direction. Neurocomputing, : p. 128111. (2024).
Sadeghi, Z. et al. A review of explainable artificial intelligence in healthcare. Computers Electr. Eng. 118, 109370 (2024).
Arsenault, P. D., Wang, S. & Patenaude, J. M. A survey of explainable artificial intelligence (XAI) in financial time series forecasting. ACM Comput. Surveys. 57 (10), 1–37 (2025).
Zhou, B., Khosla, A., Lapedriza, A., Oliva, A. & Torralba, A. Learning deep features for discriminative localization. in Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. (2016).
Wang, H. et al. Score-CAM: Score-weighted visual explanations for convolutional neural networks. in Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition workshops. (2020).
Lai, Q., Khan, S., Nie, Y., Sun, H. & Shen, J. J.I.T.o.M. Shao, Understanding more about human and machine attention in deep neural networks. IEEE Trans. Multimedia. 23, 2086–2099 (2020).
Cui, X., Wang, D., Z.J.J.I.T.o, M. & Wang Feature-flow interpretation of deep convolutional neural networks. IEEE Trans. Multimedia. 22 (7), 1847–1861 (2020).
Shi, X., Khademi, S., Li, Y. & van Gemert, J. Zoom-CAM: Generating fine-grained pixel annotations from image labels. in 25th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR). 2021. IEEE. 2021. IEEE. (2020).
Li, Y., Liang, H., R.J.I.T.o, M. & Yu BI-CAM: generating explanations for deep neural networks using bipolar information. IEEE Trans. Multimedia. 26, 568–580 (2023).
Englebert, A., Cornu, O. & Vleeschouwer, C. D. J. M. V. Poly-cam: high resolution class activation map for convolutional neural networks. Mach. Vis. Appl. Math. 35 (4), 89 (2024).
Ibrahim, R. & Shafiq, M. O. J. K. B. S. Augmented Score-CAM: high resolution visual interpretations for deep neural networks. Knowl. Based Syst. 252, 109287 (2022).
Zhang, Y., Zhang, Y., Xiao, Y. & Wang, T. Spatiotemporal Dual-Branch Feature-Guided Fusion Network for Driver Attention Prediction p. 128564 (Expert Systems with Applications, 2025).
Zhang, Y., Xiao, Y., Zhang, Y. & Zhang, T. Video saliency prediction via single feature enhancement and Temporal recurrence. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 160, 111840 (2025).
Jiang, P. T., Zhang, C. B., Hou, Q. & Cheng, M. M. J.I.T.o.I.P. Wei, Layercam: exploring hierarchical class activation maps for localization. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 30, 5875–5888 (2021).
Zeng, C. et al. Abs-CAM: a gradient optimization interpretable approach for explanation of convolutional neural networks. Signal, Image Video Processing, 17(4): pp. 1069–1076. (2023).
Storn, R. K.J.J.o.g.o. Price, Differential evolution–a simple and efficient heuristic for global optimization over continuous spaces. J. Global Optim. 11 (4), 341–359 (1997).
Russakovsky, O. et al. Imagenet large scale visual recognition challenge. Int. J. Comput. Vision. 115 (3), 211–252 (2015).
Minh, A. P. T.J.a.p.a., Overview of class activation maps for visualization explainability. arXiv preprint arXiv:.14304, (2023).
Selvaraju, R. R. et al. Grad-cam: Visual explanations from deep networks via gradient-based localization. in Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision. (2017).
Zhang, Z. et al. Finer-cam: Spotting the difference reveals finer details for visual explanation. in Proceedings of the Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Conference. (2025).
He, H., Pan, X. & Yao, Y. CF-CAM: Cluster Filter Class Activation Mapping for Reliable Gradient-Based Interpretability. arXiv (2025).
Li, Y., Liang, H., Zheng, H. & Yu, R. Cr-Cam: generating explanations for deep neural networks by contrasting and ranking features. Pattern Recogn. 149, 110251–110251 (2024).
Wang, D., Xia, Y., Pedrycz, W., Li, Z. & Yu, Z. Feature similarity Group-Class activation mapping (FSG-CAM): clarity in deep learning models and enhancement of visual explanations. Expert Syst. Appl. 282, 127553 (2025).
Liu, Y., Guo, W., Lu, X., Kong, L. & Yan, Z. Class activation map guided backpropagation for discriminative explanations. Appl. Sci. 15 (1), 379 (2025).
Singh, A. K., Chaudhuri, D. & Singh, M. P. and S.J.a.p.a. Chattopadhyay, Integrative CAM: adaptive layer fusion for comprehensive interpretation of CNNs. arXiv preprint arXiv:.2412.01354, 2024.
Kuroki, M. & Yamasaki, T. CE-FAM: Concept-Based Explanation via Fusion of Activation Maps. in Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. (2025).
Zhou, Y., Zhu, Y., Ye, Q., Qiu, Q. & Jiao, J. Weakly supervised instance segmentation using class peak response. in Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. (2018).
Achanta, R. et al. SLIC superpixels compared to state-of-the-art superpixel methods. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. 34 (11), 2274–2282 (2012).
Everingham, M. et al. The Pascal visual object classes challenge: A retrospective. Int. J. Comput. Vision. 111 (1), 98–136 (2015).
Zeiler, M. D. & Fergus, R. Visualizing and understanding convolutional networks. in European conference on computer vision. Springer. (2014).
Ramaswamy, H. G. Ablation-cam: Visual explanations for deep convolutional network via gradient-free localization. in proceedings of the IEEE/CVF winter conference on applications of computer vision. (2020).
Fu, R., Hu, Q., Dong, X., Guo, Y. & Gao, Y. and B.J.a.p.a. Li, Axiom-based grad-cam: Towards accurate visualization and explanation of cnns. arXiv preprint arXiv:.02312, 2020.
Funding
This work was supported in part by the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangxi Provincial under Grant 20232ACB205001, the Major Discipline Academic and Technical Leaders Training Program of Jiangxi Province under Grant 20232BCJ22025, and the Wenzhou Major S&T Innovation Project for Key Breakthroughs under Grant ZG2024049.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
**Zhiqing Chen: ** Conceptualization, Methodology, Software, Validation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Data Curation, Writing – Original Draft, Visualization.**Yuejin Zhang: ** Conceptualization, Supervision, Project administration, Funding acquisition, Writing – Review & Editing.**Lei Pan: ** Investigation, Resources, Writing – Review & Editing.**Zhi Lei: ** Investigation, Resources, Writing – Review & Editing.**Zhiyuan Zhou: ** Investigation, Resources, Writing – Review & Editing.**Jinsuo Huang: ** Conceptualization, Supervision, Project administration, Writing – Review & Editing.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Compliance with ethical standards
No applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Z., Zhang, Y.J., Pan, L. et al. SSG–CAM: enhancing visual interpretability through refined second-order gradients and evolutionary multi-layer fusion. Sci Rep (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-37278-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-37278-4